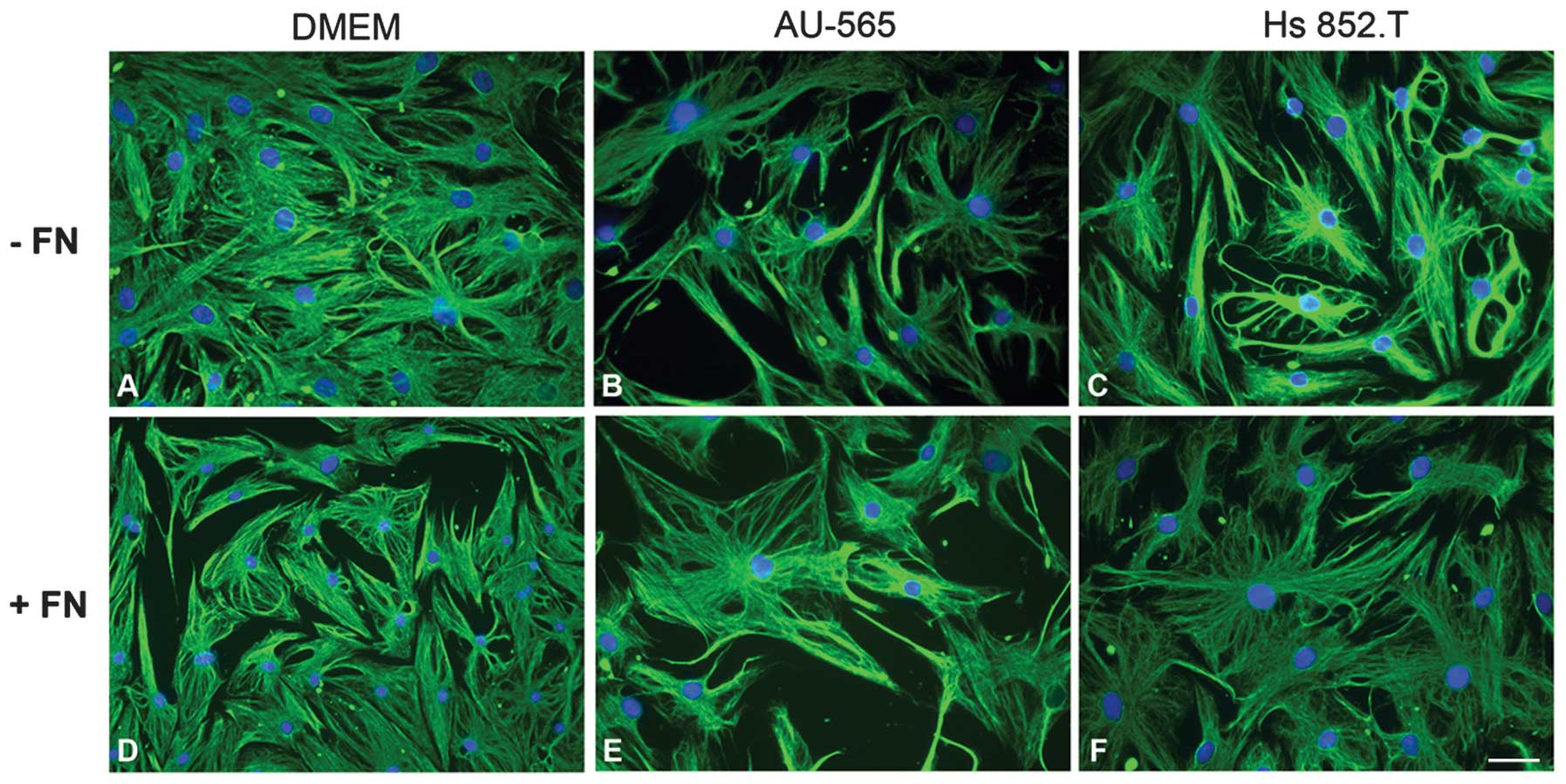
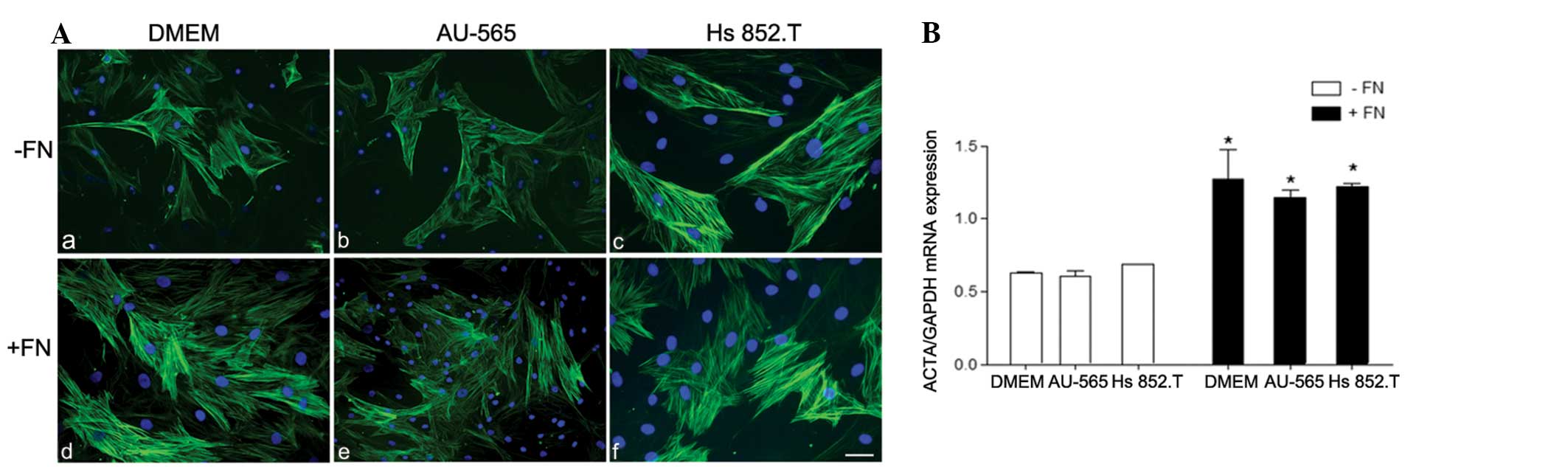
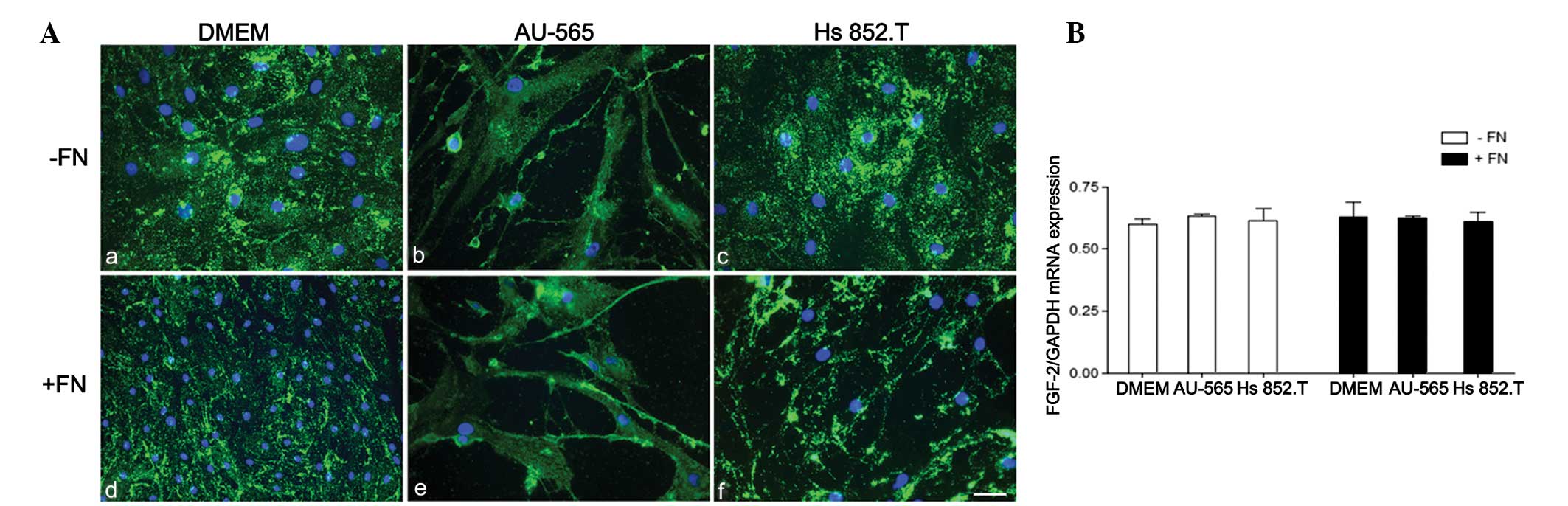
|
1
|
Barsky SH and Karlin NJ: Mechanisms of
disease: breast tumor pathogenesis and the role of the
myoepithelial cell. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 3:138–151. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nguyen M, Lee MC, Wang JL, Tomlinson JS,
Shao ZM, Alpaugh ML and Barsky SH: The human myoepithelial cell
displays a multifaceted anti-angiogenic phenotype. Oncogene.
19:3449–3459. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Deugnier MA, Teulière J, Faraldo MM,
Thiery JP and Glukhova MA: The importance of being a myoepithelial
cell. Breast Cancer Res. 4:224–230. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Polyak K and Hu M: Do myoepithelial cells
hold the key for breast tumor progression? J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 10:231–247. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
da Silva A, Silva CA, Montalli VA,
Martinez EF, de Araújo VC and Furuse C: In vitro evaluation of the
suppressor potential of conditioned medium from benign
myoepithelial cells from pleomorphic adenoma in malignant cell
invasion. J Oral Pathol Med. 41:610–614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bissell MJ, Kenny PA and Radisky DC:
Microenvironmental regulators of tissue structure and function also
regulate tumor induction and progression: the role of extracellular
matrix and its degrading enzymes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol.
70:343–356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
de Araújo VC, Altemani A, Furuse C,
Martins MT and de Araújo NS: Immunoprofile of reatctive salivary
myoepithelial cells in intraductal areas of carcinoma
ex-pleomorphic adenoma. Oral Oncol. 42:1011–1016. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Martinez EF, Demasi AP, Miguita L,
Altemani A, de Araújo NS and de Araújo VC: FGF-2 is overexpressed
in myoepithelial cells of carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma in situ
structures. Oncol Rep. 24:155–160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Martinez EF, Demasi AP, Napimoga MH,
Arana-Chavez VE, Altemani A, de Araújo NS and de Araújo VC: In
vitro influence of the extracellular matrix in myoepithelial cells
stimulated by malignant conditioned medium. Oral Oncol. 48:102–109.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Martinez EF, Montaldi PT, de Araújo NS,
Altemani A and de Araújo VC: A proposal of an in vitro model which
mimics in situ areas of carcinoma. J Cell Comun Signal. 6:107–109.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Canel M, Serrels A, Frame MC and Brunton
VG: E-cadherin-integrin crosstalk in cancer invasion and
metastasis. J Cell Sci. 126:393–401. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Altemani A, Martins MT, Freitas L, Soares
F, Araújo NS and Araújo VC: Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
(CXPA): immunoprofile of the cells involved in carcinomatous
progression. Histophatol. 46:635–641. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pia-Foschini M, Reis-Filho JS, Eusebi V
and Lakhani SR: Salivary gland-like tumors of the breast: surgical
and molecular pathology. J Clin Pathol. 56:497–506. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gudjonsson T, Adriance MC, Sternlicht MD,
Petersen OW and Bissel MJ: Myoepithelial cells: their origin and
function in breast morphogenesis and neoplasia. J Mammary Gland
Biol Neoplasia. 10:261–272. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kang KH, Ling TY, Liou HH, Huang YK, Hour
MJ, Liou HC and Fu WM: Enhancement role of host 12/15-lipoxygenase
in melanoma progression. Eur J Cancer. 49:2747–2759. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Araújo VC, Furuse C, Cury PR, Altemani A,
Alves VA and de Araújo NS: Tenascin and fibronectin expression in
carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol.
16:48–53. 2008.
|
|
17
|
Araújo VC, Demasi AP, Furuse C, Altemani
A, Alves VA, Freitas LL and Araújo NS: Collagen type I may
influence the expression of E-cadherin and beta-catenin in
carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol.
17:312–318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park J and Schwarzbauer JE: Mammary
epithelial cell interactions with fibronectin stimulate
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 27:1649–1657. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gehler S, Ponik SM, Riching KM and Keely
PJ: Bi-directional signaling: extracellular matrix and integrin
regulation of breast tumor progression. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene
Expr. 23:139–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Whiteside TL: The role of death receptor
ligands in shaping tumor microenvironment. Immunol Invest.
36:25–46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bianchi G, Borgonovo G, Pistoia V and
Raffaghello L: Immunosuppressive cells and tumour microenvironment:
focus on mesenchymal stem cells and myeloid derived suppressor
cells. Histol Histopathol. 26:941–951. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Martinez EF, Napimoga MH, Montalli VA, de
Araújo NS and de Araújo VC: In vitro cytokine expression in in
situ-like areas of malignant neoplasia. Arch Oral Biol. 58:552–557.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sternlicht MD, Kedeshian P, Shao ZM,
Safarians S and Barsky SH: The human myoepithelial cell is a
natural tumor suppressor. Clin Cancer Res. 3:1949–1958. 1997.
|
|
24
|
Sternlicht MD and Barsky SH: The
myoepithelial defense: a host defense against cancer. Med
Hypotheses. 48:37–46. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Barsky SH and Alpaugh ML: Myoepithelium:
methods of culture and study. Culture of Human Tumor Cells.
Freshney RI: Wiley-Liss; New Jersey: pp. 221–261. 2004
|