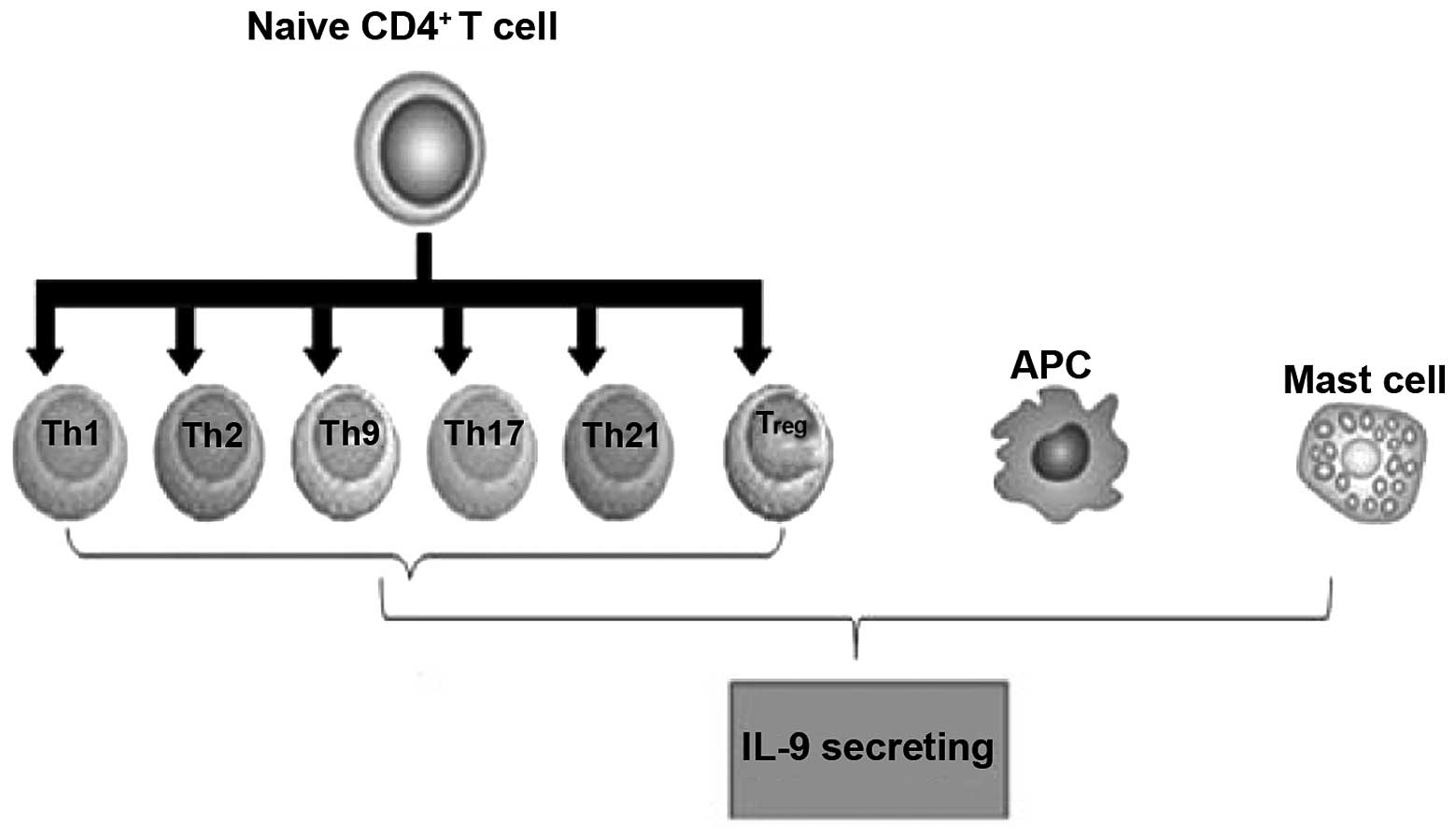
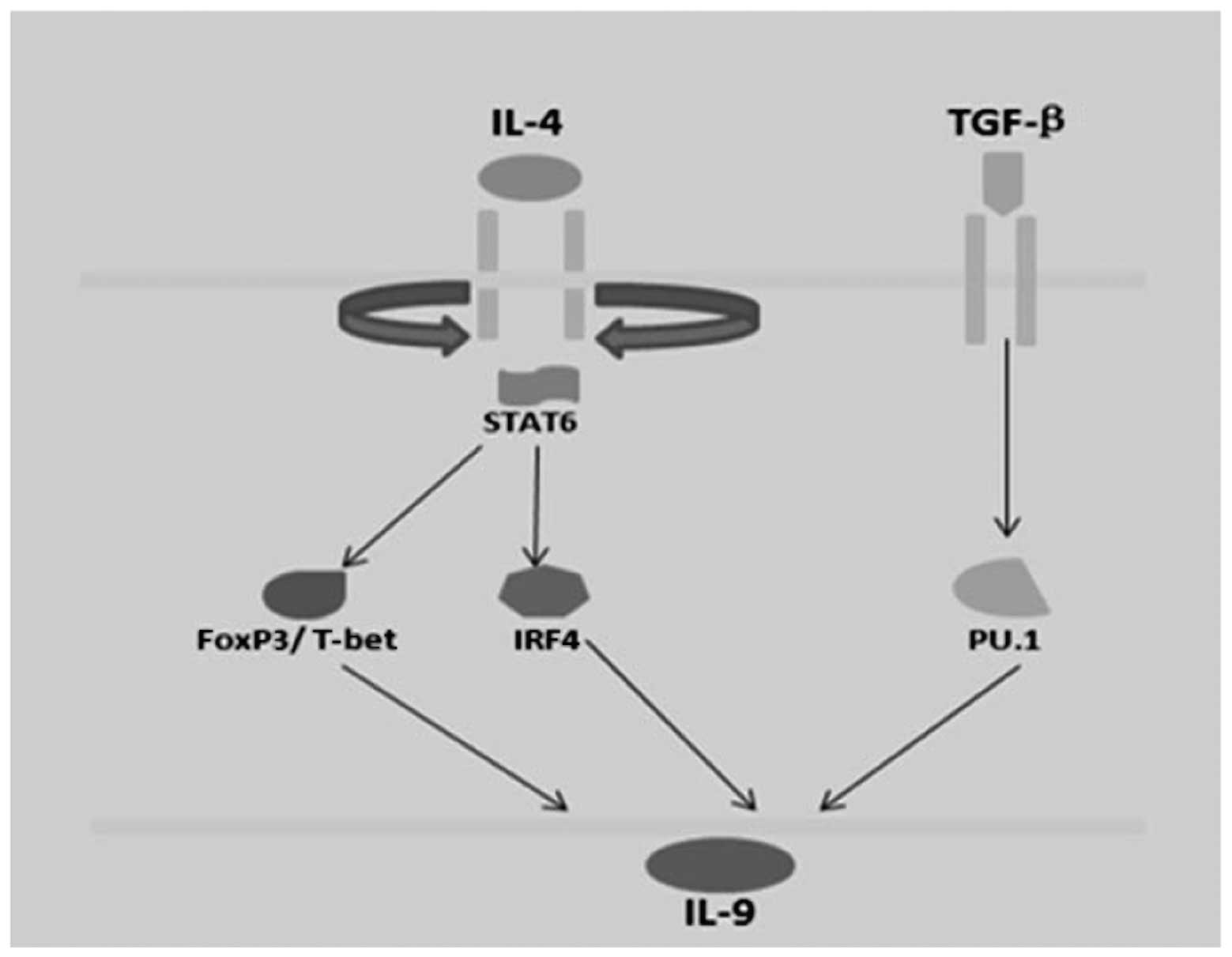
|
1
|
Namkung JH, Lee JE, Kim E, et al: An
association between IL-9 and IL-9 receptor gene polymorphisms and
atopic dermatitis in a Korean population. J Dermatol Sci. 62:16–21.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Knoops L and Renauld JC: IL-9 and its
receptor: from signal transduction to tumorigenesis. Growth
Factors. 22:207–215. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Putheti P, Awasthi A, Popoola J, Gao W and
Strom TB: Human CD4 memory T cells can become CD4+IL-9+ T cells.
PLoS One. 5:e87062010.
|
|
4
|
van den Ham HJ, de Waal L, Andeweg AC and
de Boer RJ: Identification of helper T cell master regulator
candidates using the polar score method. J Immunol Methods.
361:98–109. 2010.
|
|
5
|
Chang HC, Han L, Jabeen R, Carotta S, Nutt
SL and Kaplan MH: PU.1 regulates TCR expression by modulating
GATA-3 activity. J Immunol. 183:4887–4894. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chang HC, Zhang S, Thieu VT, Slee RB,
Bruns HA, Laribee RN, Klemsz MJ and Kaplan MH: PU.1 expression
delineates heterogeneity in primary Th2 cells. Immunity.
22:693–703. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chang HC, Sehra S, Goswami R, Yao W, Yu Q,
Stritesky GL, Jabeen R, McKinley C, Ahyi AN, Han L, et al: The
transcription factor PU.1 is required for the development of
IL-9-producing T cells and allergic inflammation. Nat Immunol.
11:527–534. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Staudt V, Bothur E, Klein M, Lingnau K,
Reuter S, Grebe N, Gerlitzki B, Hoffmann M, Ulges A, Taube C, et
al: Interferon-regulatory factor 4 is essential for the
developmental program of T helper 9 cells. Immunity. 33:192–202.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ahyi AN, Chang HC, Dent AL, Nutt SL and
Kaplan MH: IFN regulatory factor 4 regulates the expression of a
subset of Th2 cytokines. J Immunol. 183:1598–1606. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brustle A, Heink S, Huber M, Rosenplanter
C, Stadelmann C, Yu P, Arpaia E, Mak TW, Kamradt T and Lohoff M:
The development of inflammatory T(H)-17 cells requires
interferon-regulatory factor 4. Nat Immunol. 8:958–966. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lohoff M, Mittrucker HW, Prechtl S,
Bischof S, Sommer F, Kock S, Ferrick DA, Duncan GS, Gessner A and
Mak TW: Dysregulated T helper cell differentiation in the absence
of interferon regulatory factor 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:11808–11812. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hültner L, Kölsch S, Stassen M, Kaspers U,
Kremer JP, Mailhammer R, Moeller J, Broszeit H and Schmitt E: In
activated mast cells, IL-1 up-regulates the production of several
Th2-related cytokines including IL-9. J Immunol. 164:5556–5563.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stassen M, Arnold M, Hültner L, Müller C,
Neudörfl C, Reineke T and Schmitt E: Murine bone marrow-derived
mast cells as potent producers of IL-9: costimulatory function of
IL-10 and kit ligand in the presence of IL-1. J Immunol.
164:5549–5555. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stassen M, Müller C, Arnold M, Hültner L,
Klein-Hessling S, Neudörfl C, Reineke T, Serfling E and Schmitt E:
IL-9 and IL-13 production by activated mast cells is strongly
enhanced in the presence of lipopolysaccharide: NF-kappa B is
decisively involved in the expression of IL-9. J Immunol.
166:4391–4398. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Stassen M, Klein M, Becker M, Bopp T,
Neudörfl C, Richter C, Heib V, Klein-Hessling S, Serfling E, Schild
H and Schmitt E: p38 MAP kinase drives the expression of mast
cell-derived IL-9 via activation of the transcription factor
GATA-1. Mol Immunol. 44:926–933. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Osterfeld H, Ahrens R, Strait R, Finkelman
FD, Renauld JC and Hogan SP: Differential roles for the IL-9/IL-9
receptor alpha-chain pathway in systemic and oral antigen-induced
anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125:469–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Demoulin JB, Louahed J, Dumoutier L,
Stevens M and Renauld JC: MAP kinase activation by interleukin-9 in
lymphoid and mast cell lines. Oncogene. 22:1763–1770. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cosmi L, Liotta F, Angeli R, Mazzinghi B,
Santarlasci V, Manetti R, Lasagni L, Vanini V, Romagnani P, Maggi
E, et al: Th2 cells are less susceptible than Th1 cells to the
suppressive activity of CD25+ regulatory thymocytes because of
their responsiveness to different cytokines. Blood. 103:3117–3121.
2004.
|
|
19
|
Druez C, Coulie P, Uyttenhove C and Van
Snick J: Functional and biochemical characterization of mouse
P40/IL-9 receptors. J Immunol. 145:2494–2499. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abdelilah S, Latifa K, Esra N, Cameron L,
Bouchaib L, Nicolaides N, Levitt R and Hamid Q: Functional
expression of IL-9 receptor by human neutrophils from asthmatic
donors: role in IL-8 release. J Immunol. 166:2768–2774. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kearley J, Erjefalt JS, Andersson C,
Benjamin E, Jones CP, Robichaud A, Pegorier S, Brewah Y, Burwell
TJ, Bjermer L, et al: IL-9 governs allergen-induced mast cell
numbers in the lung and chronic remodeling of the airways. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 183:865–875. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nowak EC, Weaver CT, Turner H, Begum-Haque
S, Becher B, Schreiner B, Coyle AJ, Kasper LH and Noelle RJ: IL-9
as a mediator of Th17-driven inflammatory disease. J Exp Med.
206:1653–1660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu LF, Lind EF, Gondek DC, Bennett KA,
Gleeson MW, Pino-Lagos K, Scott ZA, Coyle AJ, Reed JL, Van Snick J,
et al: Mast cells are essential intermediaries in regulatory T-cell
tolerance. Nature. 442:997–1002. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Knoops L, Louahed J and Renauld JC:
IL-9-induced expansion of B-1b cells restores numbers but not
function of B-1 lymphocytes in xid mice. J Immunol. 172:6101–6106.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vink A, Warnier G, Brombacher F and
Renauld JC: Interleukin 9-induced in vivo expansion of the B-1
lymphocyte population. J Exp Med. 189:1413–1423. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dugas B, Renauld JC, Pene J, Bonnefoy JY,
Peti-Frère C, Braquet P, Bousquet J, Van Snick J and Mencia-Huerta
JM: Interleukin-9 potentiates the interleukin-4-induced
immunoglobulin (IgG, IgM and IgE) production by normal human B
lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 23:1687–1692. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Petit-Frere C, Dugas B, Braquet P and
Mencia-Huerta JM: Interleukin-9 potentiates the
interleukin-4-induced IgE and IgG1 release from murine B
lymphocytes. Immunology. 79:146–151. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fawaz LM, Sharif-Askari E, Hajoui O,
Soussi-Gounni A, Hamid Q and Mazer BD: Expression of IL-9 receptor
alpha chain on human germinal center B cells modulates IgE
secretion. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 120:1208–1215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Renauld JC, Druez C, Kermouni A, Houssiau
F, Uyttenhove C, Van Roost E and Van Snick J: Expression cloning of
the murine and human interleukin 9 receptor cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 89:5690–5694. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen J, Petrus M, Bryant BR, Phuc Nguyen
V, Stamer M, Goldman CK, Bamford R, Morris JC, Janik JE and
Waldmann TA: Induction of the IL-9 gene by HTLV-I Tax stimulates
the spontaneous proliferation of primary adult T-cell leukemia
cells by a paracrine mechanism. Blood. 111:5163–5172. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Umezu-Goto M, Kajiyama Y, Kobayashi N,
Kaminuma O, Suko M and Mori A: IL-9 production by peripheral blood
mononuclear cells of atopic asthmatics. Int Arch Allergy Immunol.
143(Suppl 1): 76–79. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen J, Petrus M, Bryant BR, Nguyen VP,
Goldman CK, Bamford R, Morris JC, Janik JE and Waldmann TA:
Autocrine/paracrine cytokine stimulation of leukemic cell
proliferation in smoldering and chronic adult T-cell leukemia.
Blood. 116:5948–5956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Merz H, Kaehler C, Hoefig KP, et al:
Interleukin-9 (IL-9) and NPM-ALK each generate mast cell
hyperplasia as single ‘hit’ and cooperate in producing a
mastocytosis-like disease in mice. Oncotarget. 1:104–119.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin Q, Lai R, Chirieac LR, Li C, Thomazy
VA, Grammatikakis I, Rassidakis GZ, Zhang W, Fujio Y, Kunisada K,
et al: Constitutive activation of JAK3/STAT3 in colon carcinoma
tumors and cell lines: inhibition of JAK3/STAT3 signaling induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of colon carcinoma cells. Am J
Pathol. 167:969–980. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Dahéron L, Opitz SL, Zaehres H, Lensch MW,
Andrews PW, Itskovitz-Eldor J and Daley GQ: LIF/STAT3 signaling
fails to maintain self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells. Stem
Cells. 22:770–778. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Raptis L, Arulanandam R, Geletu M and
Turkson J: The R(h)oads to Stat3: Stat3 activation by the Rho
GTPases. Exp Cell Res. 317:1787–1795. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kidder BL, Yang J and Palmer S: STAT3 and
c-Myc genome-wide promoter occupancy in embryonic stem cells. PLoS
One. 3:e39322008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen X, Xu H, Yuan P, Fang F, Huss M, Vega
VB, Wong E, Orlov YL, Zhang W, Jiang J, et al: Integration of
external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network
in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 133:1106–1117. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kuznetsov VA, Singh O and Jenjaroenpun P:
Statistics of protein-DNA binding and the total number of binding
sites for a transcription factor in the mammalian genome. BMC
Genomics. 11(Suppl 1): S122010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ying QL, Nichols J, Chambers I and Smith
A: BMP induction of Id proteins suppresses differentiation and
sustains embryonic stem cell self-renewal in collaboration with
STAT3. Cell. 115:281–292. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ramana CV, Chatterjee-Kishore M, Nguyen H
and Stark GR: Complex roles of STAT1 in regulating gene expression.
Oncogene. 19:2619–2627. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bourillot PY, Aksoy I, Schreiber V, Wianny
F, Schulz H, Hummel O, Hubner N and Savatier P: Novel STAT3 target
genes exert distinct roles in the inhibition of mesoderm and
endoderm differentiation in cooperation with Nanog. Stem Cells.
27:1760–1771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yu Z, Zhang W and Kone BC: Signal
transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) inhibits
transcription of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene by
interacting with nuclear factor κB. Biochem J. 367:97–105.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang X, Wrzeszczynska MH, Horvath CM and
Darnell JE Jr: Interacting regions in STAT3 and c-Jun that
participate in cooperative transcriptional activation. Mol Cell
Biol. 19:7138–7146. 1999.
|
|
45
|
Giraud S, Bienvenu F, Avril S, Gascan H,
Heery DM and Coqueret O: Functional interaction of STAT3
transcription factor with the coactivator NcoA/SRC1a. J Biol Chem.
277:8004–8011. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Youn MY, Yoo HS, Kim MJ, Hwang SY, Choi Y,
Desiderio SV and Yoo JY: hCTR9, a component of Paf1 complex,
participates in the transcription of interleukin 6-responsive genes
through regulation of STAT3-DNA interactions. J Biol Chem.
282:34727–34734. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ni Z and Bremner R: Brahma-related gene
1-dependent STAT3 recruitment at IL-6-inducible genes. J Immunol.
178:345–351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Giraud S, Hurlstone A, Avril S and
Coqueret O: Implication of BRG1 and cdk9 in the STAT3-mediated
activation of the p21waf1 gene. Oncogene. 23:7391–7398. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ho L, Jothi R, Ronan JL, Cui K, Zhao K and
Crabtree GR: An embryonic stem cell chromatin remodeling complex,
esBAF, is an essential component of the core pluripotency
transcriptional network. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:5187–5191.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ho L, Ronan JL, Wu J, Staahl BT, Chen L,
Kuo A, Lessard J, Nesvizhskii AI, Ranish J and Crabtree GR: An
embryonic stem cell chromatin remodeling complex, esBAF, is
essential for embryonic stem cell self-renewal and pluripotency.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:5181–5186. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Singhal N, Graumann J, Wu G, Araúzo-Bravo
MJ, Han DW, Greber B, Gentile L, Mann M and Schöler HR:
Chromatin-remodeling components of the BAF complex facilitate
reprogramming. Cell. 141:943–955. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Guiter C, Dusanter-Fourt I, Copie-Bergman
C, Boulland ML, Le Gouvello S, Gaulard P, Leroy K and Castellano F:
Constitutive STAT6 activation in primary mediastinal large B-cell
lymphoma. Blood. 104:543–549. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gerber M and Shilatifard A:
Transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II and histone
methylation. J Biol Chem. 278:26303–26306. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ding L, Paszkowski-Rogacz M, Nitzsche A,
Slabicki MM, Heninger AK, de Vries I, Kittler R, Junqueira M,
Shevchenko A, Schulz H, et al: A genome-scale RNAi screen for Oct4
modulators defines a role of the Paf1 complex for embryonic stem
cell identity. Cell Stem Cell. 4:403–415. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ponnusamy MP, Deb S, Dey P, Chakraborty S,
Rachagani S, Senapati S and Batra SK: RNA polymerase II associated
factor 1/PD2 maintains self-renewal by its interaction with Oct3/4
in mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 27:3001–3011.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lessard JA and Crabtree GR: Chromatin
regulatory mechanisms in pluripotency. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
6:503–532. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Skinnider BF, Elia AJ, Gascoyne RD,
Patterson B, Trumper L, Kapp U and Mak TW: Signal transducer and
activator of transcription 6 is frequently activated in Hodgkin and
Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 99:618–626. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wei L, Vahedi G, Sun HW, Watford WT,
Takatori H, Ramos HL, Takahashi H, Liang J, Gutierrez-Cruz G, Zang
C, et al: Discrete roles of STAT4 and STAT6 transcription factors
in tuning epigenetic modifications and transcription during T
helper cell differentiation. Immunity. 32:840–851. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Elo LL, Järvenpää H, Tuomela S, Raghav S,
Ahlfors H, Laurila K, Gupta B, Lund RJ, Tahvanainen J, Hawkins RD,
et al: Genome-wide profiling of interleukin-4 and STAT6
transcription factor regulation of human Th2 cell programming.
Immunity. 32:852–862. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Takeda K, Tanaka T, Shi W, Matsumoto M,
Minami M, Kashiwamura S, Nakanishi K, Yoshida N, Kishimoto T and
Akira S: Essential role of STAT6 in IL-4 signalling. Nature.
380:627–630. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ansel KM, Djuretic I, Tanasa B and Rao A:
Regulation of Th2 differentiation and Il4 locus accessibility. Annu
Rev Immunol. 24:607–656. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dardalhon V, Awasthi A, Kwon H, Galileos
G, Gao W, Sobel RA, Mitsdoerffer M, Strom TB, Elyaman W, Ho IC,
Khoury S, Oukka M and Kuchroo VK: IL-4 inhibits TGF-beta-induced
Foxp3+ T cells and, together with TGF-beta, generates IL-9+ IL-10+
Foxp3(−) effector T cells. Nat Immunol. 9:1347–1355.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Perumal NB and Kaplan MH: Regulating Il9
transcription in T helper cells. Trends Immunol. 32:146–150. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Veldhoen M, Uyttenhove C, van Snick J,
Helmby H, Westendorf A, Buer J, Martin B, Wilhelm and Stockinger B:
Transforming growth factor-beta ‘reprograms’ the differentiation of
T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset.
Nat Immunol. 9:1341–1346. 2008.
|
|
65
|
Kaplan MH, Daniel C, Schindler U and
Grusby MJ: STAT proteins control lymphocyte proliferation by
regulating p27Kip1 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 18:1996–2003.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhu J, Guo L, Min B, Watson CJ, Hu-Li J,
Young HA, Tsichlis PN and Paul WE: Growth factor independent-1
induced by IL-4 regulates Th2 cell proliferation. Immunity.
16:733–744. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kaplan MH, Wurster AL, Smiley ST and
Grusby MJ: STAT6-dependent and -independent pathways for IL-4
production. J Immunol. 163:6536–6540. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Bruns HA, Schindler U and Kaplan MH:
Expression of a constitutively active STAT6 in vivo alters
lymphocyte homeostasis with distinct effects in T and B cells. J
Immunol. 170:3478–3487. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kaplan MH, Whitfield JR, Boros DL and
Grusby MJ: Th2 cells are required for the Schistosoma mansoni
egg-induced granulomatous response. J Immunol. 160:1850–1856.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wurster AL, Rodgers VL, White MF,
Rothstein TL and Grusby MJ: Interleukin-4-mediated protection of
primary B cells from apoptosis through STAT6-dependent
up-regulation of Bcl-xL. J Biol Chem. 277:27169–27175. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Takeda K, Kamanaka M, Tanaka T, Kishimoto
T and Akira S: Impaired IL-13-mediated functions of macrophages in
STAT6-deficient mice. J Immunol. 157:3220–3222. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Martinez FO, Helming L and Gordon S:
Alternative activation of macrophages: an immunologic functional
perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:451–483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Huber S, Hoffmann R, Muskens F and
Voehringer D: Alternatively activated macrophages inhibit T-cell
proliferation by STAT6-dependent expression of PD-L2. Blood.
116:3311–3320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Szanto A, Balint BL, Nagy ZS, Barta E,
Dezso B, Pap A, Szeles L, Poliska S, Oros M, Evans RM, et al: STAT6
transcription factor is a facilitator of the nuclear receptor
PPARgamma-regulated gene expression in macrophages and dendritic
cells. Immunity. 33:699–712. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yao Y, Li W, Kaplan MH and Chang CH:
Interleukin (IL)-4 inhibits IL-10 to promote IL-12 production by
dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 201:1899–1903. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Furqan M, Mukhi N, Lee B and Liu D:
Dysregulation of JAK-STAT pathway in hematological malignancies and
JAK inhibitors for clinical application. Biomark Res. 1:52013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bito T, Sumita N, Ashida M, Budiyanto A,
Ueda M, Ichihashi M, Tokura Y and Nishigori C: Inhibition of
epidermal growth factor receptor and PI3K/Akt signaling suppresses
cell proliferation and survival through regulation of Stat3
activation in human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Skin
Cancer. 2011:8745712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jeres A, Clemente MJ, Makishima H, Koskela
H, Leblanc F, Peng Ng K, Olson T, Przychodzen B, Afable M,
Gomez-Segui I, et al: STAT3 mutations unify the pathogenesis of
chronic lymphoproliferative disorders of NK cells and T-cell large
granular lymphocyte leukemia. Blood. 120:3048–3057. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Hazan-Halevy I, Harris D, Liu Z, Liu J, Li
P, Chen X, Shanker S, Ferrajoli A, Keating MJ and Estrov Z: STAT3
is constitutively phosphorylated on serine 727 residues, binds DNA,
and activates transcription in CLL cells. Blood. 115:2852–2863.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Ding BB, Yu JJ, Yu RY, Mendez LM,
Shaknovich R, Zhang Y, Cattoretti G and Ye BH: Constitutively
activated STAT3 promotes cell proliferation and survival in the
activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood.
111:1515–1523. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ritz O, Guiter C, Castellano F, Dorsch K,
Melzner J, Jais JP, Dubois G, Gaulard P, Moller P and Leroy K:
Recurrent mutations of the STAT6 DNA binding domain in primary
mediastinal B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 114:1236–1242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kis LL, Gerasimcik N, Salamon D, Persson
EK, Nagy N, Klein G, Severinson E and Klein E: STAT6 signaling
pathway activated by the cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 induces
expression of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein LMP-1 in
absence of EBNA-2: implications for the type II EBV latent gene
expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 117:165–174. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G,
Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C and Darnell JE Jr: STAT3 as an
oncogene. Cell. 98:295–303. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J and Jove R:
STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 19:2474–2488. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Haura EB, Turkson J and Jove R: Mechanisms
of disease: Insights into the emerging role of signal transducers
and activators of transcription in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol.
2:315–324. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Frank DA, Mahajan S and Ritz J: B
lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia contain
signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 and STAT3
constitutively phosphorylated on serine residues. J Clin Invest.
100:3140–3148. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Mora LB, Buettner R, Seigne J, Diaz J,
Ahmad N, Garcia R, Bowman T, Falcone R, Fairclough R, Cantor A, et
al: Constitutive activation of STAT3 in human proSTATe tumors and
cell lines: direct inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis
of proSTATe cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:6659–6666. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Diaz N, Minton S, Cox C, Bowman T, Gritsko
T, Garcia R, Eweis I, Wloch M, Livingston S, Seijo E, et al:
Activation of STAT3 in primary tumors from high-risk breast cancer
patients is associated with elevated levels of activated SRC and
survivin expression. Clin Cancer Res. 12:20–28. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Scholz A, Heinze S, Detjen KM, Peters M,
Welzel M, Hauff P, Schirner M, Wiedenmann B and Rosewicz S:
Activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
(STAT3) supports the malignant phenotype of human pancreatic
cancer. Gastroenterology. 125:891–905. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Eifan AO, Furukido K, Dumitru A, Jacobson
MR, Schmidt-Weber C, Banfield G, Durham SR and Nouri-Aria KT:
Reduced T-bet in addition to enhanced STAT6 and GATA3 expressing T
cells contribute to human allergen-induced late responses. Clin Exp
Allergy. 42:891–900. 2012.
|
|
91
|
Hadjur S, Bruno L, Hertweck A, Cobb BS,
Taylor B, Fisher AG and Merkenschlager M: IL4 blockade of inducible
regulatory T cell differentiation: the role of Th2 cells, Gata3 and
PU.1. Immunol Lett. 122:37–43. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|