|
1
|
Marks LS, Fradet Y, Deras IL, Blase A,
Mathis J, Aubin SM, Cancio AT, Desaulniers M, Ellis WJ, Rittenhouse
H, et al: PCA3 molecular urine assay for prostate cancer in men
undergoing repeat biopsy. Urology. 69:532–535. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Andriole GL, Crawford ED, Grubb RL III,
Buys SS, Chia D, Church TR, Fouad MN, Isaacs C, Kvale PA, Reding
DJ, et al: Prostate cancer screening in the randomized prostate,
lung, colorectal, and ovarian cancer screening trial: Mortality
results after 13 years of follow-up. J Natl Cancer Inst.
104:125–132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ,
Tammela TL, Ciatto S, Nelen V, Kwiatkowski M, Lujan M, Lilja H,
Zappa M, et al: Prostate-cancer mortality at 11 years of follow-up.
N Engl J Med. 366:981–990. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alhasan AH, Kim DY, Daniel WL, Watson E,
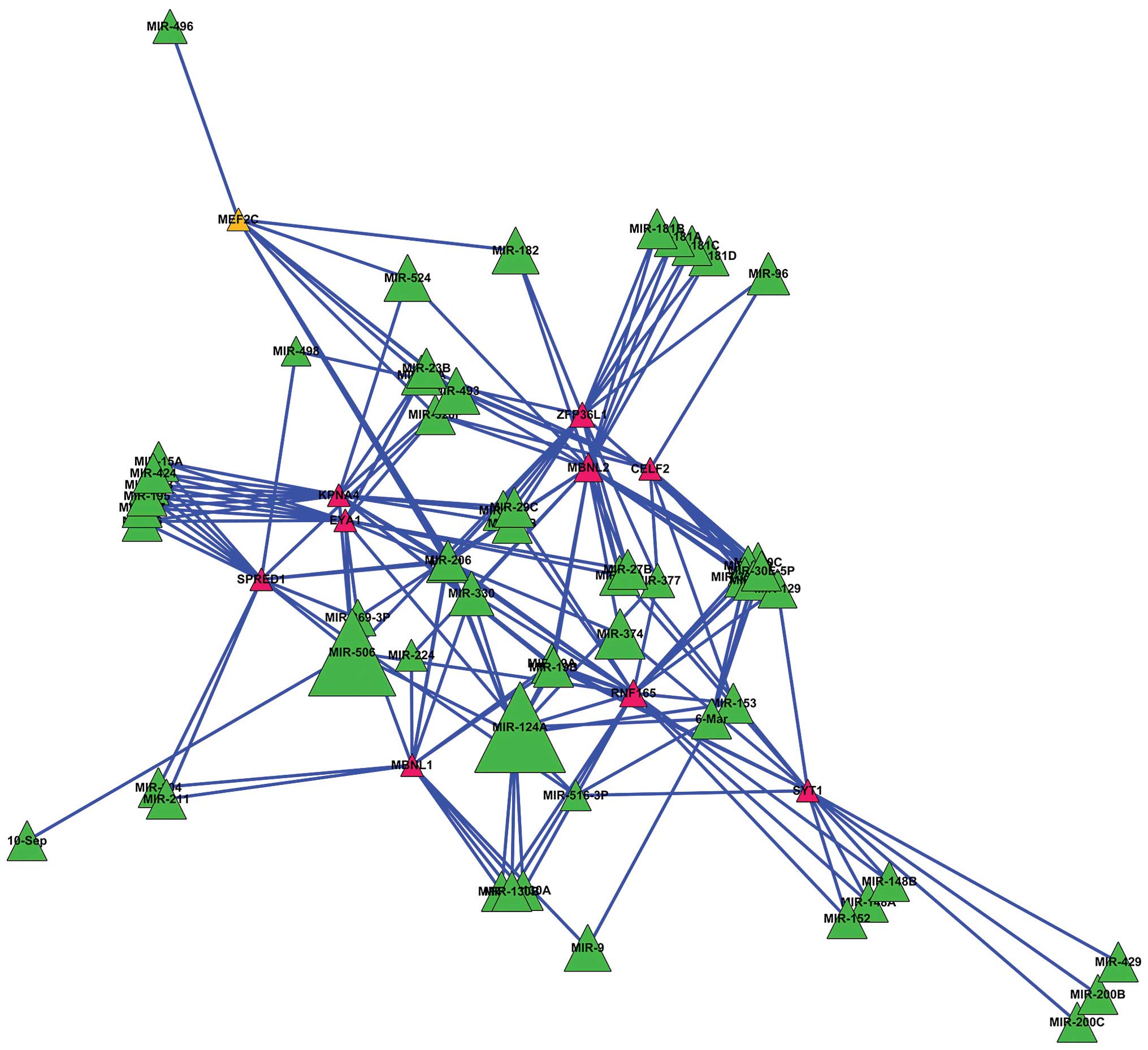
Meeks JJ, Thaxton CS and Mirkin CA: Scanometric MicroRNA array
profiling of prostate cancer markers using spherical nucleic
acid-gold nanoparticle conjugates. Anal Chem. 84:4153–4160. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hessels D, Klein Gunnewiek JMT, van Oort
I, Karthaus HF, van Leenders GJ, van Balken B, Kiemeney LA, Witjes
JA and Schalken JA: DD3 (PCA3)-based molecular urine analysis for
the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 44:8–15. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Struewing JP, Hartge P, Wacholder S, Baker
SM, Berlin M, McAdams M, Timmerman MM, Brody LC and Tucker MA: The
risk of cancer associated with specific mutations of BRCA1 and
BRCA2 among Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med. 336:1401–1408. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoshida S, Tsutsumi S, Muhlebach G,
Sourbier C, Lee MJ, Lee S, Vartholomaiou E, Tatokoro M, Beebe K,
Miyajima N, et al: Molecular chaperone TRAP1 regulates a metabolic
switch between mitochondrial respiration and aerobic glycolysis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E1604–E1612. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee C, Zhang Q, Zi X, Dash A, Soares MB,
Rahmatpanah F, Jia Z, McClelland M and Mercola D: TGF-β mediated
DNA methylation in prostate cancer. Transl Androl Urol. 1:78–88.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Senapati S, Rachagani S, Chaudhary K,
Johansson SL, Singh RK and Batra SK: Overexpression of macrophage
inhibitory cytokine-1 induces metastasis of human prostate cancer
cells through the FAK-RhoA signaling pathway. Oncogene.
29:1293–1302. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin JK, Dayyani F and Gallick GE: Steps in
prostate cancer progression that lead to bone metastasis. Int J
Cancer. 128:2545–2561. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aryee MJ, Liu W, Engelmann JC, Nuhn P,
Gurel M, Haffner MC, Esopi D, Irizarry RA, Getzenberg RH, Nelson
WG, et al: DNA methylation alterations exhibit intraindividual
stability and interindividual heterogeneity in prostate cancer
metastases. Sci Transl Med. 5:169ra1102013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
R Development Core Team, . R: A Language
and Environment for Statistical Computing. http://www.r-project.org/R Foundation for
Statistical Computing; Vienna, Austria: 2008
|
|
13
|
Davis S and Meltzer PS: GEOquery: A bridge
between the gene expression omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor.
Bioinformatics. 23:1846–1847. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Diboun I, Wernisch L, Orengo CA and
Koltzenburg M: Microarray analysis after RNA amplification can
detect pronounced differences in gene expression using limma. BMC
Genomics. 7:2522006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barrett T, Troup DB, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data
sets-10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D1005–D1010. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smyth GK: Linear models and empirical
bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray
experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 3:: 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kelder T, van Iersel MP, Hanspers K,
Kutmon M, Conklin BR, Evelo CT and Pico AR: WikiPathways: Building
research communities on biological pathways. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:D1301–D1307. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pico AR, Kelder T, van Iersel MP, Hanspers
K, Conklin BR and Evelo C: WikiPathways: Pathway editing for the
people. PLoS Biol. 6:e1842008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang B, Kirov S and Snoddy J: WebGestalt:
An integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological
contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:W741–W748. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liberzon A, Subramanian A, Pinchback R,
Thorvaldsdóttir H, Tamayo P and Mesirov JP: Molecular signatures
database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics. 27:1739–1740. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Roy Statist Soc Ser B (Methodological).
57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
22
|
Lamb J, Crawford ED, Peck D, Modell JW,
Blat IC, Wrobel MJ, Lerner J, Brunet JP, Subramanian A, Ross KN, et
al: The Connectivity Map: Using gene-expression signatures to
connect small molecules, genes, and disease. Science.
313:1929–1935. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES, et al: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baldi P and Long AD: A Bayesian framework
for the analysis of microarray expression data: Regularized t-test
and statistical inferences of gene changes. Bioinformatics.
17:509–519. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Amankwah EK, Sellers TA and Park JY: Gene
variants in the angiogenesis pathway and prostate cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 33:1259–1269. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hinoi E, Nakamura Y, Takada S, Fujita H,
Iezaki T, Hashizume S, Takahashi S, Odaka Y, Watanabe T and Yoneda
Y: Growth differentiation factor-5 promotes brown adipogenesis in
systemic energy expenditure. Diabetes. 63:162–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rivoltini L, Carrabba M, Huber V, Castelli
C, Novellino L, Dalerba P, Mortarini R, Arancia G, Anichini A, Fais
S, et al: Immunity to cancer: attack and escape in T
lymphocyte-tumor cell interaction. Immunol Rev. 188:97–113. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin X, Miller JW, Mankodi A, Kanadia RN,
Yuan Y, Moxley RT, Swanson MS and Thornton CA: Failure of
MBNL1-dependent post-natal splicing transitions in myotonic
dystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 15:2087–2097. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hao M, Akrami K, Wei K, De Diego C, Che N,
Ku JH, Tidball J, Graves MC, Shieh PB and Chen F: Muscleblind-like
2 (Mbnl2)-deficient mice as a model for myotonic dystrophy. Dev
Dyn. 237:403–410. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Miyazaki Y, Adachi H, Katsuno M,
Minamiyama M, Jiang YM, Huang Z, Doi H, Matsumoto S, Kondo N, Iida
M, et al: Viral delivery of miR-196a ameliorates the SBMA phenotype
via the silencing of CELF2. Nat Med. 18:1136–1141. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Braunagel SC, Williamson ST, Ding Q, Wu X
and Summers MD: Early sorting of inner nuclear membrane proteins is
conserved. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:9307–9312. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stumpo DJ, Byrd NA, Phillips RS, Ghosh S,
Maronpot RR, Castranio T, Meyers EN, Mishina Y and Blackshear PJ:
Chorioallantoic fusion defects and embryonic lethality resulting
from disruption of Zfp36L1, a gene encoding a CCCH tandem zinc
finger protein of the Tristetraprolin family. Mol Cell Biol.
24:6445–6455. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yamazaki T, Kawamura Y, Minami A and
Uemura M: Calcium-dependent freezing tolerance in
Arabidopsis involves membrane resealing via synaptotagmin
SYT1. Plant Cell. 20:3389–3404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Poduri A, Chopra SS, Neilan EG, Elhosary
PC, Kurian MA, Meyer E, Barry BJ, Khwaja OS, Salih MA, Stödberg T,
et al: Homozygous PLCB1 deletion associated with malignant
migrating partial seizures in infancy. Epilepsia. 53:e146–e150.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brems H, Chmara M, Sahbatou M, Denayer E,
Taniguchi K, Kato R, Somers R, Messiaen L, De Schepper S, Fryns JP,
et al: Germline loss-of-function mutations in SPRED1 cause a
neurofibromatosis 1-like phenotype. Nat Genet. 39:1120–1126. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kelly CE, Thymiakou E, Dixon JE, Tanaka S,
Godwin J and Episkopou V: Rnf165/Ark2C enhances BMP-Smad signaling
to mediate motor axon extension. PLoS Biol. 11:e10015382013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wink M: Molecular modes of action of
cytotoxic alkaloids: from DNA intercalation, spindle poisoning,
topoisomerase inhibition to apoptosis and multiple drug resistance.
Alkaloids Chem Biol. 64:1–47. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mei L, Chen Y, Wang Z, Wang J, Wan J, Yu
C, Liu X and Li W: Synergistic anti-tumour effects of tetrandrine
and chloroquine combination therapy in human cancer: a potential
antagonistic role for p21. Br J Pharmacol. 172:2232–2245. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Solomon VR and Lee H: Quinoline as a
privileged scaffold in cancer drug discovery. Curr Med Chem.
18:1488–1508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cordell GA, Quinn-Beattie ML and
Farnsworth NR: The potential of alkaloids in drug discovery.
Phytother Res. 15:183–205. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|