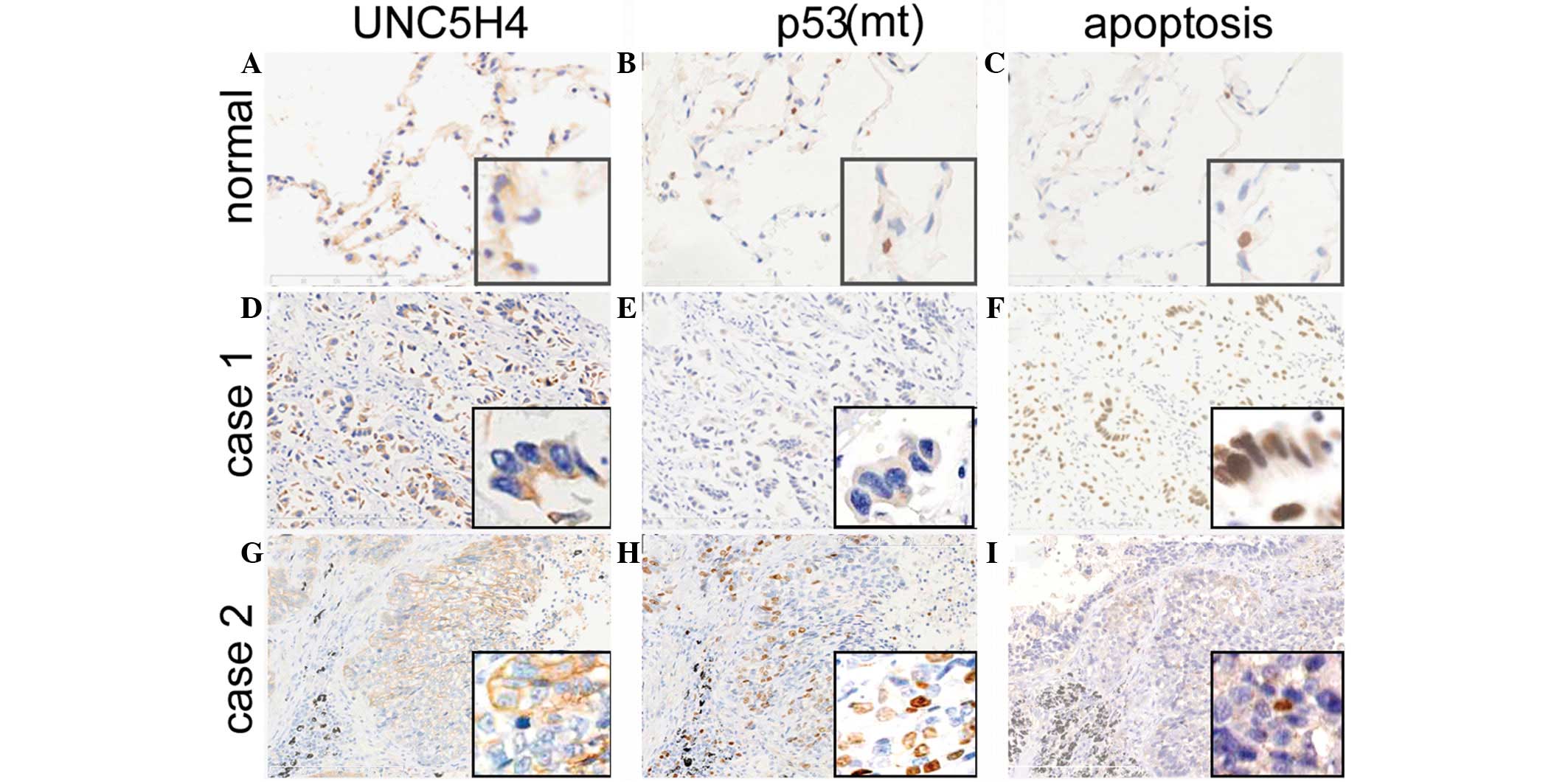
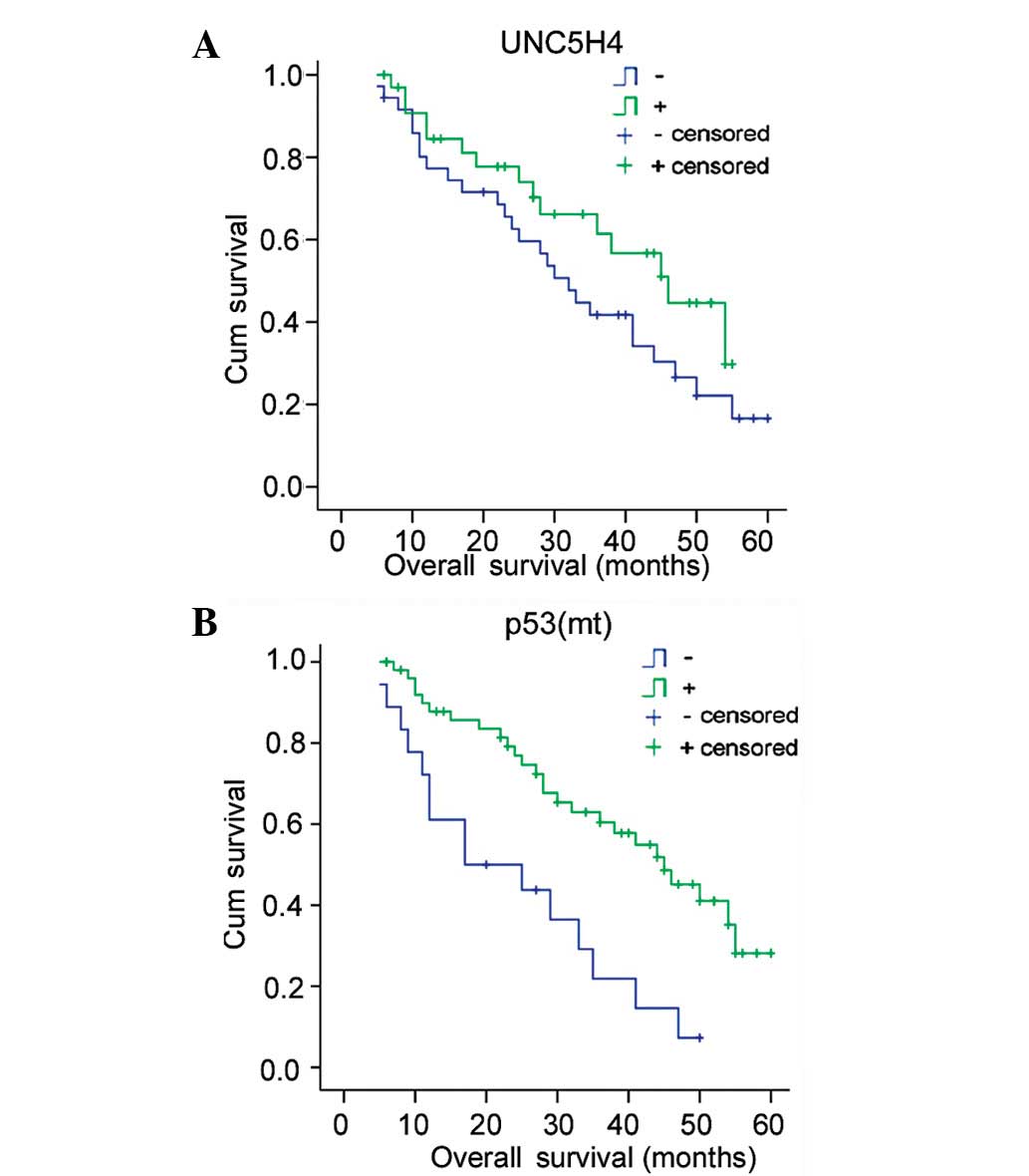
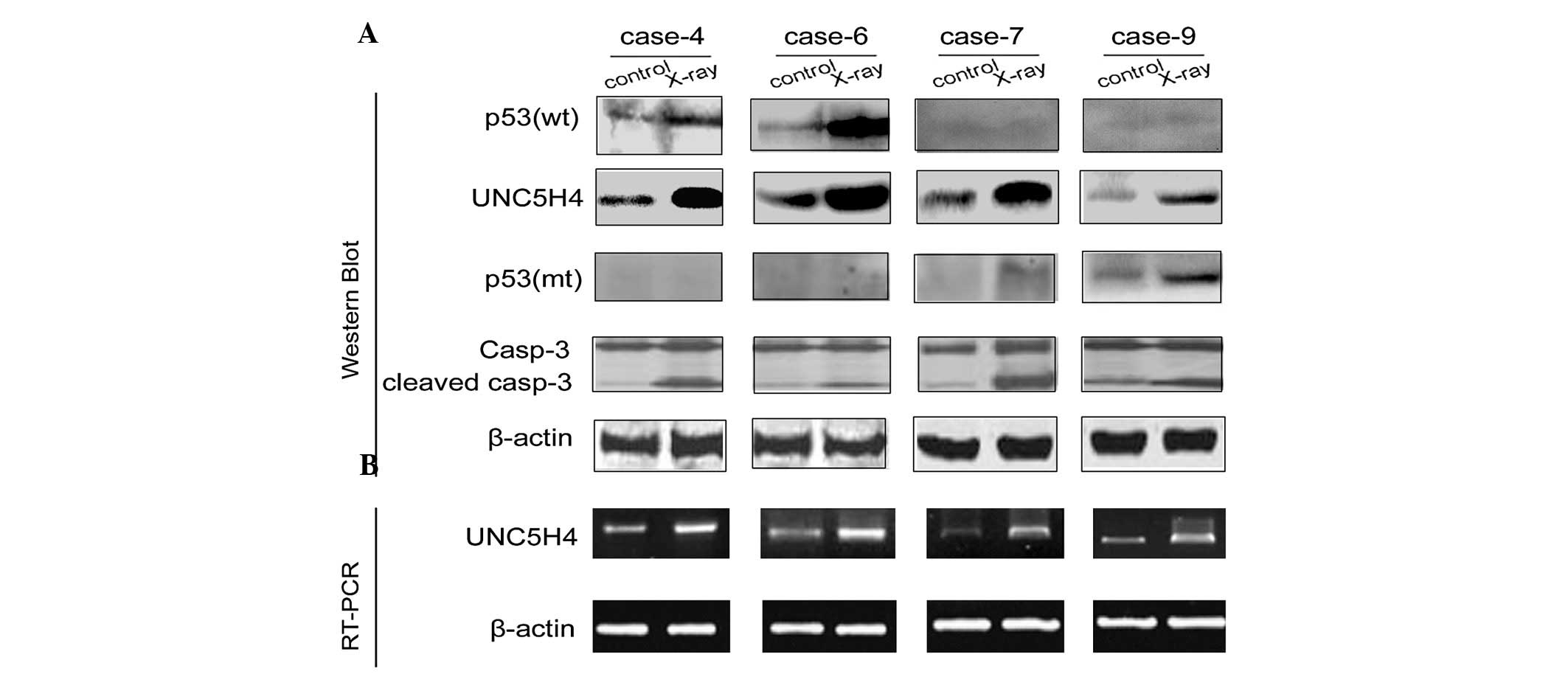
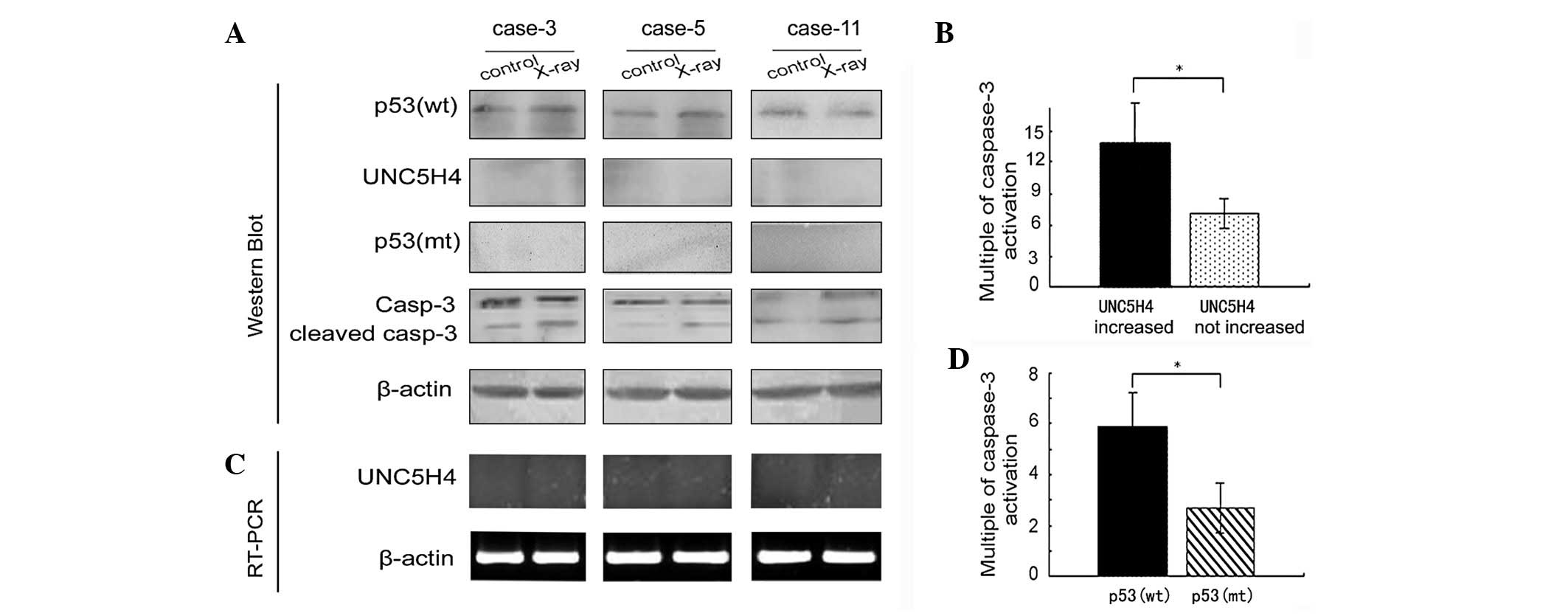
|
1
|
Hong K, Hinck L, Nishiyama M, Poo MM,
Tessier-Lavigne M and Stein E: A ligand-gated association between
cytoplasmic domains of UNC5 and DCC family receptors converts
netrin-induced growth cone attraction to repulsion. Cell.
97:927–941. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Leonardo ED, Hinck L, Masu M, Keino-Masu
K, Ackerman SL and Tessier-Lavigne M: Vertebrate homologues of C.
elegans UNC-5 are candidate netrin receptors. Nature. 386:833–838.
1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tessier-Lavigne M and Goodman CS: The
molecular biology of axon guidance. Science. 274:1123–1133. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Merz DC, Zheng H, Killeen MT, Krizus A and
Culotti JG: Multiple signaling mechanisms of the UNC-6/netrin
receptors UNC-5 and UNC-40/DCC in vivo. Genetics. 158:1071–1080.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llambi F, Causeret F, Bloch-Gallego E and
Mehlen P: Netrin-1 acts as a survival factor via its receptors
UNC5H and DCC. Embo J. 20:2715–2722. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang H, Ozaki T, Shamim Hossain M,
Nakamura Y, Kamijo T, Xue X and Nakagawara A: A newly identified
dependence receptor UNC5H4 is induced during DNA damage-mediated
apoptosis and transcriptional target of tumor suppressor p53.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 370:594–598. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang X, Cheung RM, Komaki R, Fang B and
Chang JY: Radiotherapy sensitization by tumor-specific TRAIL gene
targeting improves survival of mice bearing human non-small cell
lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:6657–6668. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Masunaga S, Ono K, Takahashi A, Ohnishi T,
Kinashi Y and Takagaki M: Radiobiological characteristics of solid
tumours depending on the p53 status of the tumour cells, with
emphasis on the response of intratumour quiescent cells. Eur J
Cancer. 38:718–727. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kanzawa T, Iwado E, Aoki H, Iwamaru A,
Hollingsworth EF, Sawaya R, Kondo S and Kondo Y: Ionizing radiation
induces apoptosis and inhibits neuronal differentiation in rat
neural stem cells via the c-JUN NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway.
Oncogene. 25:3638–3648. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux
DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V and Sobin L;
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
International Staging Committee; Participating Institutions. The
IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of
the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the
TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2:706–714.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink
HK and Harris CC: WHO and TNM classification. Pathology and
Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. IARC
Press; Lyon: 2004
|
|
12
|
Rusch V, Klimstra D, Venkatraman E, Oliver
J, Martini N, Gralla R, Kris M and Dmitrovsky E: Aberrant p53
expression predicts clinical resistance to cisplatin-based
chemotherapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer
Res. 55:5038–5042. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thornberry NA, Rano TA, Peterson EP,
Rasper DM, Timkey T, Garcia-Calvo M, Houtzager VM, Nordstrom PA,
Roy S, Vaillancourt JP, et al: A combinatorial approach defines
specificities of members of the caspase family and granzyme B.
Functional relationships established for key mediators of
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 272:17907–17911. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Thiebault K, Mazelin L, Pays L, Llambi F,
Joly MO, Scoazec JY, Saurin JC, Romeo G and Mehlen P: The netrin-1
receptors UNC5H are putative tumor suppressors controlling cell
death commitment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:4173–4178. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hartwell L: Defects in a cell cycle
checkpoint may be responsible for the genomic instability of cancer
cells. Cell. 71:543–546. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ullrich SJ, Anderson CW, Mercer WE and
Appella E: The p53 tumor suppressor protein, a modulator of cell
proliferation. J Biol Chem. 267:15259–15262. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yin Y, Tainsky MA, Bischoff FZ, Strong LC
and Wahl GM: Wild-type p53 restores cell cycle control and inhibits
gene amplification in cells with mutant p53 alleles. Cell.
70:937–948. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|