Introduction
Clear cell carcinomas that occur in the lower
urinary tract are usually variants of more frequently diagnosed
cancers, including prostatic adenocarcinoma and transitional cell
carcinoma (1), however, they may also
be a less common type of carcinoma, such as clear cell carcinoma,
which is similar to Müllerian tumors and metastatic renal cell
carcinomas (RCCs) (2). RCC is the
most common subtype of clear cell carcinoma, which originates from
renal tubular epithelial cells and accounts for 85% of all renal
tumors (3). Patients with RCC are
usually asymptomatic in the early stages of the disease, however,
as the tumor size increases patients most commonly present with a
lump in the lower abdomen or back, lower back pain and hematuria
(4). The most common sites of RCC
metastases are the lungs, bone and liver (5,6). However,
metastases affecting the lower urinary tract, namely the prostate
and bladder, are extremely rare (7,8). In 2012,
the worldwide age-standardized mortality rate for RCC was 1.8
deaths per 100,000 individuals (9).
At present, treatment for RCC includes radical surgery,
immunotherapy and chemotherapy (10).
To the best of our knowledge, renal-type clear cell carcinoma
occurring as a primary tumor in an extra-renal location has only
been described in three other previous studies (11–13) which
revealed that RCC of the prostate is a novel pathological entity,
that exhibits histological and immunhistochemical features similar
to those of RCC.
Case report
A 64-year-old male with a two-year history of
urinary frequency, urgency and difficulty, that had undergone
treatment with a detaining urethral catheter for eight days, was
referred to the San Ai Tang Hospital (Lanzhou, China) due to lower
urinary tract obstructive symptoms on January 3, 2009. A rectal
examination revealed third-degree diffuse enlargement of the
prostate, nodosity and disappearance of the central sulcus, with
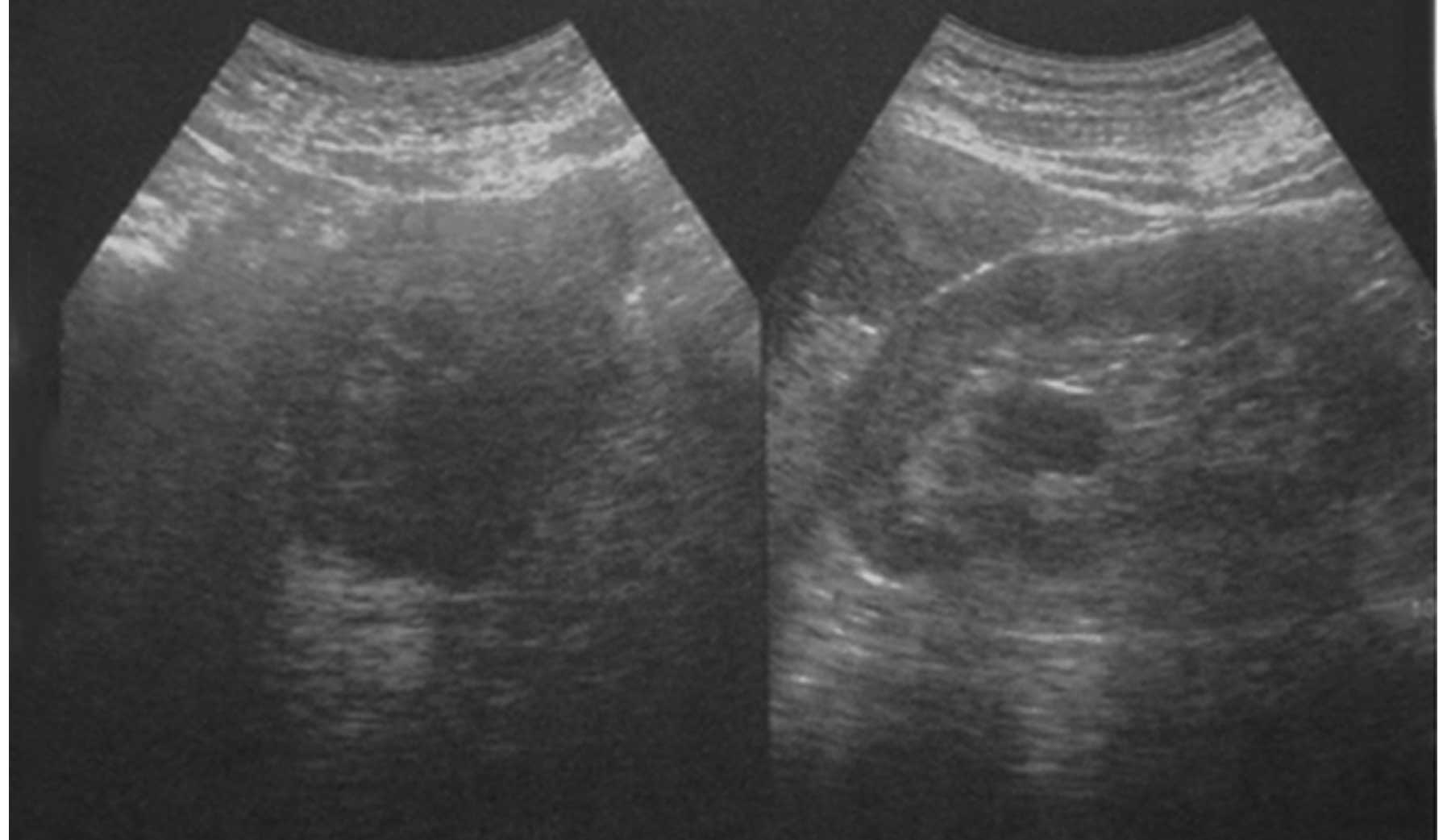
the absence of any tenderness. An ultrasound examination revealed
prostate hyperplasia (Fig. 1). The
serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) value was 10.2 ng/ml, which
was slightly higher than normal (normal range, <4 ng/ml). The
cystourethroscopy findings were unremarkable. A computed tomography
(CT) scan identified hyperplasia of the prostate. The suggested
diagnosis was that of clear cell carcinoma, which had most likely
originated from the kidneys. However, a review of the radiological
imaging studies revealed the absence of a renal tumor. Furthermore,
metastatic lesions were identified in the lungs, sternum and
clavicles. In addition, right pleural thickening and a small amount
of effusion in the pleural cavity were observed. The results of
samples retrieved from random cystoscopic biopsies of the bladder
and prostatic urethra, as well as bladder washings, were benign.
The urinary bladder demonstrated no evidence of dysplasia or
neoplasia. Subsequent to thorough counseling, the patient elected
to undergo transurethral resection of the prostate in order to
relieve the symptoms. In total, 12 g of tissue was resected. The
first 10 blocks of tissue submitted for microscopic analysis were
primarily malignant, and exhibited morphological and
immunohistochemical characteristics similar to those of clear cell
carcinomas of the kidney. Clear cell carcinoma was subsequently
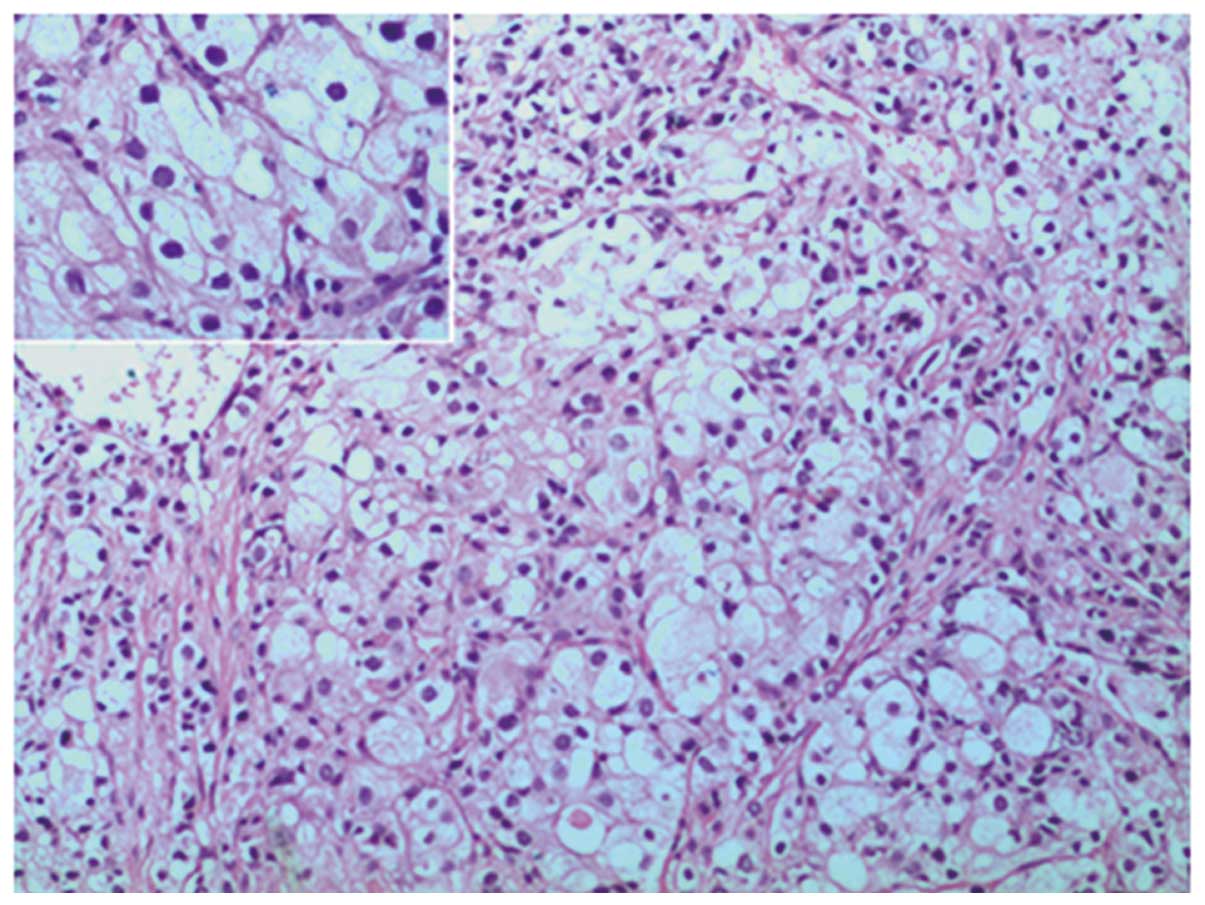
identified throughout, with surrounding regions of ordinary-type
prostatic adenocarcinoma [Gleason score (14), 4+4]. In addition, confluent nests
and/or tubules, composed of epithelium with uniformly clear
cytoplasm and atypical, enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli,
were observed (Fig. 2). An
interstitial lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate and an extensive,
thin-walled vascular network were associated with the tumor cells.
No evidence of significant mitotic activity was observed. The clear
cell lesion appeared to have originated from the prostate, but
exhibited no desmoplastic stromal response. Standard
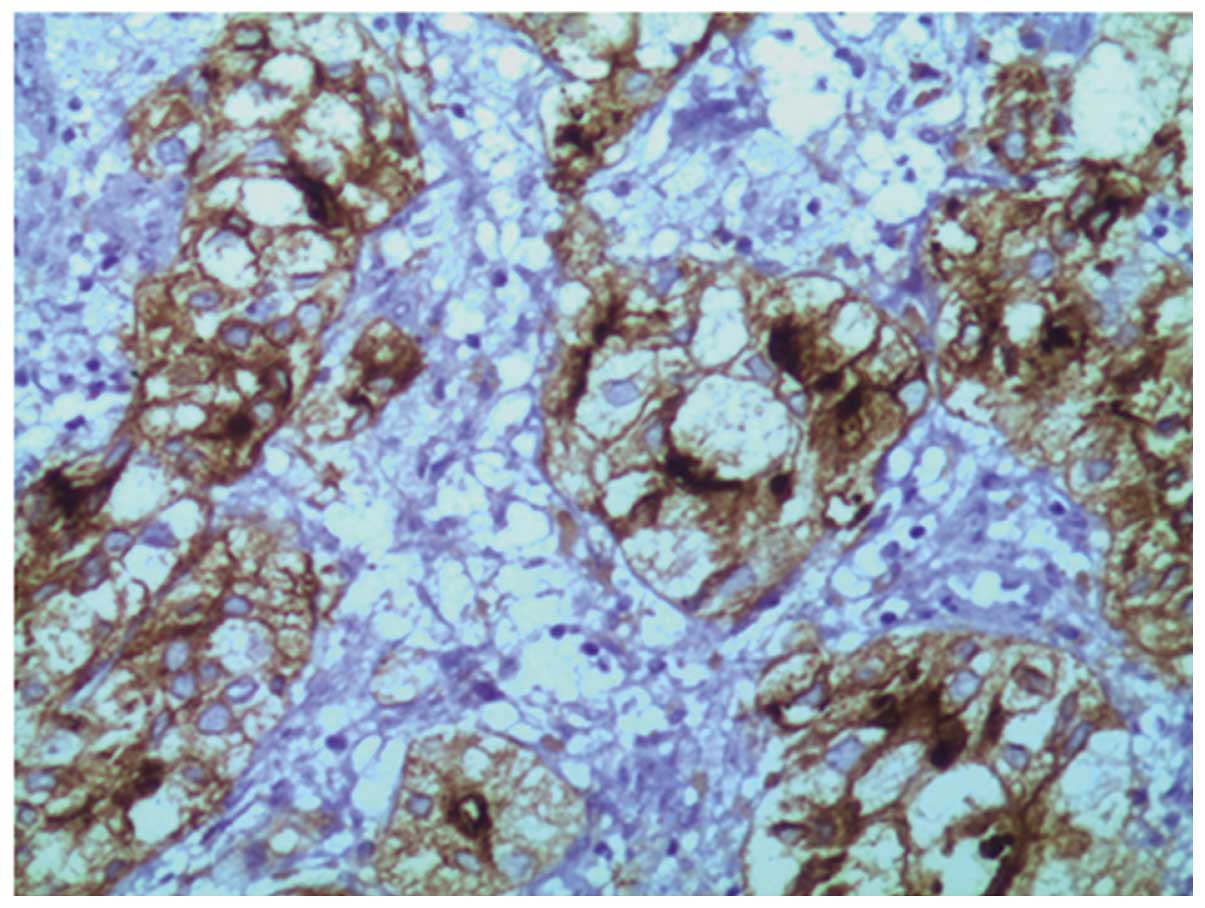
immunohistochemical procedures using paraffin sections revealed
that the lesion demonstrated positive immunoreactivity for vimentin
(VIM), epithelial membrane antigen, membrane metalloendopeptidase
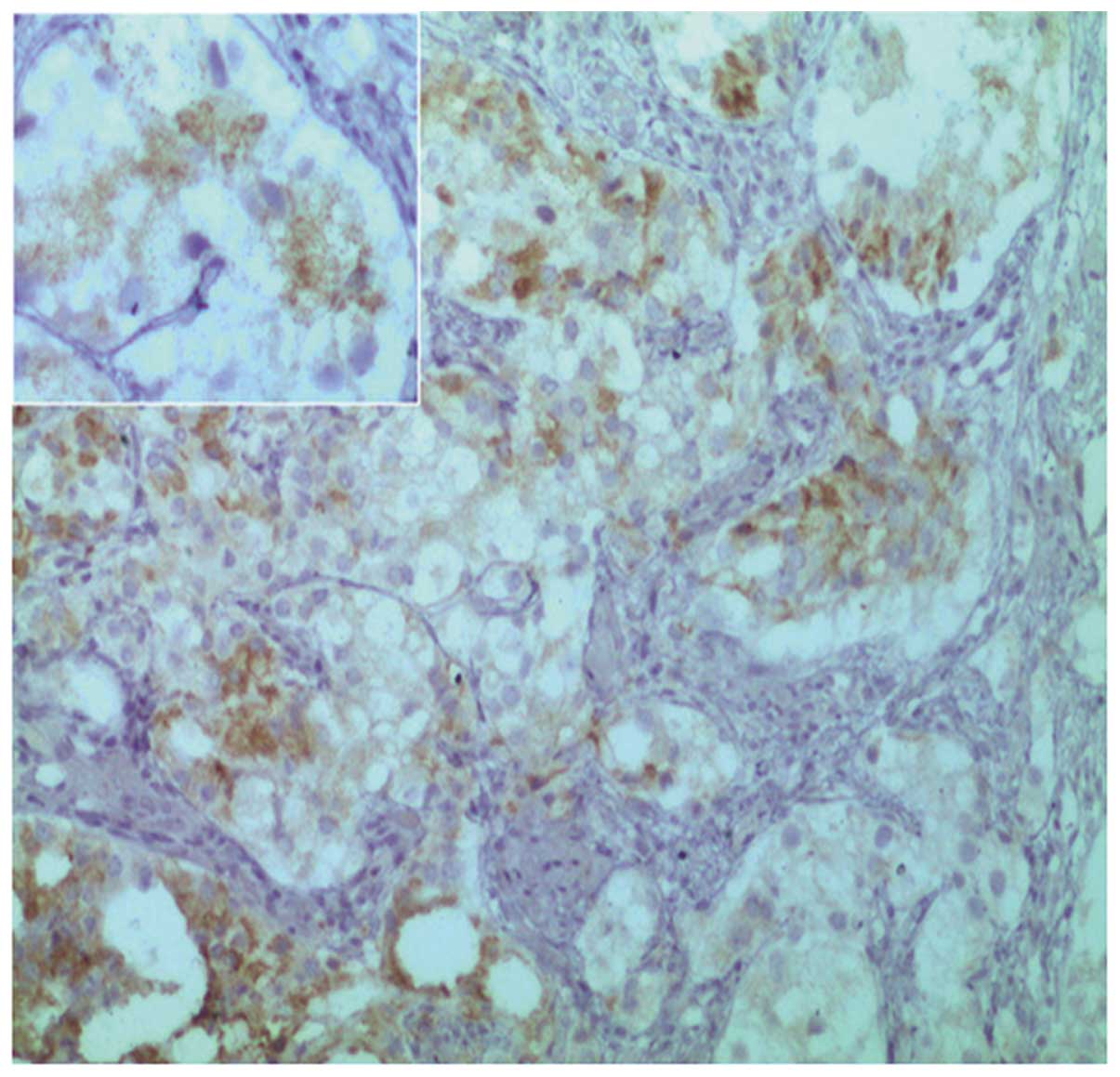
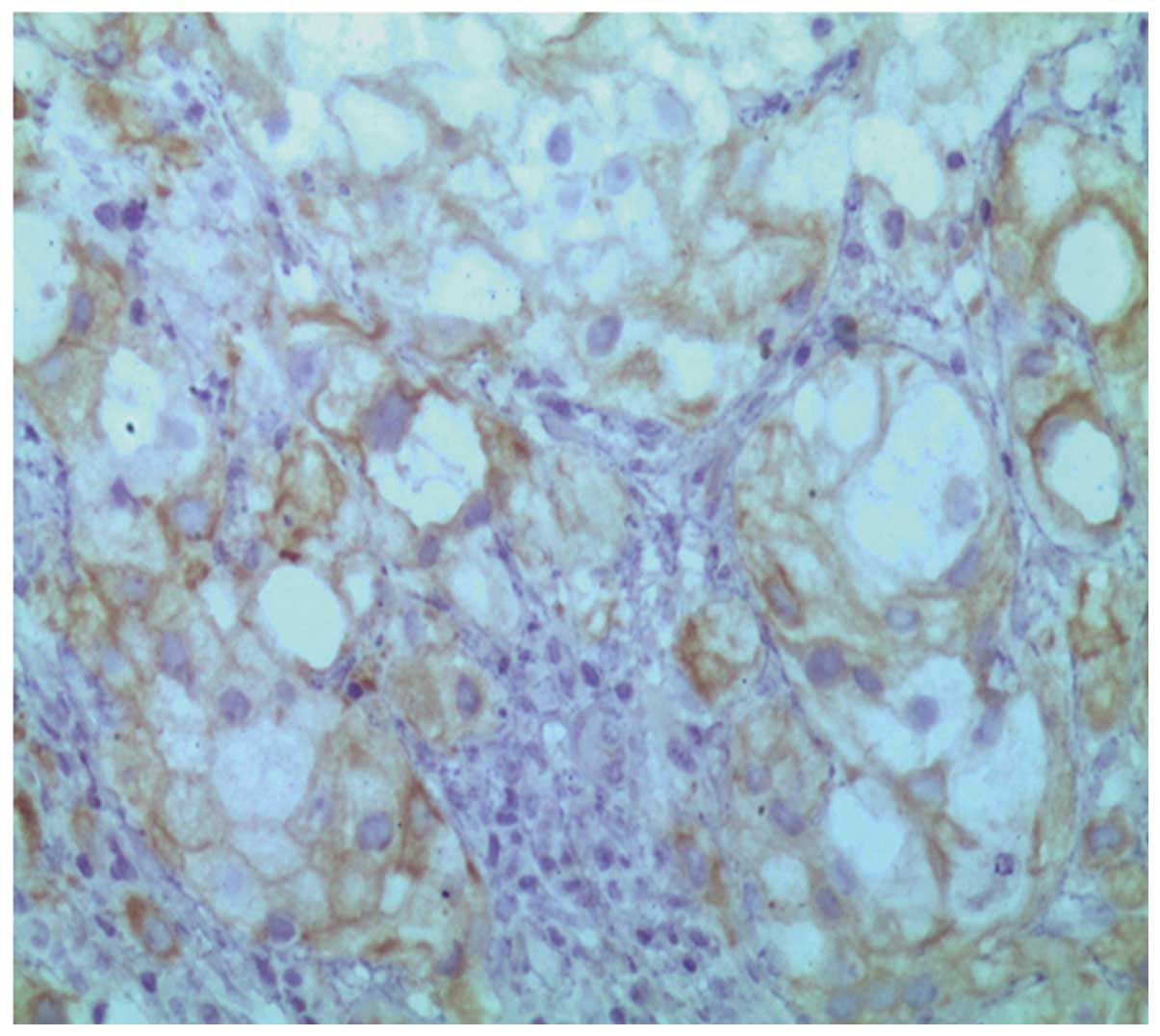
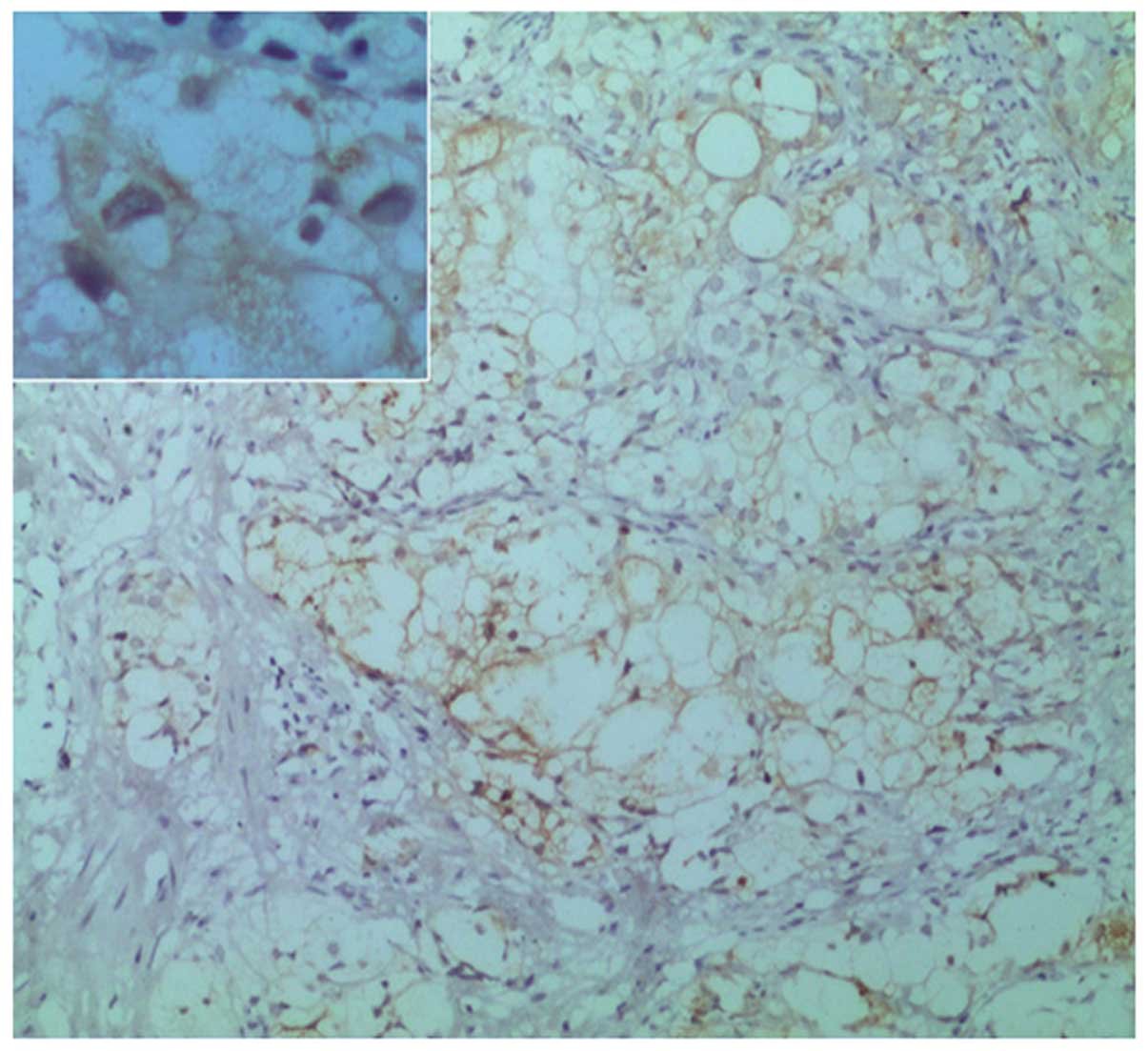
(MME; also known as cluster of differentiation 10) (Fig. 3), α-methylacyl-CoA racemase (P504S;
Fig. 4), low molecular weight
cytokeratin (Fig. 5) and
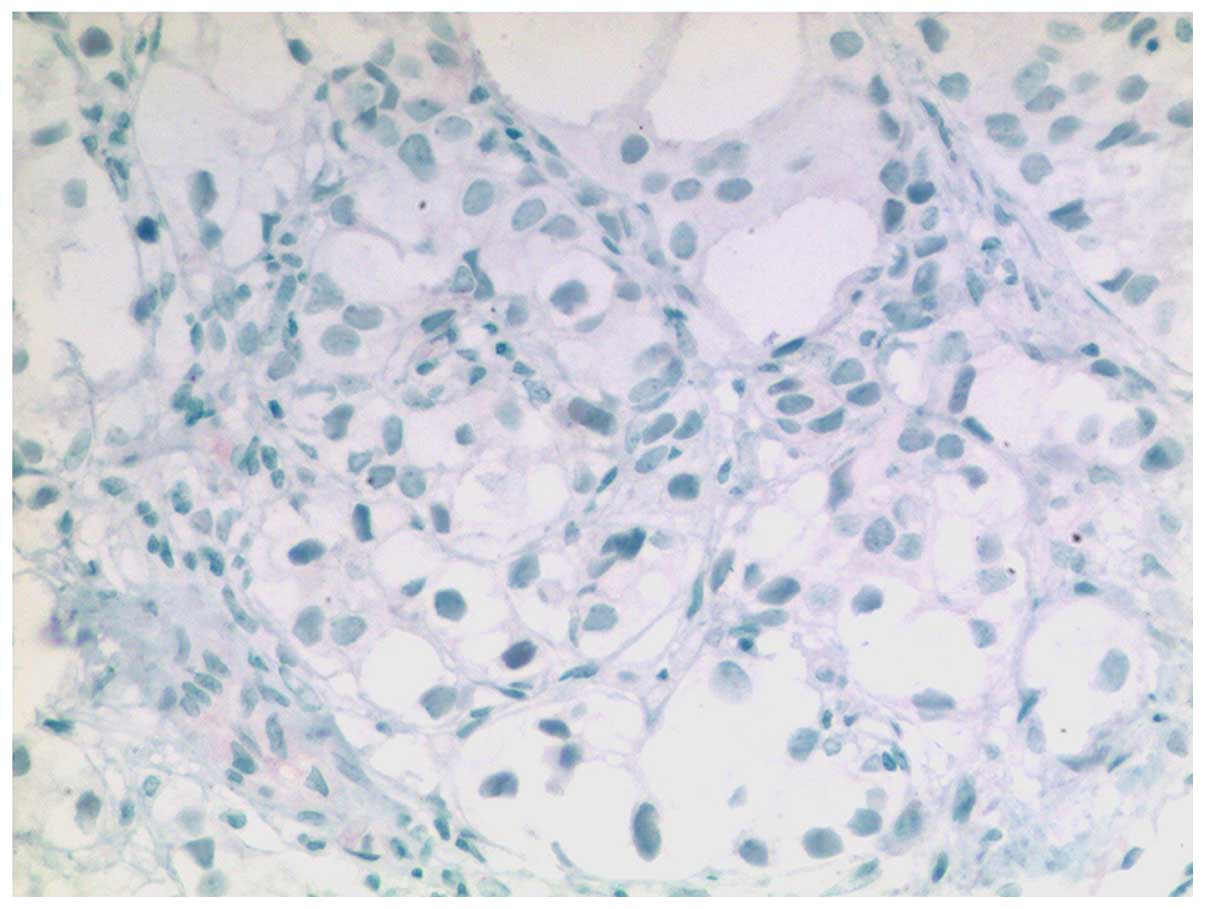
prostate-specific acid phosphatase (PSAP; Fig. 6). By contrast, no immunoreactivity was
noted for PSA, broad-spectrum cytokeratin, high molecular weight
cytokeratin, paired box 8 (PAX8; Fig.
7) or carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). With the exception of
PAX8, the results of the immunostaining analysis were almost
identical to those obtained from clear cell carcinomas of the
kidney.
The patient succumbed to the disease six months
after surgery due to multi-organ system failure. Prior to
mortality, the follow-up CT examination again failed to identify a
second renal mass. Written informed consent for the publication of
this case report and accompanying images was obtained from the
patient's family.
Discussion
RCC is associated with a number of specific
cytological features, including atypical, enlarged and prominent
nuclei, with classic structural features, such as tubules, solid
nests or sheets in a richly vascularized stroma, with an
interstitial inflammatory infiltrate (15,16).
Metastatic RCC of the prostate is an extremely rare disease.
Although prostate carcinomas may exhibit clear cell morphologies,
the confluent nests of clear cells differ in that they usually lack
marked vascularity and inflammatory cells, stain positive for
broad-spectrum cytokeratin and PSAP, and do not generally
co-express VIM (17). The clear cell
lesion identified in the present study demonstrated an
immunohistochemical profile almost identical to that of RCC, with
positive expression of VIM, low molecular weight cytokeratin,
epithelial membrane antigen, MME, PSAP and P504S, and a negative
result for high molecular weight cytokeratin, CEA, broad-spectrum
cytokeratin and PAX8. The expression of PAX8 is particularly
noteworthy, as it is a marker of primary malignant tumors of the
prostate (16). In addition, the
lesion consisted entirely of clear cells, which exhibited large,
prominent nucleoli. By contrast, nephrogenic adenomas contain cells
in which the nucleoli are generally inconspicuous. The differential
diagnosis was therefore suggestive of metastatic RCC, or a disease
entity that has not yet been described; renal-type clear cell
carcinoma arising in the prostate (18).
In the present study, an ultrasound inspection and
CT scan of the abdomen did not identify the presence of a renal
lesion. Therefore, it was concluded that the lesion represented a
primary renal-type clear cell carcinoma that had arisen from the
periurethral region of the prostate, and thus was treated
appropriately with a radical cystoprostatectomy. To the best of our
knowledge, no previous studies have described RCC presenting with
metastases to the prostate at the time of initial diagnosis, but
three cases of metachronous prostate involvement by primary RCCs
have been reported (7,8). At diagnosis, these renal tumors were
notably large, and following metastasis to the prostate, additional
sites, including the lung and bone, were also affected. These
previous cases indicate that RCC tumor dissemination occurs via
hematogenous mechanisms (7,8). In the present study, the
immunohistochemical staining results and the absence of detectable
continuity between the two tumors supported the diagnosis of a
pre-malignant role of nephrogenic carcinoma. It was concluded that
the tumor represented a primary renal-type clear cell carcinoma
that had arisen in the prostate. To the best our knowledge, this
type of extra-renal lesion has only been described in three
previous studies. The mechanisms that underlie the development and
biological course of renal-type clear cell carcinomas in the
prostate are yet to elucidated.
In summary, the present study described a case of
renal-type clear cell carcinoma of the prostate. This particular
lesion is a novel pathological entity, with histological and
immunohistochemical features that are extremely similar to those of
renal clear cell carcinomas. However, whether or not its biological
course is comparable to that of a renal clear cell carcinoma is yet
to be investigated, as does the tissue origin of this novel type of
tumor.
References
|
1
|
Pan CC, Chiang H, Chang YH and Epstein JI:
Tubulocystic clear cell adenocarcinoma arising within the prostate.
Am J Surg Pathol. 24:1433–1436. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Humphrey PA: Clear cell neoplasms of the
urinary tract and male reproductive system. Semin Diagn Pathol.
14:240–252. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI and
Sesterhenn IA: Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Urinary
System and Male Genital OrgansIn: World Health Organization
Classification of Tumours. IARC Press; Lyon: pp. 4–19. 2004
|
|
4
|
Ljungberg B, Cowan NC, Hanbury DC, et al:
European Association of Urology Guideline Group: EAU guidelines on
renal cell carcinoma: the 2010 update. Eur Urol. 58:398–406. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ritchie AW and Chisholm GD: The natural
history of renal carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 10:390–400.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Flanigan RC, Campbell SC, Clark JI and
Picken MM: Metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 4:385–390. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cihak RW, Haas R Jr, Koenen CT and
Chinchinian H: Metastatic renal carcinoma to the prostate gland:
presentation as prostatic hypertrophy. J Urol. 123:791–792.
1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
King DH, Centeno AS, Saldivar VA and
Sarosdy MF: Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the gallbladder or
prostate: two case reports. Urology. 46:722–725. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, et al:
Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methodsand major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:359–386. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang H and Yang H: The recent advances in
the treatment of renal clear cell carcinoma of internal and adverse
drug reactions. Chinese Journal of Medicine. 41:11–14. 2006.
|
|
11
|
Singh H, Flores-Sandoval N and Abrams J:
Renal-type clear cell carcinoma occurring in the prostate. Am J
Surg Patho. 27:407–410. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pal DK and Chowdhury MK: Renal type clear
cell carcinoma of prostate. Indian J Surg. 69:812007.
|
|
13
|
Permi HS, Laxminarayana KP, Yeshvanth SK
and Shetty JK: Renal type clear cell carcinoma of the prostate: a
diagnostic dilemma. J Lab Physicians. 3:132–133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Epstein JI, Allsbrook WC Jr, Amin MB and
Egevad LL: ISUP Grading Committee: The 2005 International Society
of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason
Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 29:1228–1242.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Allan CH and Epstein JI: Nephrogenic
adenoma of the prostatic urethra: a mimicker of prostate
adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 25:80–808. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gilcrease MZ, Delgrado R, Vuitch F and
Albores-Saavedra J: Clear cell adenocarcinoma and nephrogenic
adenoma of the urethra and urinary bladder: a histopathologic and
immunohistochemical comparison. Hum Pathol. 29:1451–1456. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alsanjari N, Lynch MJ, Fisher C and
Parkinson MC: Vesical clear cell adenocarcinoma. V. Nephrogenic
adenoma: a diagnostic problem. Histopathology. 27:43–49. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Malpica A, Ro JY, Troncoso P, et al:
Nephrogenic adenoma of the prostatic urethra involving the prostate
gland: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of eight
cases. Hum Pathol. 25:390–395. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|