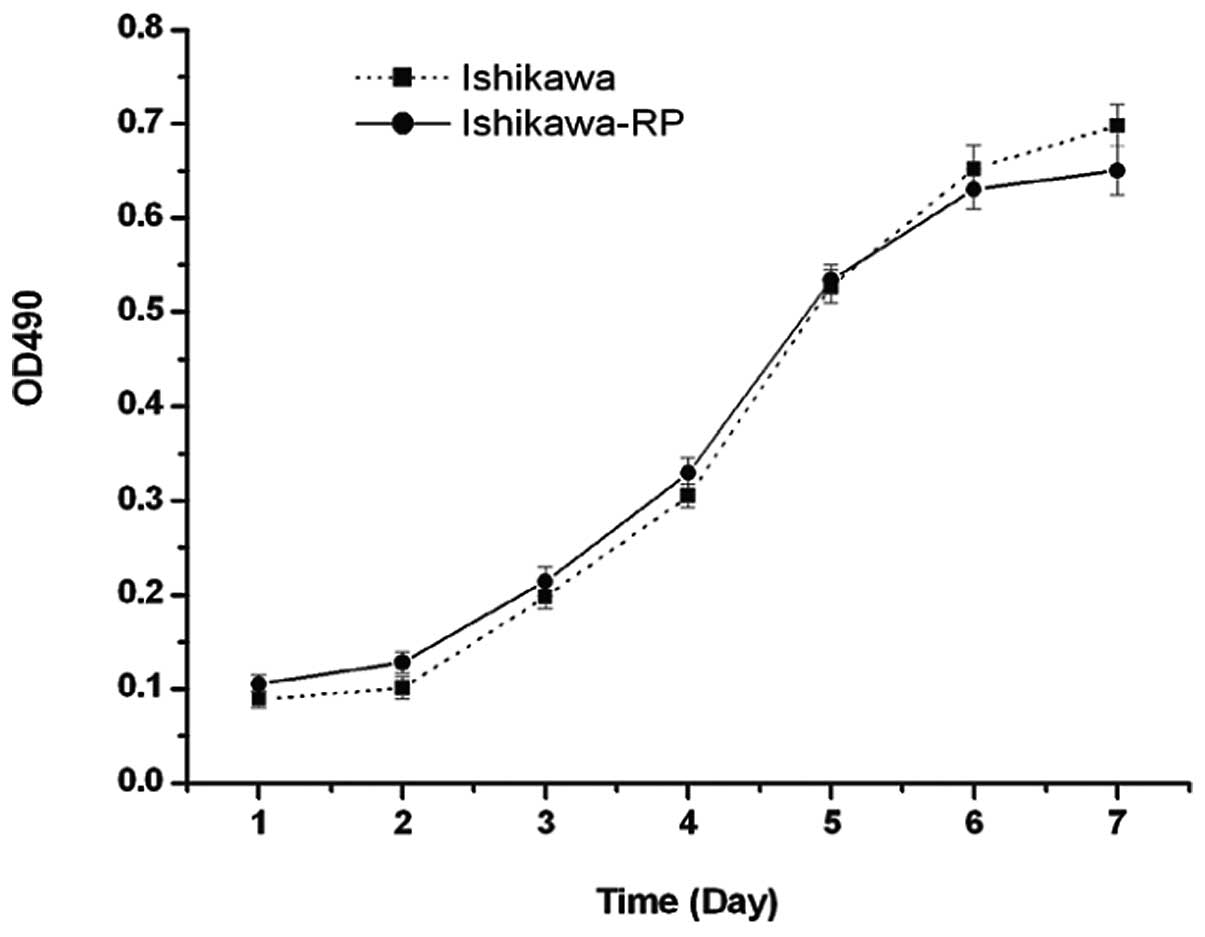
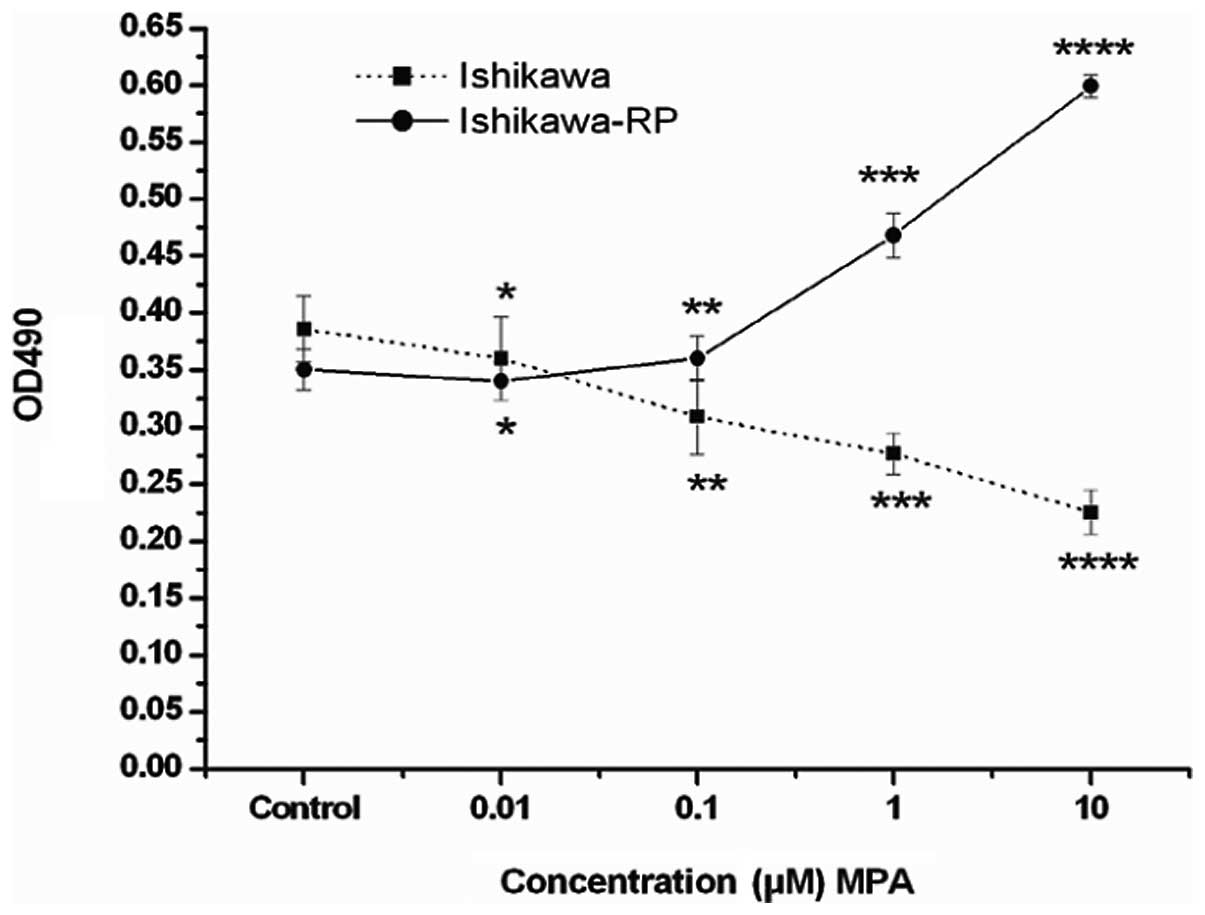
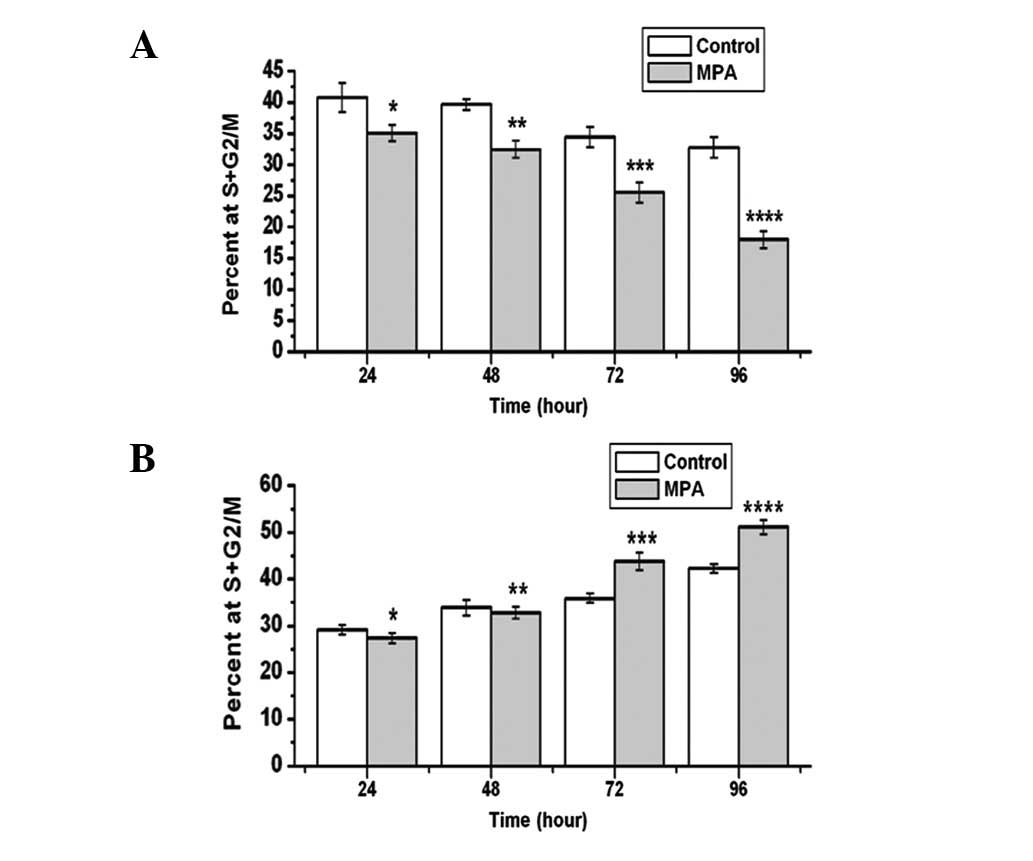
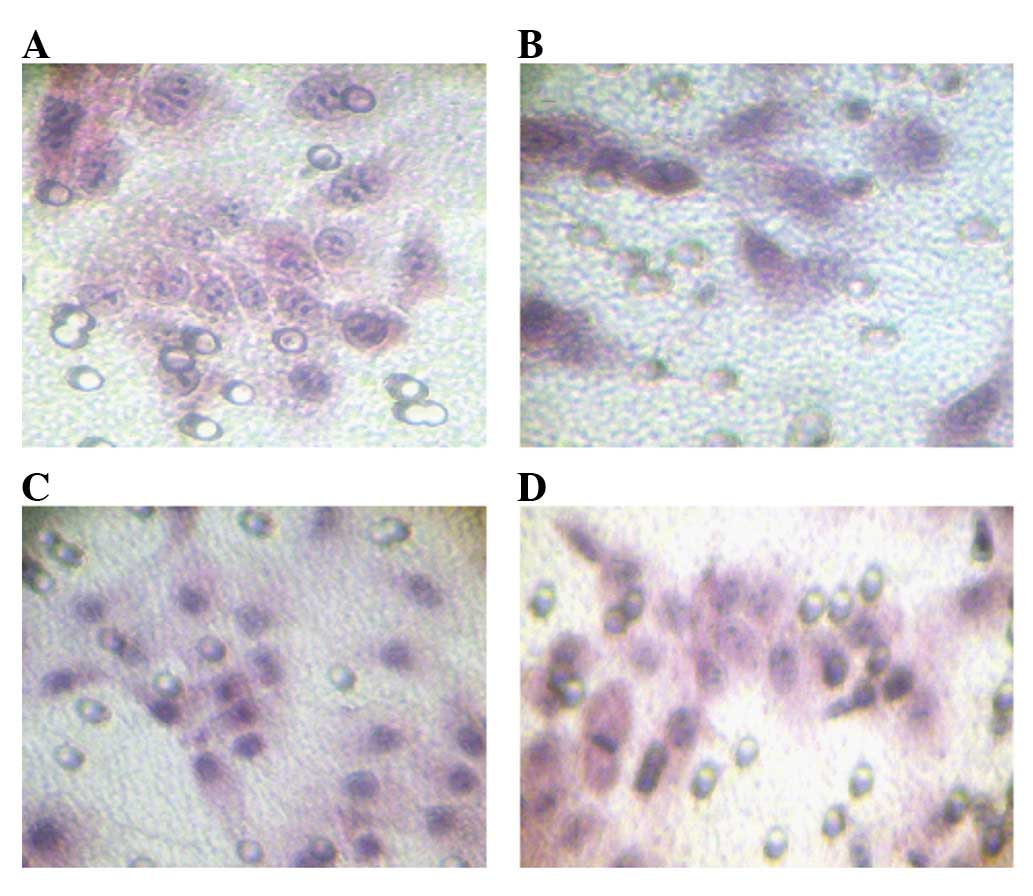
|
1
|
Kim JJ and Chapman-Davis E: Role of
progesterone in endometrial cancer. Semin Reprod Med. 28:81–90.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jadoul P and Donnez J: Conservative
treatment may be beneficial for young women with atypical
endometrial hyperplasia or endometrial adenocarcinoma. Fertil
Steril. 80:1315–1324. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cade TJ, Quinn MA, Rome RM and Neesham D:
Progestogen treatment options for early endometrial cancer. BJOG.
117:879–884. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Niwa K, Tagami K, Lian Z, Onogi K, Mori H
and Tamaya T: Outcome of fertility-preserving treatment in young
women with endometrial carcinomas. BJOG. 112:317–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Laurelli G, Di Vagno G, Scaffa C, Losito
S, Del Giudice M and Greggi S: Conservative treatment of early
endometrial cancer: preliminary results of a pilot study. Gynecol
Oncol. 120:43–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Murphy LC, Dotzlaw H, Wong MS, Miller T
and Murphy LJ: Mechanisms involved in the evolution of progestin
resistance in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 51:2051–2057.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Coldham NG, Patel K and Braunsberg H:
Hormone and cytotoxic drug responsiveness of cultured human breast
cancer cells resistant to specific hormones. Int J Cancer.
45:712–718. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Herman ME and Katzenellembogen BS:
Response-specific antiestrogen resistance in a newly characterized
MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line resulting from long-term
exposure to trans-hydroxytamoxifen. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
59:121–134. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nishida M, Kasahara K, Kaneko M, Iwasaki H
and Hayashi K: Establishment of a new human endometrial
adenocarcinoma cell line, Ishikawa cells, containing estrogen and
progesterone receptors. Nippon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi.
37:1103–1111. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ito K, Utsunomiya H, Yaegashi N and Sasano
H: Biological roles of estrogen and progesterone in human
endometrial carcinoma - new developments in potential endocrine
therapy for endometrial cancer. Endocr J. 54:667–679. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zaino RJ, Clarke CL, Mortel R and
Satyaswaroop PG and Satyaswaroop PG: Heterogeneity and
progesterone-receptor distribution in endometrial adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Res. 48:1889–1895. 1988.
|
|
12
|
Jongen V, Briët J, de Jong R, ten Hoor K,
Boezen M, van der Zee A and Nijman H: Expression of estrogen
receptor-alpha and -beta and progesterone receptor-A and -B in a
large cohort of patients with endometrioid endometrial cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 112:537–542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stoian SC, Simionescu C, Mărgăritescu C,
Stepan A and Nurciu M: Endometrial carcinomas: correlation between
ER, PR, Ki67 status and histopathological prognostic parameters.
Rom J Morphol Embryol. 52:631–636. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hall JM and McDonnell DP: The estrogen
receptor beta-isoform (ERbeta) of the human estrogen receptor
modulates ERalpha transcriptional activity and is a key regulator
of the cellular response to estrogens and antiestrogens.
Endocrinology. 140:5566–5578. 1999.
|
|
15
|
Ali SH, O’Donnell AL, Mohamed S, Mousa S
and Dandona P: Overexpression of estrogen receptor-alpha in the
endometrial carcinoma cell line Ishikawa: inhibition of growth and
angiogenic factors. Gynecol Oncol. 95:637–645. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ali SH, O’Donnell AL, Balu D, Pohl MB,
Seyler MJ, Mohamed S, Mousa S and Dandona P: Estrogen
receptor-alpha in the inhibition of cancer growth and angiogenesis.
Cancer Res. 60:7094–7098. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miyamoto T, Watanabe J, Hata H, Jobo T,
Kawaguchi M, Hattori M, Saito M and Kuramoto H: Significance of
progesterone receptor-A and -B expressions in endometrial
adenocarcinoma. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2:110–118.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Smid-Koopman E, Kuhne LC, Hanekamp EE,
Gielen SC, De Ruiter PE, Grootegoed JA, Helmerhorst TJ, Burger CW,
Brinkmann AO, Huikeshoven FJ and Blok LJ: Progesterone-induced
inhibition of growth and differential regulation of gene expression
in PRA- and/or PRB-expressing endometrial cancer cell lines. J Soc
Gynecol Invest. 12:285–292. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dai D, Wolf DM, Litman ES, White MJ and
Leslie KK: Progesterone inhibits human endometrial cancer cell
growth and invasiveness: down-regulation of cellular adhesion
molecules through progesterone B receptors. Cancer Res. 62:881–886.
2002.
|
|
20
|
Aghajanova L, Velarde MC and Giudice LC:
Altered gene expression profiling in endometrium: evidence for
progesterone resistance. Semin Reprod Med. 28:51–58. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Arpino G, Weiss H, Lee AV, Schiff R, De
Placido S, Osborne CK and Elledge RM: Estrogen receptor-positive,
progesterone receptor-negative breast cancer: association with
growth factor receptor expression and tamoxifen resistance. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 97:1254–1261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang S, Pudney J, Song J, Mor G, Schwartz
PE and Zheng W: Mechanisms involved in the evolution of progestin
resistance in human endometrial hyperplasia - precursor of
endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 88:108–117. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang S, Thiel KW and Leslie KK:
Progesterone: the ultimate endometrial tumor suppressor. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 22:145–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Engelsen IB, Stefansson IM, Akslen LA and
Salvesen HB: GATA3 expression in estrogen receptor alpha-negative
endometrial carcinomas identifies aggressive tumors with high
proliferation and poor patient survival. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
199:543–547. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Rubel CA, Jeong JW, Tsai SY, Lydon JP and
Demayo FJ: Epithelial-stromal interaction and progesterone
receptors in the mouse uterus. Semin Reprod Med. 28:27–35. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|