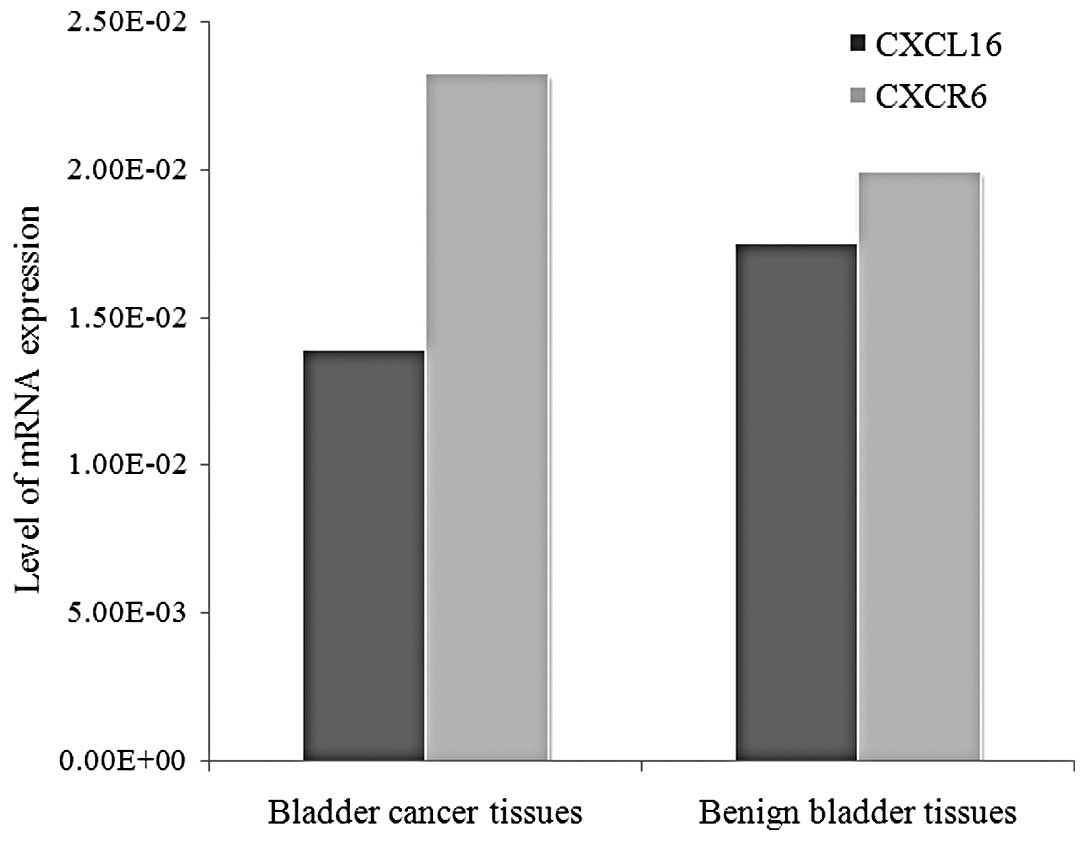
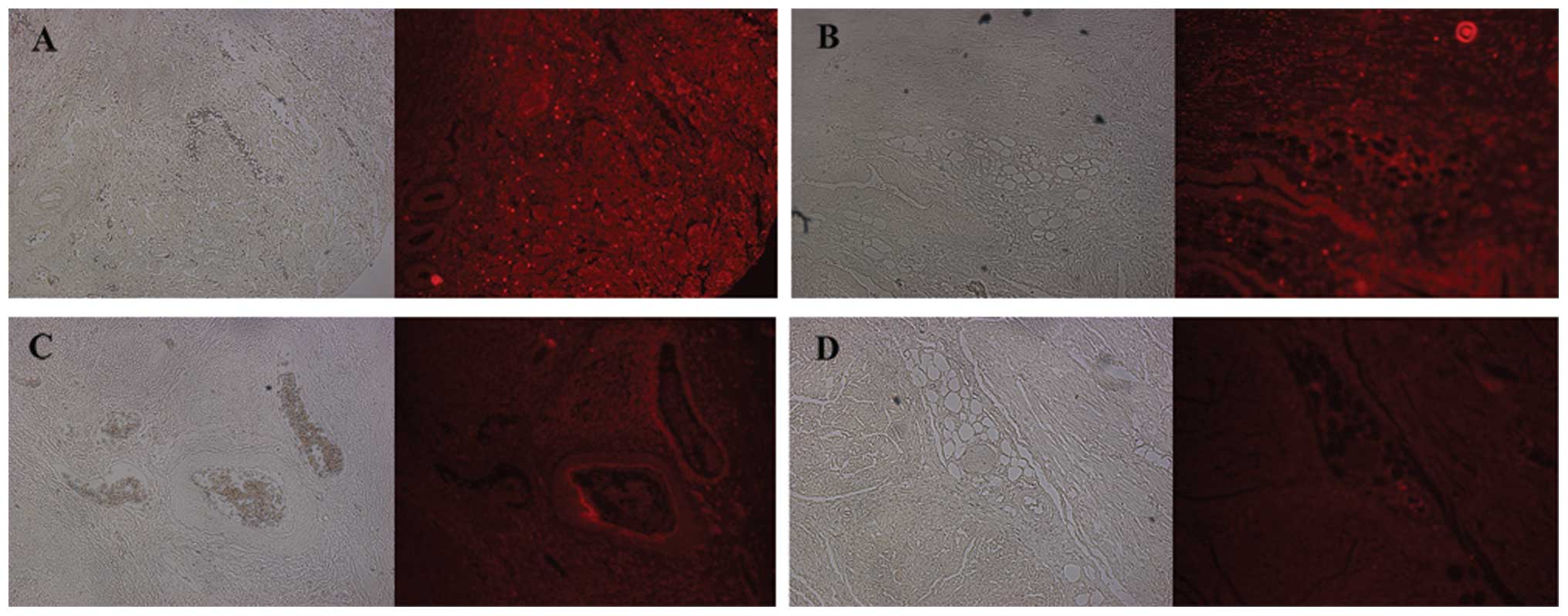
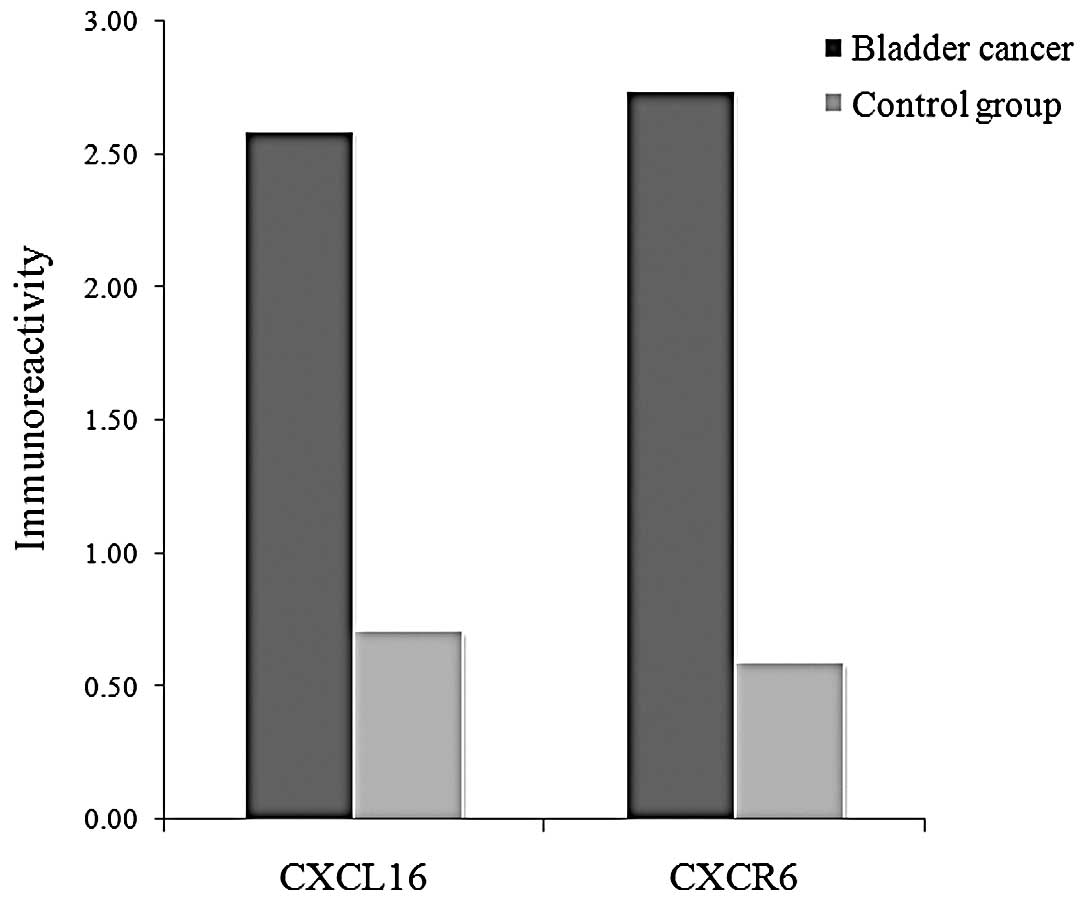
|
1
|
Latini DM, Lerner SP, Wade SW, Lee DW and
Quale DZ: Bladder cancer detection, treatment and outcomes:
Opportunities and challenges. Urology. 75:334–339. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, et al:
Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer:
Long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol. 19:666–675.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nishizawa K, Nishiyama H, Oishi S, et al:
Fluorescent imaging of high-grade bladder cancer using a specific
antagonist for chemokine receptor CXCR4. Int J Cancer.
127:1180–1187. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eisenhardt A, Frey U, Tack M, Rosskopf D,
Lummen G, Rubben H and Siffert W: Expression analysis and potential
functional role of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor in bladder cancer.
Eur Urol. 47:111–117. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Lu Y, Koch AE, Zhang J and
Taichman RS: CXCR6 induces prostate cancer progression by the
AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway. Cancer Res.
68:10367–10376. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koizumi K, Hojo S, Akashi T, Yasumoto K
and Saiki I: Chemokine receptors in cancer metastasis and cancer
cell-derived chemokines in host immune response. Cancer Sci.
98:1652–1658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hojo S, Koizumi K, Tsuneyama K, et al:
High-level expression of chemokine CXCL16 by tumor cells correlates
with a good prognosis and increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 67:4725–4731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ludwig A, Schulte A, Schnack C, et al:
Enhanced expression and shedding of the transmembrane chemokine
CXCL16 by reactive astrocytes and glioma cells. J Neurochem.
93:1293–1303. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Scholz F, Schulte A, Adamski F, et al:
Constitutive expression and regulated release of the transmembrane
chemokine CXCL16 in human and murine skin. J Invest Dermatol.
127:1444–1455. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tabata S, Kadowaki N, Kitawaki T, et al:
Distribution and kinetics of SR-PSOX/CXCL16 and CXCR6 expression on
human dendritic cell subsets and CD4+ T cells. J Leukoc Biol.
77:777–786. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Retz MM, Sidhu SS, Blaveri E, et al: CXCR4
expression reflects tumor progression and regulates motility of
bladder cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 114:182–189. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Saxman SB, Propert KJ, Einhorn LH, et al:
Long-term follow-up of a phase iii intergroup study of cisplatin
alone or in combination with methotrexate, vinblastine, and
doxorubicin in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma: A
cooperative group study. J Clin Oncol. 15:2564–2569.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lehmann J, Retz M and Stockle M: Is there
standard chemotherapy for metastatic bladder cancer? Quality of
life and medical resources utilization based on largest to date
randomized trial. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 47:171–179. 2003.
|
|
14
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
de Visser KE, Eichten A and Coussens LM:
Paradoxical roles of the immune system during cancer development.
Nat Rev Cancer. 6:24–37. 2006.
|
|
17
|
Ha HK, Lee W, Park HJ, Lee SD, Lee JZ and
Chung MK: Clinical significance of CXCL16/CXCR6 expression in
patients with prostate cancer. Mol Med Report. 4:419–424.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luster AD: Chemokines-chemotactic
cytokines that mediate inflammation. N Engl J Med. 338:436–445.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Struyf S, Proost P and Van Damme J:
Regulation of the immune response by the interaction of chemokines
and proteases. Adv Immunol. 81:1–44. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Balkwill F: The significance of cancer
cell expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Semin Cancer Biol.
14:171–179. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun YX, Wang J, Shelburne CE, et al:
Expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 (SDF-1) in human prostate cancers
(PCa) in vivo. J Cell Biochem. 89:462–473. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu W, Zhen X, Xiong B, Wang B, Zhang W and
Zhou W: CXCR6 is expressed in human prostate cancer in vivo and is
involved in the in vitro invasion of PC3 and LNCap cells. Cancer
Sci. 99:1362–1369. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Staller P, Sulitkova J, Lisztwan J, Moch
H, Oakeley EJ and Krek W: Chemokine receptor CXCR4 downregulated by
von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor pVHL. Nature. 425:307–311.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu Y, Wang J, Xu Y, et al: CXCL16
functions as a novel chemotactic factor for prostate cancer cells
in vitro. Mol Cancer Res. 6:546–554. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Darash-Yahana M, Gillespie JW, Hewitt SM,
et al: The chemokine CXCL16 and its receptor, CXCR6, as markers and
promoters of inflammation-associated cancers. PLoS One.
4:e66952009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Deng L, Chen N, Li Y, Zheng H and Lei Q:
CXCR6/CXCL16 functions as a regulator in metastasis and progression
of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1806:42–49. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Belperio JA, Keane MP, Arenberg DA, et al:
CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol. 68:1–8. 2000.
|
|
28
|
Gaida MM, Gunther F, Wagner C, et al:
Expression of the CXCR6 on polymorphonuclear neutrophils in
pancreatic carcinoma and in acute, localized bacterial infections.
Clin Exp Immunol. 154:216–223. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Held-Feindt J, Rehmke B, Mentlein R, et
al: Overexpression of CXCL16 and its receptor CXCR6/bonzo promotes
growth of human schwannomas. Glia. 56:764–774. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gutwein P, Schramme A, Sinke N, et al:
Tumoural CXCL16 expression is a novel prognostic marker of longer
survival times in renal cell cancer patients. Eur J Cancer.
45:478–489. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ou DL, Chen CL, Lin SB, Hsu CH and Lin LI:
Chemokine receptor expression profiles in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
and their association with metastasis and radiotherapy. J Pathol.
210:363–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|