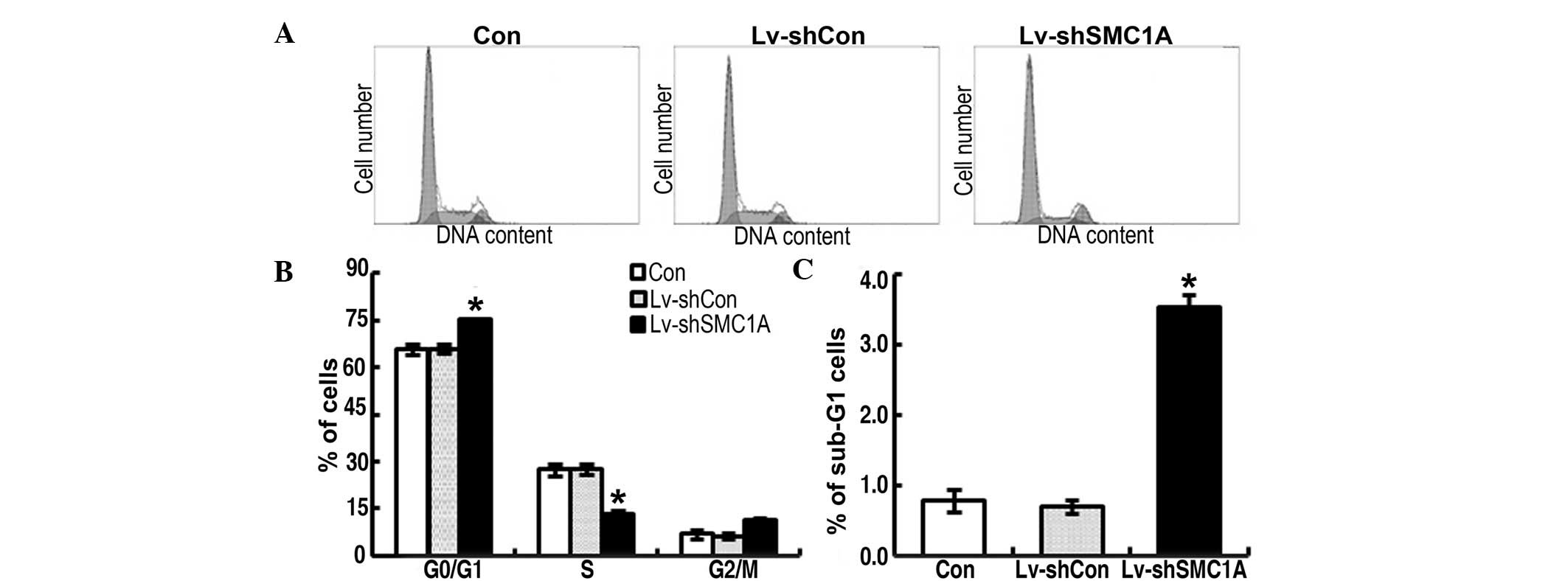
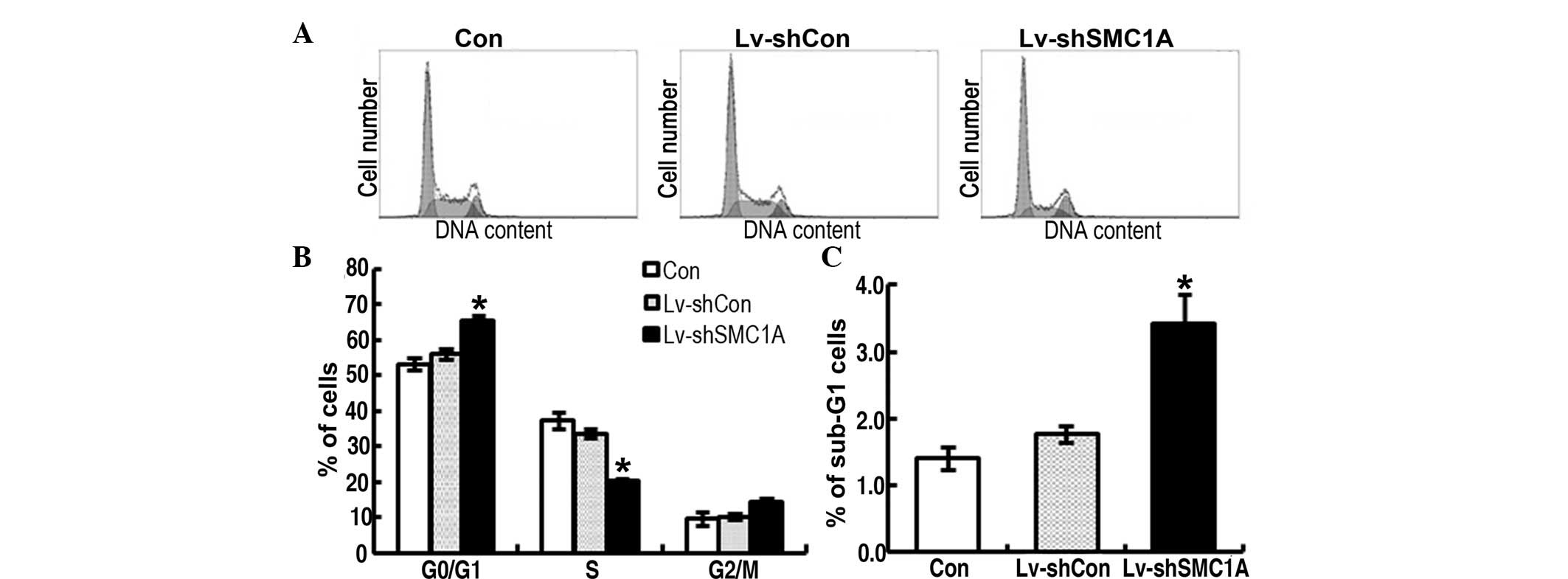
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ellison LF and Gibbons L; Canadian Cancer
Survival Analysis Group: Five-year relative survival from prostate,
breast, colorectal and lung cancer. Health Rep. 13:23–34.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Paleari L, Russo P, Cesario A and Granone
P: Factors predicting poor survival after resection of stage IA
non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 136:241–242.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miller YE: Pathogenesis of lung cancer:
100 year report. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 33:216–223.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Normanno N, Bianco C, De Luca A, Maiello
MR and Salomon DS: Target-based agents against ErbB receptors and
their ligands: a novel approach to cancer treatment. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 10:1–21. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun S, Schiller JH, Spinola M and Minna
JD: New molecularly targeted therapies for lung cancer. J Clin
Invest. 117:2740–2750. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al:
Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor
underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Negrini S, Gorgoulis VG and Halazonetis
TD: Genomic instability - an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 11:220–228. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haering CH, Löwe J, Hochwagen A and
Nasmyth K: Molecular architecture of SMC proteins and the yeast
cohesin complex. Mol Cell. 9:773–788. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Michaelis C, Ciosk R and Nasmyth K:
Cohesins: chromosomal proteins that prevent premature separation of
sister chromatids. Cell. 91:35–45. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guacci V, Koshland D and Strunnikov A: A
direct link between sister chromatid cohesion and chromosome
condensation revealed through the analysis of MCD1 in S.
cerevisiae. Cell. 91:47–57. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hauf S, Waizenegger IC and Peters JM:
Cohesin cleavage by separase required for anaphase and cytokinesis
in human cells. Science. 293:1320–1323. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nasmyth K and Haering CH: Cohesin: its
roles and mechanisms. Annu Rev Genet. 43:525–558. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jessberger R: Cohesin’s dual role in the
DNA damage response: repair and checkpoint activation. EMBO J.
28:2491–2493. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Watrin E and Peters JM: The cohesin
complex is required for the DNA damage-induced G2/M checkpoint in
mammalian cells. EMBO J. 28:2625–2635. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu H, Yan M, Patra J, et al: Enhanced
RAD21 cohesin expression confers poor prognosis and resistance to
chemotherapy in high grade luminal, basal and HER2 breast cancers.
Breast Cancer Res. 13:R92011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Homme C, Krug U, Tidow N, et al: Low SMC1A
protein expression predicts poor survival in acute myeloid
leukemia. Oncol Rep. 24:47–56. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barber TD, McManus K, Yuen KW, et al:
Chromatid cohesion defects may underlie chromosome instability in
human colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3443–3448.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo S, Sun M, Jiang R, Wang G and Zhang X:
Establishment of promary mouse lung adenocarcinoma cell culture.
Oncol Lett. 2:629–623. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim ST, Xu B and Kastan MB: Involvement of
the cohesin protein, Smc1, in Atm-dependent and independent
responses to DNA damage. Genes Dev. 16:560–570. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yazdi PT, Wang Y, Zhao S, Patel N, Lee EY
and Qin J: SMC1 is a downstream effector in the ATM/NBS1 branch of
the human S-phase checkpoint. Genes Dev. 16:571–582. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kitagawa R, Bakkenist CJ, McKinnon PJ and
Kastan MB: Phosphorylation of SMC1 is a critical downstream event
in the ATM-NBS1-BRCA1 pathway. Genes Dev. 18:1423–1438. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sjögren C and Nasmyth K: Sister chromatid
cohesion is required for postreplicative double-strand break repair
in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Biol. 11:991–995.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barber TD, McManus K, Yuen KW, et al:
Chromatid cohesion defects may underlie chromosome instability in
human colorectal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3443–3448.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Musio A, Montagna C, Mariani T, et al:
SMC1 involvement in fragile site expression. Hum Mol Genet.
14:525–533. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Porkka KP, Tammela TL, Vessella RL and
Visakorpi T: RAD21 and KIAA0196 at 8q24 are amplified and
overexpressed in prostate cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
39:1–10. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Oishi Y, Nagasaki K, Miyata S, et al:
Functional pathway characterized by gene expression analysis of
supraclavicular lymph node metastasis-positive breast cancer. J Hum
Genet. 52:271–279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ghiselli G and Iozzo RV: Overexpression of
bamacan/SMC3 causes transformation. J Biol Chem. 275:20235–20238.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hömme C, Krug U, Tidow N, et al: Low SMC1A
protein expression predicts poor survival in acute myeloid
leukemia. Oncol Rep. 24:47–56. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yamamoto G, Irie T, Aida T, Nagoshi Y,
Tsuchiya R and Tachikawa T: Correlation of invasion and metastasis
of cancer cells, and expression of the RAD21 gene in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 448:435–441. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim DH, Behlke MA, Rose SD, Chang MS, Choi
S and Rossi JJ: Synthetic dsRNA Dicer substrates enhance RNAi
potency and efficacy. Nat Biotechnol. 23:222–226. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo W, Zhang Y, Chen T, et al: Efficacy of
RNAi targeting of pyruvate kinase M2 combined with cisplatin in a
lung cancer model. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:65–72. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Manilla P, Rebello T, Afable C, et al:
Regulatory considerations for novel gene therapy products: a review
of the process leading to the first clinical lentiviral vector. Hum
Gene Ther. 16:17–25. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gao N, Zhang XY, Jiang R, et al:
Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference and over-expression of CDK2AP1
cDNA regulate CDK2AP1 expression in human lung cancer A549 cells.
Chem Res Chin Univ. 27:445–449. 2011.
|
|
35
|
Sun M, Jiang R, Li JD, et al: MED19
promotes proliferation and tumorigenesis of lung cancer. Mol Cell
Biochem. 355:27–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
37
|
Elstein KH and Zucker RM: Comparison of
cellular and nuclear flow cytometric techniques for discriminating
apoptotic subpopulations. Exp Cell Res. 211:322–331. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Riccardi C and Nicoletti I: Analysis of
apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. Nat
Protoc. 1:1458–1461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen HY, Yu SL, Chen CH, et al: A
five-gene signature and clinical outcome in non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 356:11–20. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mannini L and Musio A: The dark side of
cohesin: the carcinogenic point of view. Mutat Res. 728:81–87.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lin RK, Wu CY, Chang JW, et al:
Dysregulation of p53/Sp1 control leads to DNA methyltransferase-1
overexpression in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 70:5807–5817. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Altundag O, Altundag K, Morandi P and
Gunduz M: Cytokines and chemokines as predictive markers in
non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases. Lung
Cancer. 47:291–292. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shaozhang Z, Xiaomei L, Aiping Z, Jianbo
H, Xiangqun S and Qitao Y: Detection of EML4-ALK fusion genes in
non-small cell lung cancer patients with clinical features
associated with EGFR mutations. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
51:925–932. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang CG, Wang R, Sun M, Li J, Gao N, Zhang
XY, Shi DL and Jin CY: In vivo antitumor effect of siRNA against
STAT3 on transplanted Lewis lung cancer in mice. Chem Res Chin
Univ. 24:330–337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|