|
1.
|
Hildebrandt B and Wust P: The biologic
rationale of hyperthermia. Cancer Treat Res. 134:171–184.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
van der Zee J: Heating the patient: a
promising approach? Ann Oncol. 13:1173–1184. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Yonezawa M, Otsuka T, Matsui N, et al:
Hyperthermia induces apoptosis in malignant fibrous histiocytoma
cells in vitro. Int J Cancer. 66:347–351. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
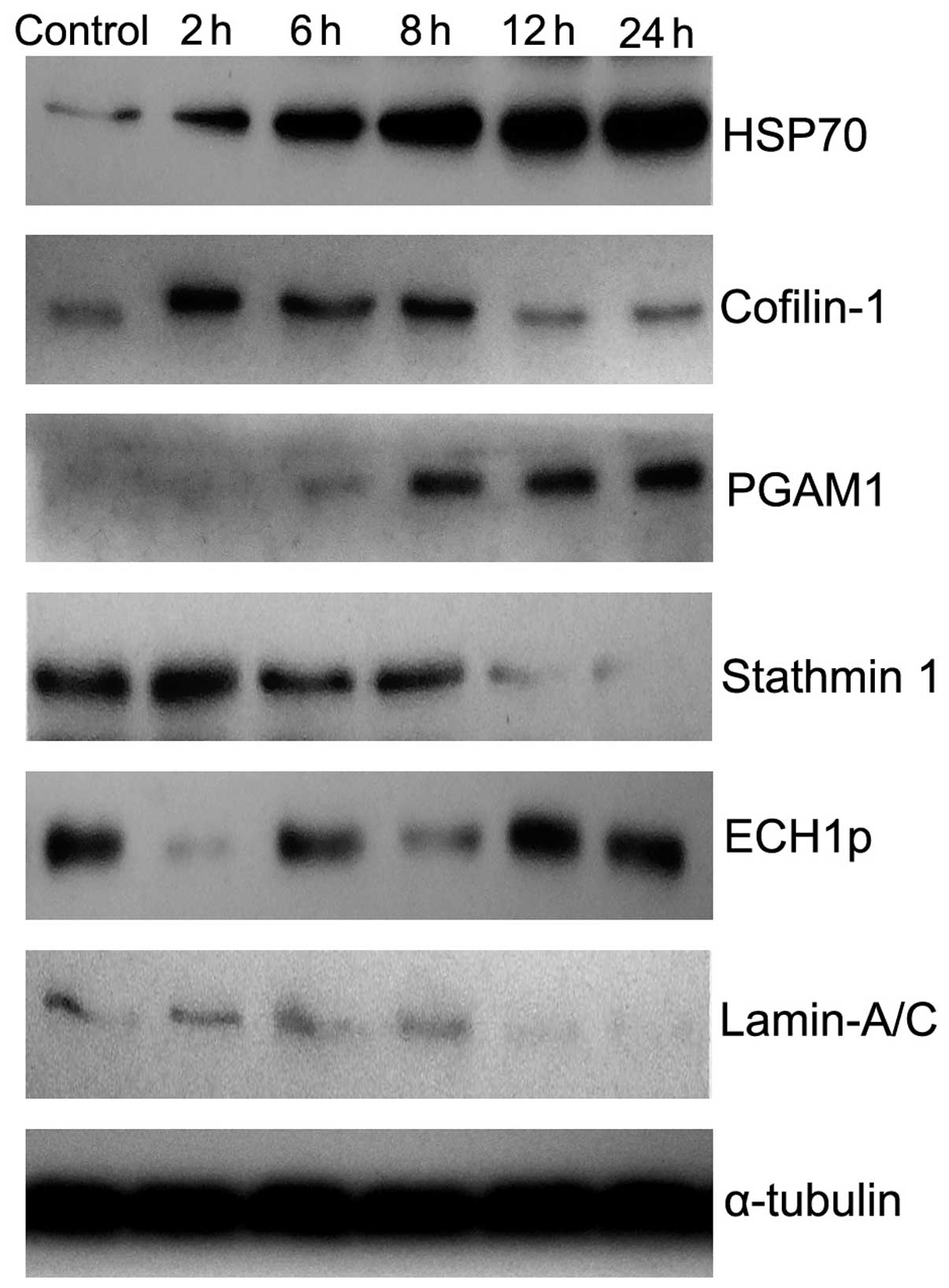
|
Dewhirst MW, Vujaskovic Z, Jones E and
Thrall D: Re-setting the biologic rationale for thermal therapy.
Int J Hyperthermia. 21:779–790. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Basile A, Biziato D, Sherbet GV, Comi P
and Cajone F: Hyperthermia inhibits cell proliferation and induces
apoptosis: relative signaling status of P53, S100A4, and Notch in
heat sensitive and resistant cell lines. J Cell Biochem.
103:212–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Milleron RS and Bratton SB: ‘Heated’
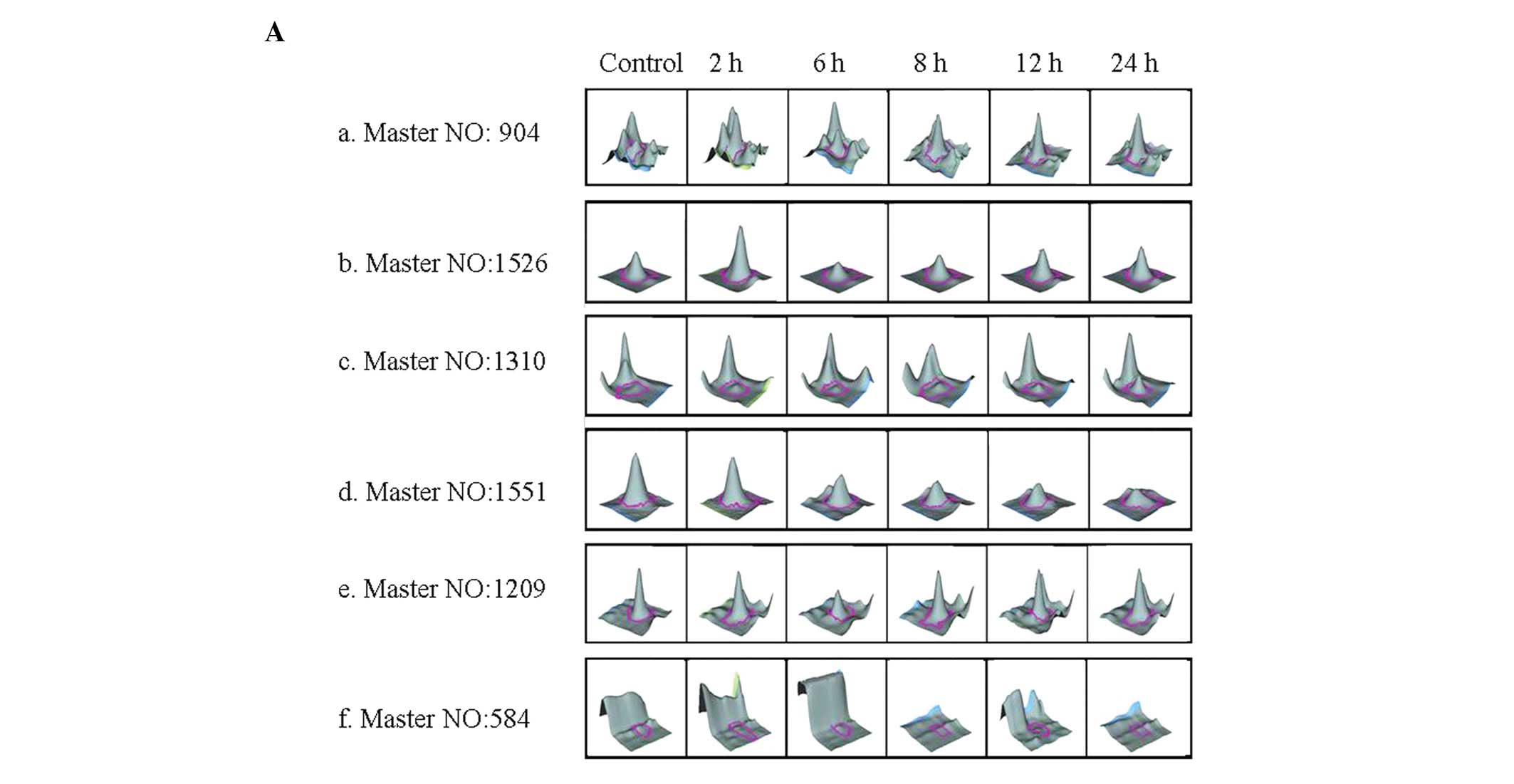
debates in apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:2329–2333. 2007.
|
|
7.
|
Harmon BV, Takano YS, Winterford CM and
Gobé GC: The role of apoptosis in the response of cells and tumours
to mild hyperthermia. Int J Radiat Biol. 59:489–501. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Moriyama-Gonda N, Igawa M, Shiina H,
Urakami S, Shigeno K and Terashima M: Modulation of heat-induced
cell death in PC-3 prostate cancer cells by the antioxidant
inhibitor diethyldithiocarbamate. BJU Int. 90:317–325. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Shelton SN, Dillard CD and Robertson JD:
Activation of caspase-9, but not caspase-2 or caspase-8, is
essential for heat-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells. J Biol Chem.
285:40525–40533. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Yoo J, Kim HR and Lee YJ: Hyperthermia
enhances tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
(TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells. Int J
Hyperthermia. 22:713–728. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Moulin M, Dumontet C and Arrigo AP:
Sensitization of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis by hyperthermia. Cancer Lett. 250:117–127.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Tran S, Meinander A, Holmström T, et al:
Heat stress down-regulates FLIP and sensitizes cells to Fas
receptor-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 10:1137–1147. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Zhao QL, Fujiwara Y and Kondo T: Mechanism
of cell death induction by nitroxide and hyperthermia. Free Radic
Biol Med. 40:1131–1143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Katschinski DM, Boos K, Schindler SG and
Fandrey J: Pivotal role of reactive oxygen species as intracellular
mediators of hyperthermia-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
275:21094–21098. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Ahmed K, Zhao QL, Matsuya Y, et al:
Enhancement of macrosphelide-induced apoptosis by mild
hyperthermia. Int J Hyperthermia. 23:353–361. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Hashimoto T, Shibata M, Ito Y, Nakao KI,
Sasaki S and Otsuki Y: Elevated levels of intracellular
Ca2+ and apoptosis in human lung cancer cells given
heat-shock. Int J Hyperthermia. 19:178–192. 2003.
|
|
17.
|
Klostergaard J, Leroux ME, Auzenne E, et
al: Hyperthermia engages the intrinsic apoptotic pathway by
enhancing upstream caspase activation to overcome apoptotic
resistance in MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem.
98:356–369. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Pagliari LJ, Kuwana T, Bonzon C, et al:
The multidomain proapoptotic molecules Bax and Bak are directly
activated by heat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:17975–17980. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Shellman YG, Howe WR, Miller LA, et al:
Hyperthermia induces endoplasmic reticulum-mediated apoptosis in
melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer cells. J Invest Dermatol.
128:949–956. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Bonzon C, Bouchier-Hayes L, Pagliari LJ,
Green DR and Newmeyer DD: Caspase-2-induced apoptosis requires bid
cleavage: a physiological role for bid in heat shock-induced death.
Mol Biol Cell. 17:2150–2157. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Beere HM: Death versus survival:
functional interaction between the apoptotic and stress-inducible
heat shock protein pathways. J Clin Invest. 115:2633–2639. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Banerjee Mustafi S, Chakraborty PK, Dey RS
and Raha S: Heat stress upregulates chaperone heat shock protein 70
and antioxidant manganese superoxide dismutase through reactive
oxygen species (ROS), p38MAPK, and Akt. Cell Stress Chaperones.
14:579–589. 2009.
|
|
23.
|
Shackley DC, Haylett A, Whitehurst C, et
al: Comparison of the cellular molecular stress responses after
treatments used in bladder cancer. BJU Int. 90:924–932. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Li GC and Calderwood SK: Hyperthermia
classic article commentary: ‘Re-induction of hsp70 synthesis: an
assay for thermotolerance’ by Gloria C. Li and Johnson Y. Mak,
International Journal of Hyperthermia 1989;5:389–403. Int J
Hyperthermia. 25:258–261. 2009.
|
|
25.
|
Watanabe N, Tsuji N, Akiyama S, et al:
Induction of heat shock protein 72 synthesis by endogenous tumor
necrosis factor via enhancement of the heat shock element-binding
activity of heat shock factor 1. Eur J Immunol. 27:2830–2834. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Strasser A and Anderson RL: Bcl-2 and
thermotolerance cooperate in cell survival. Cell Growth Differ.
6:799–805. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Stankiewicz AR, Livingstone AM, Mohseni N
and Mosser DD: Regulation of heat-induced apoptosis by Mcl-1
degradation and its inhibition by Hsp70. Cell Death Differ.
16:638–647. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Jiang W, Bian L, Ma LJ, Tang RZ, Xun S and
He YW: Hyperthermia-induced apoptosis in Tca8113 cells is inhibited
by heat shock protein 27 through blocking phospholipid scramblase 3
phosphorylation. Int J Hyperthermia. 26:523–537. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
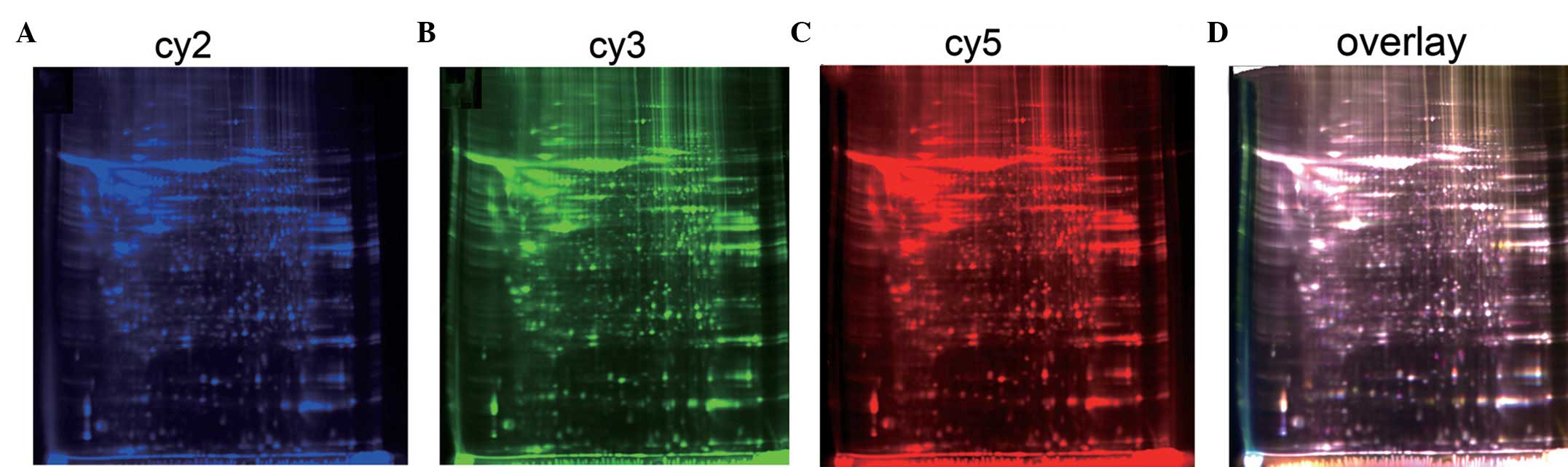
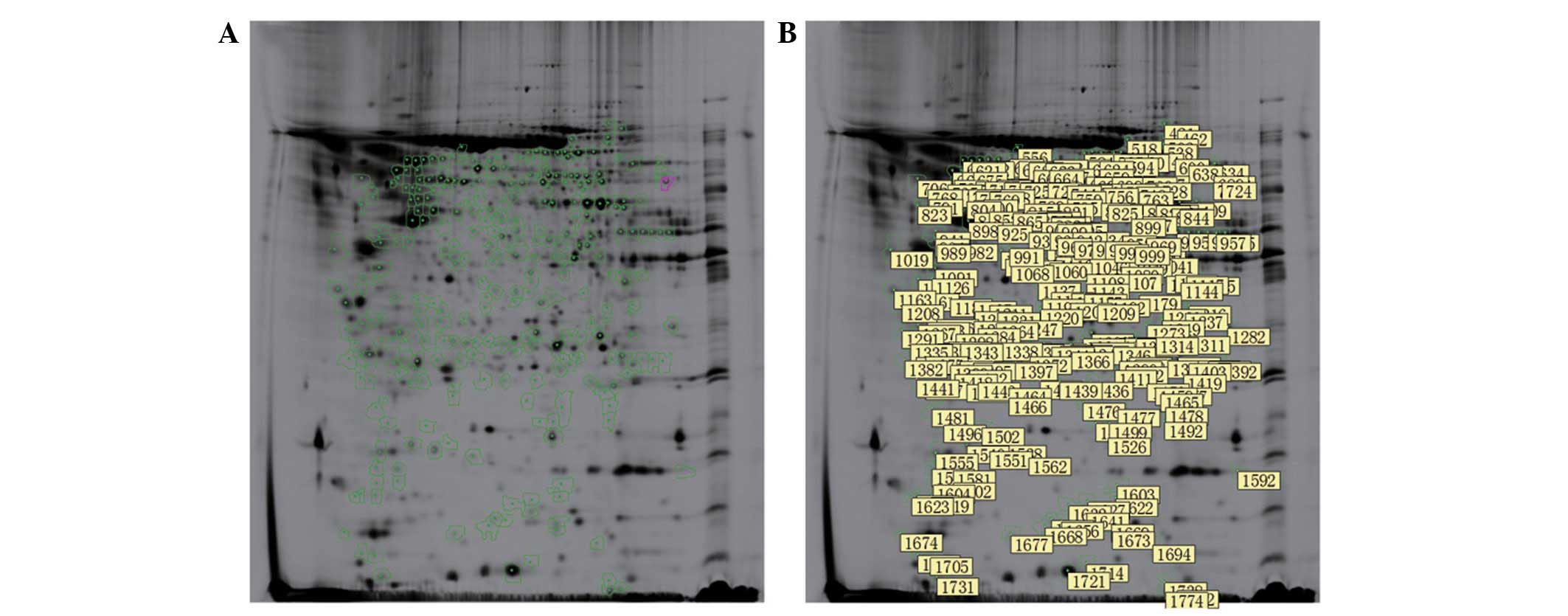
Tannu NS and Hemby SE: Two-dimensional
fluorescence difference gel electrophoresis for comparative
proteomics profiling. Nat Protoc. 1:1732–1742. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Hara MR, Agrawal N, Kim SF, et al:
S-nitrosylated GAPDH initiates apoptotic cell death by nuclear
translocation following Siah1 binding. Nat Cell Biol. 7:665–674.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Steták A, Veress R, Ovádi J, Csermely P,
Kéri G and Ullrich A: Nuclear translocation of the tumor marker
pyruvate kinase M2 induces programmed cell death. Cancer Res.
67:1602–1608. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Goodwin BL, Solomonson LP and Eichler DC:
Argininosuccinate synthase expression is required to maintain
nitric oxide production and cell viability in aortic endothelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 279:18353–18360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Ren F, Wu H, Lei Y, et al: Quantitative
proteomics identification of phosphoglycerate mutase 1 as a novel
therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
9:812010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Lee KW, Lee DJ, Lee JY, Kang DH, Kwon J
and Kang SW: Peroxiredoxin II restrains DNA damage-induced death in
cancer cells by positively regulating JNK-dependent DNA repair. J
Biol Chem. 286:8394–8404. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Park JJ, Chang HW, Jeong EJ, et al:
Peroxiredoxin IV protects cells from radiation-induced apoptosis in
head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 73:1196–1202. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Lundkvist A, Reichenbach A, Betsholtz C,
Carmeliet P, Wolburg H and Pekny M: Under stress, the absence of
intermediate filaments from Müller cells in the retina has
structural and functional consequences. J Cell Sci. 117:3481–3488.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Lau AT and Chiu JF: The possible role of
cytokeratin 8 in cadmium-induced adaptation and carcinogenesis.
Cancer Res. 67:2107–2113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Bhat KM and Setaluri V:
Microtubule-associated proteins as targets in cancer chemotherapy.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:2849–2854. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Prasad S, Soldatenkov Va, Srinivasarao G
and Dritschilo A: Intermediate filament proteins during
carcinogenesis and apoptosis (Review). Int J Oncol. 14:563–570.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Rana S, Maples PB, Senzer N and Nemunaitis
J: Stathmin 1: a novel therapeutic target for anticancer activity.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 8:1461–1470. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Kouzu Y, Uzawa K, Koike H, et al:
Overexpression of stathmin in oral squamous-cell carcinoma:
correlation with tumour progression and poor prognosis. Br J
Cancer. 94:717–723. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Nakamura K, Zhang X, Kuramitsu Y, et al:
Analysis on heat stress-induced hyperphosphorylation of stathmin at
serine 37 in Jurkat cells by means of two-dimensional gel
electrophoresis and tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A.
1106:181–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Cajone F and Sherbet GV: Stathmin is
involved in S100A4-mediated regulation of cell cycle progression.
Clin Exp Metastasis. 17:865–871. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Rabenhorst U, Beinoraviciute-Kellner R,
Brezniceanu ML, et al: Overexpression of the far upstream element
binding protein 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma is required for tumor
growth. Hepatology. 50:1121–1129. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Rauch J, O’Neill E, Mack B, et al:
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H blocks MST2-mediated
apoptosis in cancer cells by regulating A-Raf transcription. Cancer
Res. 70:1679–1688. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Li AL, Li HY, Jin BF, et al: A novel eIF5A
complex functions as a regulator of p53 and p53-dependent
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 279:49251–49258. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Izquierdo JM: Fas splicing regulation
during early apoptosis is linked to caspase-mediated cleavage of
U2AF65. Mol Biol Cell. 19:3299–3307. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Zhu B, Zhai J, Zhu H and Kyprianou N:
Prohibitin regulates TGF-beta induced apoptosis as a downstream
effector of Smad-dependent and -independent signaling. Prostate.
70:17–26. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Wang S, Nath N, Adlam M and Chellappan S:
Prohibitin, a potential tumor suppressor, interacts with RB and
regulates E2F function. Oncogene. 18:3501–3510. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|