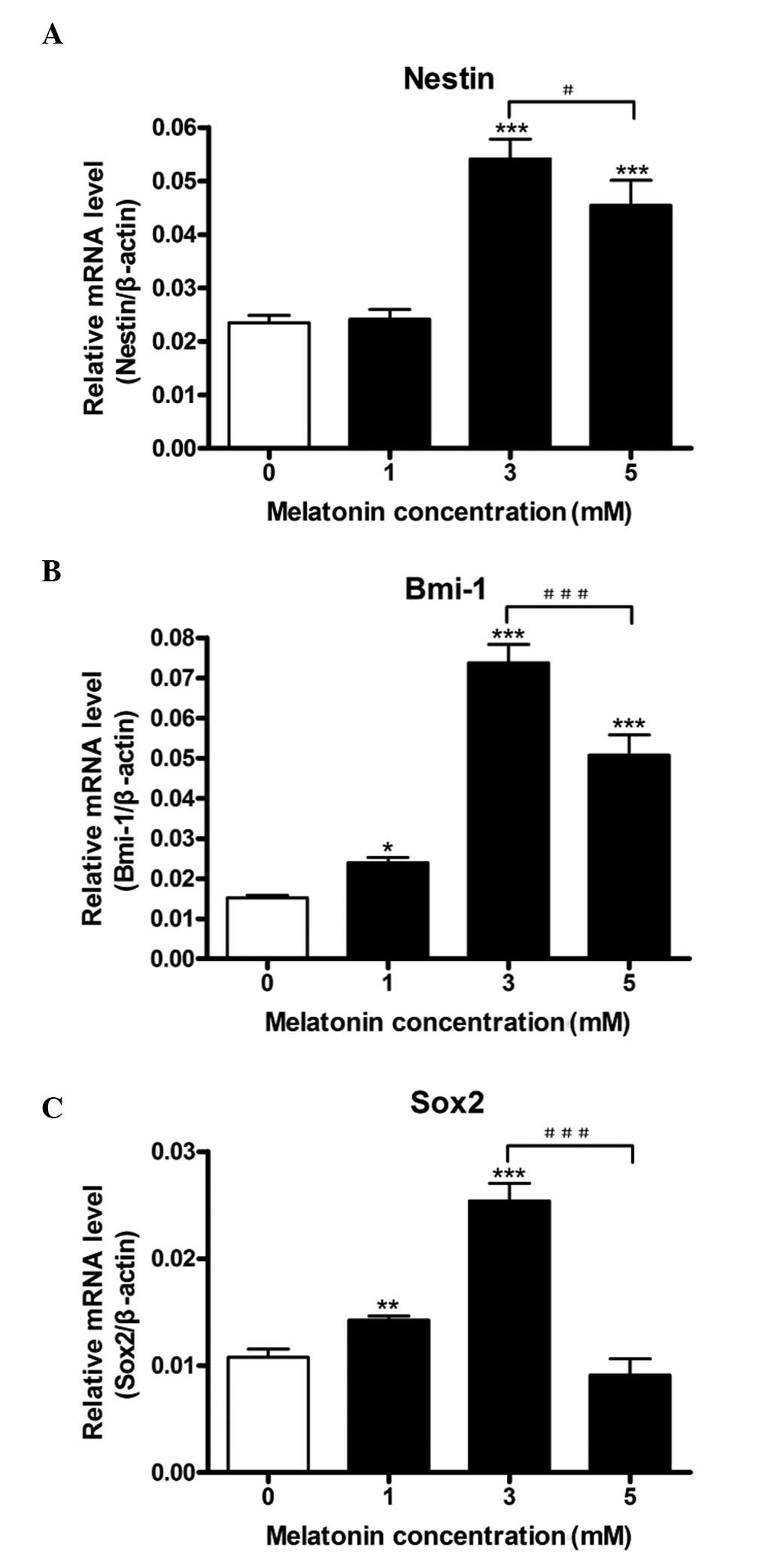
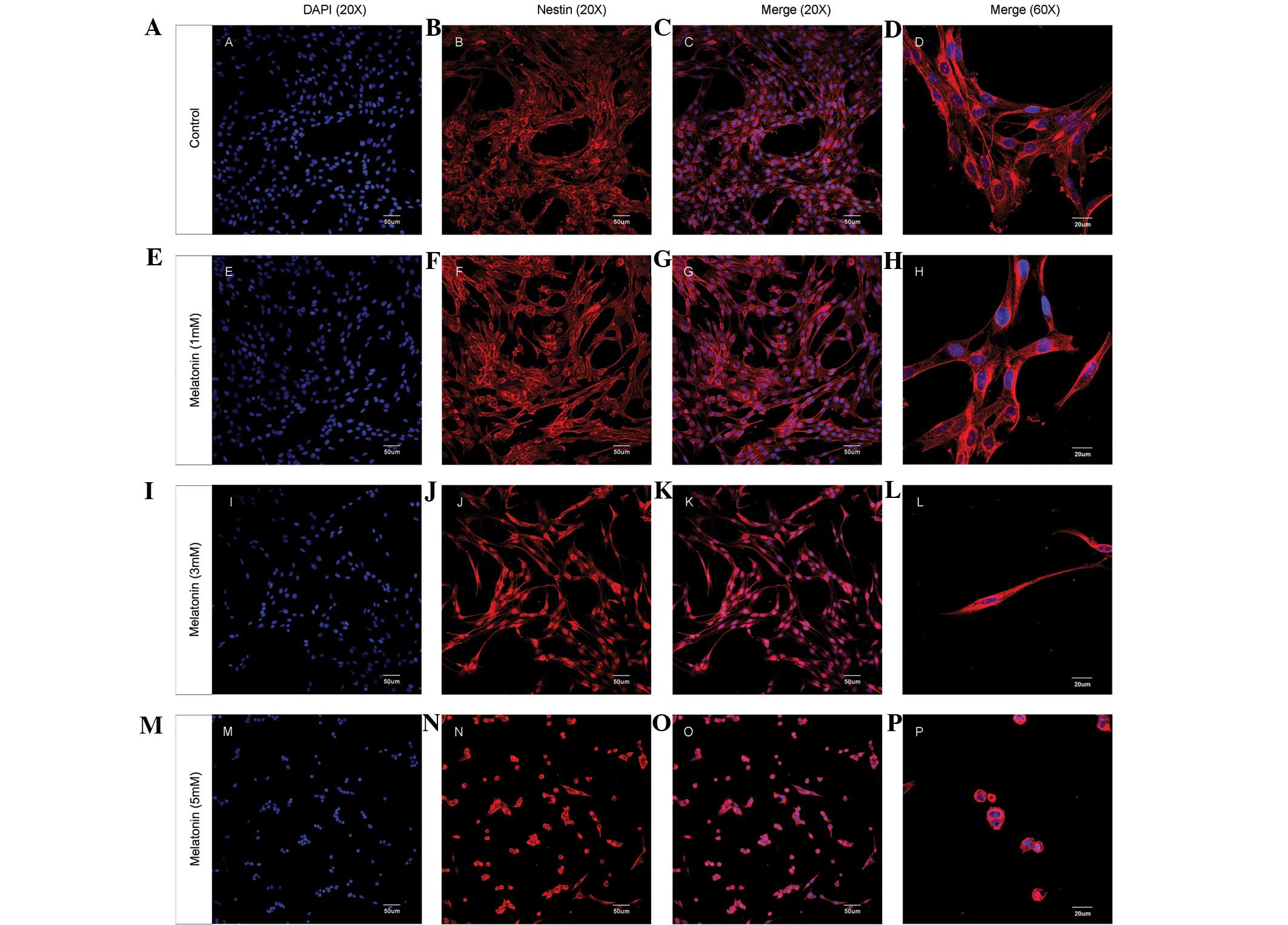
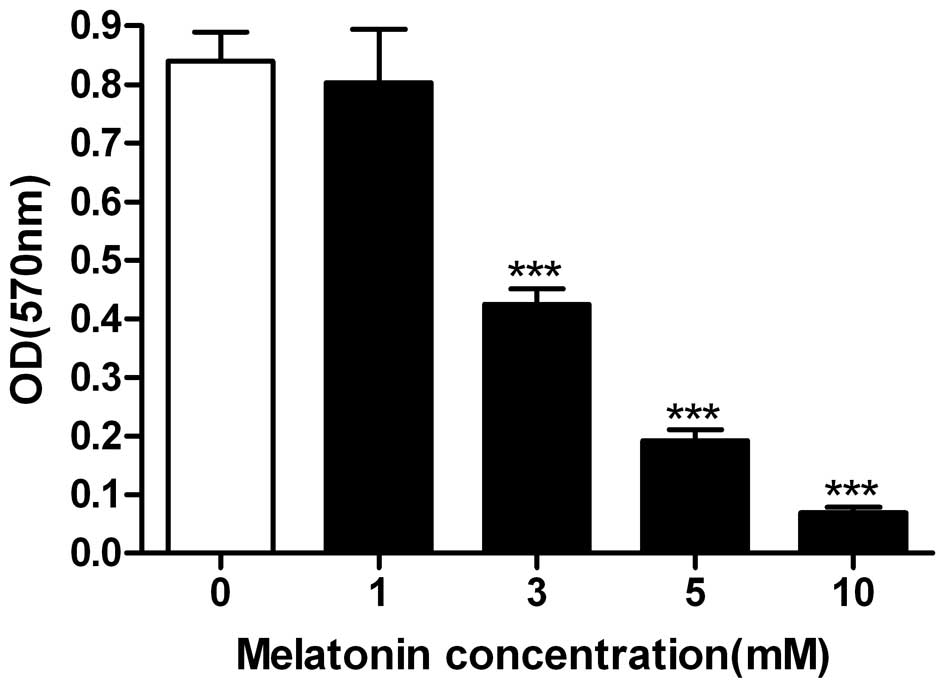
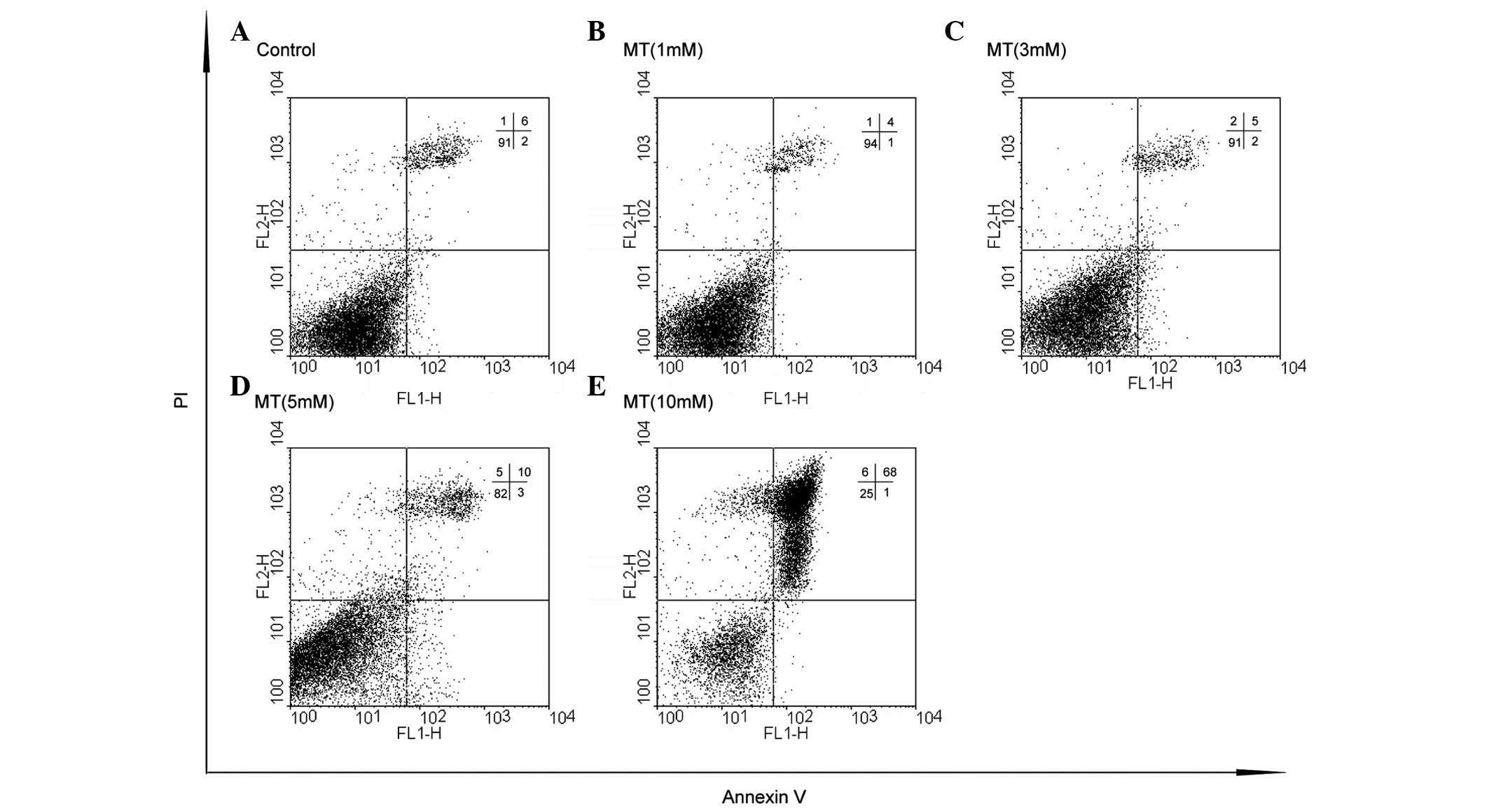
|
1.
|
Sánchez-Hidalgo M, Guerrero JM, Villegas
I, Packham G and de la Lastra CA: Melatonin, a natural programmed
cell death inducer in cancer. Curr Med Chem. 19:3805–3821.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Manchester LC, et al:
Chemical and physical properties and potential mechanisms:
melatonin as a broad spectrum antioxidant and free radical
scavenger. Curr Top Med Chem. 2:181–197. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Chakravarty S and Rizvi SI: Circadian
modulation of human erythrocyte plasma membrane redox system by
melatonin. Neurosci Lett. 518:32–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Reiter RJ: Oxidative damage in the central
nervous system: protection by melatonin. Prog Neurobiol.
56:359–384. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Altun A and Ugur-Altun B: Melatonin:
therapeutic and clinical utilization. Int J Clin Pract. 61:835–845.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Wu YH and Swaab DF: The human pineal gland
and melatonin in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. J Pineal Res.
38:145–152. 2005.
|
|
7.
|
Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Tan DX, Antolín I,
Rodríguez C and Reiter RJ: Melatonin and Parkinson’s disease.
Endocrine. 27:169–178. 2005.
|
|
8.
|
Tamarkin L, Cohen M, Roselle D, Reichert
C, Lippman M and Chabner B: Melatonin inhibition and pinealectomy
enhancement of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced mammary
tumors in the rat. Cancer Res. 41:4432–4436. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lissoni P, Meregalli S, Nosetto L, et al:
Increased survival time in brain glioblastomas by a
radioneuroendocrine strategy with radiotherapy plus melatonin
compared to radiotherapy alone. Oncology. 53:43–46. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Wang J, Hao H, Yao L, et al: Melatonin
suppresses migration and invasion via inhibition of oxidative
stress pathway in glioma cells. J Pineal Res. 53:180–187. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Martín V, Herrera F, Carrera-Gonzalez P,
et al: Intracellular signaling pathways involved in the cell growth
inhibition of glioma cells by melatonin. Cancer Res. 66:1081–1088.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Martín V, Herrera F, García-Santos G, et
al: Involvement of protein kinase C in melatonin’s oncostatic
effect in C6 glioma cells. J Pineal Res. 43:239–244. 2007.
|
|
13.
|
Vijayalaxmi, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Herman TS
and Thomas CR Jr: Melatonin as a radioprotective agent: a review.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 59:639–653. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Andrabi SA, Sayeed I, Siemen D, Wolf G and
Horn TF: Direct inhibition of the mitochondrial permeability
transition pore: a possible mechanism responsible for
anti-apoptotic effects of melatonin. FASEB J. 18:869–871.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Radogna F, Paternoster L, Albertini MC, et
al: Melatonin antagonizes apoptosis via receptor interaction in
U937 monocytic cells. J Pineal Res. 43:154–162. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Esposito E, Iacono A, Muià C, et al:
Signal transduction pathways involved in protective effects of
melatonin in C6 glioma cells. J Pineal Res. 44:78–87.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Sharma R, Ottenhof T, Rzeczkowska PA and
Niles LP: Epigenetic targets for melatonin: induction of histone H3
hyperacetylation and gene expression in C17.2 neural stem cells. J
Pineal Res. 45:277–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Matsuda M, Katoh-Semba R, Kitani H and
Tomooka Y: A possible role of the nestin protein in the developing
central nervous system in rat embryos. Brain Res. 723:177–189.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Lendahl U, Zimmerman LB and McKay RD: CNS
stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein.
Cell. 60:585–595. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Wan F, Herold-Mende C, Campos B, et al:
Association of stem cell-related markers and survival in astrocytic
gliomas. Biomarkers. 16:136–143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Rushing EJ, Sandberg GD and
Horkayne-Szakaly I: High-grade astrocytomas show increased Nestin
and Wilms’s tumor gene (WT1) protein expression. Int J Surg Pathol.
18:255–259. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Zhang M, Song T, Yang L, et al: Nestin and
CD133: valuable stem cell-specific markers for determining clinical
outcome of glioma patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 27:852008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Rutka JT, Ivanchuk S, Mondal S, et al:
Co-expression of nestin and vimentin intermediate filaments in
invasive human astrocytoma cells. Int J Dev Neurosci. 17:503–515.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Flørenes VA, Holm R, Myklebost O, Lendahl
U and Fodstad O: Expression of the neuroectodermal intermediate
filament nestin in human melanomas. Cancer Res. 54:354–356.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Contesso G, Mouriesse H, Friedman S, Genin
J, Sarrazin D and Rouesse J: The importance of histologic grade in
long-term prognosis of breast cancer: a study of 1,010 patients,
uniformly treated at the Institut Gustave-Roussy. J Clin Oncol.
5:1378–1386. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Liu R, Wang X, Chen GY, et al: The
prognostic role of a gene signature from tumorigenic breast-cancer
cells. N Engl J Med. 356:217–226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
van der Lugt NM, Domen J, Linders K, et
al: Posterior transformation, neurological abnormalities, and
severe hematopoietic defects in mice with a targeted deletion of
the bmi-1 protooncogene. Genes Dev. 8:757–769. 1994.
|
|
28.
|
Episkopou V: SOX2 functions in adult
neural stem cells. Trends Neurosci. 28:219–221. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Papp B and Müller J: Histone
trimethylation and the maintenance of transcriptional ON and OFF
states by trxG and PcG proteins. Genes Dev. 20:2041–2054. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Leung C, Lingbeek M, Shakhova O, et al:
Bmi1 is essential for cerebellar development and is overexpressed
in human medulloblastomas. Nature. 428:337–341. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Boyer LA, Lee TI, Cole MF, et al: Core
transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic stem cells.
Cell. 122:947–956. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Yu CC, Lo WL, Chen YW, et al: Bmi-1
regulates snail expression and promotes metastasis ability in head
and neck squamous cancer-derived ALDH1 positive cells. J Oncol.
2011:6092592011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, et al: The
polycomb group protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN
and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human
nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 119:3626–3636.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Lu Y, Futtner C, Rock JR, et al: Evidence
that SOX2 overexpression is oncogenic in the lung. PLoS One.
5:e110222010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Yang S, Zheng J, Ma Y, et al: Oct4 and
Sox2 are overexpressed in human neuroblastoma and inhibited by
chemotherapy. Oncol Rep. 28:186–192. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Neumann J, Bahr F, Horst D, et al: SOX2
expression correlates with lymph-node metastases and distant spread
in right-sided colon cancer. BMC Cancer. 11:5182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Jia X, Li X, Xu Y, et al: SOX2 promotes
tumorigenesis and increases the anti-apoptotic property of human
prostate cancer cell. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:230–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Yoo YM, Jung EM, Choi KC and Jeung EB:
Effect of melatonin on mRNA expressions of transcription factors in
murine embryonic stem cells. Brain Res. 1385:1–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Bexell D, Gunnarsson S, Siesjö P, Bengzon
J and Darabi A: CD133+ and nestin+
tumor-initiating cells dominate in N29 and N32 experimental
gliomas. Int J Cancer. 125:15–22. 2009.
|
|
40.
|
Sobottka SB and Berger MR: Assessment of
antineoplastic agents by MTT assay: partial underestimation of
antiproliferative properties. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
30:385–393. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Cajochen C, Kräuchi K and Wirz-Justice A:
Role of melatonin in the regulation of human circadian rhythms and
sleep. J Neuroendocrinol. 15:432–437. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Armstrong KJ and Niles LP: Induction of
GDNF mRNA expression by melatonin in rat C6 glioma cells.
Neuroreport. 13:473–475. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Feng Z and Zhang JT: Protective effect of
melatonin on beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis in rat astroglioma C6
cells and its mechanism. Free Radic Biol Med. 37:1790–1801. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Liu ZG, Liu L, Xu LH, et al: Bmi-1 induces
radioresistance in MCF-7 mammary carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep.
27:1116–1122. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Krupkova O Jr, Loja T, Redova M, et al:
Analysis of nuclear nestin localization in cell lines derived from
neurogenic tumors. Tumour Biol. 32:631–639. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Loja T, Chlapek P, Kuglik P, et al:
Characterization of a GM7 glioblastoma cell line showing CD133
positivity and both cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of nestin.
Oncol Rep. 21:119–127. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Veselska R, Kuglik P, Cejpek P, et al:
Nestin expression in the cell lines derived from glioblastoma
multiforme. BMC Cancer. 6:322006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Thomas SK, Messam CA, Spengler BA, Biedler
JL and Ross RA: Nestin is a potential mediator of malignancy in
human neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 279:27994–27999. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|