|
1
|
Vuhahula EA: Salivary gland tumors in
Uganda: clinical pathological study. Afr Health Sci. 4:15–23.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pinkston JA and Cole P: Incidence rates of
salivary gland tumors: results from a population-based study.
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 120:834–840. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Clayman MA, Clayman SM and Seagle MB: A
review of the surgical and medical treatment of Frey syndrome. Ann
Plast Surg. 57:581–584. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ali NS, Nawaz A, Rajput S and Ikram M:
Parotidectomy: a review of 112 patients treated at a teaching
hospital in Pakistan. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 11:1111–1113.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nitzan D, Kronenberg J, Horowitz Z, et al:
Quality of life following parotidectomy for malignant and benign
disease. Plast Reconstr Surg. 114:1060–1067. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dulguerov P, Marchal F and Gysin C: Frey
syndrome before Frey: the correct history. Laryngoscope.
109:1471–1473. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koch M, Zenk J and Iro H: Long-term
results of morbidity after parotid gland surgery in benign disease.
Laryngoscope. 120:724–730. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Bree R, van der Waal I and Leemans CR:
Management of Frey syndrome. Head Neck. 29:773–778. 2007.
|
|
9
|
Dulguerov P, Quinodoz D, Vaezi A, Cosendai
G, Piletta P and Lehmann W: New objective and quantitative tests
for gustatory sweating. Acta Otolaryngol. 119:599–603. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sanabria A, Kowalski LP, Bradley PJ, et
al: Sternocleidomastoid muscle flap in preventing Frey’s syndrome
after parotidectomy: a systematic review. Head Neck. 34:589–598.
2012.
|
|
11
|
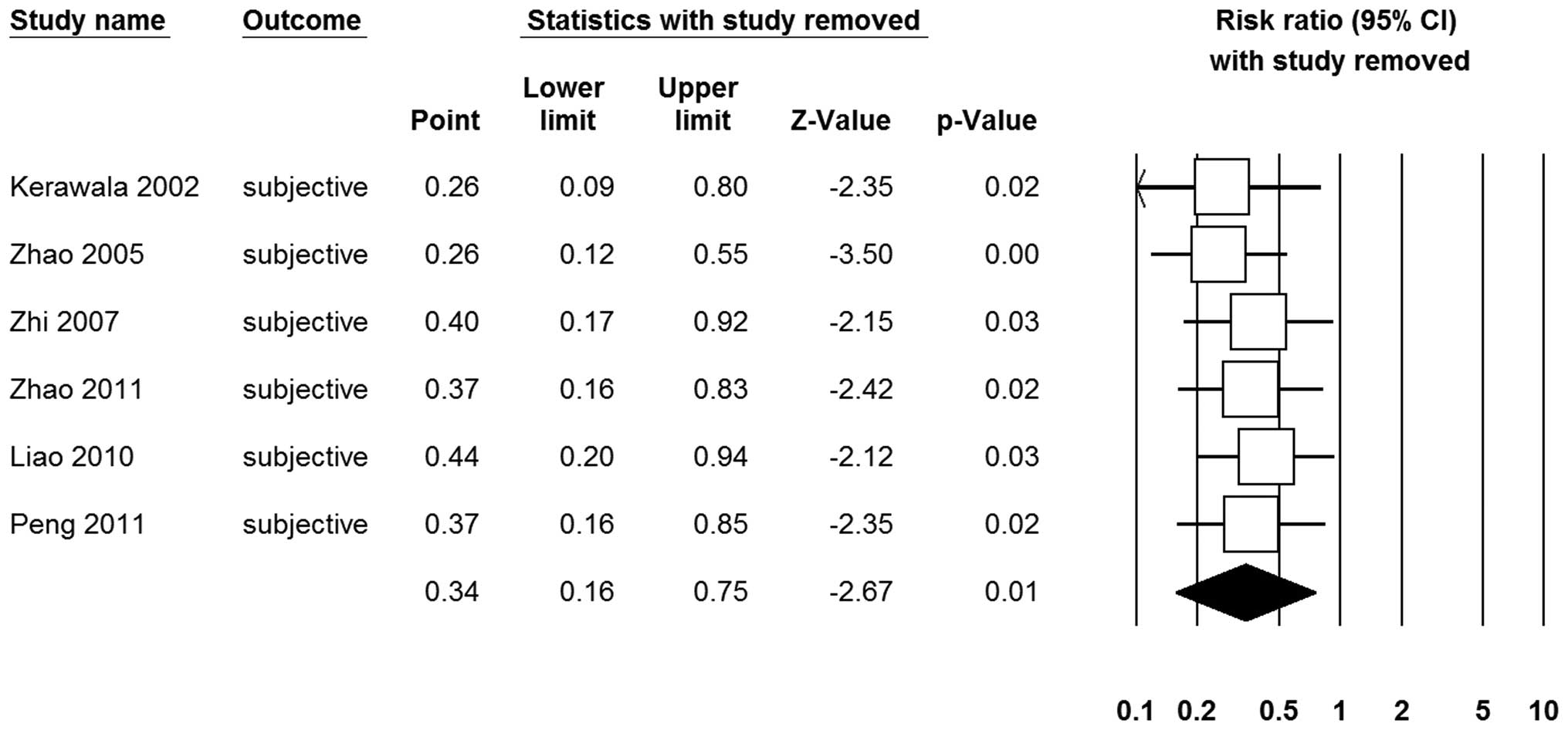
Kerawala CJ, McAloney N and Stassen LF:
Prospective randomised trial of the benefits of a
sternocleidomastoid flap after superficial parotidectomy. Br J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 40:468–472. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Asal K, Köybaşioğlu A, Inal E, et al:
Sternocleidomastoid muscle flap reconstruction during parotidectomy
to prevent Frey’s syndrome and facial contour deformity. Ear Nose
Throat J. 84:173–176. 2005.
|
|
13
|
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al:
The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and
meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions:
explanation and elaboration. J Clin Epidemiol. 62:e1–e34. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zeng XT, Bao CP, Cao SY and Liu JY: The
third part in meta-analysis series: Tools for assessing the quality
of randomized controlled trials. Chin J Evid Based Cardiovasc Med.
4:183–185. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
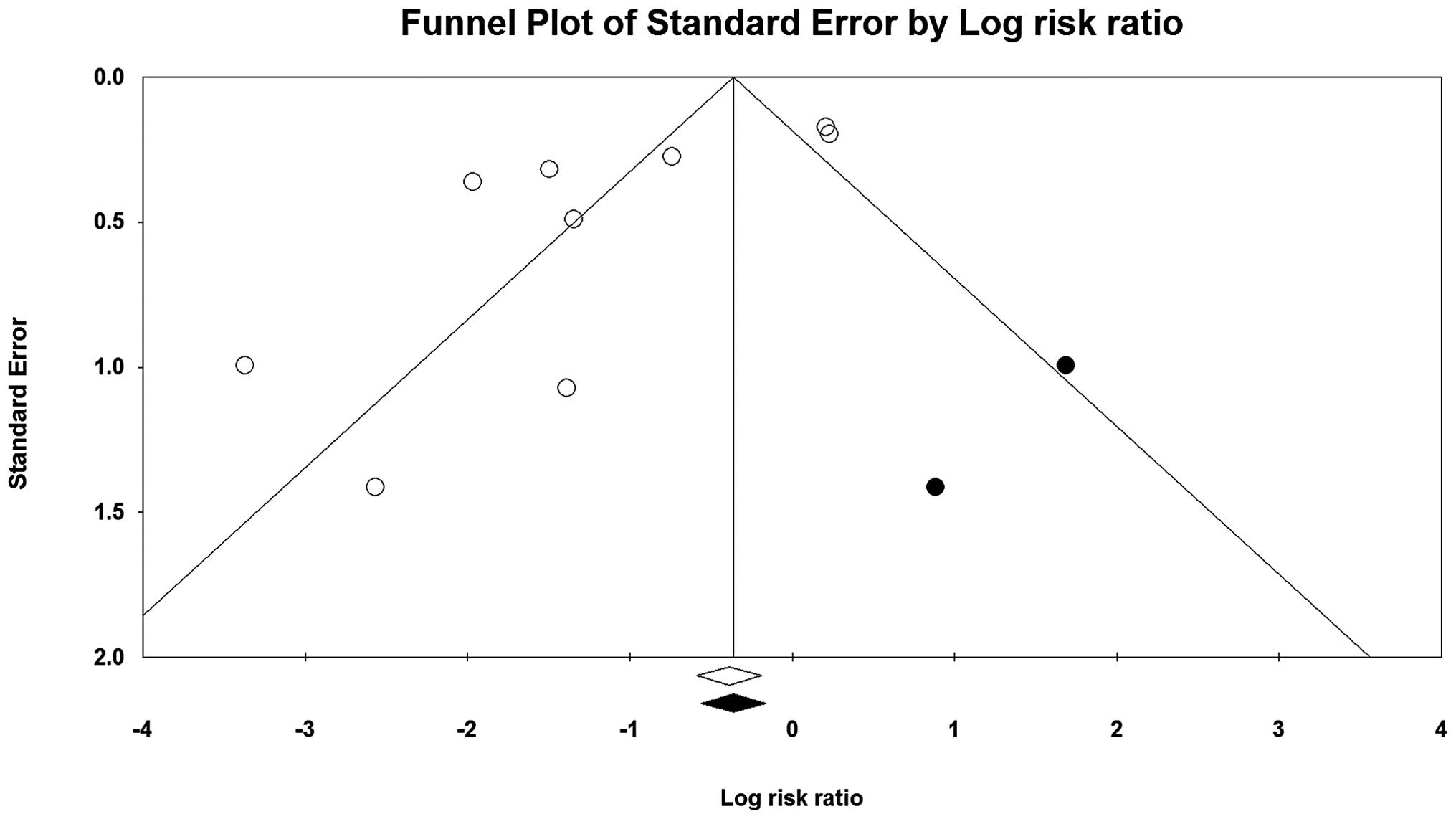
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Duval S and Tweedie R: Trim and fill: A
simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for
publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 56:455–463. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Borenstein M, Hedges L and Rothstein H:
Comprehensive Meta-analysis. Biostat; Englewood, New Jersey: 2005,
(computer software).
|
|
19
|
Zhao HW, Li LJ, Han B, Liu H and Pan J: A
retrospective study on the complications after modified
parotidectomy in benign tumors of parotid gland. Hua Xi Kou Qiang
Yi Xue Za Zhi. 23:53–56. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Chen R and Yang K: Clinical observation of
sternocleidomastoid muscle flap to repair tissue defect and in
preventing Frey syndrome after parotidectomy. Chongqing Yi Yao.
33:94–95. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Zhi KQ, Wen YM and Li LJ: Prevention and
treatment of complications following benign parotid neoplasms
dissection. Xi’an Jiao Tong Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 28:116–117.
2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Ding YF, Zhou PG, Gu YC and Chen Y:
Applicatian of sterno-cleidomastoid muscle flap in benign
parotidectomies. J Dental Preven Treat. 18:88–90. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Liao SK, Li JC, Zhang K, Xu JC, Xu T and
Chen YF: Clinical study of 48 cases of sternocleidomastoid muscle
flap in parotidectomy. Shi Yong Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 3:106–108.
2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Deng YQ, Zheng CS and Zhu YM: Application
of sternocleidomastoid muscle flap and parotid fascia flap in
operation on parotid benign tumor. J Oral Sci Res. 27:893–895.
2011.
|
|
25
|
Peng YF and Chen YD: Clinical analysis of
45 cases of parotid gland tumor. Zhong Wai Jian Kang Wen Zhai.
8:2412011.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Zhao J, Yu HQ and Liu AG: Comparative
study of using heterogeneous acellular dermal matrix and
reconstruction of parotid masseter faseial in prevention of Frey’s
syndrome after parotidectomy. Stomatology. 31:356–359. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Li MD and Xu JM: Clinical study of veiled
incision and sternocleidomastoid flap in the operation of parotid
gland tumor. Zhong Wai Yi Liao. 31:44–46. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Li C, Fan JC, Li B, et al: Meta-analysis
of surgical techniques for preventing Frey syndrome and a concave
facial deformity after parotidectomy. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou
Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 46:580–585. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Glaister DH, Hearnshaw JR, Heffron PF,
Peck AW and Patey DH: The mechanism of post-parotidectomy gustatory
sweating (the auriculo-temporal syndrome). Br Med J. 2:942–946.
1958. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rubinstein RY, Rosen A and Leeman D: Frey
syndrome: treatment with temporoparietal fascia flap interposition.
Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 125:808–811. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moulton-Barrett R, Allison G and Rappaport
I: Variation’s in the use of SMAS (superficial musculoaponeurotic
system) to prevent Frey’s syndrome after parotidectomy. Int Surg.
81:174–176. 1996.
|
|
32
|
Zeng XT, Tang XJ, Wang XJ, et al: AlloDerm
implants for prevention of Frey syndrome after parotidectomy: a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Med Rep. 5:974–980.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oliveira LR, Soave DF, Oliveira-Costa JP,
Zorgetto VA and Ribeiro-Silva A: Prognostic factors in patients
with malignant salivary gland neoplasms in a Brazilian population.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:363–368. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nguansangiam S, Jesdapatarakul S, Dhanarak
N and Sosrisakorn K: Accuracy of fine needle aspiration cytology of
salivary gland lesions: routine diagnostic experience in Bangkok,
Thailand. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:1583–1588. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|