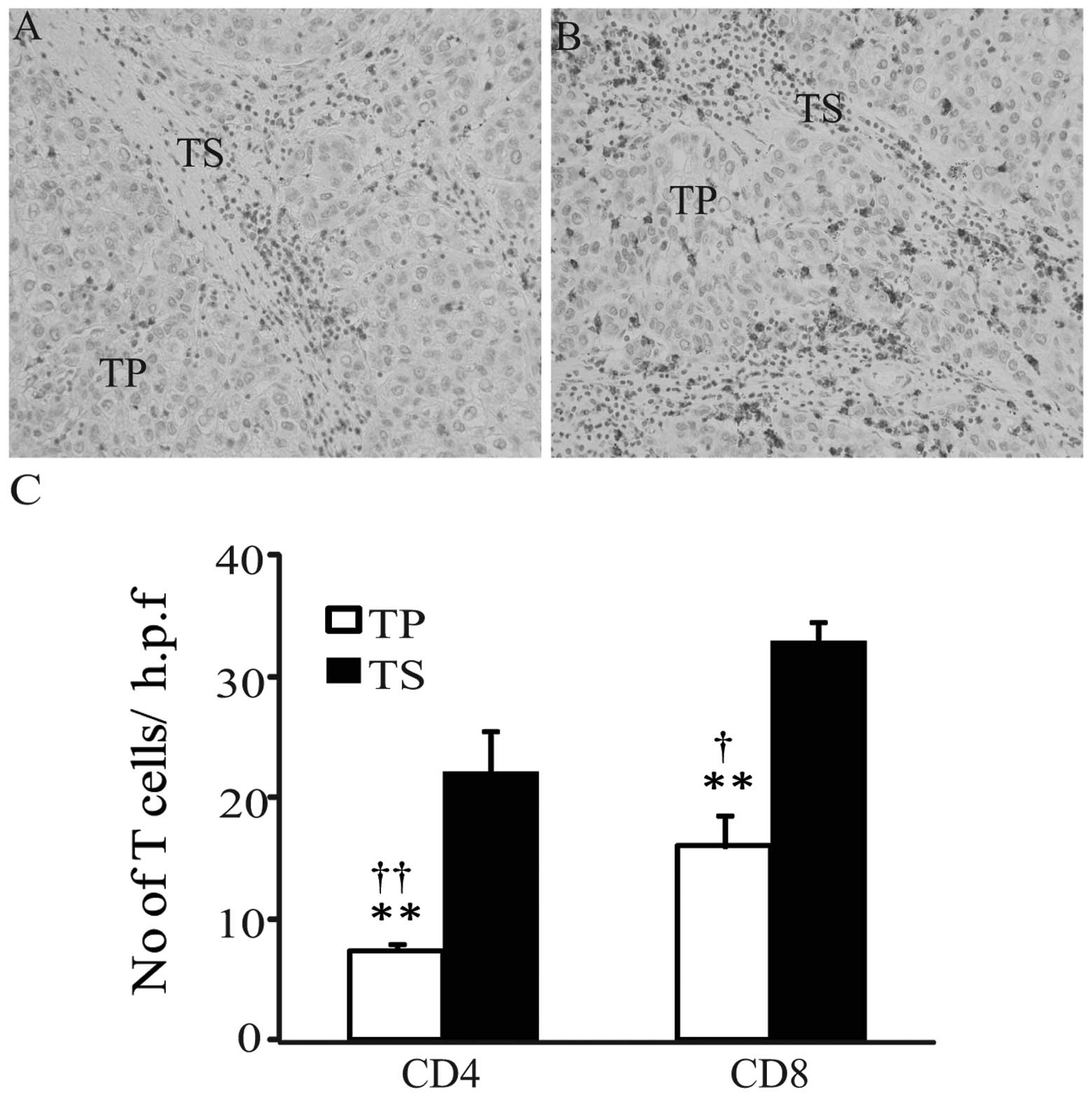
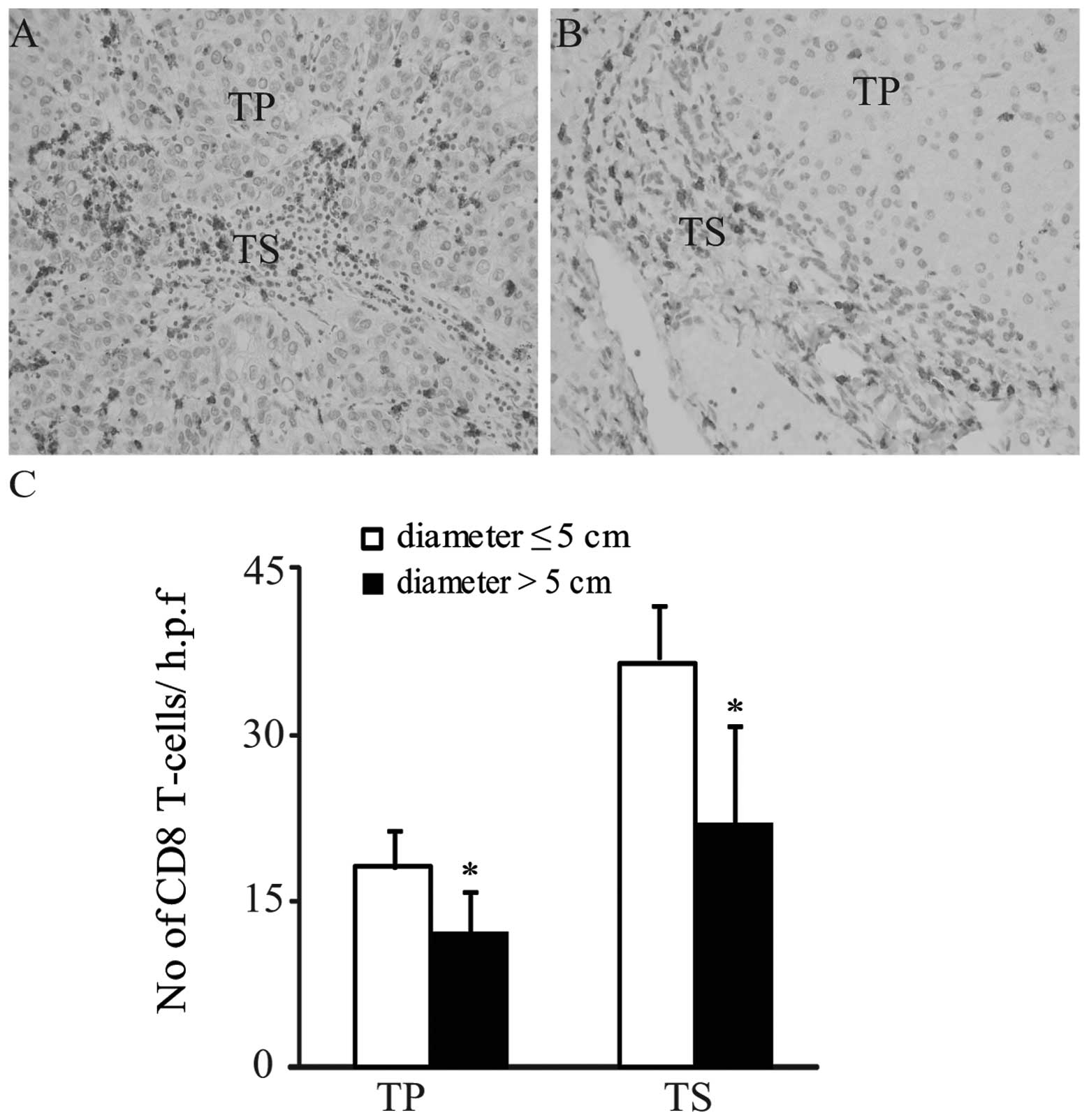
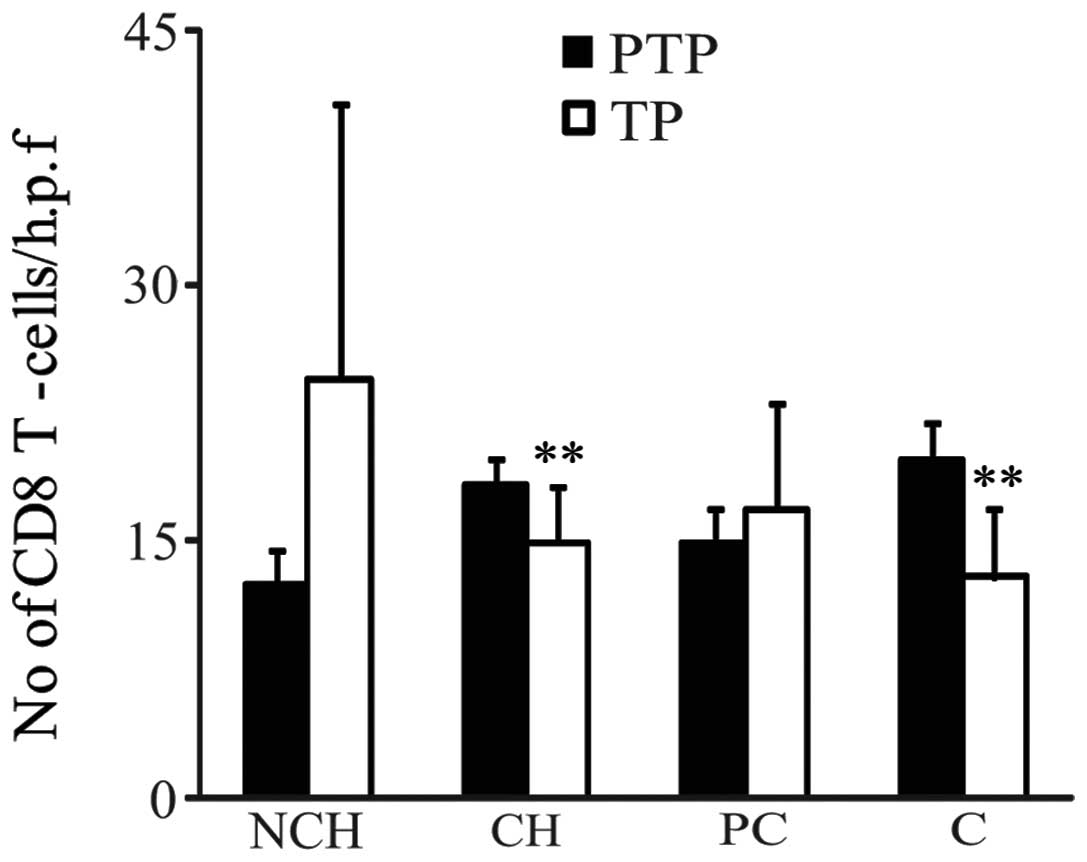
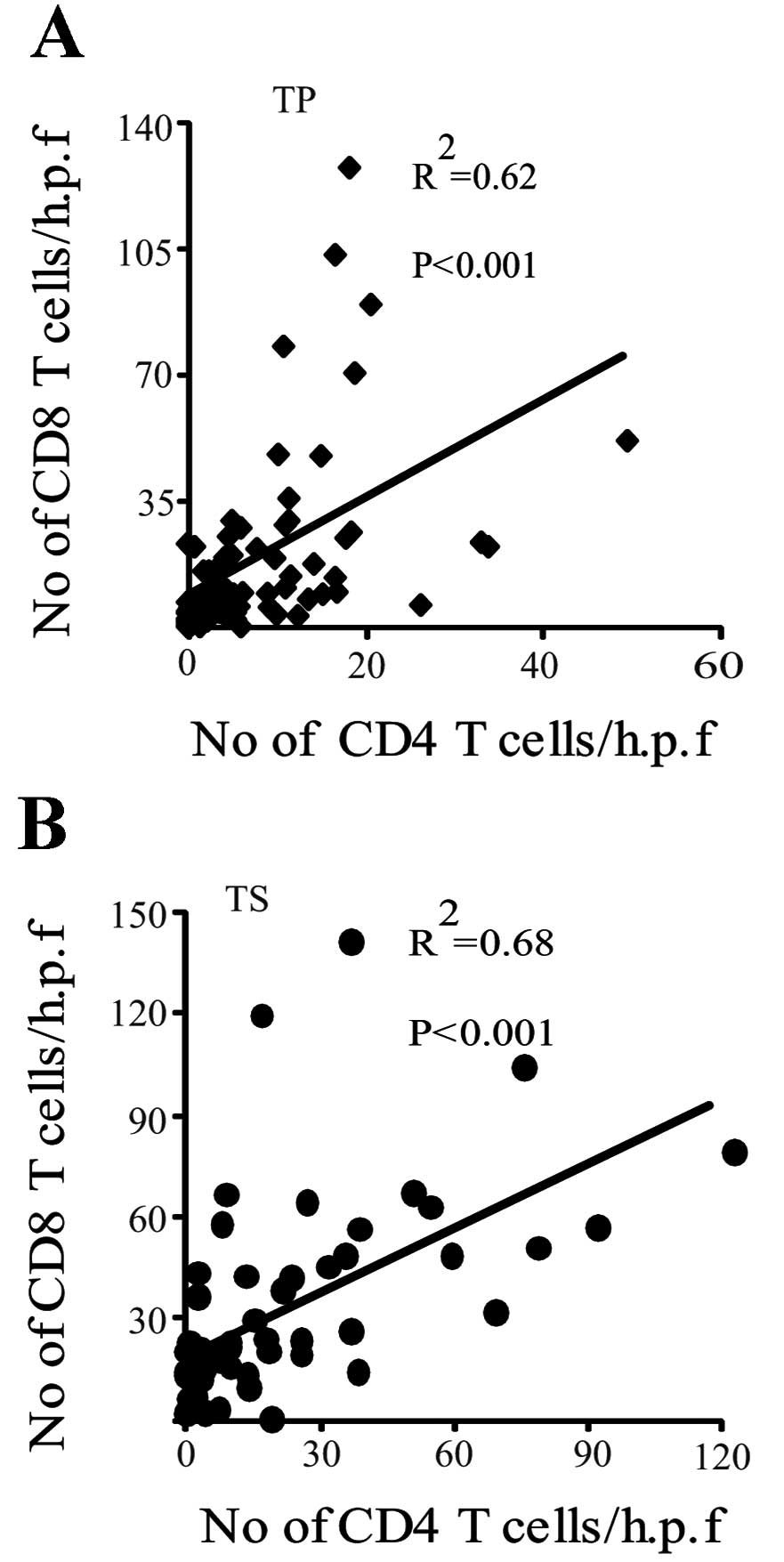
|
1
|
Schütte K, Bornschein J and Malfertheiner
P: Hepatocellular carcinoma - epidemiological trends and risk
factors. Dig Dis. 27:80–92. 2009.
|
|
2
|
Kremsdorf D, Soussan P, Paterlini-Brechot
P and Brechot C: Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
carcinoma: paradigms for viral-related human carcinogenesis.
Oncogene. 25:3823–3833. 2006.
|
|
3
|
Nakamoto Y, Guidotti LG, Kuhlen CV, Fowler
P and Chisari FV: Immune pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
J Exp Med. 188:341–350. 1998.
|
|
4
|
Fattovich G and Llovet JM: Risk factors
for hepatocellular carcinoma in HCV-cirrhosis: what we know and
what is missing. J Hepatol. 44:1013–1016. 2006.
|
|
5
|
Naugler WE, Sakurai T, Kim S, et al:
Gender disparity in liver cancer due to sex differences in
MyD88-dependent IL-6 production. Science. 317:121–124. 2007.
|
|
6
|
Parmiani G and Anichini A: T cell
infiltration and prognosis in HCC patients. J Hepatol. 45:178–181.
2006.
|
|
7
|
Tobe T, Uchino J, Endo Y, Oto M, Okamoto
E, Kojiro M, et al: Predictive factors for long term prognosis
after partial hepatectomy for patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma in Japan. The Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. Cancer.
74:2772–2780. 1994.
|
|
8
|
Levy I and Sherman M: Liver Cancer Study
Group of the University of Toronto: Staging of hepatocellular
carcinoma: assessment of the CLIP, Okuda, and Child-Pugh staging
systems in a cohort of 257 patients in Toronto. Gut. 50:881–885.
2002.
|
|
9
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001.
|
|
10
|
de Visser KE, Eichten A and Coussens LM:
Paradoxical roles of the immune system during cancer development.
Nat Rev Cancer. 6:24–37. 2006.
|
|
11
|
Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, et al:
Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal
tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. 313:1960–1964. 2006.
|
|
12
|
Dieu-Nosjean MC, Antoine M, Danel C, et
al: Long-term survival for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer
with intratumoral lymphoid structures. J Clin Oncol. 26:4410–4417.
2008.
|
|
13
|
Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, et al: Stromal
gene expression predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nat
Med. 14:518–527. 2008.
|
|
14
|
Chew V, Tow C, Teo M, et al: Inflammatory
tumour microenvironment is associated with superior survival in
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J Hepatol. 52:370–379. 2010.
|
|
15
|
Wada Y, Nakashima O, Kutami R, Yamamoto O
and Kojiro M: Clinicopathological study on hepatocellular carcinoma
with lymphocytic infiltration. Hepatology. 27:407–414. 1998.
|
|
16
|
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, et al: Intratumoral
balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin
Oncol. 25:2586–2593. 2007.
|
|
17
|
Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, et
al: Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial
ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 348:203–213. 2003.
|
|
18
|
Kashef E and Roberts JP: Transplantation
for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 28:497–502. 2001.
|
|
19
|
Lu XY, Xi T, Lau WY, et al:
Pathobiological features of small hepatocellular carcinoma:
correlation between tumor size and biological behavior. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 137:567–575. 2011.
|
|
20
|
Zhang B, Zhang Y, Bowerman NA, et al:
Equilibrium between host and cancer caused by effector T cells
killing tumor stroma. Cancer Res. 68:1563–1571. 2008.
|
|
21
|
The general rules for the clinical and
pathological study of primary liver cancer. Liver Cancer Study
Group of Japan. Jpn J Surg. 19:98–129. 1989.
|
|
22
|
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, et al:
Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol.
22:696–699. 1995.
|
|
23
|
Edmondson HA and Steiner PE: Primary
carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900
necropsies. Cancer. 7:462–503. 1954.
|
|
24
|
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, et
al: Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of
tumor specimens. Nat Med. 4:844–847. 1998.
|
|
25
|
Hatta H, Tsuneyama K, Kumada T, et al:
Freshly prepared immune complexes with intermittent microwave
irradiation result in rapid and high-quality immunostaining. Pathol
Res Pract. 202:439–445. 2006.
|
|
26
|
Kumada T, Tsuneyama K, Hatta H, Ishizawa S
and Takano Y: Improved 1-h rapid immunostaining method using
intermittent microwave irradiation: practicability based on 5 years
application in Toyama Medical and Pharmaceutical University
Hospital. Mod Pathol. 17:1141–1149. 2004.
|
|
27
|
Sato E, Olson SH, Ahn J, et al:
Intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high
CD8+/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable
prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:18538–18543. 2005.
|
|
28
|
Liotta LA and Kohn EC: The
microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature. 411:375–379.
2001.
|
|
29
|
Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ, Wang HH, Dvorak
AM and Dvorak HF: Principles of cancer pathology. Holland-Frei
Cancer Medicine. Bast RC Jr, Kufe DW, Pollock RE, Weichselbaum RR,
Holland JF and Frei E III: BC Decker, Inc.; Hamiton, ON, Canada:
pp. 384–399. 2000
|
|
30
|
Zerbini A, Pilli M, Soliani P, et al: Ex
vivo characterization of tumor-derived melanoma antigen encoding
gene-specific CD8+cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
J Hepatol. 40:102–109. 2004.
|
|
31
|
Spiotto MT and Schreiber H: Rapid
destruction of the tumor microenvironment by CTLs recognizing
cancer-specific antigens cross-presented by stromal cells. Cancer
Immun. 5:82005.
|
|
32
|
Singh S, Ross SR, Acena M, Rowley DA and
Schreiber H: Stroma is critical for preventing or permitting
immunological destruction of antigenic cancer cells. J Exp Med.
175:139–146. 1992.
|
|
33
|
Blankenstein T: The role of tumor stroma
in the interaction between tumor and immune system. Curr Opin
Immunol. 17:180–186. 2005.
|
|
34
|
Kobayashi N, Hiraoka N, Yamagami W, et al:
FOXP3+ regulatory T cells affect the development and progression of
hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 13:902–911. 2007.
|