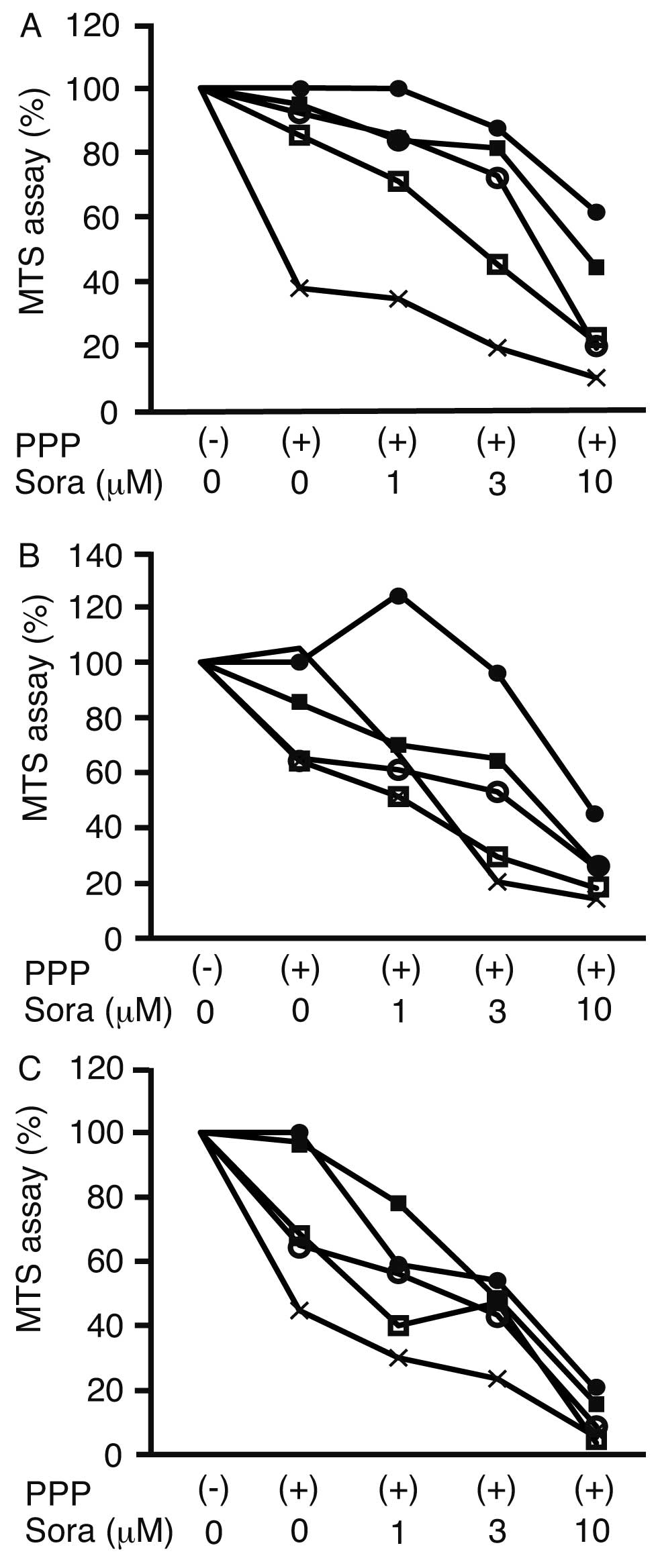
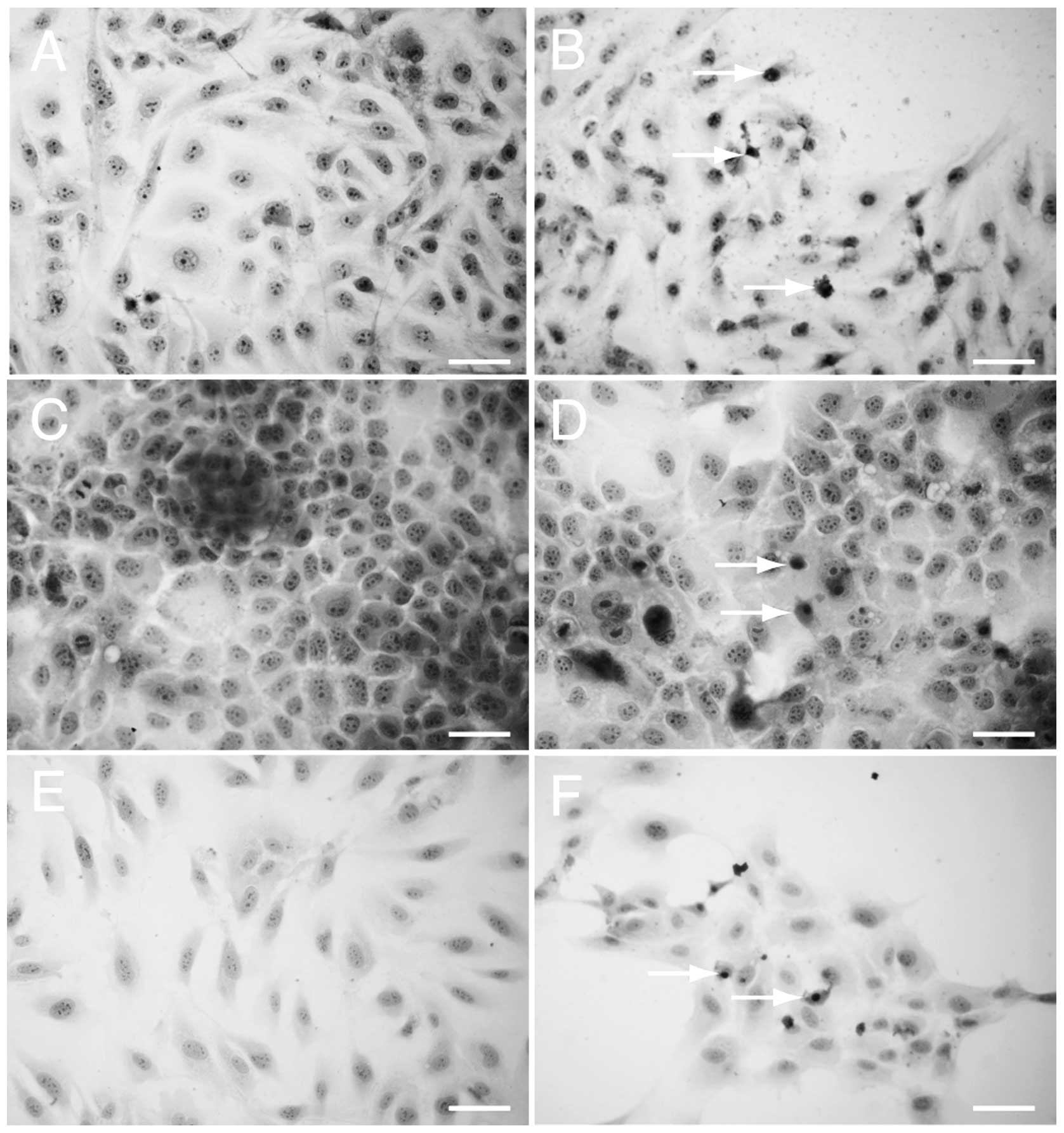
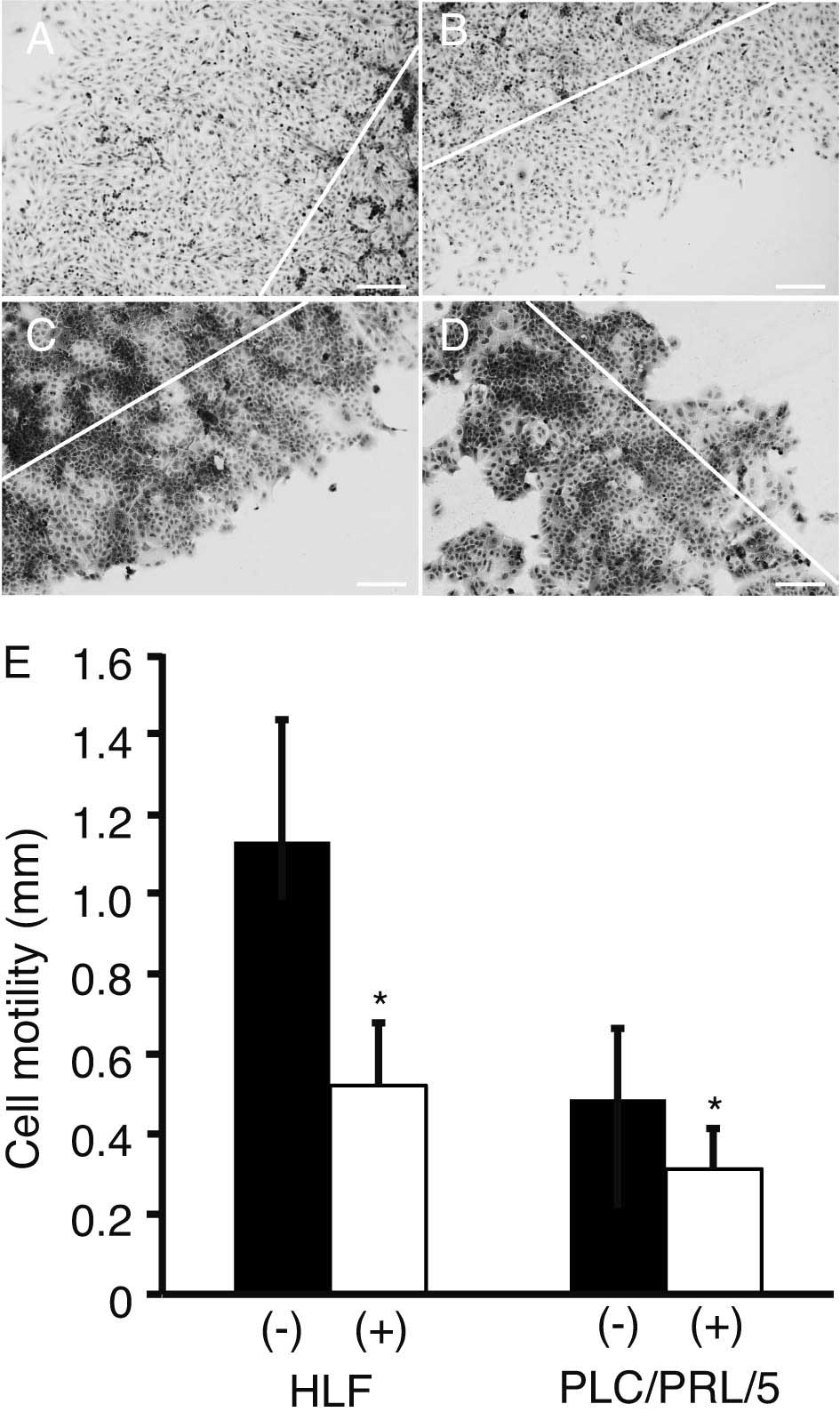
|
1
|
El-Assal ON, Yamanoi A, Soda Y, et al:
Clinical significance of microvessel density and vascular
endothelial growth factor expression in hepatocellular carcinoma
and surrounding liver: possible involvement of vascular endothelial
growth factor in the angiogenesis of cirrhotic liver. Hepatology.
27:1554–1562. 1998.
|
|
2
|
Chao Y, Li CP, Chau GY, et al: Prognostic
significance of vascular endothelial growth factor, basic
fibroblast growth factor, and angiogenin in patients with
resectable hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery. Ann Surg Oncol.
10:355–362. 2003.
|
|
3
|
Shin JW and Chung YH: Molecular targeted
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current and future. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:6144–6155. 2013.
|
|
4
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al:
SHARP Investigators Study Group: Sorafenib in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 359:378–390. 2008.
|
|
5
|
Villanueva A and Llovet JM: Targeted
therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
140:1410–1426. 2011.
|
|
6
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, et al: Sorafenib
blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and
induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model
PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006.
|
|
7
|
Zhai B and Sun XY: Mechanisms of
resistance to sorafenib and the corresponding strategies in
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 5:345–352. 2013.
|
|
8
|
Zhang X, Yang XR, Huang XW, et al:
Sorafenib in treatment of patients with advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma: a systematic review. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
11:458–466. 2012.
|
|
9
|
Bai S, Nasser MW, Wang B, et al:
MicroRNA-122 inhibits tumorigenic properties of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells and sensitizes these cells to sorafenib. J Biol
Chem. 284:32015–32027. 2009.
|
|
10
|
Brown AL, Graham DE, Nissley SP, et al:
Developmental regulation of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA in
different rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 261:13144–13150. 1986.
|
|
11
|
Girnita A, Girnita L, del Prete F, et al:
Cyclolignans as inhibitors of the insulin-like growth factor-1
receptor and malignant cell growth. Cancer Res. 64:236–242.
2004.
|
|
12
|
Tomizawa M, Shinozaki F, Sugiyama T, et
al: Insulin-like growth factor I receptor involvement in
proliferation of NOR-P1 cells in serum-free media. J Cell Biochem.
113:2714–2720. 2012.
|
|
13
|
Tomizawa M and Saisho H: Signaling pathway
of insulin-like growth factor-II as a target of molecular therapy
for hepatoblastoma. World J Gastroenterol. 12:6531–6535. 2006.
|
|
14
|
Tomizawa M and Yokosuka O:
Picropodophyllin suppresses the proliferation and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma under serum starvation. Mol Med Rep.
1:685–688. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Pennisi PA, Barr V, Nunez NP, Stannard B
and Le Roith D: Reduced expression of insulin-like growth factor I
receptors in MCF-7 breast cancer cells leads to a more metastatic
phenotype. Cancer Res. 62:6529–6537. 2002.
|
|
16
|
Ou DL, Lee BS, Chang YC, et al:
Potentiating the efficacy of molecular targeted therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the insulin-like growth
factor pathway. PLoS One. 8:e665892013.
|
|
17
|
Huynh H, Ngo VC, Koong HN, et al: AZD6244
enhances the anti-tumor activity of sorafenib in ectopic and
orthotopic models of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J
Hepatol. 52:79–87. 2010.
|
|
18
|
Gedaly R, Angulo P, Hundley J, et al:
PKI-587 and sorafenib targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MAPK
pathways synergistically inhibit HCC cell proliferation. J Surg
Res. 176:542–548. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Tomizawa M, Kondo F and Kondo Y: Growth
patterns and interstitial invasion of small hepatocellular
carcinoma. Pathol Int. 45:352–358. 1995.
|
|
20
|
Tomizawa M, Shinozaki F, Sugiyama T, et
al: Sorafenib suppresses the cell cycle and induces the apoptosis
of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines in serum-free media. Exp
Ther Med. 1:863–866. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Xiong YQ, Sun HC, Zhang W, et al: Human
hepatocellular carcinoma tumor-derived endothelial cells manifest
increased angiogenesis capability and drug resistance compared with
normal endothelial cells. Clin Cancer Res. 15:4838–4846. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Bid HK, London CA, Gao J, et al: Dual
targeting of the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor and its
ligands as an effective antiangiogenic strategy. Clin Cancer Res.
19:2984–2994. 2013.
|