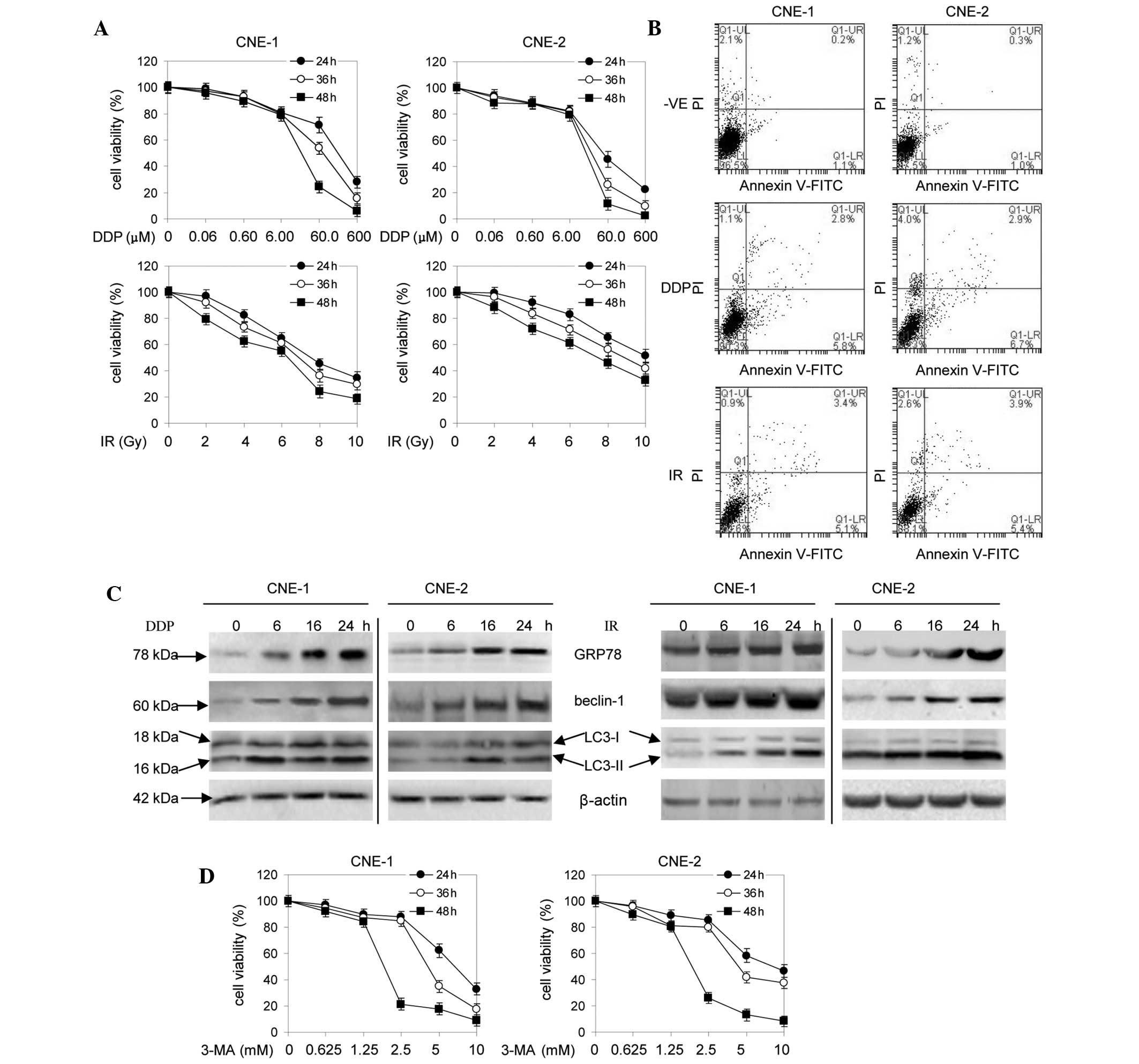
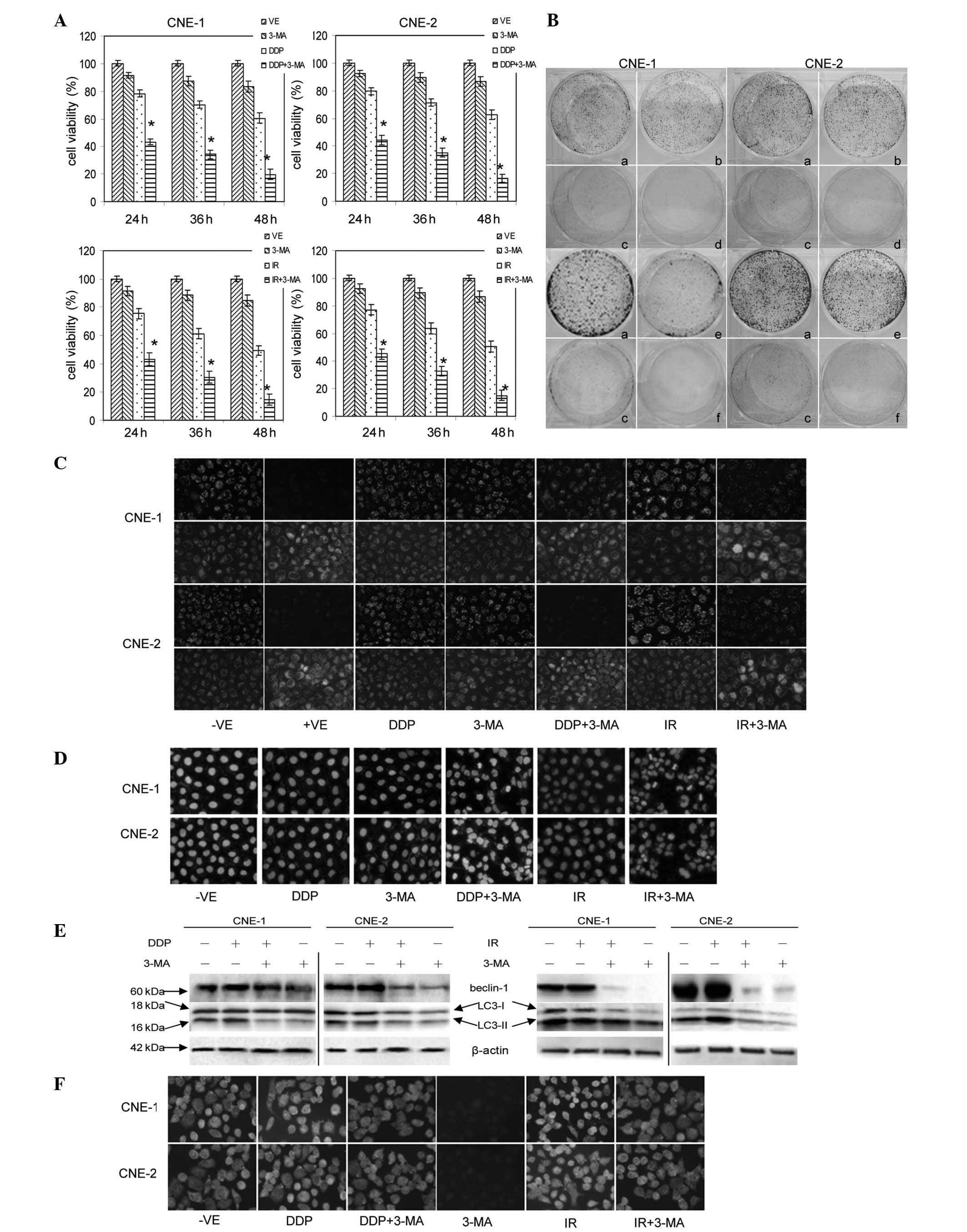
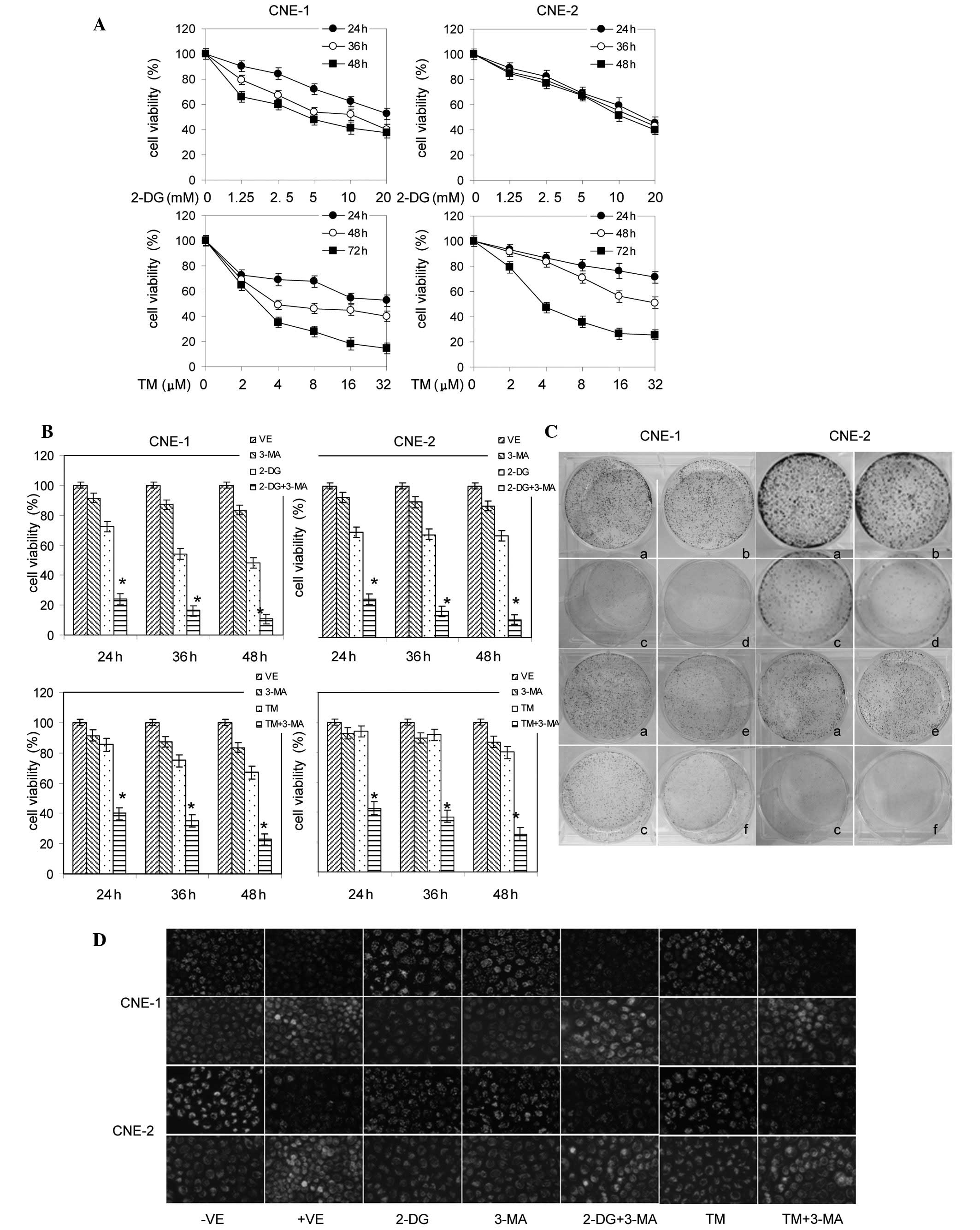
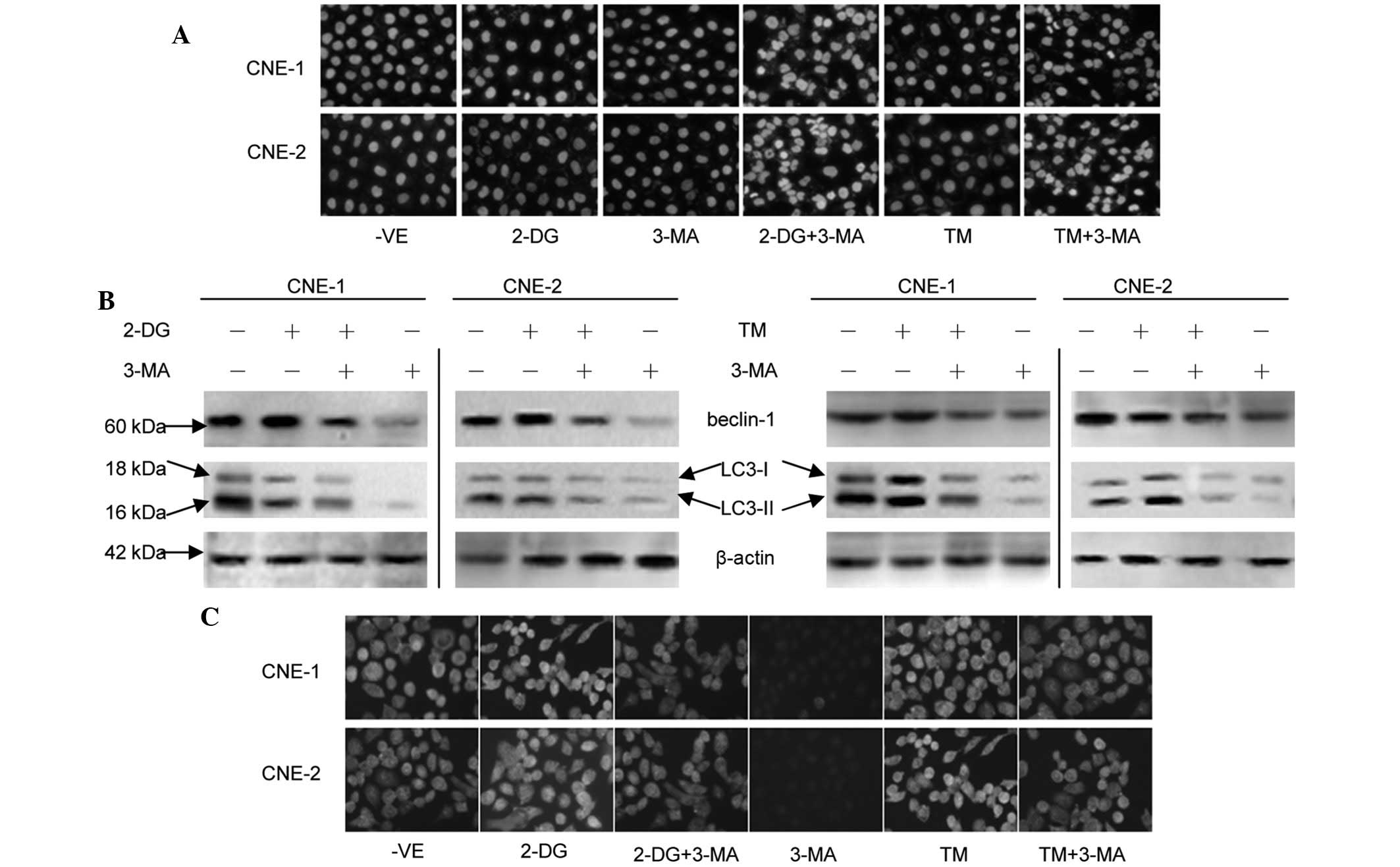
|
1
|
Simons MJ: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma as a
paradigm of cancer genetics. Chin J Cancer. 30:79–84. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee N, Harris J, Garden AS, Straube W,
Glisson B, Xia P, Bosch W, Morrison WH, Quivey J, Thorstad W, Jones
C and Ang KK: Intensity-modulated radiation therapy with or without
chemotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: radiation therapy
oncology group phase II trial 0225. J Clin Oncol. 27:3684–3690.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hassan KA, Ang KK, El-Naggar AK, Story MD,
Lee JI, Liu D, Hong WK and Mao L: Cyclin B1 overexpression and
resistance to radiotherapy in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 62:6414–6417. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sasaki N, Kudo N, Nakamura K, Lim SY,
Murakami M, Kumara WR, Tamura Y, Ohta H, Yamasaki M and Takiguchi
M: Activation of microbubbles by short-pulsed ultrasound enhances
the cytotoxic effect of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) in a
canine thyroid adenocarcinoma cell line in vitro. Ultrasound Med
Biol. 38:109–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oberoi HS, Laquer FC, Marky LA, Kabanov AV
and Bronich TK: Core cross-linked block ionomer micelles as
pH-responsive carriers for cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). J
Control Release. 153:64–72. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shrivastav M, De Haro LP and Nickoloff JA:
Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Cell
Res. 18:134–147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Witko-Sarsat V: Apoptosis, cell death and
inflammation. J Innate Immun. 2:201–203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bhogal RH, Weston CJ, Curbishley SM, Adams
DH and Afford SC: Autophagy: A cyto-protective mechanism which
prevents primary human hepatocyte apoptosis during oxidative
stress. Autophagy. 8:545–558. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kobayashi S, Xu X, Chen K and Liang Q:
Suppression of autophagy is protective in high glucose-induced
cardiomyocyte injury. Autophagy. 8:577–592. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Graziotto JJ, Cao K, Collins FS and Krainc
D: Rapamycin activates autophagy in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria
syndrome: implications for normal aging and age-dependent
neurodegenerative disorders. Autophagy. 8:147–151. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gui YX, Fan XN, Wang HM, Wang G and Chen
SD: Glyphosate induced cell death through apoptotic and autophagic
mechanisms. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 34:344–349. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kovaleva V, Mora R, Park YJ, Plass C,
Chiramel AI, Bartenschlager R, Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Pscherer
A, Lichter P and Seiffert M: miRNA-130a targets ATG2B and DICER1 to
inhibit autophagy and trigger killing of chronic lymphocytic
leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 72:1763–1772. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu ZY, Zhu XF, Zhong ZD, Sun J, Wang J,
Yang D and Zeng YX: ApoG2, a novel inhibitor of antiapoptotic Bcl-2
family proteins, induces apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts. Int J Cancer. 123:2418–2429.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang T, Gao Y, Mao Y, Zhang Q, Lin C, Lin
P, Zhang J and Wang X: Growth inhibition and apoptotic effect of
alpha-eleostearic acid on human breast cancer cells. J Nat Med.
66:77–84. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen LH, Jiang CC, Kiejda KA, Wang WF,
Thorne RF, Zhang XD and Hersey P: Thapsigargin sensitizes human
melanoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of
TRAIL-R2 through the unfolded protein response. Carcinogenesis.
28:2328–2336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang XD, Wu JJ, Gillespie S, Borrow J and
Hersey P: Human melanoma cells selected for resistance to apoptosis
by prolonged exposure to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand are more vulnerable to necrotic cell
death induced by cisplatin. Clin Cancer Res. 12:1355–1364. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Siddique MA, Sabur MA, Kundu SC, Mostafa
MG, Khan JA, Ahmed S, Karim MA and Hanif MA: Difficulty in
diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mymensingh Med J.
21:158–161. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carle LN, Ko CC and Castle JT:
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck Pathol. 6:364–368. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kang JH, Chang YC and Maurizi MR:
4-O-carboxymethyl ascochlorin causes er stress and induced
autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem.
287:15661–15671. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu D, Yang Y, Liu Q and Wang J:
Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA potentiates cisplatin-induced
apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Med Oncol.
28:105–111. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|