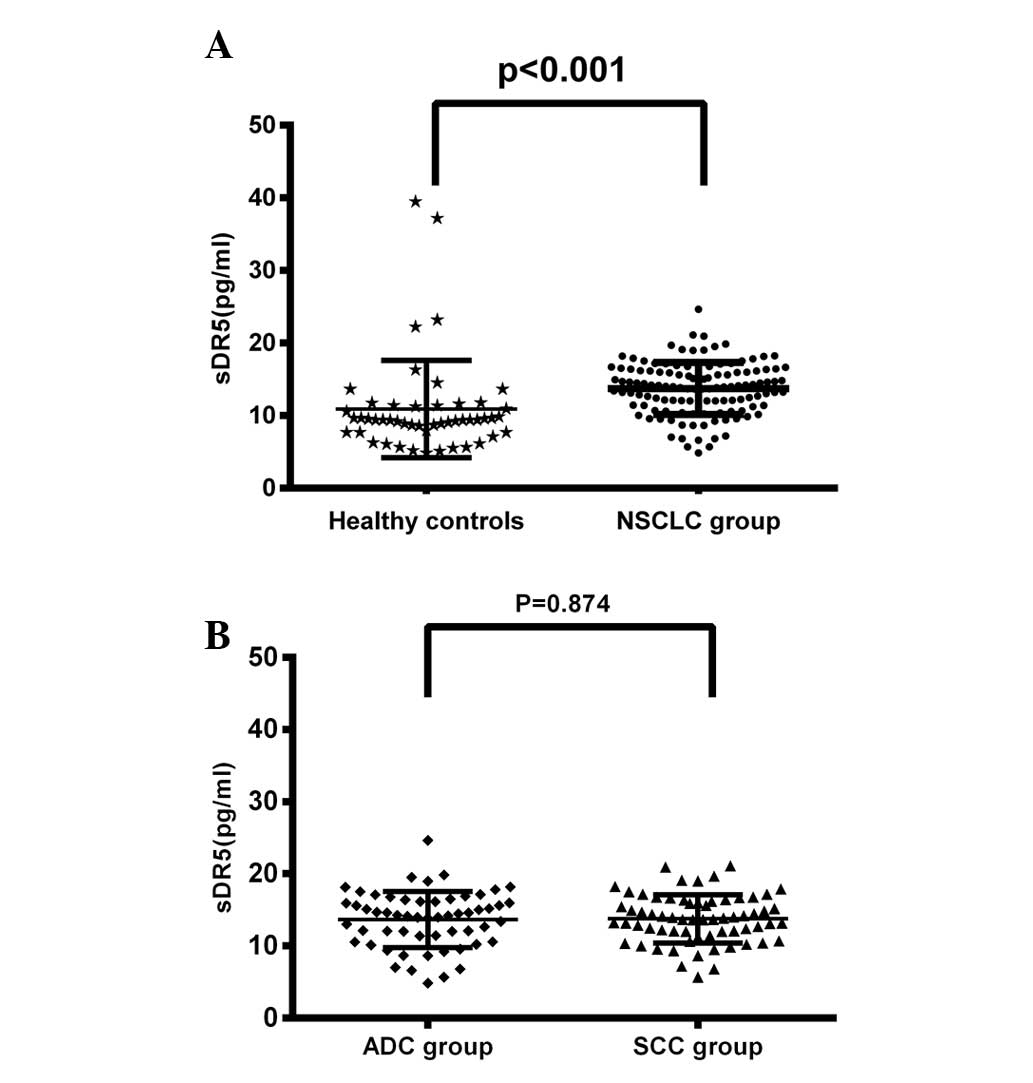
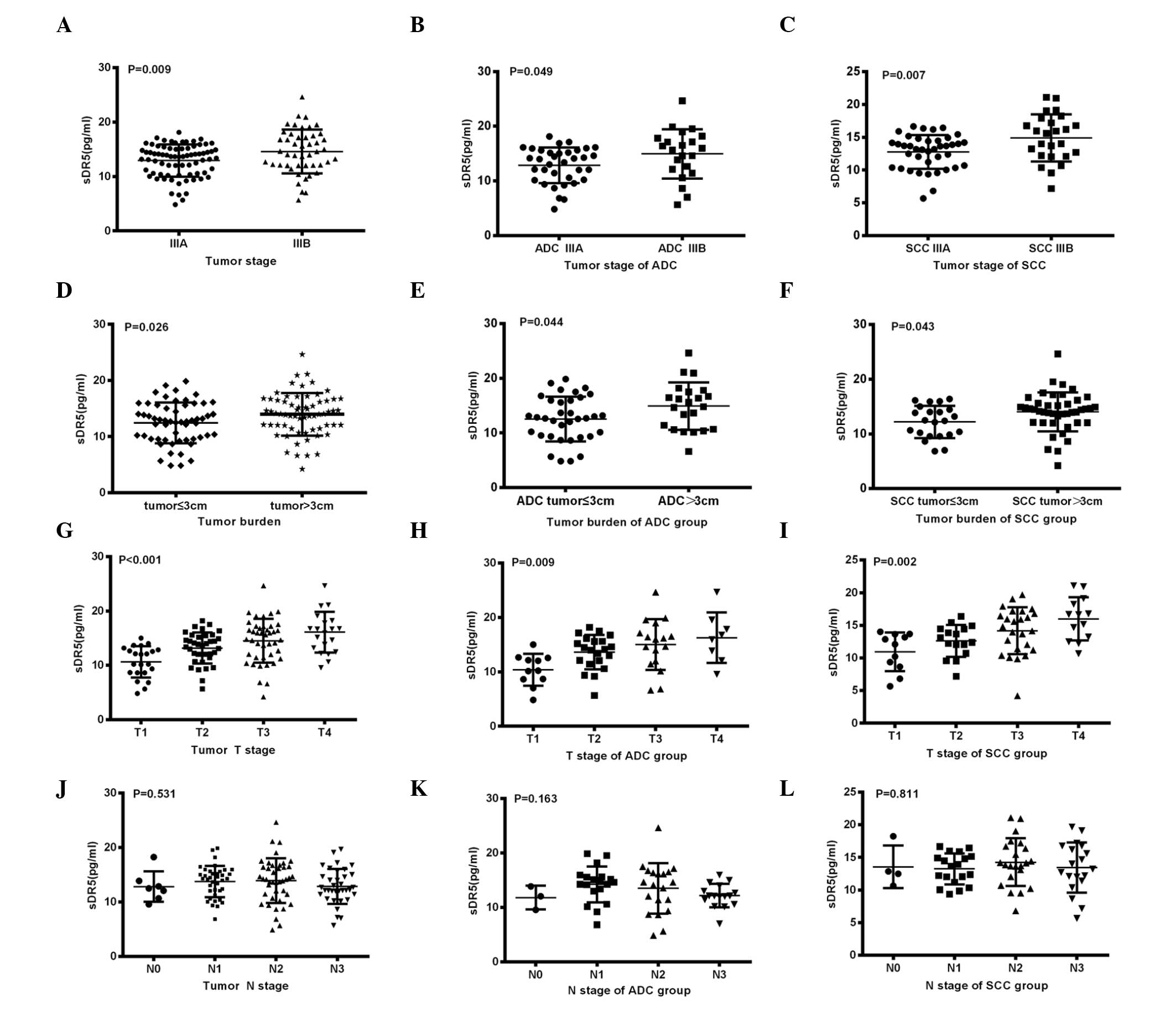
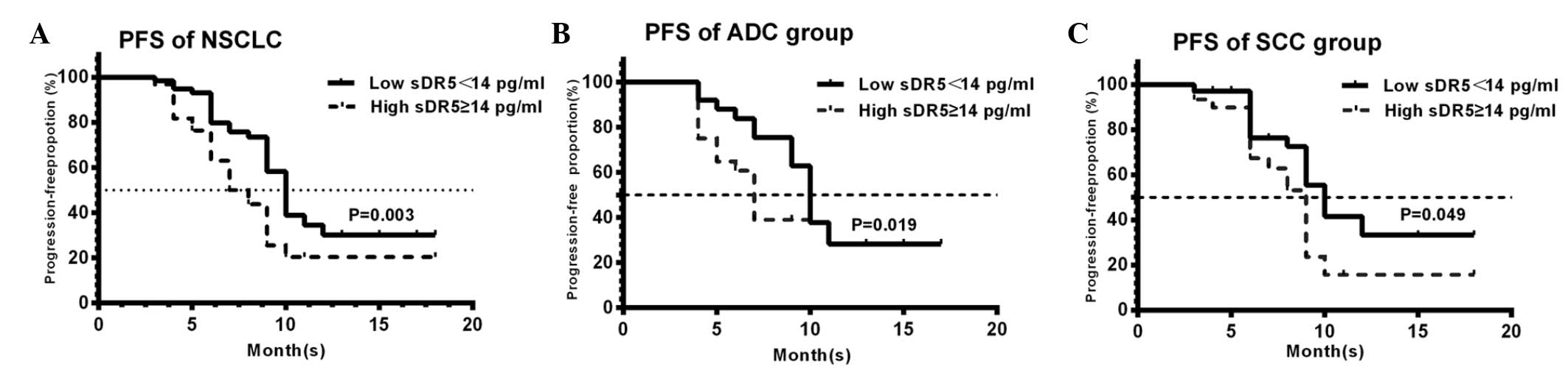
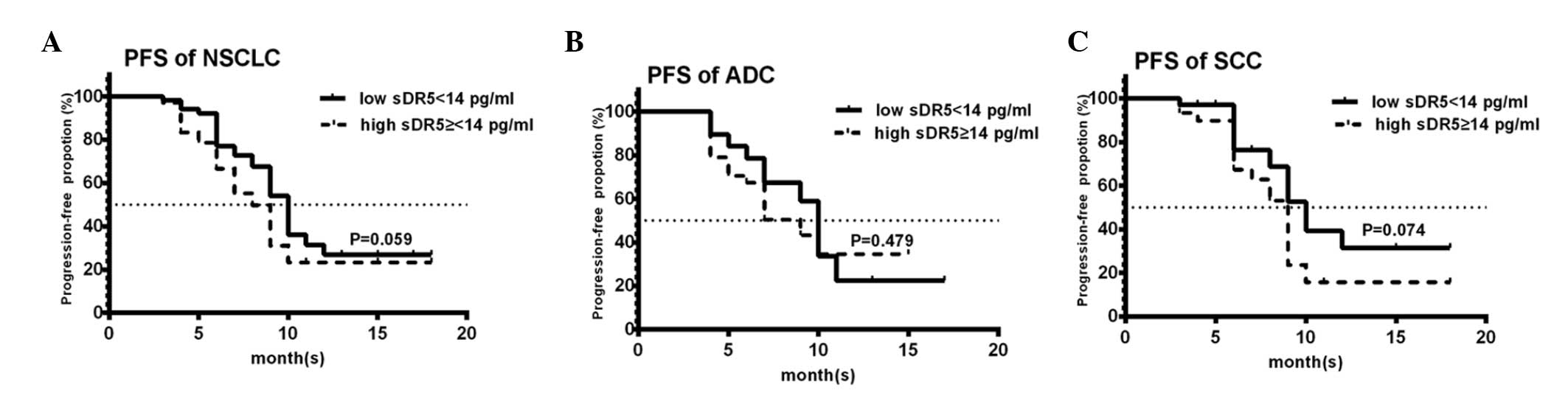
|
1
|
Spierings DC, de Vries EG, Timens W, Groen
HJ, Boezen HM and de Jong S: Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL death
receptors in stage III non-small cell lung cancer tumors. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:3397–3405. 2003.
|
|
2
|
Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Borghaei H, et al:
Non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2013. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
11:645–653. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Chute JP, Chen T, Feigal E, Simon R and
Johnson BE: Twenty years of phase III trails for patients with
extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: perceptible progress. J
Clin Oncol. 17:1794–1801. 1999.
|
|
4
|
Machtay M, Bae K, Movsas B, et al: Higher
biologically effective dose of radiotherapy is associated with
improved outcomes for locally advanced non-small cell lung
carcinoma treated with chemoradiation: an analysis of the Radiation
Therapy Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Onclo Biol Phys. 82:425–434.
2012.
|
|
5
|
Aupérin A, Le Péchoux C, Rolland E, et al:
Meta-analysis of concomitant versus sequential radiochemotherapy in
locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:2181–2191. 2010.
|
|
6
|
Igney FH and Krammer PH: Death and
anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:277–288. 2002.
|
|
7
|
Malhi H and Gores GJ: TRAIL resistance
results in cancer progression: a TRAIL to perdition? Oncogene.
25:7333–7335. 2006.
|
|
8
|
Baader E, Toloczko A, Fuchs U, et al:
Tumornecrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated
proliferation of tumor cells with receptor-proximal apoptosis
defects. Cancer Res. 65:7888–7895. 2005.
|
|
9
|
Yildiz R, Benekli M, Buyukberber S, et al:
The effect of bevacizumab on serum soluble FAS/FASL and TRAIL and
its receptors (DR4 and DR5) in metastatic colorectal cancer. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:1471–1476. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Yang H, Li H, Wang Z, Gao J and Guo Y: Is
urinary soluble fas an independent predictor of non-muscle-invasive
bladder cancer? A prospective chart study. Urol Int. 91:456–461.
2013.
|
|
11
|
van Dijk M, Halpin-McCormick A, Sessler T,
Samali A and Szegezdi E: Resistance to TRAIL in non-transformed
cells is due to multiple redundant pathways. Cell Death Dis.
4:e7022013.
|
|
12
|
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, et al:
Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF
family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 3:673–682. 1995.
|
|
13
|
LeBlanc HN and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL
and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ. 10:66–75.
2003.
|
|
14
|
Truneh A, Sharma S, Silverman C, et al:
Temperature-sensitive differential affinity of TRAIL for its
receptors. DR5 is the highest affinity receptor. J Biol Chem.
275:2319–2325. 2000.
|
|
15
|
Du J, Wang L, Han J, Gao L, Ma C and Liang
X: Serum soluble death receptor 5 concentration in patients with
chronic hepatitis B is associated with liver damage and viral
antigen level. Clin Biochem. 45:845–847. 2012.
|
|
16
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, et al:
Thorax. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition. Springer; New
York, NY: pp. 299–323. 2010
|
|
17
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, et al:
The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision
of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of
the TNM classification of malignant tumors. J Thorac Oncol.
2:706–714. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, et
al: New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid
tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer,
National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer
Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:205–216. 2000.
|
|
19
|
Takeda K, Hayakawa Y, Smyth MJ, et al:
Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand in surveillance of tumor metastasis by liver natural killer
cells. Nat Med. 7:94–100. 2001.
|
|
20
|
Kelley RF, Totpal K, Lindstrom SH, et al:
Receptor-selective mutants of apoptosis-inducing ligand 2/tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand reveal a greater
contribution of death receptor (DR) 5 than DR4 to apoptosis
signaling. J Biol Chem. 280:2205–2212. 2005.
|
|
21
|
Du J, Liang X, Liu Y, et al: Hepatitis B
virus core protein inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis of hepatocytes
by blocking DR5 expression. Cell Death Differ. 16:219–229.
2009.
|
|
22
|
Ganten TM, Sykora J, Koschny R, et al:
Prognostic significance of tumour necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand(TRAIL) receptor expression in patients
with breast cancer. J Mol Med (Berl). 87:995–1007. 2009.
|
|
23
|
Leithner K, Stacher E, Wurm R, et al:
Nuclear and cytoplasmic death receptor 5 as prognostic factors in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy.
Lung Cancer. 65:98–104. 2009.
|
|
24
|
Zhuang L, Lee CS, Scolyer RA, et al:
Progression in melanoma is associated with decreased expression of
death receptors for tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand. Hum Pathol. 37:1286–1294. 2006.
|
|
25
|
Ugurel S, Rappl G, Tilgen W and Reinhold
U: Increased soluble CD95 (sFas/CD95) serum level correlates with
poor prognosis in melanoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1282–1286.
2001.
|