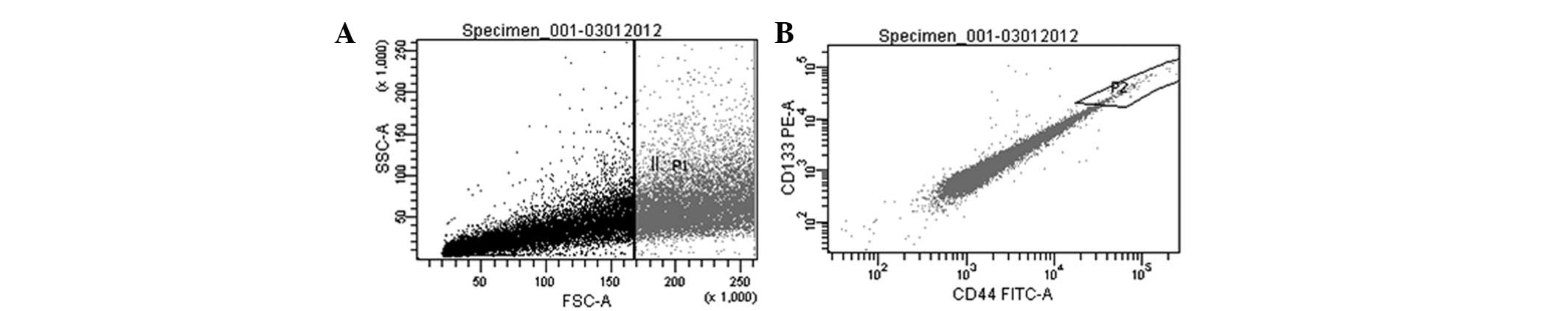
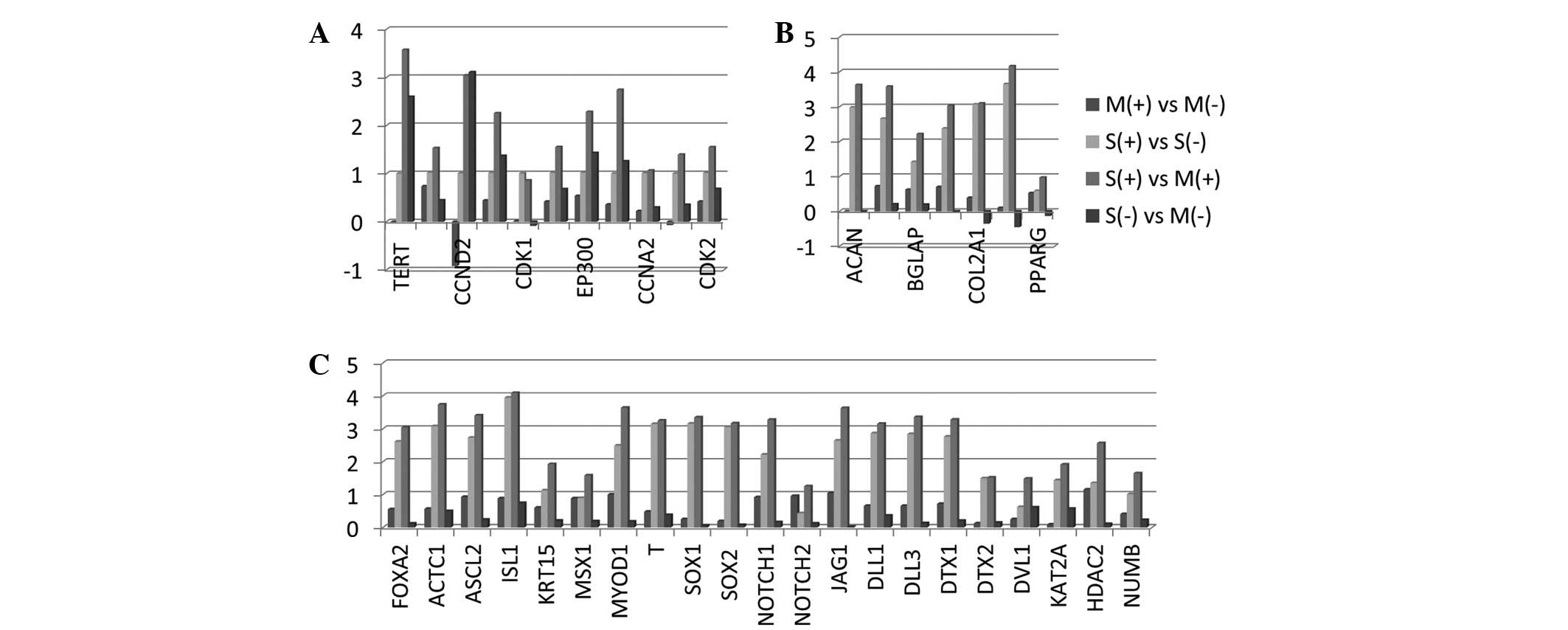
|
1
|
Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, Eaves CJ,
Jamieson CH, Jones DL, Visvader J, Weissman IL and Wahl GM: Cancer
stem cells - perspectives on current status and future directions:
AACR Workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 66:9339–9344. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Vermeulen L, Sprick MR, Kemper K, Stassi G
and Medema JP: Cancer stem cells - old concepts, new insights. Cell
Death Differ. 15:947–958. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hill RP and Perris R: ‘Destemming’ cancer
stem cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1435–1440. 2007.
|
|
4
|
Miki J and Rhim JS: Prostate cell cultures
as in vitro models for the study of normal stem cells and cancer
stem cells. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 11:32–39. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Botchkina GI, Zuniga SZ, Das M, Wang Y,
Wang H, Zhu S, Savitt AG, Rowehl RA, Leyfman Y, Ju J, et al:
New-generation taxoid SB-T-1214 inhibits stem cell-related gene
expression in 3D cancer spheroids induced by purified colon
tumor-initiating cells. Mol Cancer. 9:1922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shackleton M, Quintana E, Fearon ER and
Morrison SJ: Heterogeneity in cancer: cancer stem cells versus
clonal evolution. Cell. 138:822–829. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang DG: Understanding cancer stem cell
heterogeneity and plasticity. Cell Res. 22:457–472. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Y and Laterra J: Cancer stem cells:
distinct entities or dynamically regulated phenotypes? Cancer Res.
72:576–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, Tunici P, Ng H,
Abdulkadir IR, Lu L, Irvin D, Black KL and Yu JS: Analysis of gene
expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem
cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer. 5:672006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bussolati B, Bruno S, Grange C,
Buttiglieri S, Deregibus MC, Cantino D and Camussi G: Isolation of
renal progenitor cells from adult human kidney. Am J Pathol.
166:545–555. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Suetsugu A, Nagaki M, Aoki H, Motohashi T,
Kunisada T and Moriwaki H: Characterization of CD133+
hepatocellular carcinoma cells as cancer stem/progenitor cells.
Biochem and Biophys Res Commun. 351:820–824. 2006.
|
|
13
|
Yin S, Li J, Hu C, Chen X, et al: CD133
positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells posess high capacity for
tumorigenicity. Int J Cancer. 120:1444–1450. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
O’Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick J: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating timor
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, Aicher A,
Ellwart JW, Guba M, Bruns CJ and Heeschen C: Distinct populations
of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity
in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 1:313–323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Maitland NJ and Collins AT: Prostate
cancer stem cells: a new target for therapy. J Clin Oncol.
26:2862–2870. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shmelkov SV, St Clair R, Lyden D and Rafii
S: AC133/CD133/Prominin-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:715–719.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shmelkov SV, Butler JM, Hooper AT, Hormigo
A, Kushner J, Milde T, St Clair R, et al: CD133 expression is not
restricted to stem cells, and both CD133+ and
CD133− metastatic colon cancer cells initiate tumors. J
Clin Invest. 118:2111–2120. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Beier D, Hau P, Proescholdt M, Lohmeier A,
Wischhusen J, Oefner PJ, Aigner L, Brawanski A, Bogdahn U and Beier
CP: CD133+ and CD133− glioblastoma-derived
cancer stem cells show differential growth characteristics and
molecular profiles. Cancer Res. 67:4010–4015. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Joo KM, Kim SY, Jin X, Song SY, Kong DS,
Lee JI, Jeon JW, Kim MH, Kang BG, Jung Y, et al: Clinical and
biological implications of CD133-positive and CD133-negative cells
in glioblastomas. Lab Invest. 808:808–815. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Orian-Rousseau V: CD44, a therapeutic
target for metastasising tumours. Eur J Cancer. 46:1271–1277. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ponta H, Sherman L and Herrlich PA: CD44:
from adhesion molecules to signaling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 4:33–45. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ugolkov AV, Eisengart LJ, Luan C and Yang
XJ: Expression analysis of putative stem cell markers in human
benign and malignant prostate. Prostate. 71:18–25. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ
and Maitland NJ: Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 65:10946–10951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Robertson FM, Ogasawara MA, Ye Z, Chu K,
Pickei R, Debeb BG, Woodward WA, Hittelman WN, Cristofanilli M and
Barsky SH: Imaging and analysis of 3D tumor spheroids enriched for
a cancer stem cell phenotype. J Biomol Screen. 15:820–829. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Acker H: Microenvironmental conditions in
multicellular spheroids grown under liquid-overlay tissue culture
conditions. Recent Results Cancer Res. 95:116–133. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Oktem G, Sanci M, Bilir A, Yildirim Y,
Kececi SD, Ayla S and Inan S: Cancer stem cell and embryonic
development-associated molecules contribute to prognostic
significance in ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 22:23–29.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lai EC: Notch signaling: control of cell
communication and cell fate. Development. 131:965–973. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Parsons P, Gilbert SJ, Vaughan-Thomas A,
Sorrell DA, Notman R, Bishop M, Hayes AJ, Mason DJ and Duance VC:
Type IX collogen interacts with fibronectin providing an important
molecular bridge in articular cartilage. J Biol Chem.
286:34986972011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang CC, Wang TC, Lin BH, Wang YW,
Johnson SL and Yu J: Collagen IX is required for the integrity of
the collagen II fibrils and the regulation of vascular plexus
formation in zebrafish caudalfins. Dev Biol. 332:360–370. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Piotrowski A, Benetkiewicz M, Menzel U, et
al: Microarray-based survey of CpG islands identifies concurrent
hyper- and hypomethylation patterns in tissues derived from
patients with breast cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 45:656–667.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schmitt AM, Riniker F, Anlauf M, Schmid S,
Soltermann A, Moch H, Heitz PU, Klöppel G, Komminoth P and Perren
A: Islet 1 (Isl1) expression is a reliable marker for pancreatic
endocrine tumorsand their metasteses. Am J Surg Pathol. 32:420–425.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barzelay A, Ben-Shoshan J, Entin-Meer M,
Maysel-Auslender S, Afek A, Barshack Keren G and George J: A
potential role for islet-1 in post-natal angiogenesis and
vasculogenesis. Thromb Haemost. 103:188–197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li JL and Harris AL: Crosstalk of VEGF and
Notch pathways in tumour angiogenesis: therapeutic implications.
Front Biosci. 14:3094–3110. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sethi N, Dai X, Winter CG and Kang Y:
Tumor-derived JAGGED1 promotes osteolytic bone metastasis of breast
cancer by engaging notch signaling in bone cells. Cancer Cell.
19:192–205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Reedijk M, Odorcic S, Chang L, Zhang H,
Miller N, McCready DR, et al: High-level coexpression of JAG1 and
NOTCH1 is observed in human breast cancer and is associated with
poor overall survival. Cancer Res. 65:8530–8537. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu K, Xu L, Zhang L, Lin Z and Hou J: High
Jagged1 expression predicts poor outcome in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 41:411–416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gao J, Liu J, Fan D, Xu H, Xiong Y, Wang
Y, Xu W, Wang Y, Cheng Y and Zheng G: Up-regulated expression of
Notch1 and Jagged1 in human colon adenocarcinoma. Pathol Biol
(Paris). 59:298–302. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Santagata S, Demichelis F, Riva A,
Varambally S, Hofer MD, Kutok JL, et al: JAGGED1 expression is
associated with prostate cancer metastasis and recurrence. Cancer
Res. 64:6854–6857. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Boscolo E, Stewart CL, Greenberger S, Wu
JK, Durham JT, Herman IM, Mulliken JB, Kitajewski J and Bischoff J:
JAGGED1 signaling regulates hemangioma stem cell-to
pericyte/vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:2181–2192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sharma G, Mirza S, Prasad CP, Srivastava
A, Gupta SD and Ralhan R: Promoter hypermethylation of p16INK4A,
p14ARF, CyclinD2 and Slit2 in serum and tumor DNA from breast
cancer patients. Life Sci. 80:1873–1881. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Henrique R, Costa VL, Cerveira N, Carvalho
AL, Hoque MO, Ribeiro FR, Oliveira J, Teixeira MR, Sidransky D and
Jeronimo C: Hypermethylation of Cyclin D2 is associated with loss
of mRNA expression and tumor development in prostate cancer. J Mol
Med. 84:911–918. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|