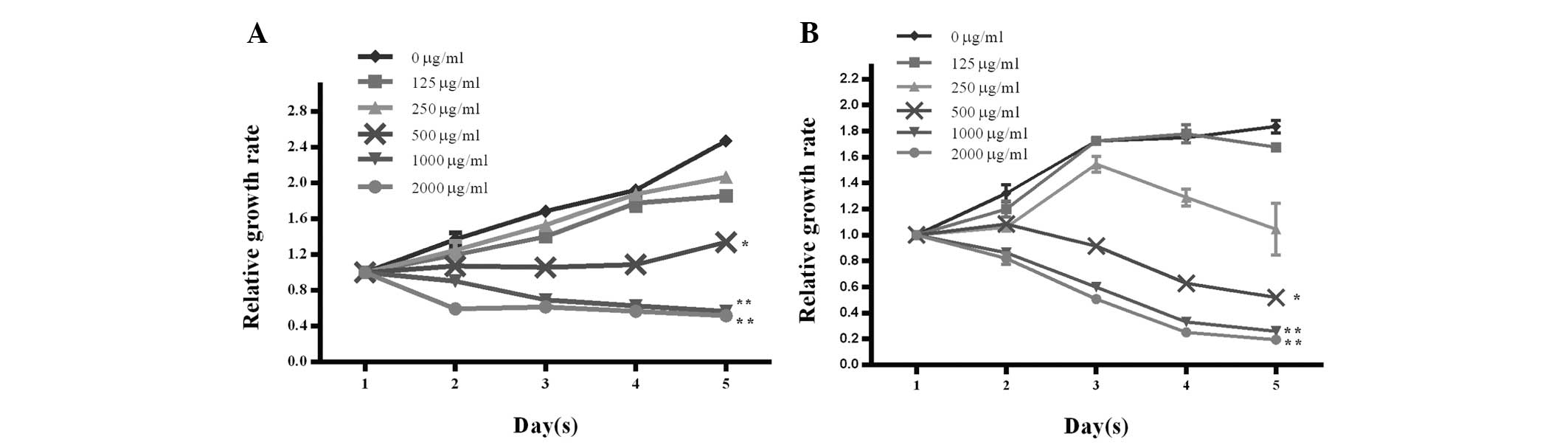
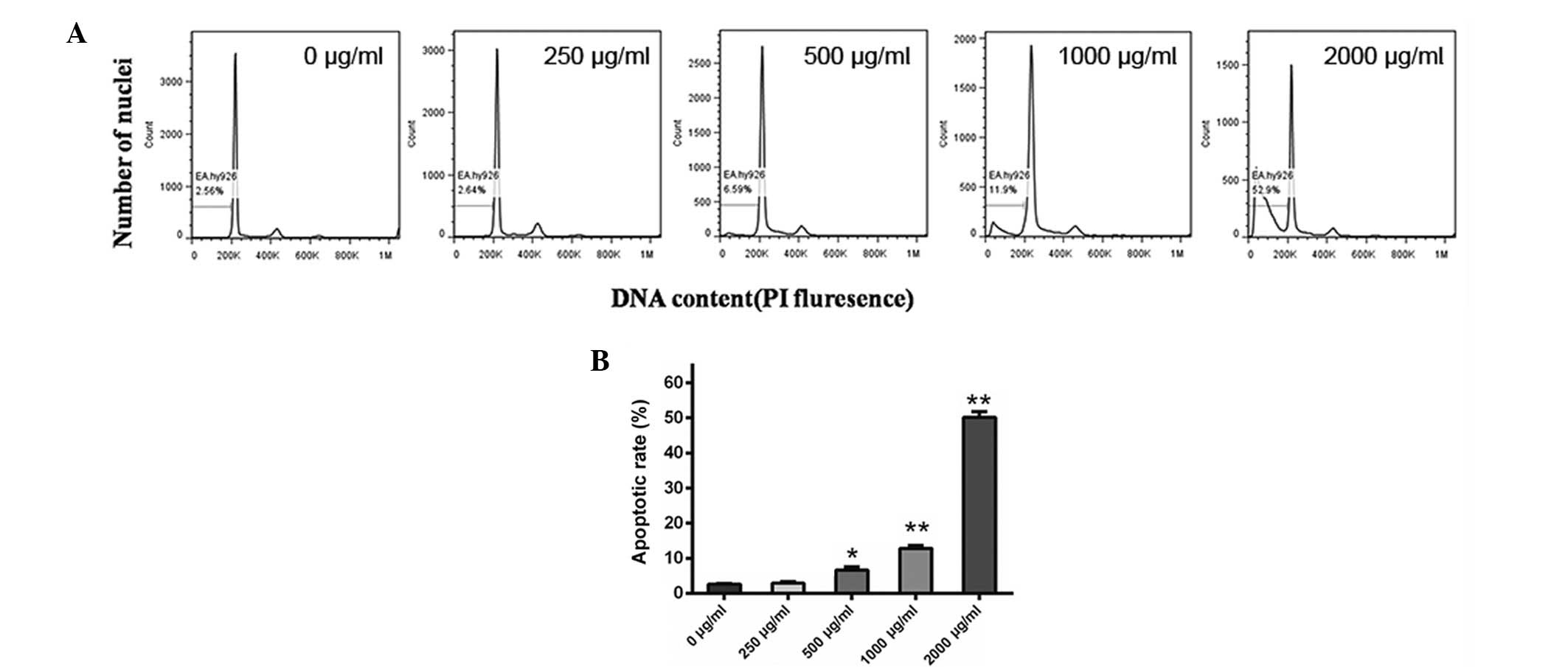
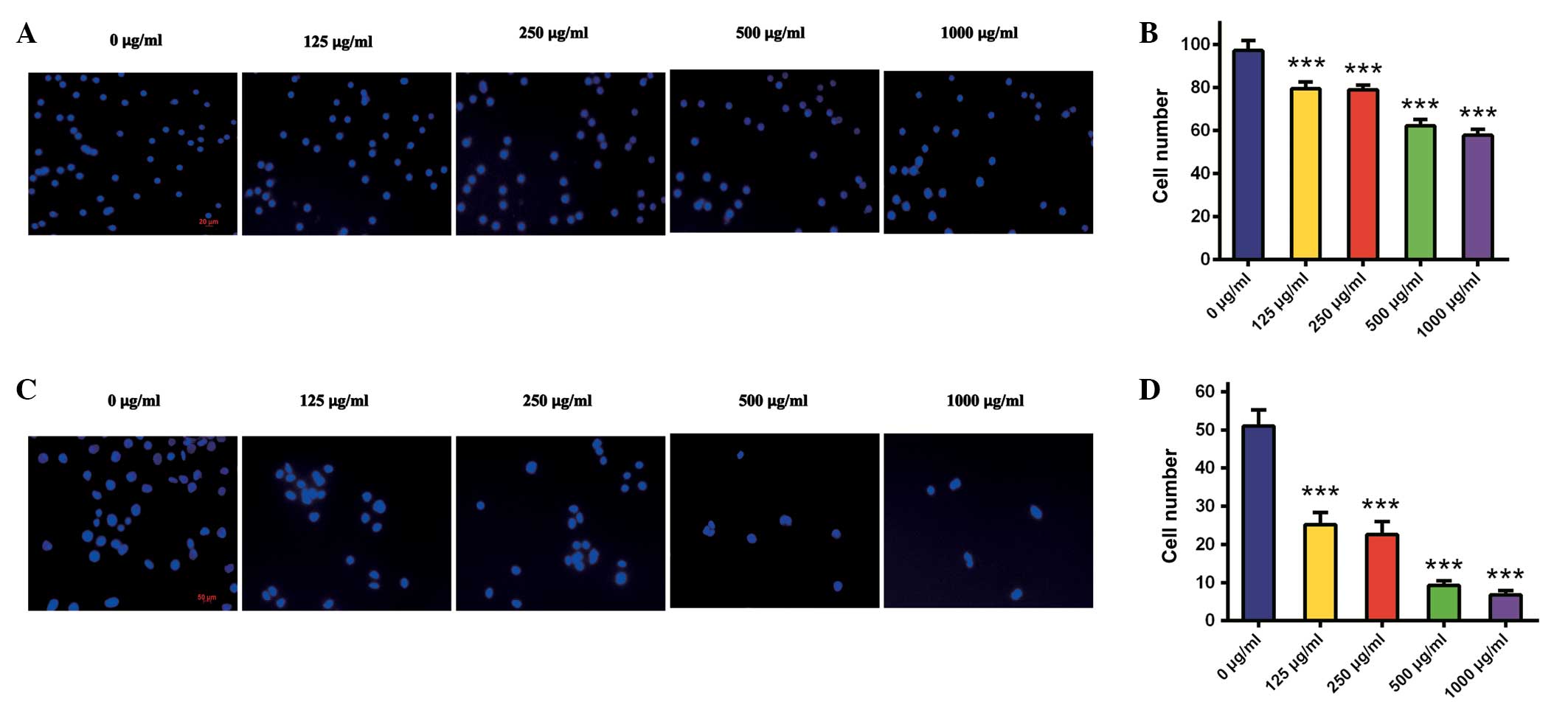
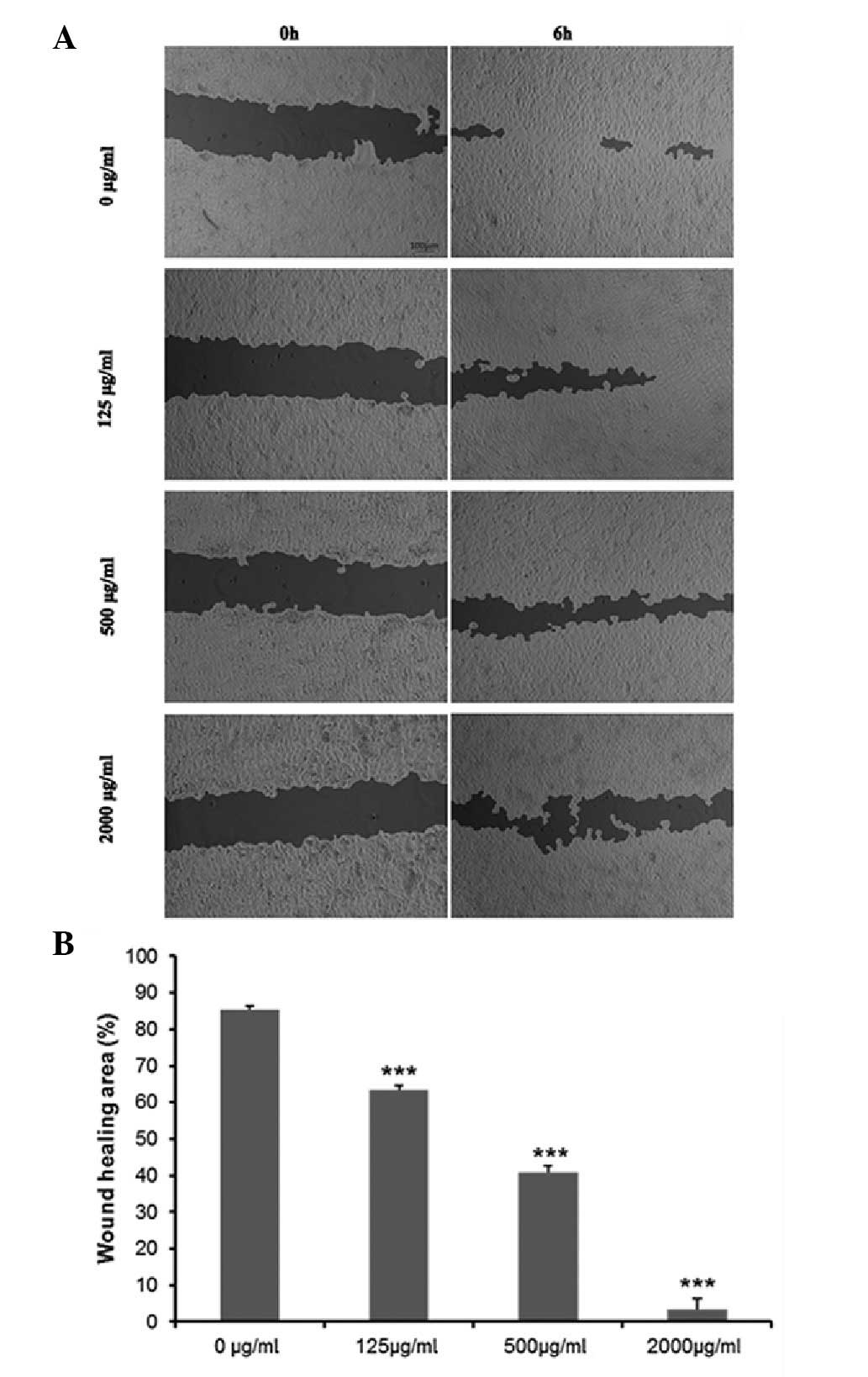
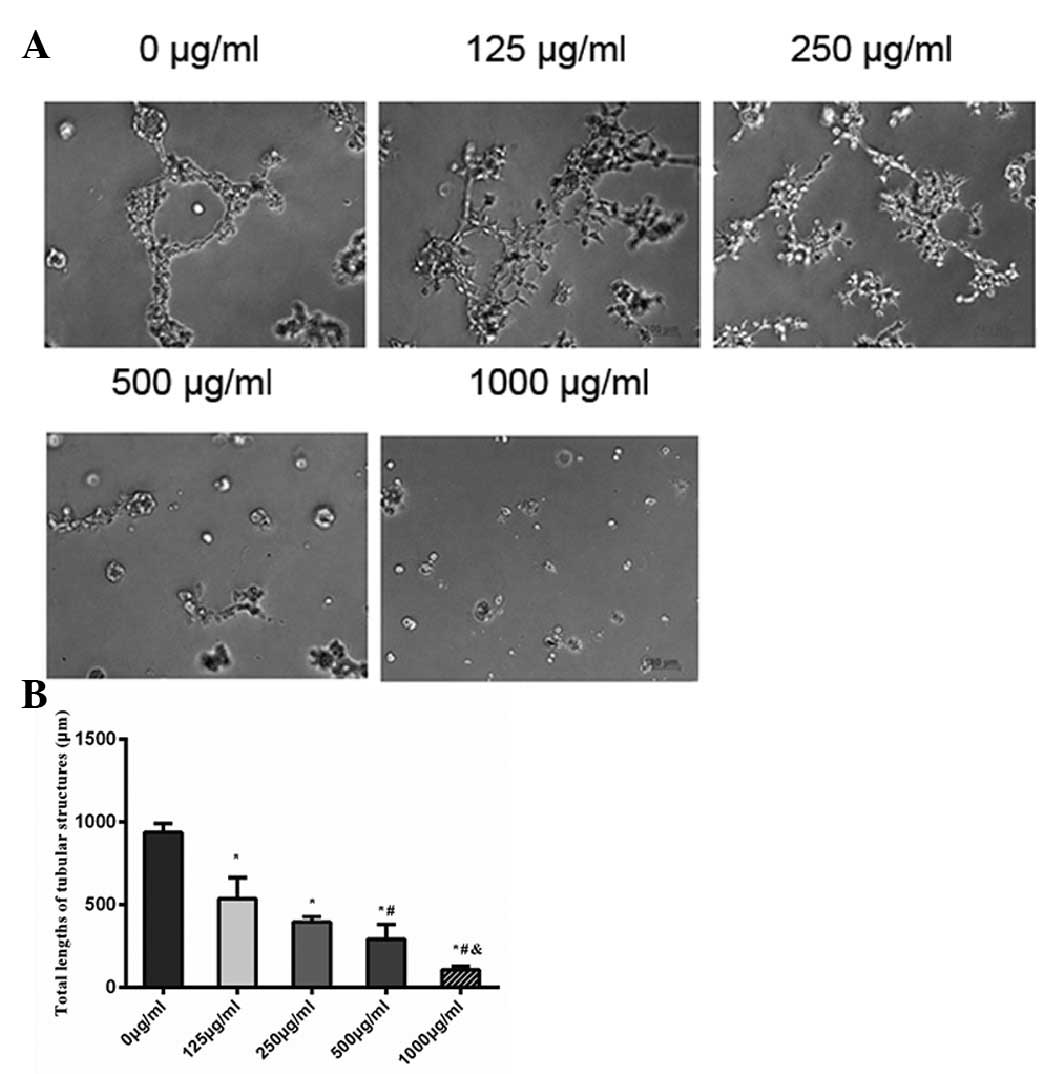
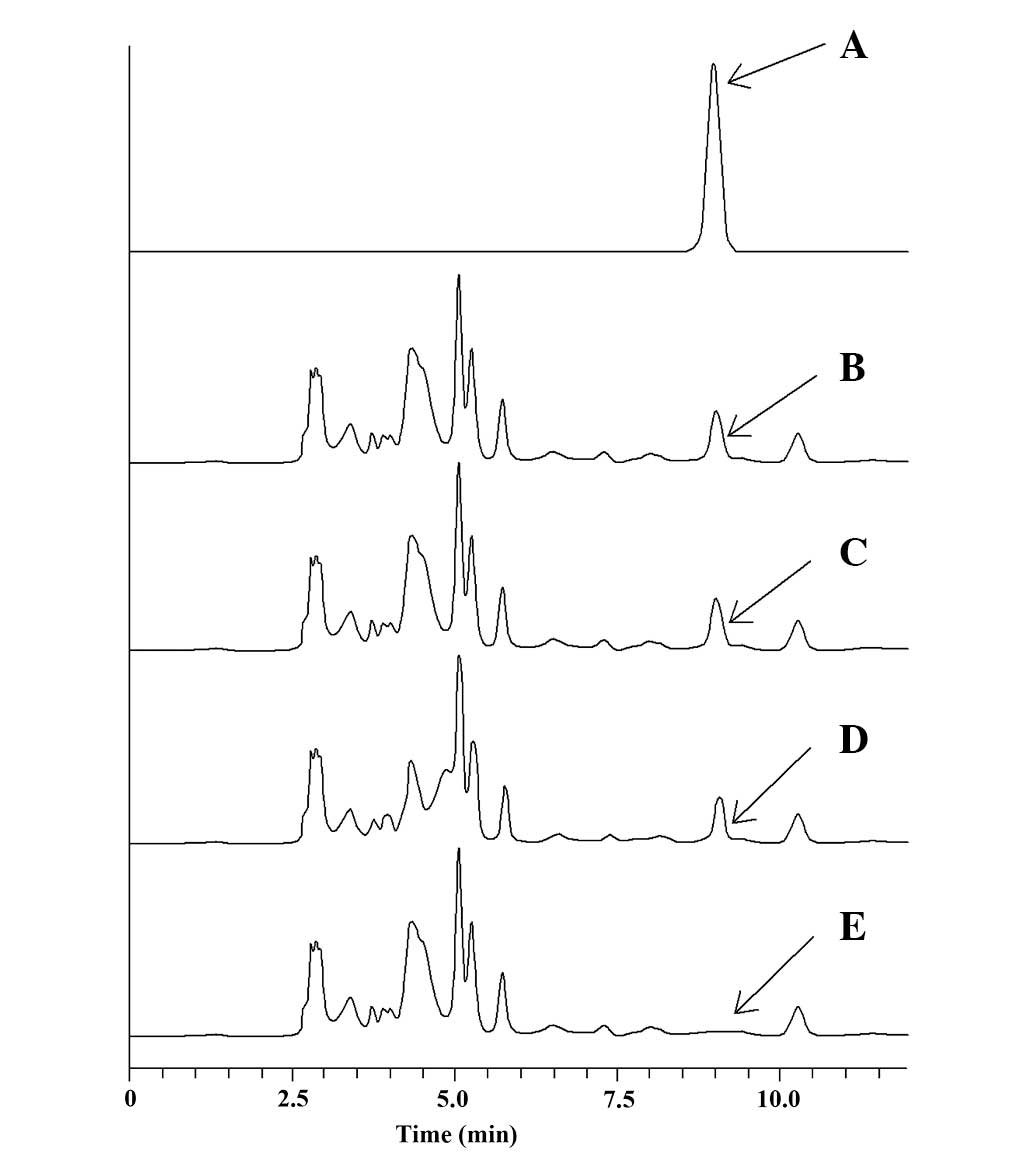
|
1
|
McGlynn KA and London WT: Epidemiology and
natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 19:3–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Azam F and Koulaouzidis A: Hepatitis B
virus and hepatocarcinogenesis. Ann Hepatol. 7:125–129.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M and Cleries R:
Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127(5 Suppl 1): S5–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Flamme I, Frolich T and Risau W: Molecular
mechanisms of vasculogenesis and embryonic angiogenesis. J Cell
Physiol. 173:206–210. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lopez PM, Villanueva A and Llovet JM:
Systematic review: evidence-based management of hepatocellular
carcinoma - an updated analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 23:1535–1547. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cunningham KG, Manson W, Spring FS and
Hutchinson SA: Cordycepin, a metabolic product isolated from
cultures of Cordyceps militaris (Linn.) Link. Nature.
166:9491950. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lennon MB and Suhadolnik RJ: Biosynthesis
of 3′-deoxyadenosine by Cordyceps militaris. Mechanism of
reduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 425:532–536. 1976.
|
|
11
|
Tsai YJ, Lin LC and Tsai TH:
Pharmacokinetics of adenosine and cordycepin, a bioactive
constituent of Cordyceps sinensis in rat. J Agric Food Chem.
58:4638–4643. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sugar AM and McCaffrey RP: Antifungal
activity of 3′-deoxyadenosine (cordycepin). Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 42:1424–1427. 1998.
|
|
13
|
Jagger DV, Kredich NM and Guarino AJ:
Inhibition of Ehrlich mouse ascites tumor growth by cordycepin.
Cancer Res. 21:216–220. 1961.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rich MA, Meyers P, Weinbaum G, Cory JG and
Suhadolnik RJ: Inhibition of human tumor cells by cordycepin.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 95:194–204. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nakamura K, Yoshikawa N, Yamaguchi Y, et
al: Antitumor effect of cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) on mouse
melanoma and lung carcinoma cells involves adenosine A3 receptor
stimulation. Anticancer Res. 26:43–47. 2006.
|
|
16
|
Wehbe-Janek H, Shi Q and Kearney CM:
Cordycepin/hydroxyurea synergy allows low dosage efficacy of
cordycepin in MOLT-4 leukemia cells. Anticancer Res. 27:3143–3146.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee SJ, Kim SK, Choi WS, Kim WJ and Moon
SK: Cordycepin causes p21WAF1-mediated G2/M cell-cycle arrest by
regulating c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation in human bladder
cancer cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 490:103–109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Choi S, Lim MH, Kim KM, Jeon BH, Song WO
and Kim TW: Cordycepin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in breast
cancer cells are independent of the estrogen receptor. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 257:165–173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee SJ, Moon GS, Jung KH, Kim WJ and Moon
SK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 is required for cordycepin-mediated
induction of G2/M cell-cycle arrest via p21WAF1 expression in human
colon cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:277–283. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jeong JW, Jin CY, Park C, et al:
Inhibition of migration and invasion of LNCaP human prostate
carcinoma cells by cordycepin through inactivation of Akt. Int J
Oncol. 40:1697–1704. 2012.
|
|
21
|
Shi P, Huang Z, Tan X and Chen G:
Proteomic detection of changes in protein expression induced by
cordycepin in human hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7402 cells.
Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 30:347–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang BJ, Won SJ, Yu ZR and Su CL: Free
radical scavenging and apoptotic effects of Cordyceps
sinensis fractionated by supercritical carbon dioxide. Food
Chem Toxicol. 43:543–552. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Robertson JB, Williams JR and Little JB:
Enhancement of radiation killing of cultured mammalian cells by
cordycepin. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 34:417–429.
1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wong YY, Moon A, Duffin R, et al:
Cordycepin inhibits protein synthesis and cell adhesion through
effects on signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 285:2610–2621. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ni H, Zhou XH, Li HH and Huang WF: Column
chromatographic extraction and preparation of cordycepin from
Cordyceps militaris waster medium. J Chromatogr B Analyt
Technol Biomed Life Sci. 877:2135–2141. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hansen MB, Nielsen SE and Berg K:
Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye
method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods.
119:203–210. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Telford WG, King LE and Fraker PJ:
Evaluation of glucocorticoid-induced DNA fragmentation in mouse
thymocytes by flow cytometry. Cell Prolif. 24:447–459. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xing YN, Liang HW, Zhao L and Xu HM: The
antitumor activity of exogenous and endogenous canstatin on
colorectal cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:2713–2716.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu J and Verkman AS: Increased migration
and metastatic potential of tumor cells expressing aquaporin water
channels. FASEB J. 20:1892–1894. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Oikawa T, Sasaki T, Nakamura M, et al: The
proteasome is involved in angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
246:243–248. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu Z, Tao X, Zhang C, Lu Y and Wei D:
Protective effects of hyperoside (quercetin-3-o-galactoside) to
PC12 cells against cytotoxicity induced by hydrogen peroxide and
tert-butyl hydroperoxide. Biomed Pharmacother. 59:481–490. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chang W, Lim S, Song H, Song BW, Kim HJ,
Cha MJ, Sung JM, Kim TW and Hwang KC: Cordycepin inhibits vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation. Eur J Pharmacol. 597:64–69. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen LS, Du-Cuny L, Vethantham V, et al:
Chain termination and inhibition of mammalian poly(A) polymerase by
modified ATP analogues. Biochem Pharmacol. 79:669–677. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nakamura K, Konoha K, Yoshikawa N,
Yamaguchi Y, Kagota S, Shinozuka K and Kunitomo M: Effect of
cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) on hematogenic lung metastatic model
mice. In Vivo. 19:137–141. 2005.
|
|
35
|
Wu WC, Hsiao JR, Lian YY, Lin CY and Huang
BM: The apoptotic effect of cordycepin on human OEC-M1 oral cancer
cell line. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 60:103–111. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Thomadaki H, Scorilas A, Tsiapalis CM and
Havredaki M: The role of cordycepin in cancer treatment via
induction or inhibition of apoptosis: implication of
polyadenylation in a cell type specific manner. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 61:251–265. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lee CW, Wong LL, Tse EY, et al: AMPK
promotes p53 acetylation via phosphorylation and inactivation of
SIRT1 in liver cancer cells. Cancer Res. 72:4394–4404. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Guo P, Kai Q, Gao J, et al: Cordycepin
prevents hyperlipidemia in hamsters fed a high-fat diet via
activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Pharmacol Sci.
113:395–403. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu JY, Zhang QX and Leung PH: Inhibitory
effects of ethyl acetate extract of Cordyceps sinensis
mycelium on various cancer cells in culture and B16 melanoma in
C57BL/6 mice. Phytomedicine. 14:43–49. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zetter BR: Angiogenesis and tumor
metastasis. Annu Rev Med. 49:407–424. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lu ZJ, Ren YQ, Wang GP, et al: Biological
behaviors and proteomics analysis of hybrid cell line EAhy926 and
its parent cell line A549. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:162009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nelson NJ: Angiogenesis research is on
fast forward. J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:820–822. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Edgell CJ, Haizlip JE, Bagnell CR, et al:
Endothelium specific Weibel-Palade bodies in a continuous human
cell line, EA.hy926. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 26:1167–1172. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Edgell CJ, McDonald CC and Graham JB:
Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen
established by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 80:3734–3737.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Adamson RH, Zaharevitz DW and Johns DG:
Enhancement of the biological activity of adenosine analogs by the
adenosine deaminase inhibitor 2′-deoxycoformycin. Pharmacology.
15:84–89. 1977.
|
|
47
|
Farthing D, Sica D, Gehr T, et al: An HPLC
method for determination of inosine and hypoxanthine in human
plasma from healthy volunteers and patients presenting with
potential acute cardiac ischemia. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol
Biomed Life Sci. 854:158–164. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|