|
1
|
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC
and van de Velde CJ: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 374:477–490. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kodera Y, Yamamura Y, Torii A, Uesaka K,
Hirai T, Yasui K, et al: The prognostic value of preoperative serum
levels of CEA and CA19-9 in patients with gastric cancer. Am J
Gastroenterol. 91:49–53. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tocchi A, Costa G, Lepre L, Liotta G,
Mazzoni G, Cianetti A and Vannini P: The role of serum and gastric
juice levels of carcinoembryonic antigen, CA19.9 and CA72.4 in
patients with gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 124:450–455.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hummel R, Hussey DJ and Haier J:
MicroRNAs: predictors and modifiers of chemo- and radiotherapy in
different tumour types. Eur J Cancer. 46:298–311. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamao T, Kai S, Kazami A, Koizumi K, Handa
T, Takemoto N and Maruyama M: Tumor markers CEA, CA19-9 and CA125
in monitoring of response to systemic chemotherapy in patients with
advanced gastric cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 29:550–555. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J,
Hundahl SA, Estes NC, Stemmermann GN, et al: Chemoradiotherapy
after surgery compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the
stomach or gastroesophageal junction. N Engl J Med. 345:725–730.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ichikawa D, Koike H, Ikoma H, Ikoma D,
Tani N, Otsuji E, et al: Detection of aberrant methylation as a
tumor marker in serum of patients with gastric cancer. Anticancer
Res. 24:2477–2481. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tani N, Ichikawa D, Ikoma D, Tomita H, Sai
S, Ikoma H, et al: Circulating cell-free mRNA in plasma as a tumor
marker for patients with primary and recurrent gastric cancer.
Anticancer Res. 27:1207–1212. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li N, Zhang J, Liang Y, Shao J, Peng F,
Sun M, et al: A controversial tumor marker: is SM22 a proper
biomarker for gastric cancer cells? J Proteome Res. 6:3304–3312.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
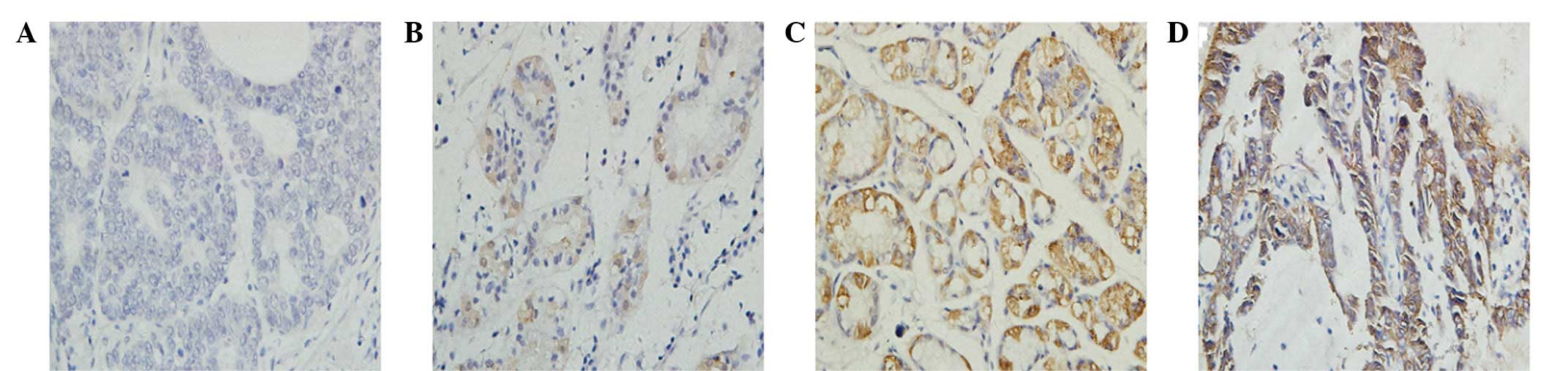
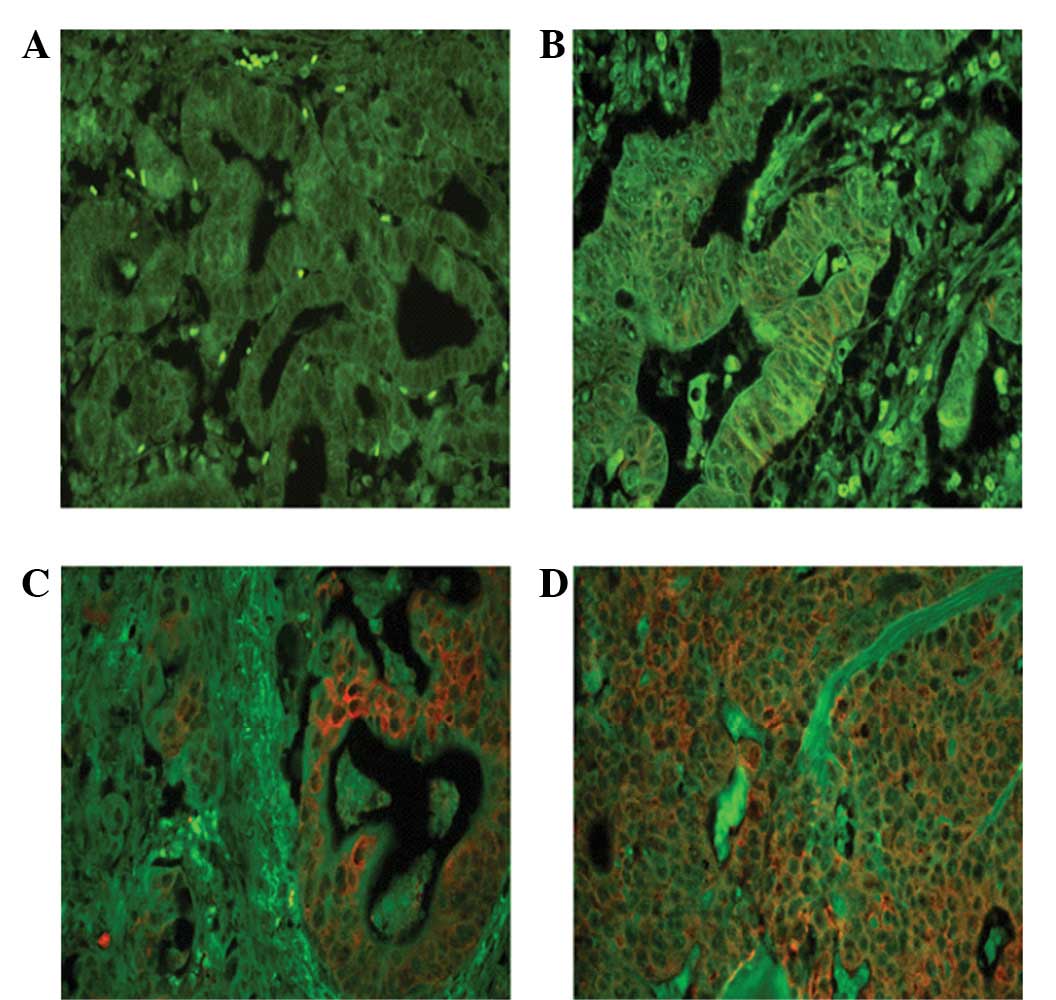
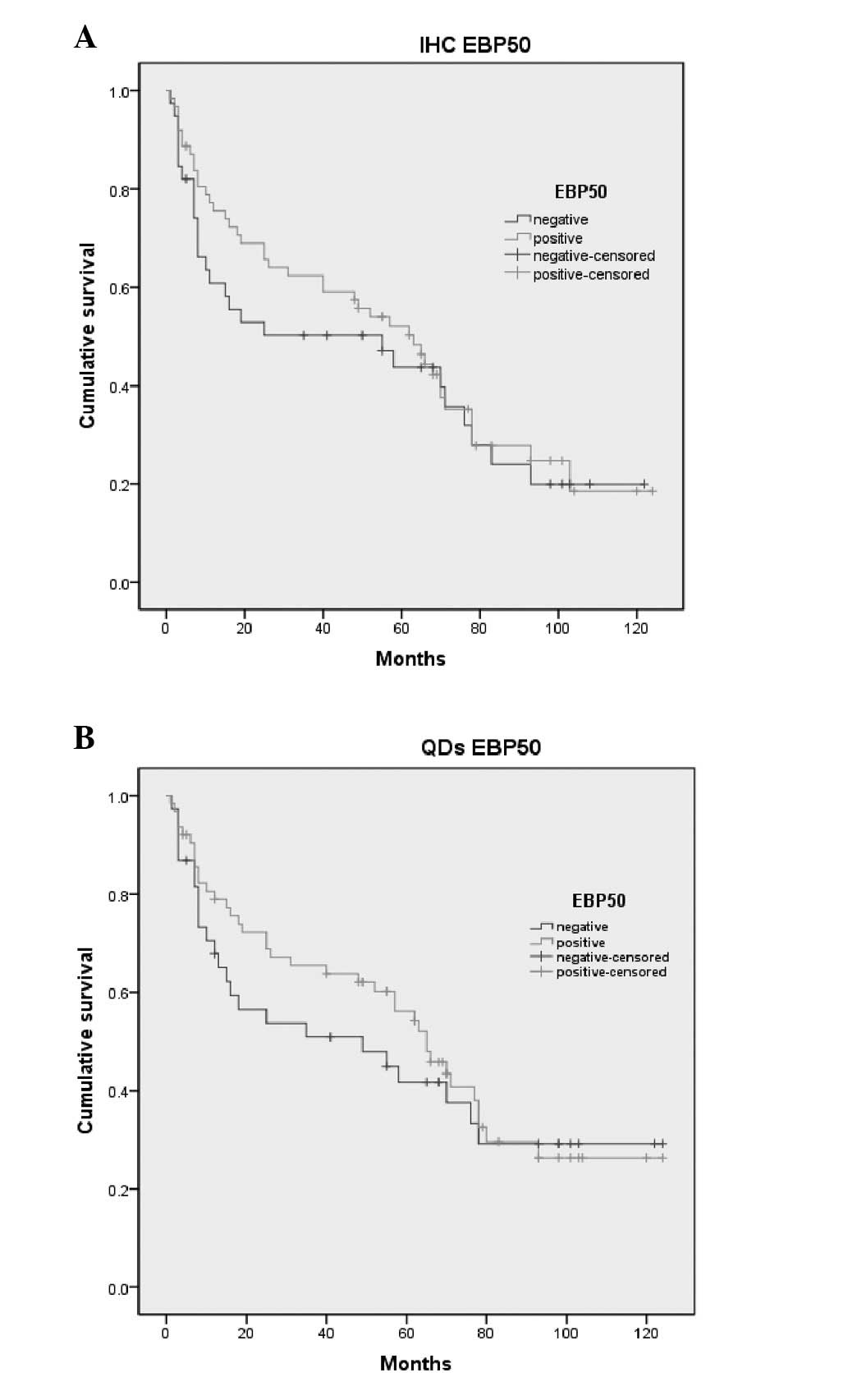
Shibata T, Chuma M, Kokubu A, Sakamoto M
and Hirohashi S: EBP50, a beta-catenin-associating protein,
enhances Wnt signaling and is over-expressed in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 38:178–186. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Song J, Bai J, Yang W, Gabrielson EW, Chan
DW and Zhang Z: Expression and clinicopathological significance of
oestrogen-responsive ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein 50
in breast cancer. Histopathology. 51:40–53. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zheng JF, Sun LC, Liu H, Huang Y, Li Y and
He J: EBP50 exerts tumor suppressor activity by promoting cell
apoptosis and retarding extracellular signal-regulated kinase
activity. Amino Acids. 38:1261–1268. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bellizzi A, Mangia A, Malfettone A,
Cardone RA, Simone G, Reshkin SJ and Paradiso A: Na+/H+ exchanger
regulatory factor 1 expression levels in blood and tissue predict
breast tumour clinical behaviour. Histopathology. 58:1086–1095.
2011.
|
|
14
|
Ingraffea J, Reczek D and Bretscher A:
Distinct cell type-specific expression of scaffolding proteins
EBP50 and E3KARP: EBP50 is generally expressed with ezrin in
specific epithelia, whereas E3KARP is not. Eur J Cell Biol.
81:61–68. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sobin LH and Fleming ID: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumors, fifth edition (1997). Union
Internationale Contre le Cancer and the American Joint Committee on
Cancer. Cancer. 80:1803–1804. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu Y, Wu Q, Liu S, Wei L, Chen X, Yan Z,
et al: Study of rice pollen grains by multispectral imaging
microscopy. Microsc Res Tech. 68:335–346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo N, Zeng L and Wu Q: A method based on
multispectral imaging technique for white blood cell segmentation.
Comput Biol Med. 37:70–76. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dickinson ME, Bearman G, Tille S, Lansford
R and Fraser SE: Multi-spectral imaging and linear unmixing add a
whole new dimension to laser scanning fluorescence microscopy.
Biotechniques. 31:12721274–1276. 12782001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen H, Xue J, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Gao J and
Yu B: Comparison of quantum dots immunofluorescence histochemistry
and conventional immunohistochemistry for the detection of
caveolin-1 and PCNA in the lung cancer tissue microarray. J Mol
Histol. 40:261–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao W, Feng D, Bian W, et al: EBP50
inhibits EGF-induced breast cancer cell proliferation by blocking
EGFR phosphorylation. Amino Acids. 43:2027–2035. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kislin KL, McDonough WS, Eschbacher JM, et
al: NHERF-1: modulator of glioblastoma cell migration and invasion.
Neoplasia. 11:377–387. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Malfettone A, Saponaro C, Paradiso A, et
al: Peritumoral vascular invasion and NHERF1 expression define an
immunophenotype of grade 2 invasive breast cancer associated with
poor prognosis. BMC Cancer. 12:1062012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bornschein J and Malfertheiner P: Gastric
carcinogenesis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 396:729–742. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kawachi T, Kurisu M, Numanyu N, Sasajima K
and Sano T: Precancerous changes in the stomach. Cancer Res.
36:2673–2677. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Muthu MS, Kulkarni SA, Raju A and Feng SS:
Theranostic liposomes of TPGS coating for targeted co-delivery of
docetaxel and quantum dots. Biomaterials. 33:3494–3501. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shao L, Gao Y and Yan F: Semiconductor
quantum dots for biomedicial applications. Sensors (Basel).
11:11736–11751. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|