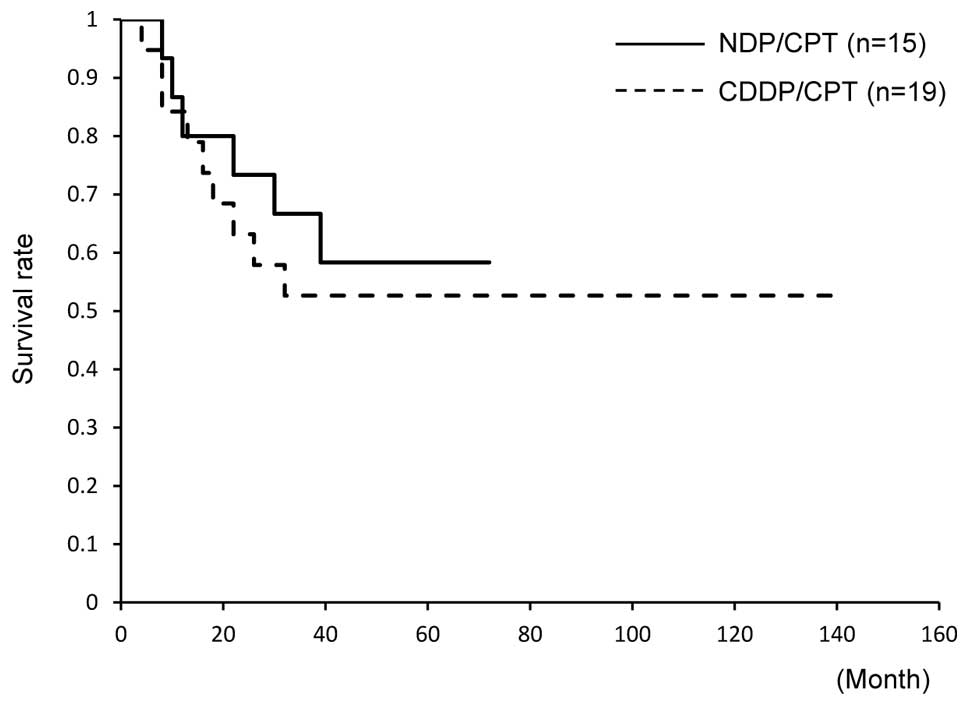
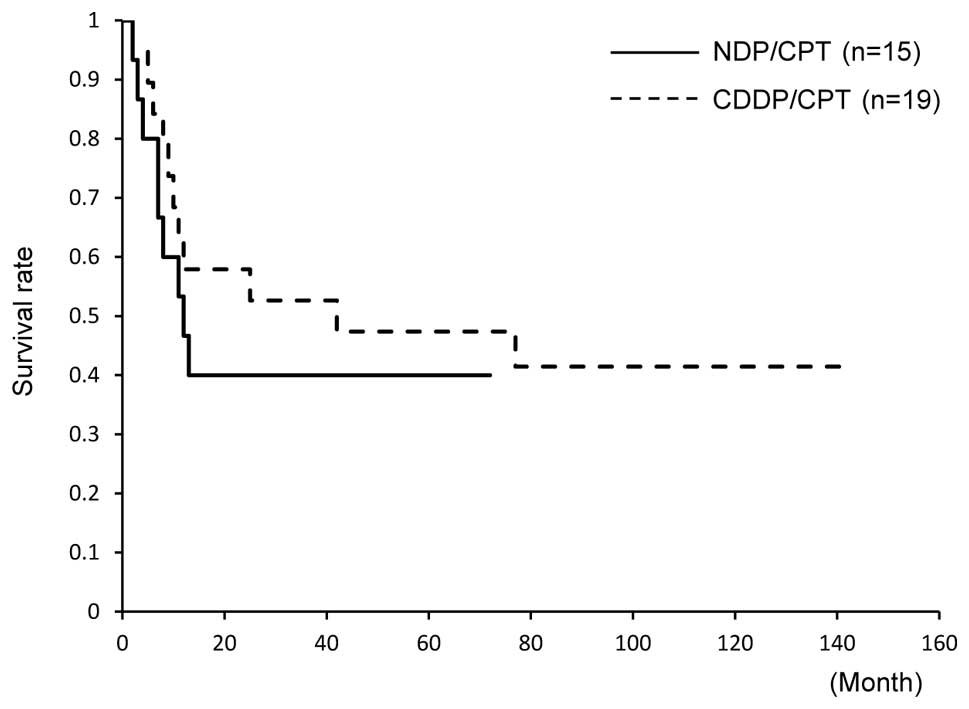
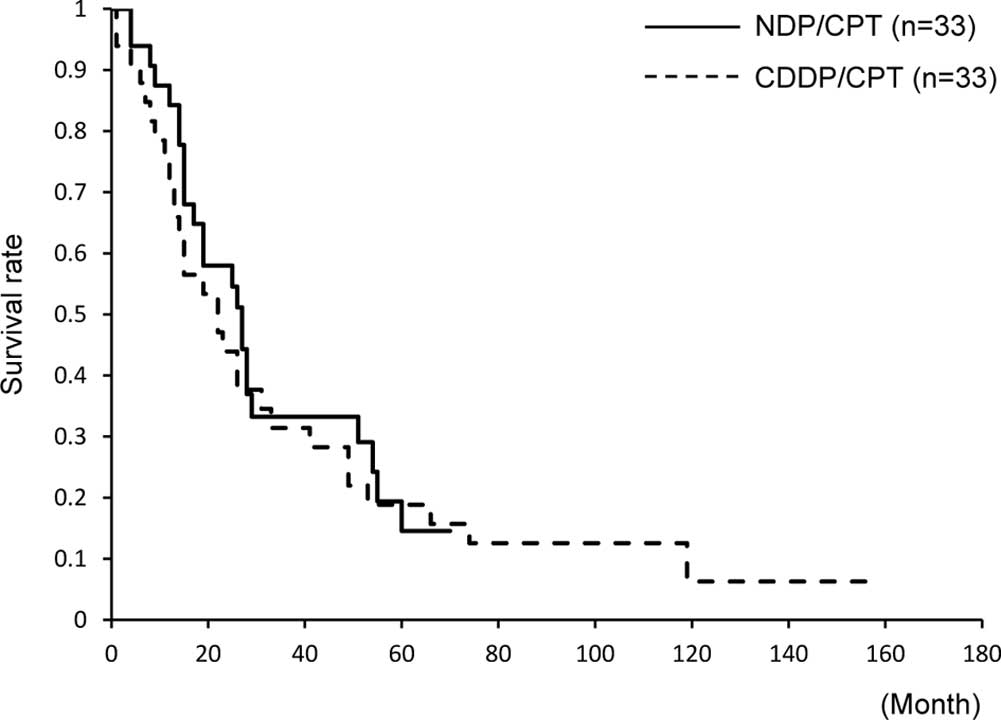
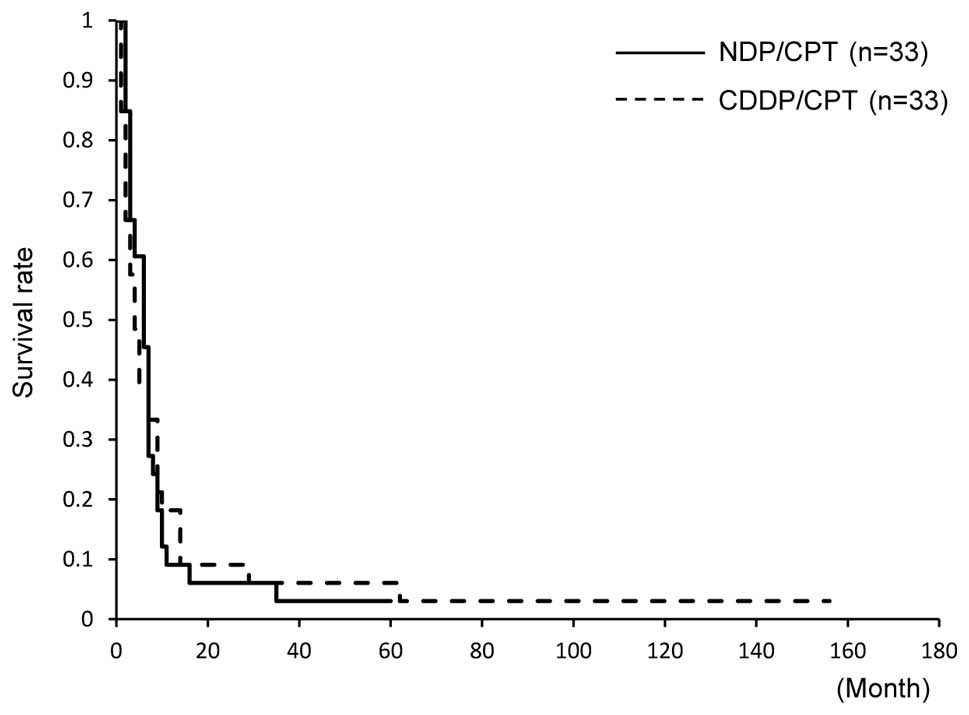
Spandidos Publications style
Machida S, Sato T, Fujiwara H, Saga Y, Takei Y, Taneichi A, Nonaka H and Suzuki M: Nedaplatin and irinotecan combination therapy is equally effective and less toxic than cisplatin and irinotecan for patients with primary clear cell adenocarcinoma of the ovary and recurrent ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Lett 4: 1017-1022, 2012.
APA
Machida, S., Sato, T., Fujiwara, H., Saga, Y., Takei, Y., Taneichi, A. ... Suzuki, M. (2012). Nedaplatin and irinotecan combination therapy is equally effective and less toxic than cisplatin and irinotecan for patients with primary clear cell adenocarcinoma of the ovary and recurrent ovarian carcinoma. Oncology Letters, 4, 1017-1022. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2012.853
MLA
Machida, S., Sato, T., Fujiwara, H., Saga, Y., Takei, Y., Taneichi, A., Nonaka, H., Suzuki, M."Nedaplatin and irinotecan combination therapy is equally effective and less toxic than cisplatin and irinotecan for patients with primary clear cell adenocarcinoma of the ovary and recurrent ovarian carcinoma". Oncology Letters 4.5 (2012): 1017-1022.
Chicago
Machida, S., Sato, T., Fujiwara, H., Saga, Y., Takei, Y., Taneichi, A., Nonaka, H., Suzuki, M."Nedaplatin and irinotecan combination therapy is equally effective and less toxic than cisplatin and irinotecan for patients with primary clear cell adenocarcinoma of the ovary and recurrent ovarian carcinoma". Oncology Letters 4, no. 5 (2012): 1017-1022. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2012.853