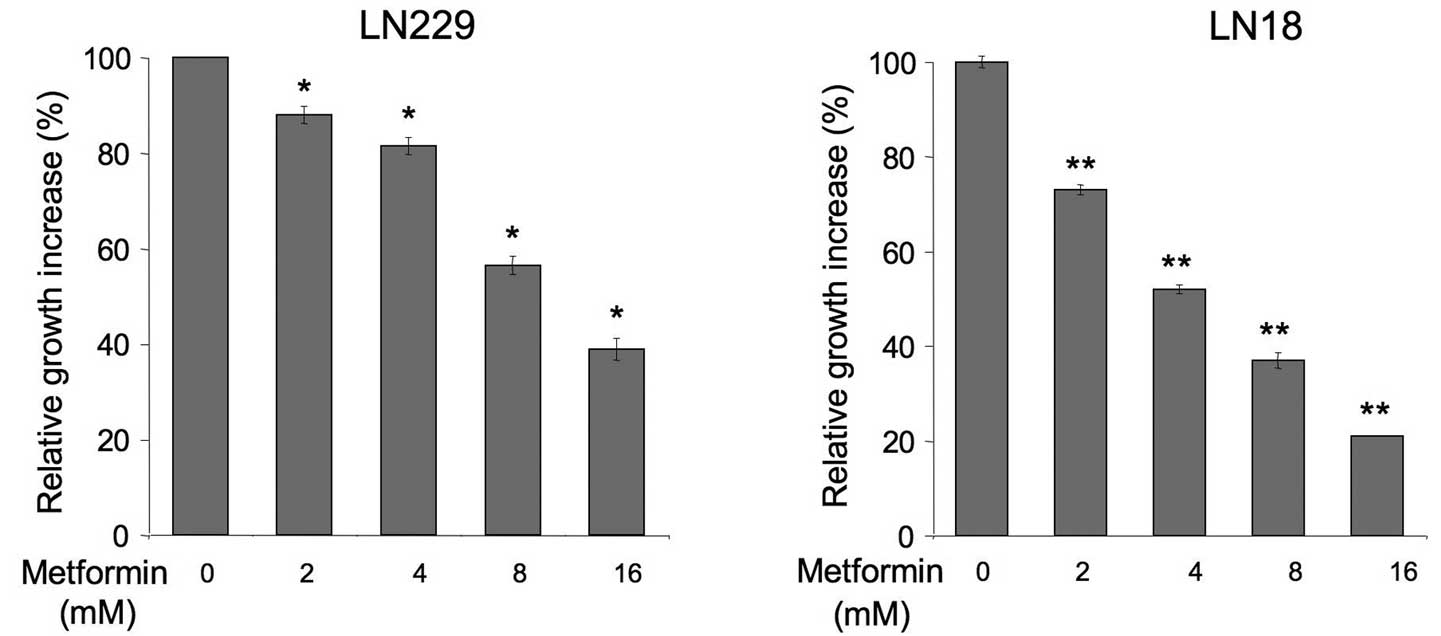
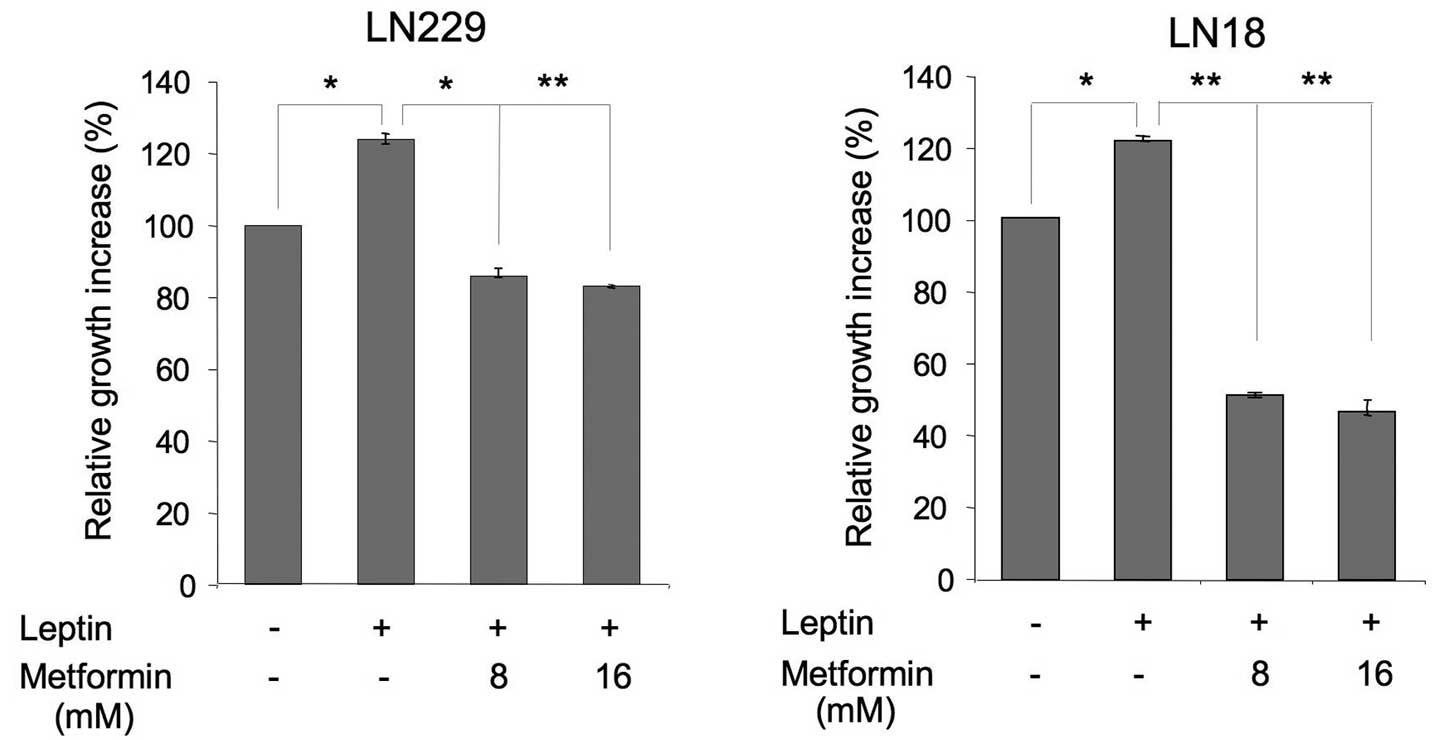
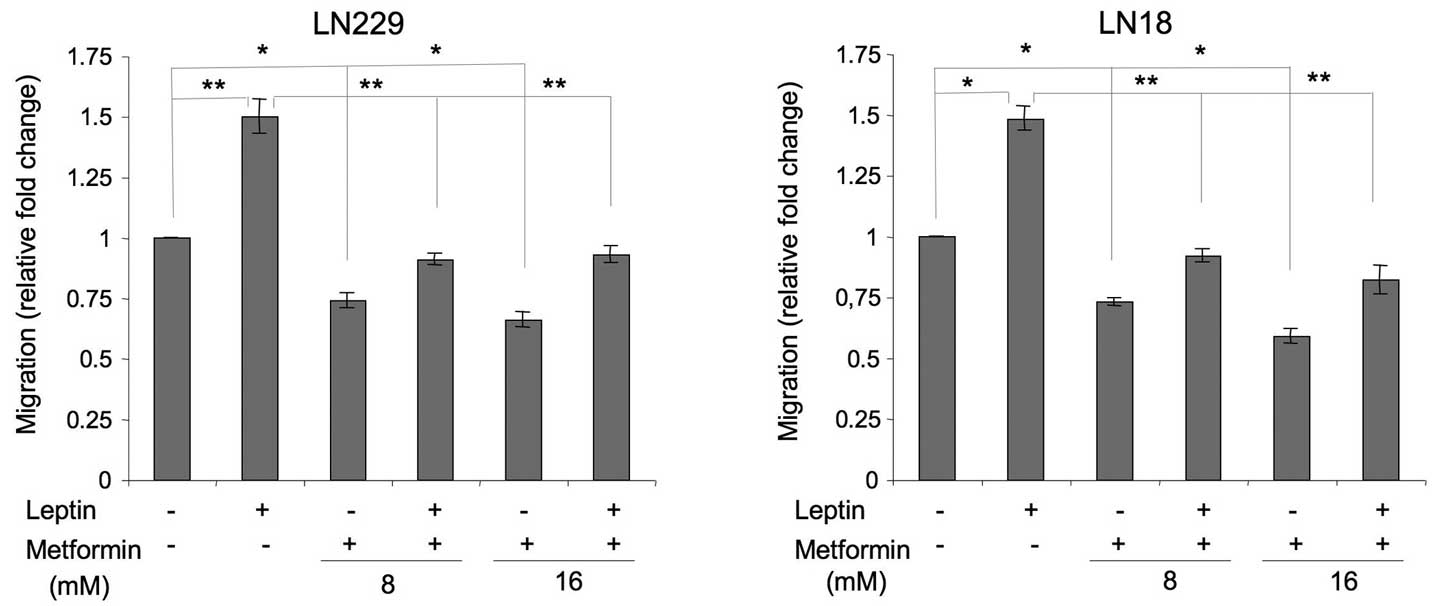
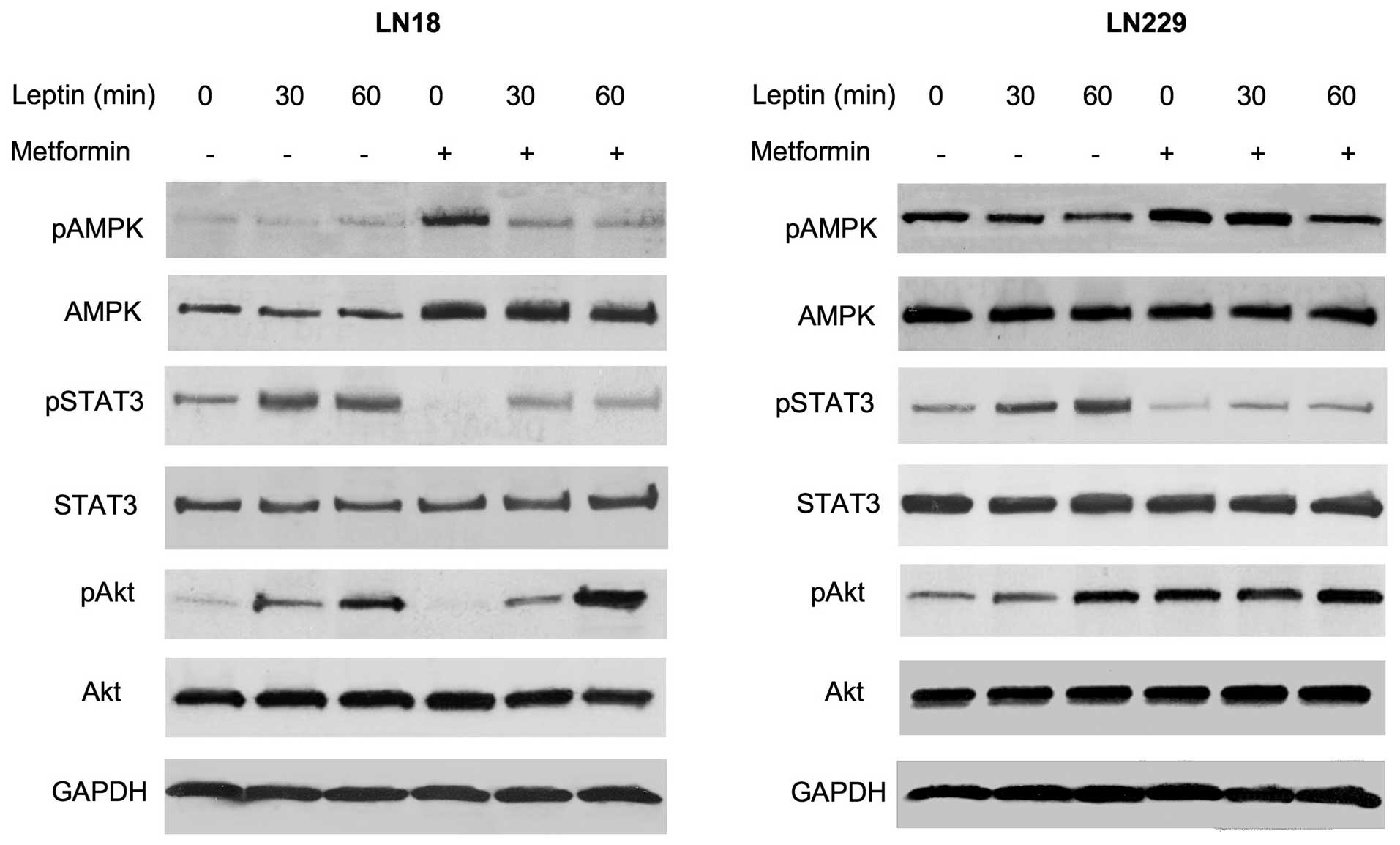
|
1.
|
E BosiMetformin - the gold standard in
type 2 diabetes: what does the evidence tell us?Diabetes Obes
Metab11Suppl 238200910.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.01031.x19385978
|
|
2.
|
A RamachandranC SnehalathaDiabetes
prevention programsMed Clin North
Am95353372viii201110.1016/j.mcna.2010.11.006
|
|
3.
|
JG BoyleIP SaltGA McKayMetformin action on
AMP-activated protein kinase: a translational research approach to
understanding a potential new therapeutic targetDiabet
Med2710971106201010.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03098.x20854376
|
|
4.
|
K JanjetovicL VucicevicM MisirkicMetformin
reduces cisplatin-mediated apoptotic death of cancer cells through
AMPK-independent activation of AktEur J
Pharmacol6514150201110.1016/j.ejphar.2010.11.00521114978
|
|
5.
|
RA MillerMJ BirnbaumAn energetic tale of
AMPK-independent effects of metforminJ Clin
Invest12022672270201010.1172/JCI4366120577046
|
|
6.
|
DG HardieThe AMP-activated protein kinase
pathway - new players upstream and downstreamJ Cell
Sci11754795487200410.1242/jcs.0154015509864
|
|
7.
|
M JalvingJA GietemaJD LefrandtMetformin:
taking away the candy for cancer?Eur J
Cancer4623692380201010.1016/j.ejca.2010.06.01220656475
|
|
8.
|
VN AnisimovMetformin for aging and cancer
preventionAging (Albany NY)2760774201021084729
|
|
9.
|
I Ben SahraY Le Marchand-BrustelJF TantiF
BostMetformin in cancer therapy: a new perspective for an old
anti-diabetic drug?Mol Cancer Ther9109210992010
|
|
10.
|
AM Gonzalez-AnguloF
Meric-BernstamMetformin: a therapeutic opportunity in breast
cancerClin Cancer
Res1616951700201010.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-180520215559
|
|
11.
|
TV KourelisRD SiegelMetformin and cancer:
new applications for an old drugMed
Oncol2913141327201210.1007/s12032-011-9846-721301998
|
|
12.
|
M PollakMetformin and other biguanides in
oncology: advancing the research agendaCancer Prev Res
(Phila)310601065201010.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-017520810670
|
|
13.
|
K HosonoH EndoH TakahashiMetformin
suppresses colorectal aberrant crypt foci in a short-term clinical
trialCancer Prev Res
(Phila)310771083201010.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-018620810669
|
|
14.
|
S EyalP HsiaoJD UnadkatDrug interactions
at the blood-brain barrier: fact or fantasy?Pharmacol
Ther12380104200910.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.03.01719393264
|
|
15.
|
D GuoTF CloughesyCG RaduPS MischelAMPK: A
metabolic checkpoint that regulates the growth of EGFR activated
glioblastomasCell Cycle9211212201010.4161/cc.9.2.1054020023392
|
|
16.
|
A IsakovicL HarhajiD StevanovicDual
antiglioma action of metformin: cell cycle arrest and
mitochondria-dependent apoptosisCell Mol Life
Sci6412901302200710.1007/s00018-007-7080-417447005
|
|
17.
|
ME BecknerGT GobbelR AbounaderGlycolytic
glioma cells with active glycogen synthase are sensitive to PTEN
and inhibitors of PI3K and gluconeogenesisLab
Invest8514571470200516170333
|
|
18.
|
F ZhangY ChenM HeimanR DimarchiLeptin:
structure, function and biologyVitam
Horm71345372200510.1016/S0083-6729(05)71012-816112274
|
|
19.
|
L ScolaroM CassoneJW KolaczynskiL Otvos
JrE SurmaczLeptin-based therapeuticsExpert Rev Endocrinol
Metab5875889201010.1586/eem.10.61
|
|
20.
|
M RiolfiR FerlaL Del ValleLeptin and its
receptor are overexpressed in brain tumors and correlate with the
degree of malignancyBrain
Pathol20481489201010.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00323.x19775291
|
|
21.
|
C GarofaloE SurmaczLeptin and cancerJ Cell
Physiol2071222200610.1002/jcp.20472
|
|
22.
|
WL YehDY LuMJ LeeWM FuLeptin induces
migration and invasion of glioma cells through MMP-13
productionGlia57454464200910.1002/glia.2077318814267
|
|
23.
|
DG HardieAMPK: a key regulator of energy
balance in the single cell and the whole organismInt J Obes
(Lond)32Suppl 4S7S12200810.1038/ijo.2008.11618719601
|
|
24.
|
Z LuoM ZangW GuoAMPK as a metabolic tumor
suppressor: control of metabolism and cell growthFuture
Oncol6457470201010.2217/fon.09.17420222801
|
|
25.
|
T TangJM LordRJ NormanE YasminAH
BalenInsulin-sensitising drugs (metformin, rosiglitazone,
pioglitazone, D-chiro-inositol) for women with polycystic ovary
syndrome, oligo amenorrhoea and subfertilityCochrane Database Syst
RevCD0030532009
|
|
26.
|
S BerezowskaS Diermeier-DaucherG
BrockhoffEffect of additional inhibition of human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2 with the bispecific tyrosine kinase inhibitor
AEE788 on the resistance to specific EGFR inhibition in glioma
cellsInt J Mol Med26713721201010.3892/ijmm_00000518
|
|
27.
|
D GuoIJ HildebrandtRM PrinsThe AMPK
agonist AICAR inhibits the growth of EGFRvIII-expressing
glioblastomas by inhibiting lipogenesisProc Natl Acad Sci
USA1061293212937200910.1073/pnas.090660610619625624
|
|
28.
|
C AngMC GuiotAV RamanakumarD RobergeP
KavanClinical significance of molecular biomarkers in
glioblastomaCan J Neurol
Sci37625630201010.1017/S031716710001080521059509
|
|
29.
|
TJ LiuT LaFortuneT HondaInhibition of both
focal adhesion kinase and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor
kinase suppresses glioma proliferation in vitro and in vivoMol
Cancer Ther613571367200710.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-047617431114
|
|
30.
|
J SchlegelG PiontekB BuddeF NeffA KrausThe
Akt/protein kinase B-dependent anti-apoptotic pathway and the
mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade are alternatively
activated in human glioblastoma multiformeCancer
Lett158103108200010.1016/S0304-3835(00)00515-210940516
|
|
31.
|
N de la IglesiaSV PuramA BonniSTAT3
regulation of glioblastoma pathogenesisCurr Mol Med95805902009
|
|
32.
|
M ZakikhaniMJ BlouinE PiuraMN
PollakMetformin and rapamycin have distinct effects on the AKT
pathway and proliferation in breast cancer cellsBreast Cancer Res
Treat123271279201010.1007/s10549-010-0763-920135346
|
|
33.
|
IN AlimovaB LiuZ FanMetformin inhibits
breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle
arrest in vitroCell Cycle8909915200910.4161/cc.8.6.793319221498
|
|
34.
|
J YangGD HolmanLong-term metformin
treatment stimulates cardiomyocyte glucose transport through an
AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent reduction in GLUT4
endocytosisEndocrinology14727282736200610.1210/en.2005-1433
|
|
35.
|
B SonntagM GotteP WulfingAN SchuringL
KieselRR GrebMetformin alters insulin signaling and viability of
human granulosa cellsFertil Steril84Suppl
211731179200510.1016/j.fertnstert.2005.04.04316210009
|