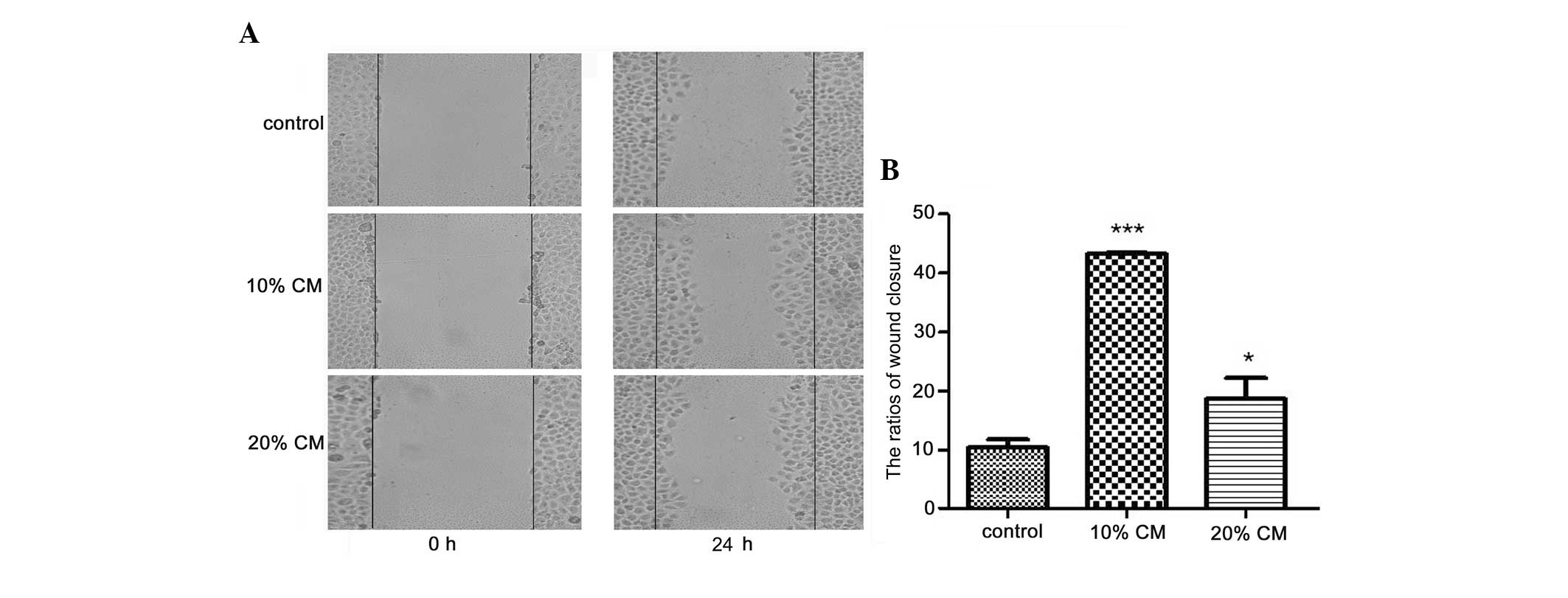
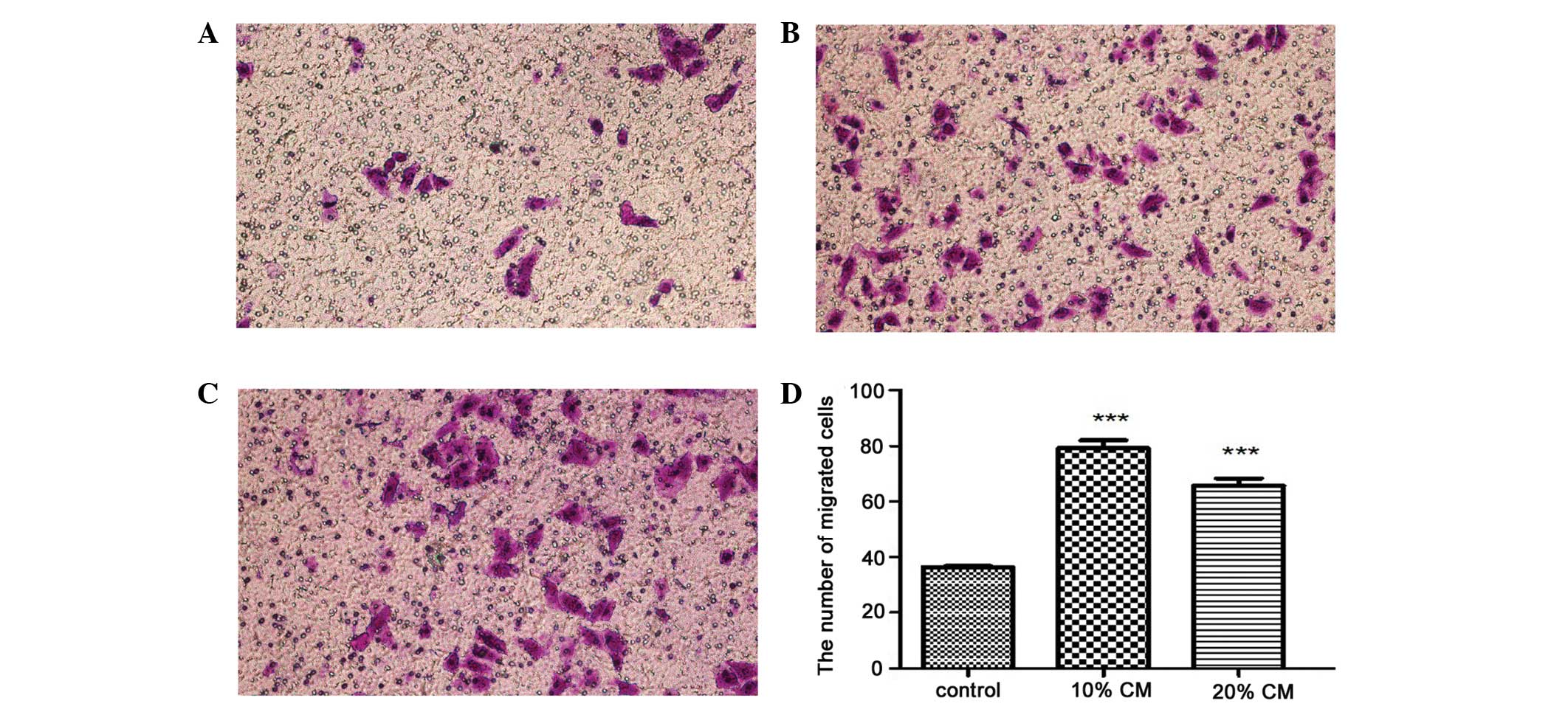
|
1
|
Lv YG, Yu F, Yao Q, Chen JH and Wang L:
The role of survivin in diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of
breast cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2:100–110. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bieback K, Kern S, Kocaömer A, Ferlik K
and Bugert P: Comparing mesenchymal stromal cells from different
human tissues: bone marrow, adipose tissue and umbilical cord
blood. Biomed Mater Eng. 18(Suppl 1): S71–S76. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Digirolamo CM, Stokes D, Colter D, Phinney
DG, Class R and Prockop DJ: Propagation and senescence of human
marrow stromal cells in culture: a simple colony-forming assay
identifies samples with the greatest potential to propagate and
differentiate. Br J Haematol. 107:275–281. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al:
Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal
cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position
statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Haynesworth SE, Baber MA and Caplan AI:
Cell surface antigens on human marrow-derived mesenchymal cells are
detected by monoclonal antibodies. Bone. 13:69–80. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mackay AM, Beck SC, Murphy JM, Barry FP,
Chichester CO and Pittenger MF: Chondrogenic differentiation of
cultured human mesenchymal stem cells from marrow. Tissue Eng.
4:415–428. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al:
Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.
Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qiao C, Xu W, Zhu W, et al: Human
mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the umbilical cord. Cell Biol
Int. 32:8–15. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu Y, Chen L, Scott PG and Tredget EE:
Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through
differentiation and angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 25:2648–2659. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu Y, Wang J, Scott PG and Tredget EE:
Bone marrow-derived stem cells in wound healing: a review. Wound
Repair Regen. 15(Suppl 1): S18–S26. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dwyer RM, Khan S, Barry FP, O’Brien T and
Kerin MJ: Advances in mesenchymal stem cell-mediated gene therapy
for cancer. Stem Cell Res Ther. 1:252010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Spaeth E, Klopp A, Dembinski J, Andreeff M
and Marini F: Inflammation and tumor microenvironments: defining
the migratory itinerary of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Ther.
15:730–738. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roorda BD, ter Elst A, Kamps WA and de
Bont ES: Bone marrow-derived cells and tumor growth: contribution
of bone marrow-derived cells to tumor micro-environments with
special focus on mesenchymal stem cells. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
69:187–198. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast cancer
metastasis. Nature. 449:557–563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu W, Xu W, Jiang R, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cells derived from bone marrow favor tumor cell growth in
vivo. Exp Mol Pathol. 80:267–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hall B, Andreeff M and Marini F: The
participation of mesenchymal stem cells in tumor stroma formation
and their application as targeted-gene delivery vehicles. Handb Exp
Pharmacol. 180:263–283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Joyce JA and Pollard JW:
Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:239–252. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin TM, Chang HW, Wang KH, et al:
Isolation and identification of mesenchymal stem cells from human
lipoma tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 361:883–889. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gibbs CP, Kukekov VG, Reith JD, et al:
Stem-like cells in bone sarcomas: implications for tumorigenesis.
Neoplasia. 7:967–976. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun X, Cai H, Qian H, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cells isolated from human uterine cervix cancer tissues. Cell
Biol Int. 35:119–123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao H, Xu W, Qian H, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cell-like cells derived from human gastric cancer tissues.
Cancer Lett. 274:61–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lis R, Touboul C, Mirshahi P, et al: Tumor
associated mesenchymal stem cells protects ovarian cancer cells
from hyperthermia through CXCL12. Int J Cancer. 128:715–725. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rhodes LV, Muir SE, Elliott S, et al:
Adult human mesenchymal stem cells enhance breast tumorigenesis and
promote hormone independence. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 121:293–300.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Salvo VA, Boué SM, Fonseca JP, et al:
Antiestrogenic glyceollins suppress human breast and ovarian
carcinoma tumorigenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 12:7159–7164. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gnecchi M and Melo LG: Bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, expansion, characterization,
viral transduction, and production of conditioned medium. Methods
Mol Biol. 482:281–294. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Molloy AP, Martin FT, Dwyer RM, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell secretion of chemokines during
differentiation into osteoblasts, and their potential role in
mediating interactions with breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
124:326–332. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iwamoto S, Mihara K, Downing JR, Pui CH
and Campana D: Mesenchymal cells regulate the response of acute
lymphoblastic leukemia cells to asparaginase. J Clin Invest.
117:1049–1057. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Giordano A, Galderisi U and Marino IR:
From the laboratory bench to the patient’s bedside: an update on
clinical trials with mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol.
211:27–35. 2007.
|
|
29
|
Mishra PJ, Mishra PJ, Glod JW and Banerjee
D: Mesenchymal stem cells: flip side of the coin. Cancer Res.
69:1255–1258. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Spaeth EL, Dembinski JL, Sasser AK, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell transition to tumor-associated fibroblasts
contributes to fibrovascular network expansion and tumor
progression. PLoS One. 4:e49922009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Y, Hu T, Shen J, et al: Separation,
cultivation and biological characteristics of oral
carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Oral Dis. 12:375–380. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gauthaman K, Yee FC, Cheyyatraivendran S,
Biswas A, Choolani M and Bongso A: Human umbilical cord Wharton’s
jelly stem cell (hWJSC) extracts inhibit cancer cell growth in
vitro. J Cell Biochem. 113:2027–2039. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Zhu W, Huang L, Li Y, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cell-secreted soluble signaling molecules potentiate tumor
growth. Cell Cycle. 10:3198–3207. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|