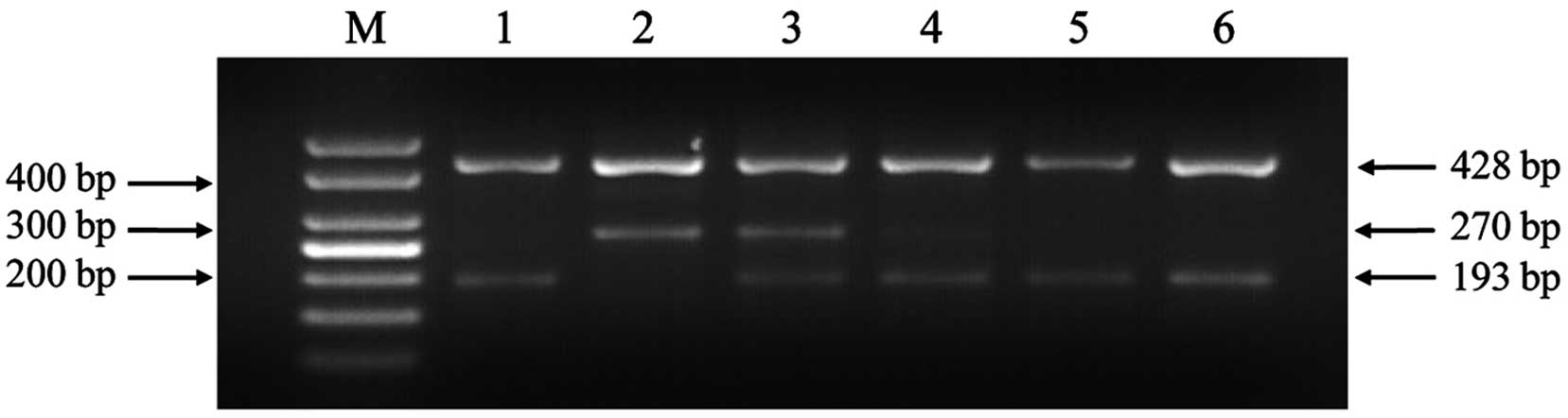
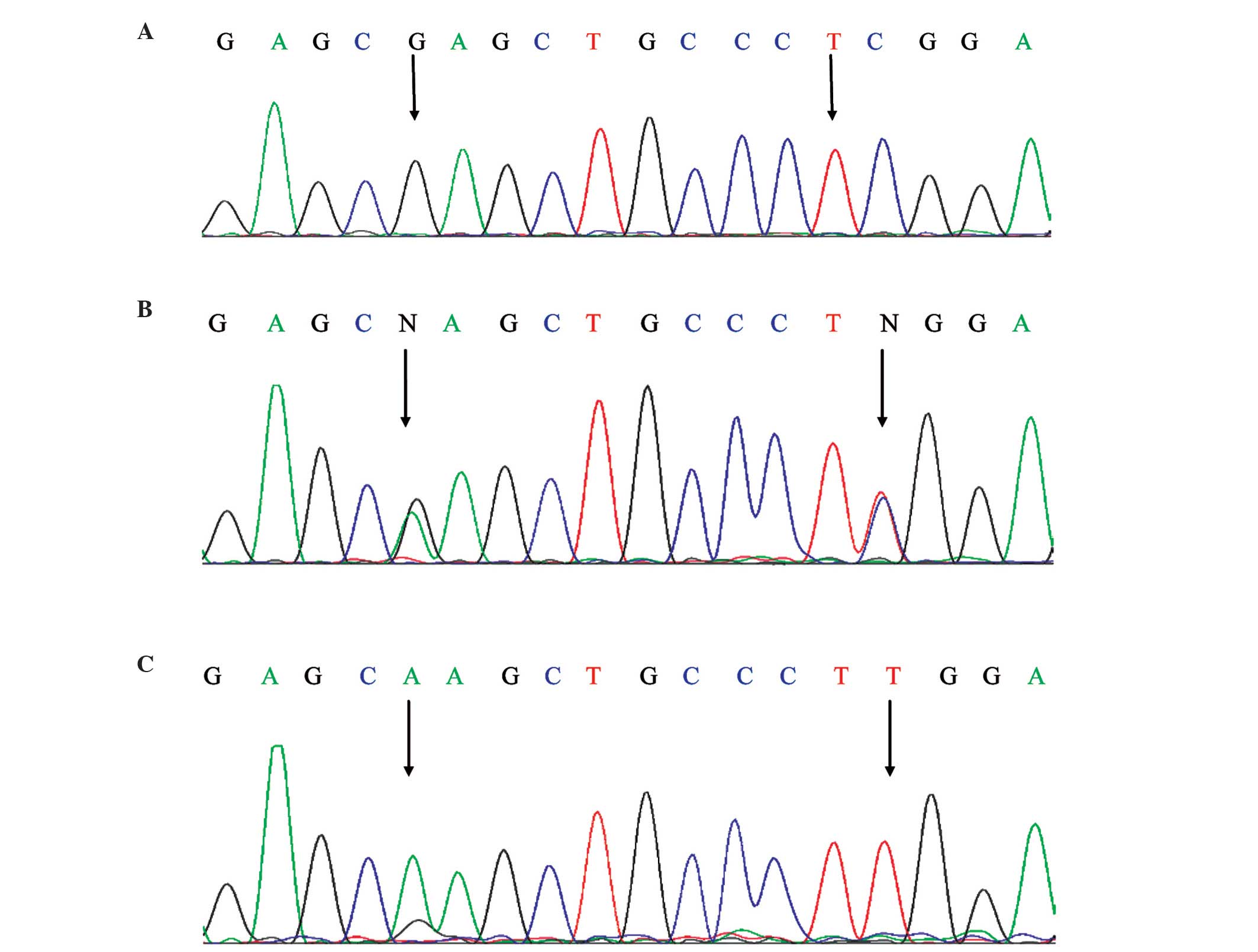
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, et al:
Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at lp36, a region
frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell.
90:809–819. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bénard J, Douc-Rasy S and Ahomadegbe JC:
TP53 family members and human cancers. Hum Mutat. 21:182–191. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moll UM, Erster S and Zaika A: p53, p63
and p73 - solos, alliances and feuds among family members. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1552:47–59. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shibukawa K, Miyokawa N, Tokusashi Y, et
al: High incidence of chromosomal abnormalities at lp36 and 9p21 in
early-stage central type squamous cell carcinoma and squamous
dysplasia of bronchus detected by autofluorescence bronchoscopy.
Oncol Rep. 22:81–87. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uramoto H, Sugio K, Oyama T, et al:
Expression of the p53 family in lung cancer. Anticancer Res.
26:1785–1790. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu K, Zhan M and Zheng P: Loss of p73
expression in six non-small cell lung cancer cell lines is
associated with 5′CpG island methylation. Exp Mol Pathol. 84:59–63.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lo Iacono M, Monica V, Saviozzi S, et al:
p63 and p73 isoform expression in non-small cell lung cancer and
corresponding morphological normal lung tissue. J Thorac Oncol.
6:473–481. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nyman U, Sobczak-Pluta A, Vlachos P, et
al: Full-length p73alpha represses drug-induced apoptosis in small
cell lung carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 280:34159–34169. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang X, Li X, Wu Z, et al: The p73
G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism is associated with risk of lung cancer
in the Han nationality of North China. Mol Carcinog. 52:387–391.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tokuchi Y, Hashimoto T, Kobayashi Y, et
al: The expression of p73 is increased in lung cancer, independent
of p53 gene alteration. Br J Cancer. 80:1623–1629. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Q, Athan E, S, Wei M, et al: TP73
allelic expression in human brain and allele frequencies in
Alzheimer's disease. BMC Med Genet. 5:5–14. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li GJ, Sturgis EM, Wang LE, et al:
Association of a p73 exon 2 G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism with risk
of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Carcinogenesis.
25:1911–1916. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ryan BM, McManus R, Daly JS, et al: A
common p73 polymorphism is associated with a reduced incidence of
oesophageal carcinamo. Br J Cancer. 85:1499–1503. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu Z, Miao X, Ma H, et al: Dinucleotide
polymorphism of p73 gene is associated with a reduced risk of lung
cancer in a Chinese population. Int J Cancer. 114:455–460. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li G, Wang LE, Chamberlain RM, et al: p73
G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism and risk of lung cancer. Cancer Res.
64:6863–6866. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Choi JE, Kang HG, Chae MH, et al: No
association between p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism and the risk of
lung cancer in a Korean population. Biochem Genet. 44:533–540.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hiraki A, Matsuo K, Hamajima N, et al:
Different risk relations with smoking for non-small cell lung
cancer: Comparison of TP53 and TP73 genotypes. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 4:107–112. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee KE, Hong YS, Kim BG, et al: p73 G4C14
to A4T14 polymorphism is associated with colorectal cancer risk and
survival. World J Gastroenterol. 16:4448–4454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Melino G, De Laurenzi V and Vousden KH:
p73: Friend or foe in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:605–615.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grob TJ, Novak U, Maisse C, et al: Human
delta Np73 regulates a dominant negative feedback loop for TAp73
and p53. Cell Death Differ. 8:1213–1223. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ishimoto O, Kawahara C, Enjo K, et al:
Possible oncogenic potential of DeltaNp73: A newly identified
isoform of human p73. Cancer Res. 62:636–641. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tomasini R, Tsuchihara K, Wilhelm M, et
al: TAp73 knockout shows genomic instability with infertility and
tumor suppressor functions. Genes Dev. 22:2677–2691. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Concin N, Becker K, Slade N, et al:
Transdominant DeltaTAp73 isoforms are frequently up-regulated in
ovarian cancer. Evidence for their roles as epigenetic p53 inhibits
in vivo. Cancer Res. 64:2449–2460. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|