Introduction
Colorectal cancer is the most common malignancy of
the gastrointestinal tract (1) and
causes 655,000 mortalities worldwide every year (2). As it has high recurrence and
metastasis rates, there is an urgent requirement to identify
specific markers that are closely associated with the bionomic
characteristics of colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRA), the outcome of
affected patients and the performance of an antigen-specific
therapeutic targeting strategy.
Insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA-binding protein 3
(IMP3), an oncofetal protein and member of the IMP family, has
become a focus of attention as it appears to play a significant
role in cell migration and adhesion in various malignant neoplasms
(3). IMP3 is a 580-amino acid
protein with four K-homology domains and two RNA recognition
motifs. The protein is encoded by a gene on chromosome 7p11.5
(4) and has been known in previous
studies as the K-homologous domain-containing protein that is
overexpressed in cancer. IMP3 is also known as L523S, a regulatory
binding protein believed to be involved in the stabilization and
intracellular trafficking of IGF-II mRNA to facilitate IGF-II
production (5). IMP3 is expressed
in a number of the cells of a developing fetus, but is absent in
the majority of adult cells, with the exception of the gonads. The
overexpression of IMP3 has been identified in a number of malignant
tumors, including renal carcinoma (6), malignant pancreatic lesions (7), endometrial carcinoma (8), uterine cervical cancer (9) and testicular cancer (10).
However, to the best of our knowledge, the
expression of IMP3 in CRA has rarely been studied. In order to
further determine the role of IMP3 in neoplastic pathology, the
present study evaluated the expression of IMP3 in CRA using
immunohistochemical techniques. The present data aimed to reveal
the correlations between IMP3 expression and the
clinicopathological features of CRA in order to determine whether
the expression of the IMP3 protein may serve as a biomarker for the
prognostic evaluation of CRA
Materials and methods
Patients and tissue samples
Tumor specimens were obtained from 186 patients (119
males and 67 females; mean age, 59.3 years; range, 25–82 years) who
underwent surgery for CRA between January 2004 and May 2007. All
the adjacent normal mucosa (ANM) tissues from the cancer resection
margins were also included and none of the patients were
administered prior chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The pathological
parameters, including patient age, gender, tumor grade, nodal
metastasis, clinical stage and survival data, were carefully
reviewed in all cases. The HE stained slides were reviewed by two
experienced pathologists and one appropriate paraffin block with
tumor and ANM tissue was selected for this study. Informed consent
was obtained from each patient prior to conducting the study and
approval for the study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of
Dandong Centre Hospital (China).
Immunohistochemistry for IMP3 in
paraffin-embedded tissues
For the immunohistochemical study using the Dako
labeled streptavidin-biotin (LSAB) kit (Dako A/S, Glostrup,
Denmark), 4-μm thick tissue sections were deparaffinized,
rehydrated and incubated with 3% H2O2 in
methanol for 15 min at room temperature (RT), in order to eliminate
endogenous peroxidase activity. The antigen was retrieved at 95ºC
for 20 min by placing the slides in 0.01 M sodium citrate buffer
(pH 6.0). The slides were then incubated with primary antibodies
(polyclonal goat antiserum for IMP3; dilution, 1:150; N-19; Santa
Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA) and monoclonal mouse
antiserum for Ki-67; MAB-0129; Maixin Technology Co., Ltd.,
Shenzen, Guangdon, China) at 4ºC overnight. Subsequent to being
incubated at RT for 30 min with biotinylated secondary antibody,
the slides were incubated with streptavidin-peroxidase complex at
RT for 30 min. Immunostaining was developed using chromogen and
3,3′-diaminobenzidine and then counterstaining with Mayer’s
hematoxylin. Goat IgG isotopes, which showed a negative staining
result, were used as controls,. The positive tissue sections were
processed omitting the primary antibody and were used as negative
controls.
Evaluation of immunohistochemical
staining
A positive stain for IMP3 was defined as a brown
stain observed in the cytoplasm, and for Ki-67, as a stain observed
in the nucleus. All specimens were examined by two pathologists who
did not possess prior knowledge of the clinical data. In the case
of discrepancies, a final score was established by reassessing the
slides on a double-headed microscope. A lack of staining for IMP3
was scored as - and the intensity of positive staining was
evaluated as weak, + or strong, ++ (11). The immunostaining for Ki-67 was
scored as - (negative, none or ≤5% positive cells) and + (positive,
>5% positive cells).
Statistical analysis
The statistical analyses were performed using SPSS
17.0 software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The correlation
between IMP3 expression and the clinicopathological characteristics
was evaluated using the χ2 and Fisher’s exact tests. The
correlation between IMP3 protein expression and Ki-67 was evaluated
using Spearman’s correlation analysis. The survival rates following
the removal of the tumor were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier
method and the difference between the survival curves was analyzed
by the log-rank test. A multivariate survival analysis was
performed on all the significant characteristics that were measured
by the univariate survival analysis through the Cox proportional
hazard regression model. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
IMP3 protein expression in various
colorectal mucosae
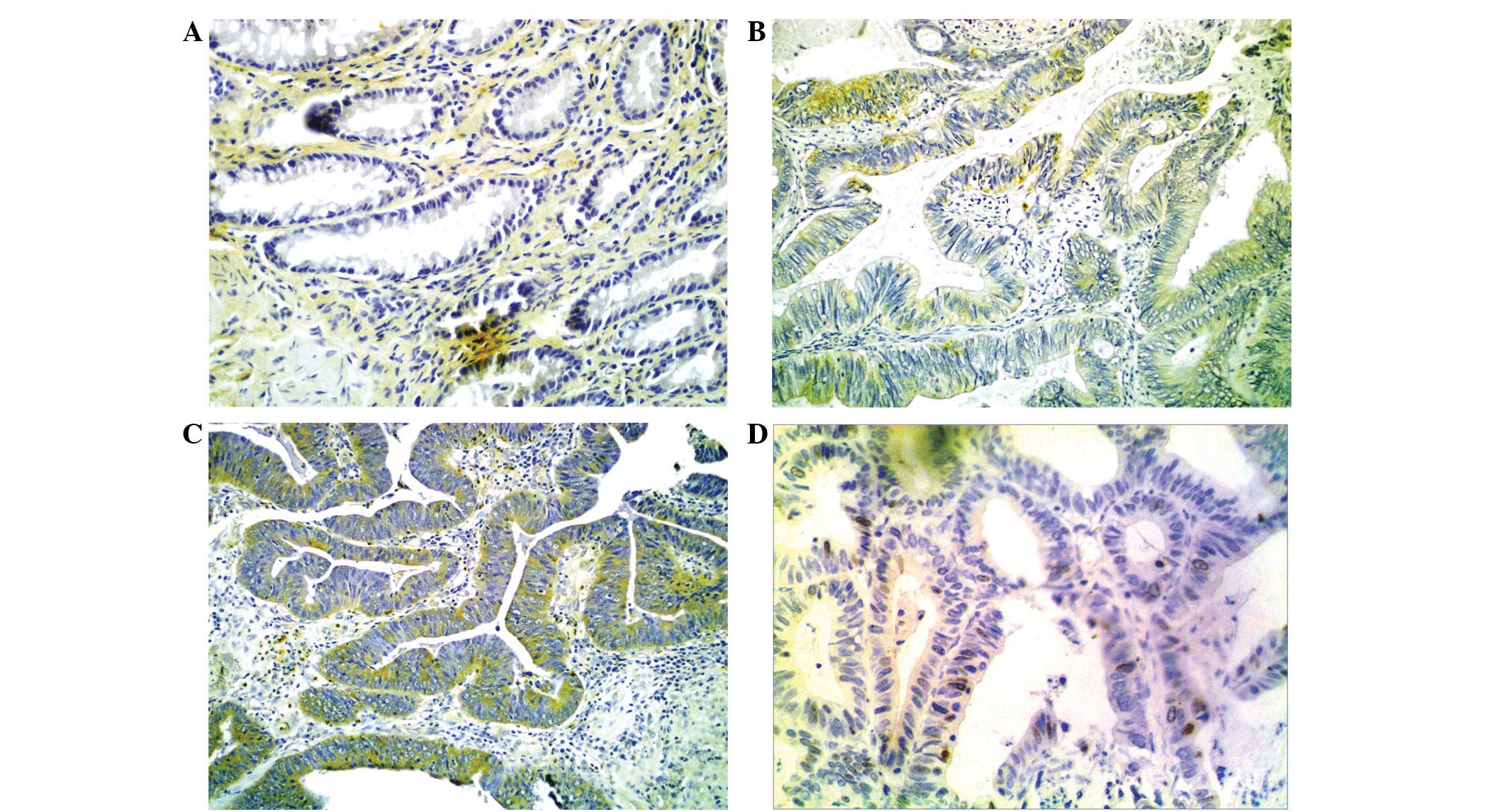
Of the 186 ANM cases, the 22 that exhibited
dysplasia demonstrated weak IMP3 expression and the 164 without
dysplasia showed no expression. Of the 186 CRA cases,
immunohistochemical staining for IMP3 was identified in 143 cases
(76.9%). The immunohistochemical reaction intensity for IMP3 was
identified to be weak in 82 cases (44.1%) and strong in 61 cases
(32.8%; Fig. 1). The expression of
IMP3 in the CRA tissues was significantly stronger than in the ANM
tissues (χ2=49.183, P<0.001; Table I).
 | Table IIMP3 protein expression in ANM and
CRA. |
Table I
IMP3 protein expression in ANM and
CRA.
| | IMP3 expression,
n | |
|---|
| |
| |
|---|
| Tissue | Cases, n | − | +/++ | P-value |
|---|
| ANM | 186 | 164 | 22 | <0.001 |
| CRA | 186 | 43 | 143 | |
Correlation between IMP3 protein
expression and clinicopathological factors
A higher IMP3-positive rate was detected in the
cases of CRA with lymphoid metastasis compared with those without
lymphoid metastasis (94/111 vs. 49/75; χ2=9.430;
P=0.002). Additionally, there was a significant difference in the
TNM stage between the CRA tissues with IMP3 expression and those
without (P=0.001; Table II). The
tumors at higher stages showed an increased level of IMP3
expression. It was indicated that IMP3 expression was not
significantly correlated with age, gender, size, histological grade
or carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level (P>0.05; Table II).
 | Table IICorrelation between IMP3 protein and
clinicopathological factors in CRA. |
Table II
Correlation between IMP3 protein and
clinicopathological factors in CRA.
| | IMP3 expression,
n | | |
|---|
| |
| | |
|---|
| Parameters | Cases, n | − | +/++ | χ2 | P-value |
|---|
| Age (years) | | | | 1.073 | 0.302 |
| >59 | 82 | 16 | 66 | | |
| ≤59 | 104 | 27 | 77 | | |
| Gender | | | | 0.034 | 0.854 |
| Male | 119 | 27 | 92 | | |
| Female | 67 | 16 | 51 | | |
| Histological
grade | | | | 3.176 | 0.076 |
|
Well-differentiated | 99 | 28 | 71 | | |
|
Moderately/poorly-differentiated | 87 | 15 | 72 | | |
| Tumor size (cm) | | | | 1.494 | 0.223 |
| ≤5 | 115 | 30 | 85 | | |
| >5 | 71 | 13 | 58 | | |
| Lymphoid
metastasis | | | | 9.430 | 0.002 |
| Present | 75 | 26 | 49 | | |
| Absent | 111 | 17 | 94 | | |
| Clinical stage | | | | 10.713 | 0.001 |
| I–II | 65 | 24 | 41 | | |
| III–IV | 121 | 19 | 102 | | |
| CEA | | | | 1.473 | 0.226 |
| Normal | 76 | 21 | 55 | | |
| Increased | 110 | 22 | 88 | | |
Correlation between IMP3 protein
expression and Ki-67 expression in CRA
As shown in Fig. 1,
the immunoreaction of Ki-67 was localized in the nucleus. The
positive Ki-67 protein expression rate was 54.8% (102/186) in the
CRA tissues. Positive IMP3 gene expression was strongly associated
with the Ki-67 labeling index (r=0.169; P=0.021; Table III).
 | Table IIICorrelation between IMP3 protein and
Ki-67 in CRA. |
Table III
Correlation between IMP3 protein and
Ki-67 in CRA.
| IMP3, n | | | |
|---|
|
| | | |
|---|
| Immunostaining | − | +/++ | n | r | P-value |
|---|
| Ki-67 |
| − | 26 | 58 | 84 | | |
| + | 17 | 85 | 102 | 0.169 | 0.021 |
Correlation between IMP3 protein
expression and prognosis
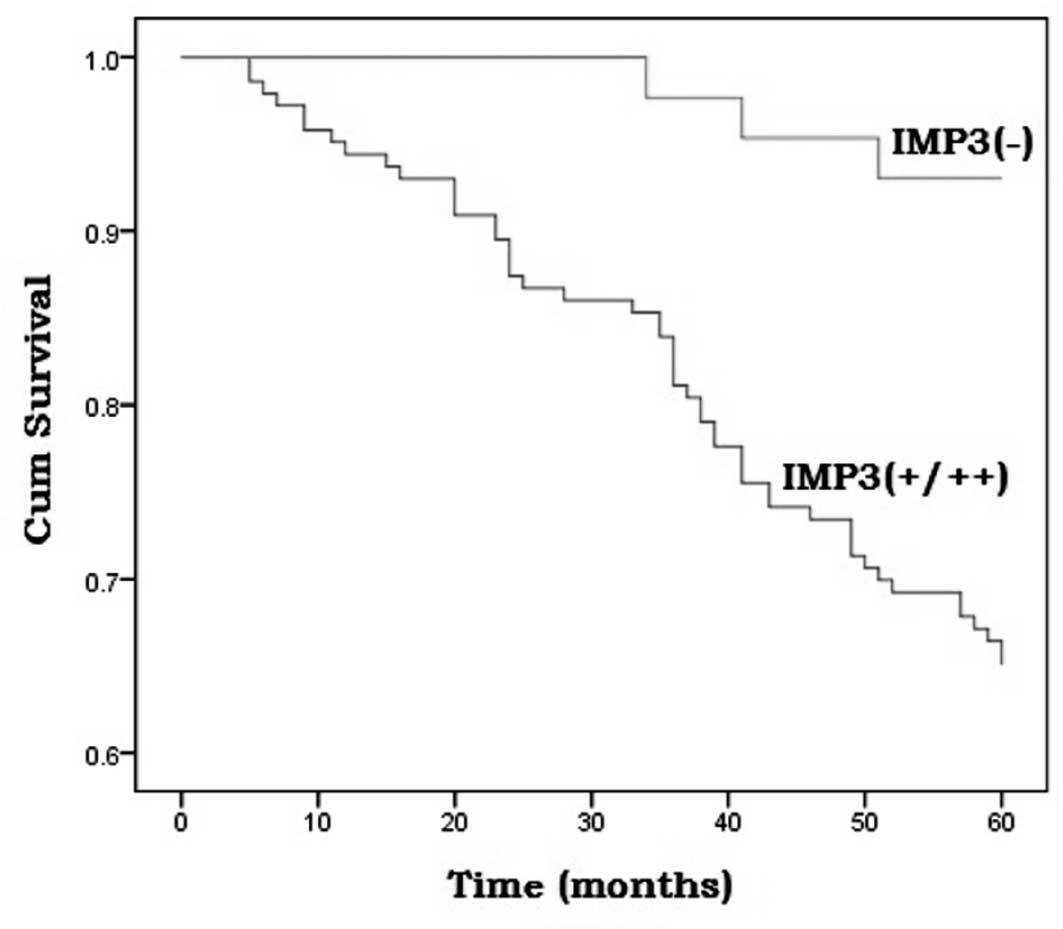
To further confirm the role of IMP3 expression in
CRA progression, the survival rates of the 186 CRA cases were
analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method. The cases that demonstrated
positive IMP3 staining (+/++) had a lower survival rate than those
that were negative for IMP3 immunoreactivity (P=0.001; Fig. 2). The multivariate analysis was
performed using the Cox proportional hazards model for all the
significant variables in the univariate analysis. IMP3 was
identified as an independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer
(HR, 0.618; 95% CI, 0.394–0.972; Wald χ2=4.343;
P=0.037).
Discussion
The IMP3 gene was originally identified from a
pancreatic tumor cDNA screen in 1996 (12) and was subsequently cloned. IMP3,
together with IMP1 and 2, are members of the human IMP family that
were first purified from the human rhabdomyosarcoma cell line, RD,
in 1999 (13). IMP3 has since been
shown to be expressed in a number of solid tumors and fetal
tissues. IMPs have been reported to play a pivotal role in the
binding, trafficking, stabilization, growth and migration of cells
during embryogenesis (3). IMP3
regulates the gene expression of IGF-II by binding to its 3′-mRNA
region. IGF-II then binds to and activates IGF-I while stimulating
the tyrosine phosphorylation of this receptor. The tyrosine
phosphorylated IGF-I receptor transmits mitogenic signals to the
cell. This is followed by cell cycle regulation loss and apoptotic
cycle disturbance, resulting in uncontrolled cell proliferation and
carcinogenesis (14,15). Therefore, it is hypothesized that
IMP family members are involved in carcinogenesis by stabilizing
IGF-II mRNA. However, the IMP proteins are also able to bind and
affect other mRNAs, which may affect the malignant potential of
cells.
The present study aimed to determine whether the
expression of the IMP3 oncoprotein may serve as a biomarker for the
prognostic evaluation of CRA. According to the present results,
IMP3 was expressed in the carcinoma lesions, but was almost absent
in the adjacent tissue counterparts. Similar associations have been
demonstrated between IMP3 expression and older age, larger tumor
size, deep tumour invasion and lymph node metastasis (16).
Ki-67 is an established marker of cell proliferation
that correlates with the progression of the cell cycle and that is
expressed in G1, S, G2 and mitosis (17). In the present study, Ki-67 was
selected to represent the proliferation status of the cells and the
Ki-67 labeling index was shown to be significantly correlated with
IMP3 expression. Studies have shown that the oncofetal protein,
IMP-3, appears to play a critical role in arranging cellular
proliferation, tumor invasion and aggressive behavior (18,19).
The present data also suggested that the IMP3 protein was a
significant proliferation marker for tumor cells.
Yaniv et al(20) reported that IMP3 in Xenopus
laevis is required for the migration of cells that form the
roof plate of the neural tube and, subsequently, for neural crest
migration, suggesting that IMP3 is important for promoting cell
migration. The expression of IMP3 in tumor cells has been
associated with an unfavorable outcome in renal clear-cell
carcinoma (7,21). In the present study, IMP3 was shown
to be highly expressed in CRAs with lymphoid metastasis compared
with non-metastatic tumors (χ2=9.430; P=0.002). The
correlation between IMP3 expression and lymphoid metastasis implies
that IMP3 may promote lymphoid metastasis in CRA. Furthermore,
significant differences in the TNM stages were observed between the
CRA tissues that expressed IMP3 and those that did not.
Survival analyses have indicated that IMP3
expression is negatively linked to a favorable prognosis for
gastric adenocarcinoma (18,22),
renal cell carcinoma (6) and
hepatocellular carcinoma (23).
IMP3 expression has been shown to significantly affect the
five-year survival rate of patients with CRA. The patients with
IMP3-positive immunoreactivity had significantly shorter survival
times compared with those who were negative for IMP3. These
findings and those of other studies may indicate a correlation
between IMP3 expression and aggressive tumor progression and
metastasis.
In conclusion, IMP3, a novel oncofetal mRNA-binding
protein, is frequently expressed in CRA. IMP3 expression is more
commonly seen in cases with poor prognostic factors of CRA, leading
to lymphoid metastasis, late-stage cases and short survival times.
Immunohistochemistry for IMP3 may be a potential biomarker to
evaluate the tumor progression and prognosis of CRA.
References
|
1
|
Lim SC and Hong R: Programmed cell death 4
(Pdcd4) expression in colorectal adenocarcinoma: Association with
clinical stage. Oncol Lett. 2:1053–1057. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alwan A: World Health Organization.
Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 1:7–8. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ikenberg K, Fritzsche FR, Zuerrer-Haerdi
U, et al: Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA binding protein 3
(IMP3) is overexpressed in prostate cancer and correlates with
higher Gleason scores. BMC Cancer. 10:3412010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mentrikoski MJ, Ma L, Pryor JG, et al:
Diagnostic utility of IMP3 in segregating metastatic melanoma from
benign nevi in lymph nodes. Mod Pathol. 22:1582–1587. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hoffmann NE, Sheinin Y, Lohse CM, et al:
External validation of IMP3 expression as an independent prognostic
marker for metastatic progression and death for patients with clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 112:1471–1479. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang Z, Chu PG, Woda BA, et al:
Combination of quantitative IMP3 and tumor stage: a new system to
predict metastasis for patients with localized renal cell
carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5579–5584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schaeffer DF, Owen DR, Lim HJ, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3)
overexpression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma correlates with
poor survival. BMC Cancer. 10:592010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Herrmann FR, Rai H,
et al: IMP3 distinguishes uterine serous carcinoma from endometrial
endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 133:899–908. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu D, Yang X, Jiang NY, et al: IMP3, a new
biomarker to predict progression of cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia into invasive cancer. Am J Surg Pathol. 35:1638–1645.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hammer NA, Hansen Tv, Byskov AG, et al:
Expression of IGF-II mRNA-binding proteins (IMPs) in gonads and
testicular cancer. Reproduction. 130:203–212. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li C, Rock KL, Woda BA, et al: IMP3 is a
novel biomarker for adenocarcinoma in situ of the uterine cervix:
an immunohistochemical study in comparison with p16(INK4a)
expression. Mod Pathol. 20:242–247. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gress TM, Müller-Pillasch F, Geng M, et
al: A pancreatic cancer-specific expression profile. Oncogene.
13:1819–1830. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nielsen J, Christiansen J, Lykke-Andersen
J, et al: A family of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding
proteins represses translation in late development. Mol Cell Biol.
19:1262–1270. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tosun Yildirim H and Sentürk N: Analysis
of IMP3 expression in prostate adenocarcinomas. Turk Patoloji Derg.
28:128–133. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liao B, Hu Y, Herrick DJ and Brewer G: The
RNA-binding protein IMP-3 is a translational activator of
insulin-like growth factor II leader-3 mRNA during proliferation of
human K562 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 280:18517–18524. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jeng YM, Wang TH, Lu SH, et al: Prognostic
significance of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein
3 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg. 96:66–73. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu C, Jiang XZ, Zhao HF, et al: The
applicability of Ki-67 marker for renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma:
experience of ten cases from a single center. Neoplasma.
60:209–214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Li HG, Xia ZS, et al: IMP3 is a
novel biomarker to predict metastasis and prognosis of gastric
adenocarcinoma: a retrospective study. Chin Med J (Engl).
123:3554–3558. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sitnikova L, Mendese G, Liu Q, et al: IMP3
predicts aggressive superficial urothelial carcinoma of the
bladder. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1701–1706. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yaniv K, Fainsod A, Kalcheim C and
Yisraeli JK: The RNA-binding protein Vg1 RBP is required for cell
migration during early neural development. Development.
130:5649–5661. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yantiss RK, Cosar E and Fischer AH: Use of
IMP3 in identification of carcinoma in fine needle aspiration
biopsies of pancreas. Acta Cytol. 52:133–138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okada K, Fujiwara Y, Nakamura Y, et al:
Oncofetal protein, IMP-3, a potential marker for prediction of
postoperative peritoneal dissemination in gastric adenocarcinoma. J
Surg Oncol. 105:780–785. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wachter DL, Kristiansen G, Soll C, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 (IMP3)
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. A clinicopathological
analysis with emphasis on diagnostic value. Histopathology.
60:278–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|