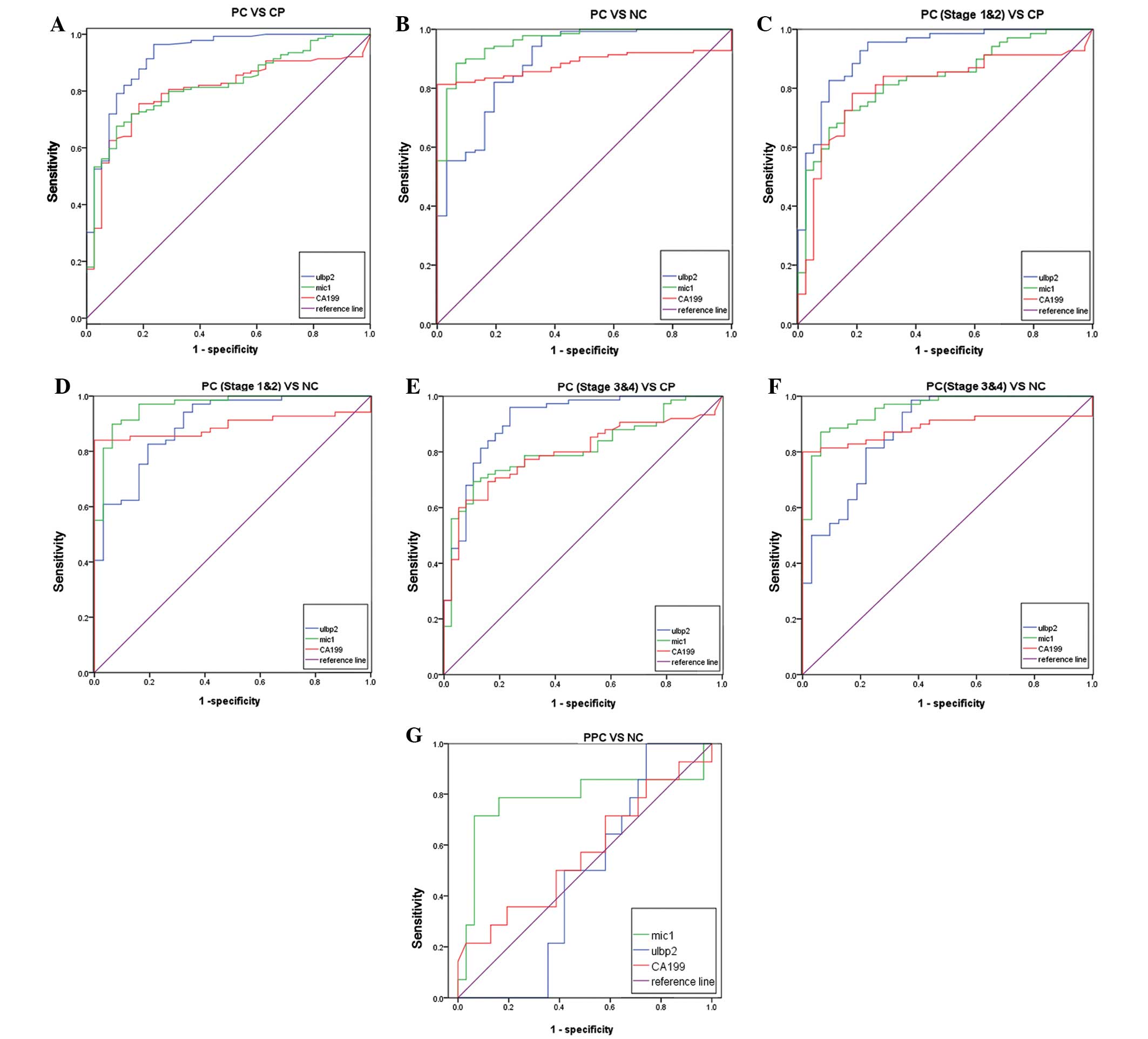
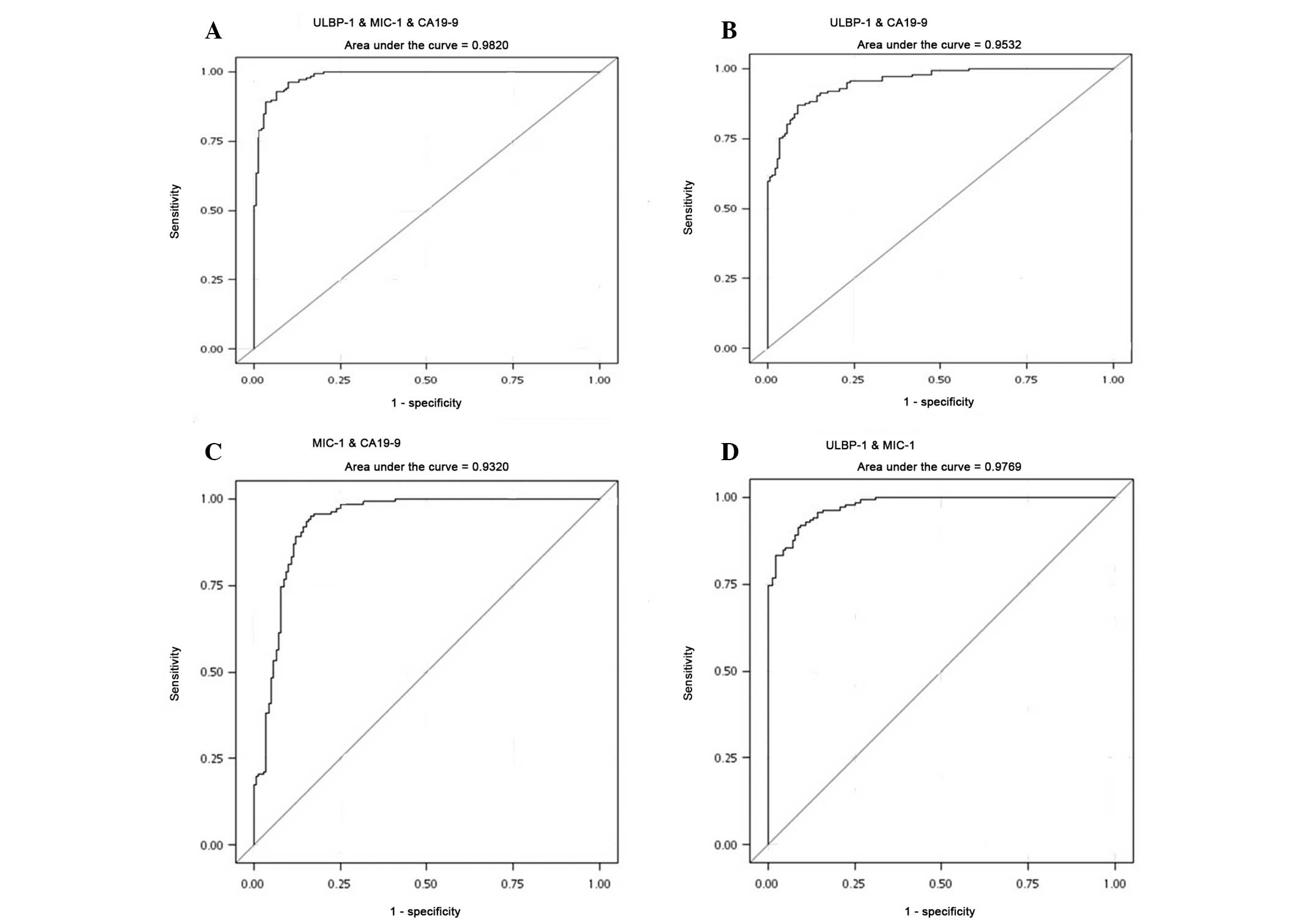
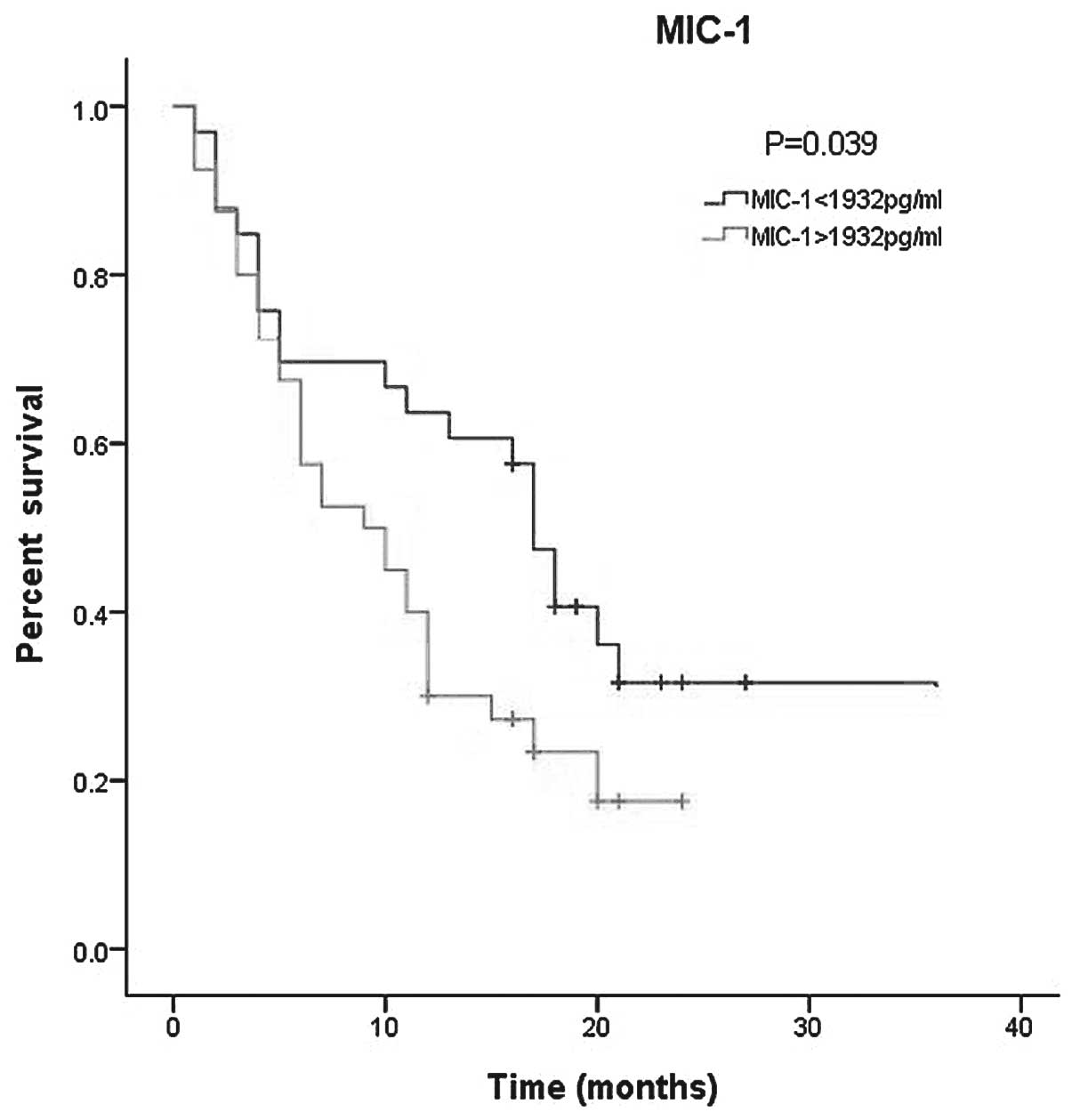
|
1
|
Berrino F, De Angelis R, Sant M, et al;
EUROCARE Working Group. Survival for eight major cancers and all
cancers combined for European adults diagnosed in 1995–99: results
of the EUROCARE-4 study. Lancet Oncol. 8:773–783. 2007.
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Ishikawa O, Ohigashi H, Imaoka S, et al:
Minute carcinoma of the pancreas measuring 1 cm or less in diameter
- collective review of Japanese case reports.
Hepatogastroenterology. 46:8–15. 1999.
|
|
4
|
Yachida S, Jones S, Bozic I, et al:
Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of
pancreatic cancer. Nature. 467:1114–1117. 2010.
|
|
5
|
Pannala R, Basu A, Petersen GM and Chari
ST: New-onset diabetes: a potential clue to the early diagnosis of
pancreatic cancer. Lancet Oncol. 10:88–95. 2009.
|
|
6
|
Cosman D, Müllberg J, Sutherland CL, et
al: ULBPs, novel MHC class I-related molecules, bind to CMV
glycoprotein UL16 and stimulate NK cytotoxicity through the NKG2D
receptor. Immunity. 14:123–133. 2001.
|
|
7
|
Bootcov MR, Bauskin AR, Valenzuela SM, et
al: MIC-1, a novel macrophage inhibitory cytokine, is a divergent
member of the TGF-beta superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:11514–11519. 1997.
|
|
8
|
Hruban RH, Maitra A, Kern SE and Goggins
M: Precursors to pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
36:831–849. 2007.
|
|
9
|
AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 6th edition.
Springer-Verlag; New York, NY: 2002
|
|
10
|
Gui JC, Yan WL and Liu XD: CA19-9 and
CA242 as tumor markers for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: a
meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med. 14:225–233. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Wu E, Zhou S, Bhat K and Ma Q: CA 19-9 and
pancreatic cancer. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 11:53–55. 2013.
|
|
12
|
Hartwig W, Strobel O, Hinz U, et al:
CA19-9 in potentially resectable pancreatic cancer: perspective to
adjust surgical and perioperative therapy. Ann Surg Oncol.
20:2188–2196. 2013.
|
|
13
|
Singh S, Tang SJ, Sreenarasimhaiah J, et
al: The clinical utility and limitations of serum carbohydrate
antigen (CA19-9) as a diagnostic tool for pancreatic cancer and
cholangiocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 56:2491–2496. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Chang YT, Wu CC, Shyr YM, et al:
Secretome-based identification of ULBP2 as a novel serum marker for
pancreatic cancer detection. PLoS One. 6:e200292011.
|
|
15
|
Koopmann J, Buckhaults P, Brown DA, et al:
Serum macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1 as a marker of pancreatic
and other periampullary cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2386–2392.
2004.
|
|
16
|
Koopmann J, Rosenzweig CN, Zhang Z, et al:
Serum markers in patients with resectable pancreatic
adenocarcinoma: macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1 versus CA19-9.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:442–446. 2006.
|
|
17
|
Yamaguchi K, Chikumi H, Shimizu A, et al:
Diagnostic and prognostic impact of serum-soluble UL16-binding
protein 2 in lung cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 103:1405–1413.
2012.
|
|
18
|
Bünger S, Laubert T, Roblick UJ and
Habermann JK: Serum biomarkers for improved diagnostic of
pancreatic cancer: a current overview. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
137:375–389. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Cerwenka A and Lanier LL: Natural killer
cells, viruses and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:41–49. 2001.
|
|
20
|
Champsaur M and Lanier LL: Effect of NKG2D
ligand expression on host immune responses. Immunol Rev.
235:267–285. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Li H, Lakshmikanth T, Garofalo C, et al:
Pharmacological activation of p53 triggers anticancer innate immune
response through induction of ULBP2. Cell Cycle. 10:3346–3358.
2011.
|
|
22
|
Brown DA, Hance KW, Rogers CJ, et al:
Serum macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1/GDF15): a potential
screening tool for the prevention of colon cancer? Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 21:337–346. 2012.
|
|
23
|
Senapati S, Rachagani S, Chaudhary K, et
al: Overexpression of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 induces
metastasis of human prostate cancer cells through the FAK-RhoA
signaling pathway. Oncogene. 29:1293–1302. 2010.
|
|
24
|
Chen SJ, Karan D, Johansson SL, et al:
Prostate-derived factor as a paracrine and autocrine factor for the
proliferation of androgen receptor-positive human prostate cancer
cells. Prostate. 67:557–571. 2007.
|
|
25
|
Proutski I, Stevenson L, Allen WL, et al:
Prostate-derived factor - a novel inhibitor of drug-induced cell
death in colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:2566–2574.
2009.
|
|
26
|
Tan M, Wang Y, Guan K and Sun Y:
PTGF-beta, a type beta transforming growth factor (TGF-beta)
superfamily member, is a p53 target gene that inhibits tumor cell
growth via TGF-beta signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:109–114. 2000.
|
|
27
|
Li PX, Wong J, Ayed A, et al: Placental
transforming growth factor-beta is a downstream mediator of the
growth arrest and apoptotic response of tumor cells to DNA damage
and p53 overexpression. J Biol Chem. 275:20127–20135. 2000.
|
|
28
|
Johnen H, Lin S, Kuffner T, et al:
Tumor-induced anorexia and weight loss are mediated by the TGF-beta
superfamily cytokine MIC-1. Nat Med. 13:1333–1340. 2007.
|