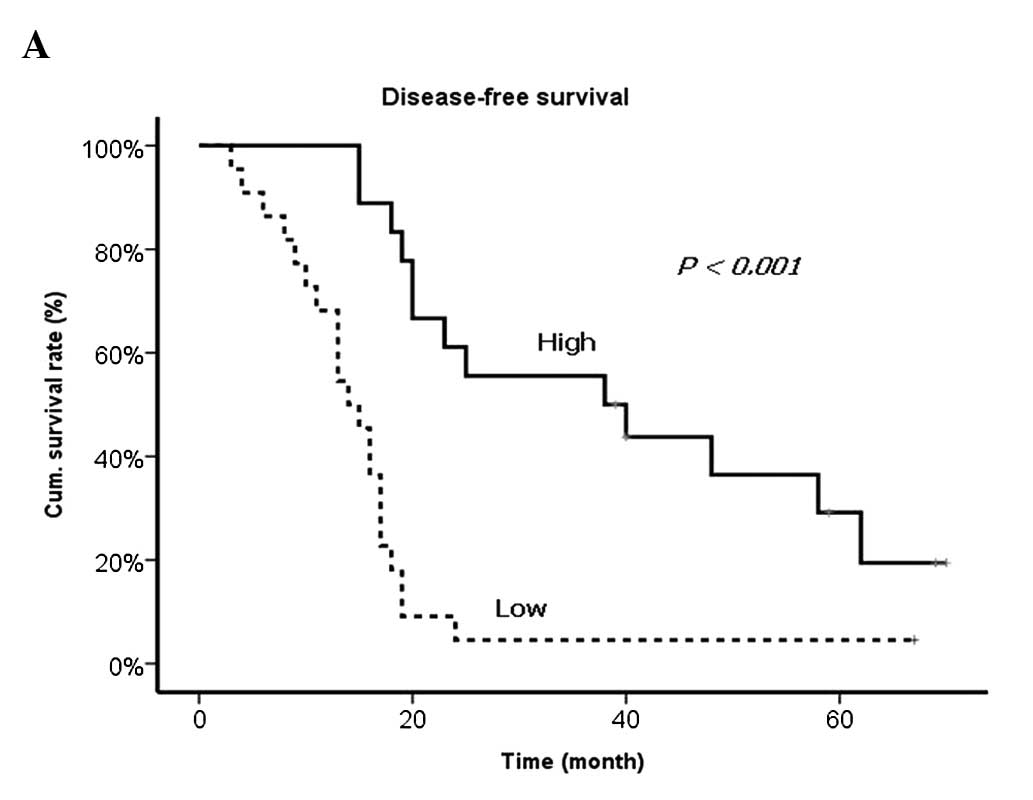
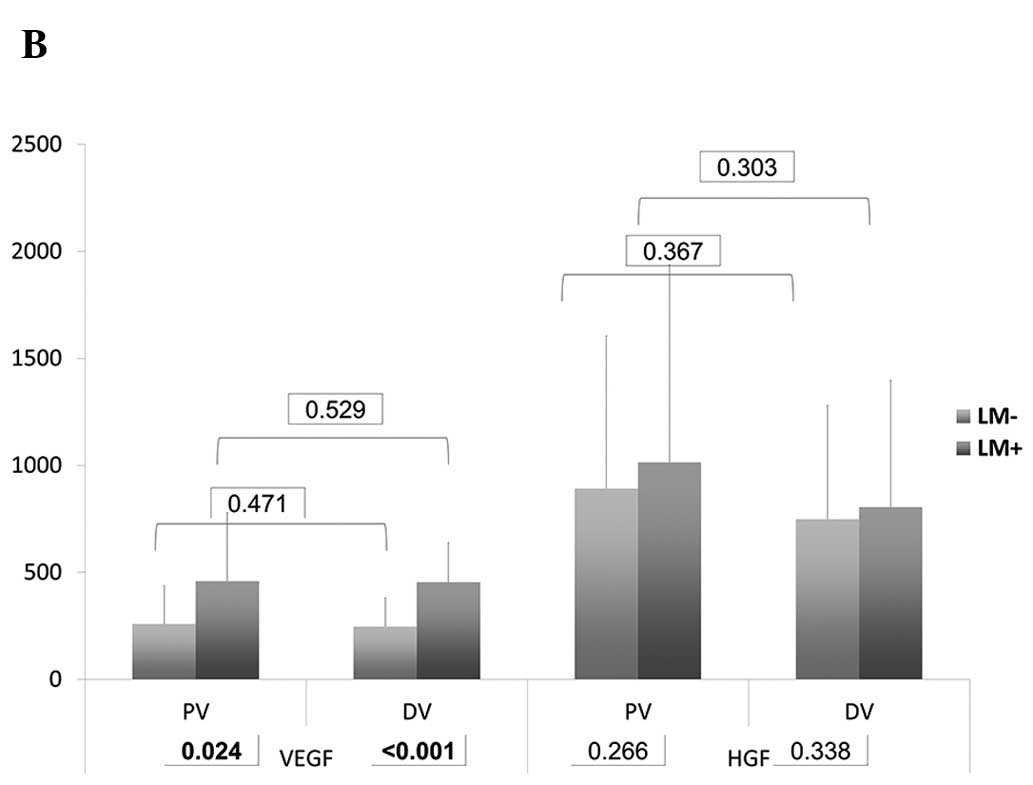
|
1
|
Ballantyne GH and Quin J: Surgical
treatment of liver metastases in patients with colorectal cancer.
Cancer. 71:4252–4266. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Choi HJ, Hyun MS, Jung GJ, Kim SS and Hong
SH: Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic predictor in colorectal
carcinoma with special reference to mode of metastasis and
recurrence. Oncology. 55:575–581. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fong Y, Cohen AM, Fortner JG, et al: Liver
resection for colorectal metastases. J Clin Oncol. 15:938–946.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bozzetti F, Doci R, Bignami P, Morabito A
and Gennari L: Patterns of failure following surgical resection of
colorectal cancer liver metastases. Rationale for a multimodal
approach. Ann Surg. 205:264–270. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ueno H, Mochizuki H, Hashiguchi Y, Hatsuse
K, Fujimoto H and Hase K: Predictors of extrahepatic recurrence
after resection of colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg.
91:327–333. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Geiger TR and Peeper DS: Metastasis
mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:293–308. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barozzi C, Ravaioli M, D’Errico A, et al:
Relevance of biologic markers in colorectal carcinoma: a
comparative study of a broad panel. Cancer. 94:647–657. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baker EA, Bergin FG and Leaper DJ:
Plasminogen activator system, vascular endothelial growth factor,
and colorectal cancer progression. Mol Pathol. 53:307–312. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoon SS, Kim SH, Gonen M, et al: Profile
of plasma angiogenic factors before and after hepatectomy for
colorectal cancer liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 13:353–362.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Waas ET, Wobbes T, Ruers T, Lomme RM and
Hendriks T: Circulating gelatinases and tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-1 in colorectal cancer metastatic liver disease.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 32:756–763. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oberg A, Hoyhtya M, Tavelin B, Stenling R
and Lindmark G: Limited value of preoperative serum analyses of
matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) and tissue inhibitors of
matrix metalloproteinases (TIMP-1, TIMP-2) in colorectal cancer.
Anticancer Res. 20:1085–1091. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tien YW, Chang KJ, Chiu YF, Huang KW and
Lee PH: Comparison of angiogenic factor levels in tumor drainage
and peripheral venous blood from colorectal cancer patients. Ann
Surg Oncol. 13:1357–1363. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Adachi Y, Yamamoto H, Itoh F, Hinoda Y,
Okada Y and Imai K: Contribution of matrilysin (MMP-7) to the
metastatic pathway of human colorectal cancers. Gut. 45:252–258.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Masaki T, Matsuoka H, Sugiyama M, et al:
Matrilysin (MMP-7) as a significant determinant of malignant
potential of early invasive colorectal carcinomas. Br J Cancer.
84:1317–1321. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zucker S and Vacirca J: Role of matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 23:101–117. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zeng ZS, Shu WP, Cohen AM and Guillem JG:
Matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression in colorectal cancer liver
metastases: evidence for involvement of MMP-7 activation in human
cancer metastases. Clin Cancer Res. 8:144–148. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bueno M, Salgado S, Beas-Zarate C and
Armendariz-Borunda J: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene
therapy in liver cirrhosis is mediated by collagens gene expression
down-regulation and up-regulation of MMPs, HGF and VEGF. J Gene
Med. 8:1291–1299. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alexiou D, Karayiannakis AJ, Syrigos KN,
et al: Serum levels of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in colorectal
cancer patients: correlations with clinicopathological features,
patient survival and tumour surgery. Eur J Cancer. 37:2392–2397.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Uner A, Akcali Z and Unsal D: Serum levels
of soluble E-selectin in colorectal cancer. Neoplasma. 51:269–274.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wittig BM, Kaulen H, Thees R, et al:
Elevated serum E-selectin in patients with liver metastases of
colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 32A:1215–1218. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roselli M, Guadagni F, Martini F, et al:
Association between serum carcinoembryonic antigen and endothelial
cell adhesion molecules in colorectal cancer. Oncology. 65:132–138.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gangopadhyay A, Lazure DA and Thomas P:
Adhesion of colorectal carcinoma cells to the endothelium is
mediated by cytokines from CEA stimulated Kupffer cells. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 16:703–712. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Agrawal D, Chen T, Irby R, et al:
Osteopontin identified as colon cancer tumor progression marker. CR
Biol. 326:1041–1043. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wai PY, Mi Z, Guo H, et al: Osteopontin
silencing by small interfering RNA suppresses in vitro and in vivo
CT26 murine colon adenocarcinoma metastasis. Carcinogenesis.
26:741–751. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Behzadian MA, Windsor LJ, Ghaly N, Liou G,
Tsai NT and Caldwell RB: VEGF-induced paracellular permeability in
cultured endothelial cells involves urokinase and its receptor.
FASEB J. 17:752–754. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|