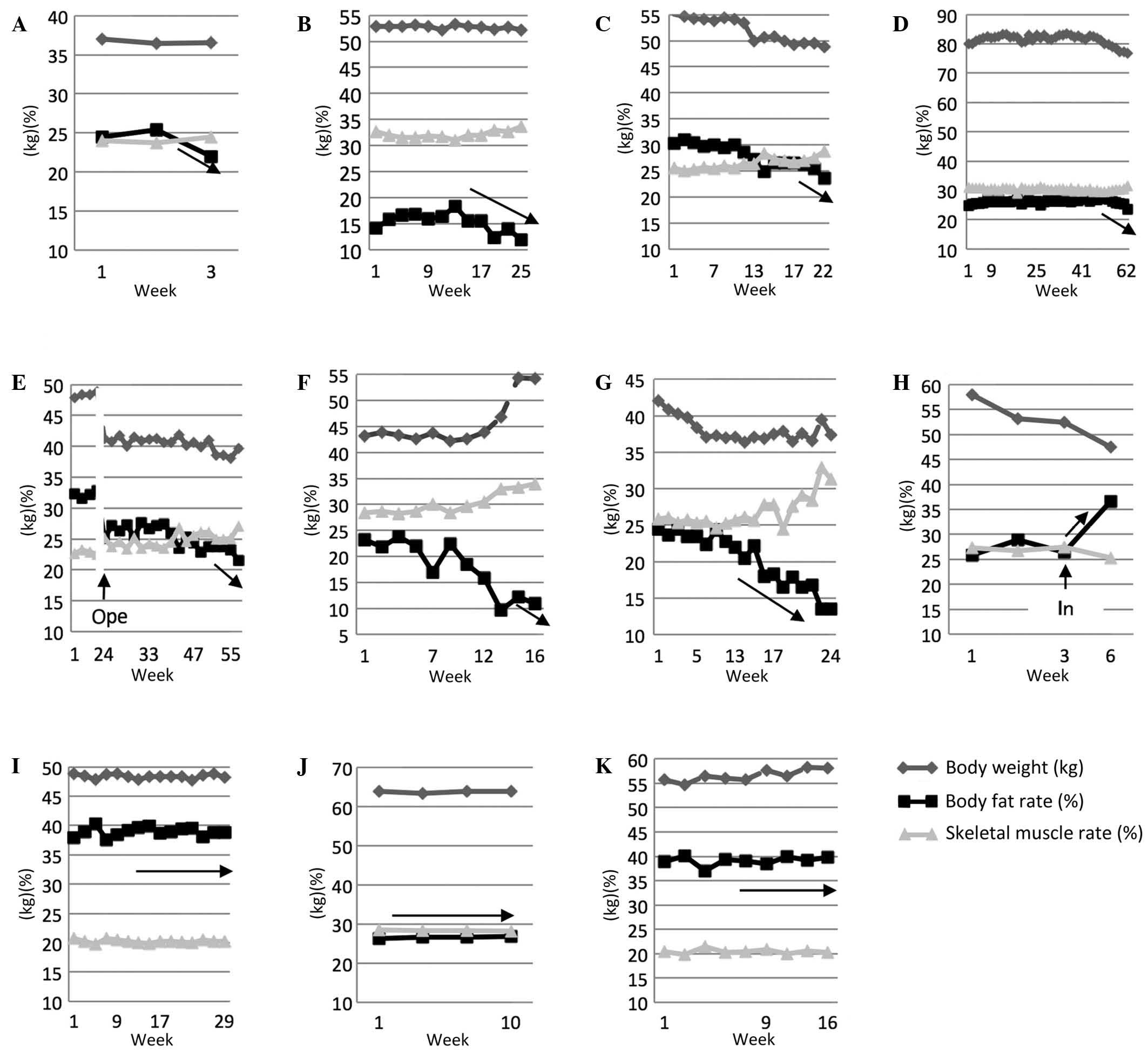
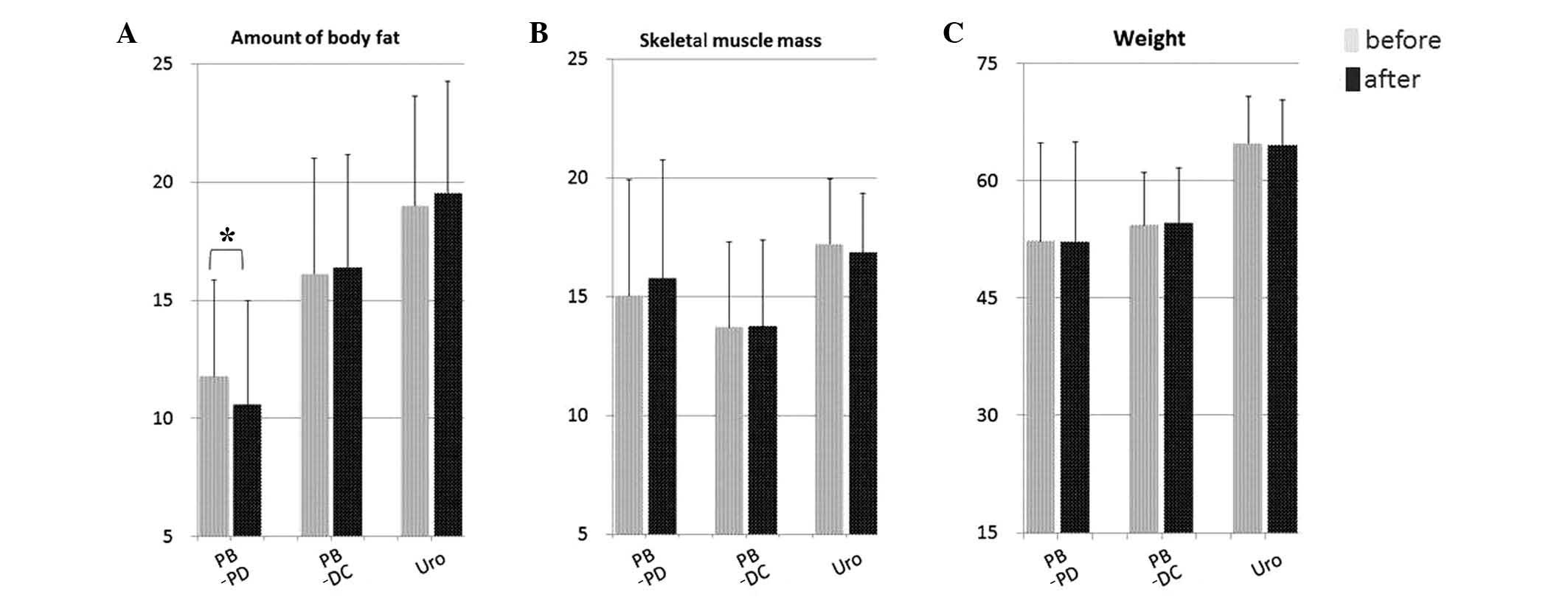
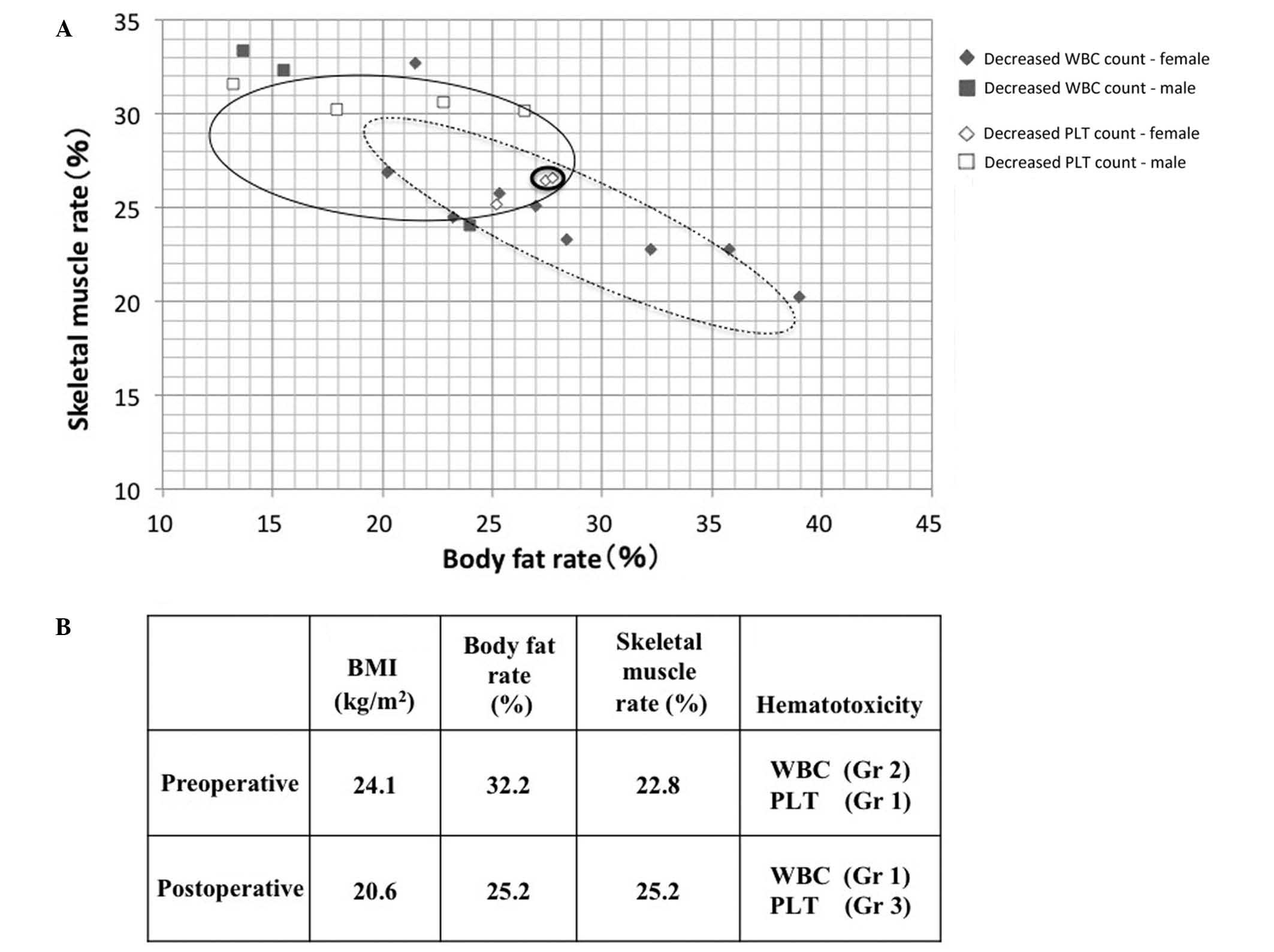
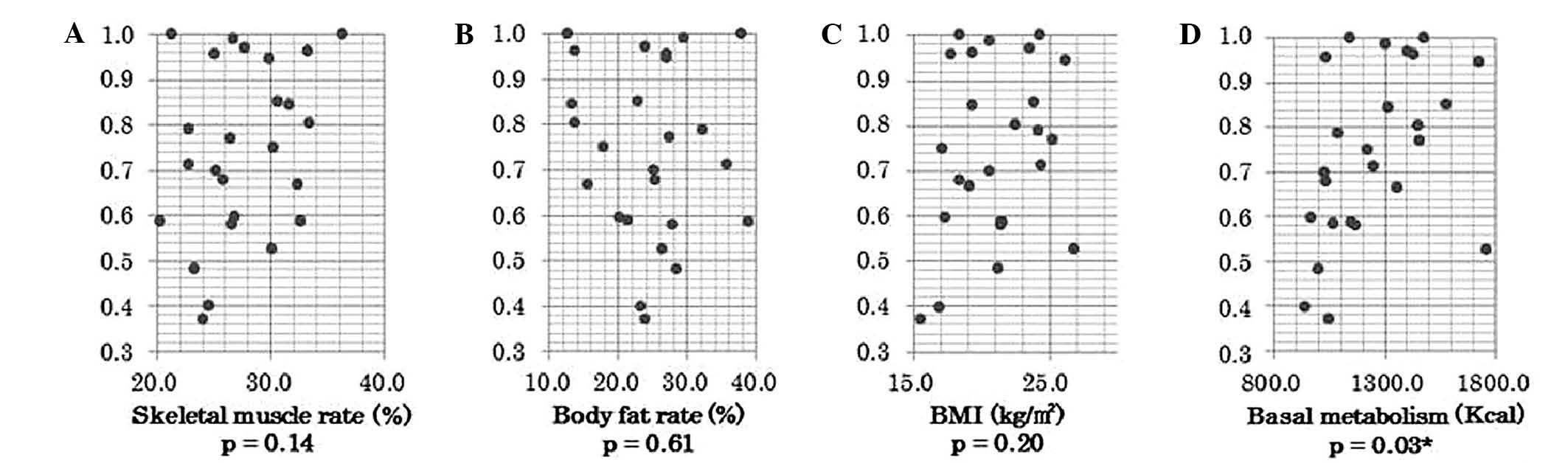
|
1
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A,
Hecht JR, Gallinger S, Au HJ, Murawa P, Walde D, Wolff RA, et al:
National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group:
Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in
patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A phase III trial of the
National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin
Oncol. 25:1960–1966. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, Cunningham D,
Anthoney A, Maraveyas A, Madhusudan S, Iveson T, Hughes S, Pereira
SP, et al: ABC-02 Trial Investigators: Cisplatin plus gemcitabine
versus gemcitabine for biliary tract cancer. N Engl J Med.
362:1273–1281. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O,
Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de
la Fouchardière C, et al: Groupe Tumeurs Digestives of Unicancer;
PRODIGE Intergroup: FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic
pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 364:1817–1825. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT,
Ricci S, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Zimmermann A and Arning
M: Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing
gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine,
doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 23:4602–4608. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sultana A, Smith CT, Cunningham D,
Starling N, Neoptolemos JP and Ghaneh P: Meta-analyses of
chemotherapy for locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 25:2607–2615. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Okusaka T, Ishii H, Funakoshi A, Yamao K,
Ohkawa S, Saito S, Saito H and Tsuyuguchi T: Phase II study of
single-agent gemcitabine in patients with advanced biliary tract
cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 57:647–653. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ozawa A, Tanji N, Ochi T, Yanagihara Y,
Kikugawa T, Yamaguchi A, Ikeda T, Shimamoto K, Aoki K, Toshino A
and Yokoyama M: Gemcitabine and cisplatin for advanced urothelial
carcinomas: The Ehime University Hospital experience. Int J Clin
Oncol. 12:279–283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Janssen I, Heymsfield SB and Ross R: Low
relative skeletal muscle mass (sarcopenia) in older persons is
associated with functional impairment and physical disability. J Am
Geriatr Soc. 50:889–896. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mitsiopoulos N, Baumgartner RN, Heymsfield
SB, Lyons W, Gallagher D and Ross R: Cadaver validation of skeletal
muscle measurement by magnetic resonance imaging and computerized
tomography. J Appl Physiol (1985). 85:115–122. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ferland M, Després JP, Tremblay A, Pinault
S, Nadeau A, Moorjani S, Lupien PJ, Thériault G and Bouchard C:
Assessment of adipose tissue distribution by computed axial
tomography in obese women: Association with body density and
anthropometric measurements. Br J Nutr. 61:139–148. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuk JL, Lee S, Heymsfield SB and Ross R:
Waist circumference and abdominal adipose tissue distribution:
Influence of age and sex. Am J Clin Nutr. 81:1330–1334.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nuñez C, Gallagher D, Grammes J,
Baumgartner RN, Ross R, Wang Z, Thornton J and Heymsfield SB:
Bioimpedance analysis: Potential for measuring lower limb skeletal
muscle mass. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 23:96–103. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pietrobelli A, Morini P, Battistini N,
Chiumello G, Nuñez C and Heymsfield SB: Appendicular skeletal
muscle mass: Prediction from multiple frequency segmental
bioimpedance analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr. 52:507–511. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Janssen I, Heymsfield SB, Baumgartner RN
and Ross R: Estimation of skeletal muscle mass by bioelectrical
impedance analysis. J Appl Physiol (1985). 89:465–471.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schwan HP and Kay CF: The conductivity of
living tissues. Ann NY Acad Sci. 65:1007–1013. 1957. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Houtkooper LB, Lohman TG, Going SB and
Howell WH: Why bioelectrical impedance analysis should be used for
estimating adiposity. Am J Clin Nutr. 64(Suppl 3): 436S–448S.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Oshima Y, Shiga T, Namba H and Kuno S:
Estimation of whole-body skeletal muscle mass by bioelectrical
impedance analysis in the standing position. Obes Res Clin Pract.
4:e1–e82. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oshima Y and Shiga T: Within-day
variability of whole-body and segmental bioelectrical impedance in
a standing position. Eur J Clin Nutr. 60:938–941. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ishiguro N, Kanehisa H, Miyatani M, Masuo
Y and Fukunaga T: A comparison of three bioelectrical impedance
analyses for predicting lean body mass in a population with a large
difference in muscularity. Eur J Appl Physiol. 94:25–35. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tanaka NI, Miyatani M, Masuo Y, Fukunaga T
and Kanehisa H: Applicability of a segmental bioelectrical
impedance analysis for predicting the whole body skeletal muscle
volume. J Appl Physiol. 103:1688–1695. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kushner RF, Kunigk A, Alspaugh M, Andronis
PT, Leitch CA and Schoeller DA: Validation of
bioelectrical-impedance analysis as a measurement of change in body
composition in obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 52:219–223. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deurenberg P, Tagliabue A and Schouten FJ:
Multi-frequency impedance for the prediction of extracellular water
and total body water. Br J Nutr. 73:349–358. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stall SH, Ginsberg NS, DeVita MV,
Zabetakis PM, Lynn RI, Gleim GW, Wang J, Pierson RN Jr and Michelis
MF: Comparison of five body-composition methods in peritoneal
dialysis patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 64:125–130. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gallagher D, Belmonte D, Deurenberg P,
Wang Z, Krasnow N, Pi-Sunyer FX and Heymsfield SB: Organ-tissue
mass measurement allows modeling of REE and metabolically active
tissue mass. Am J Physiol. 275:E249–E258. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bosy-Westphal A, Later W, Hitze B, Sato T,
Kossel E, Gluer CC, Heller M and Muller MJ: Accuracy of
bioelectrical impedance consumer devices for measurement of body
composition in comparison to whole body magnetic resonance imaging
and dual X-ray absorptiometry. Obes Facts. 1:319–324. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kataoka H: A new monitoring method for the
estimation of body fluid status by digital weight scale
incorporating bioelectrical impedance analyzer in definite heart
failure patients. J Card Fail. 15:410–418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nakajima H, Koizumi K, Tanaka T, Ishigaki
Y, Yoshitake Y, Yonekura H, Sakuma T, Fukushima T, Umehara H, Ueno
S, et al: Loss of HITS (FAM107B) expression in cancers of multiple
organs: Tissue microarray analysis. Int J Oncol. 41:1347–1357.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ministry of Health. Labour and Welfare:
Health Japan 21 - National Health and Nutrition Survery. http://www.mhlw.go.jp/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/kenkou/kenkounippon21/en/eiyouchousa/
|
|
32
|
Fearon K, Arends J and Baracos V:
Understanding the mechanisms and treatment options in cancer
cachexia. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:90–99. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nelson KA, Walsh D and Sheehan FA: The
cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 12:213–225.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Puccio M and Nathanson L: The cancer
cachexia syndrome. Semin Oncol. 24:277–287. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Parry-Billings M, Leighton B, Dimitriadis
GD, Curi R, Bond J, Bevan S, Colquhoun A and Newsholme EA: The
effect of tumour bearing on skeletal muscle glutamine metabolism.
Int J Biochem. 23:933–937. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM,
Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y,
Schneider SM, et al: Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition
and diagnosis: Report of the European working group on Sarcopenia
in older people. Age Ageing. 39:412–423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gordon JN, Green SR and Goggin PM: Cancer
cachexia. QJM. 98:779–788. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Scott HR, McMillan DC, Forrest LM, Brown
DJ, McArdle CS and Milroy R: The systemic inflammatory response,
weight loss, performance status and survival in patients with
inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 87:264–267.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
George J, Cannon T, Lai V, Richey L,
Zanation A, Hayes DN, Shores C, Guttridge D and Couch M: Cancer
cachexia syndrome in head and neck cancer patients: Part II.
Pathophysiology. Head Neck. 29:497–507. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Das SK, Eder S, Schauer S, Diwoky C,
Temmel H, Guertl B, Gorkiewicz G, Tamilarasan KP, Kumari P, Trauner
M, et al: Adipose triglyceride lipase contributes to
cancer-associated cachexia. Science. 333:233–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pelucchi C, Bosetti C, Negri E, Malvezzi M
and La Vecchia C: Mechanisms of disease: The epidemiology of
bladder cancer. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 3:327–340. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Miura A, Onoue M, Terada K, Takahashi K
and Inui K: Gender differences in hematotoxicity induced by
gemcitabine monotherapy. Jpn J Pharm Health Care Sci. 36:57–60.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Prado CM, Baracos VE, McCargar LJ,
Mourtzakis M, Mulder KE, Reiman T, Butts CA, Scarfe AG and Sawyer
MB: Body composition as an independent determinant of
5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy toxicity. Clin Cancer Res.
13:3264–3268. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Prado CM, Baracos VE, McCargar LJ, Reiman
T, Mourtzakis M, Tonkin K, Mackey JR, Koski S, Pituskin E and
Sawyer MB: Sarcopenia as a determinant of chemotherapy toxicity and
time to tumor progression in metastatic breast cancer patients
receiving capecitabine treatment. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2920–2926.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gusella M, Toso S, Ferrazzi E, Ferrari M
and Padrini R: Relationships between body composition parameters
and fluorouracil pharmacokinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 54:131–139.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ganpule AA, Tanaka S, Ishikawa-Takata K
and Tabata I: Interindividual variability in sleeping metabolic
rate in Japanese subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 61:1256–1261. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Usui C, Takahashi E, Gando Y, Sanada K,
Oka J, Miyachi M, Tabata I and Higuchi M: Relationship between
blood adipocytokines and resting energy expenditure in young and
elderly women. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 53:529–535. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wu J, Boström P, Sparks LM, Ye L, Choi JH,
Giang AH, Khandekar M, Virtanen KA, Nuutila P, Schaart G, et al:
Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in
mouse and human. Cell. 150:366–376. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cohen P, Levy JD, Zhang Y, Frontini A,
Kolodin DP, Svensson KJ, Lo JC, Zeng X, Ye L, Khandekar MJ, et al:
Ablation of PRDM16 and beige adipose causes metabolic dysfunction
and a subcutaneous to visceral fat switch. Cell. 156:304–316. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ellegård LH, Ahlén M, Körner U, Lundholm
KG, Plank LD and Bosaeus IG: Bioelectric impedance spectroscopy
underestimates fat-free mass compared to dual energy X-ray
absorptiometry in incurable cancer patients. Eur J Clin Nutr.
63:794–801. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yamakage H, Ito R, Tochiya M, Muranaka K,
Tanaka M, Matsuo Y, Odori S, Kono S, Shimatsu A and Satoh-Asahara
N: The utility of dual bioelectrical impedance analysis in
detecting intra-abdominal fat area in obese patients during weight
reduction therapy in comparison with waist circumference and
abdominal CT. Endocr J. 61:807–819. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|