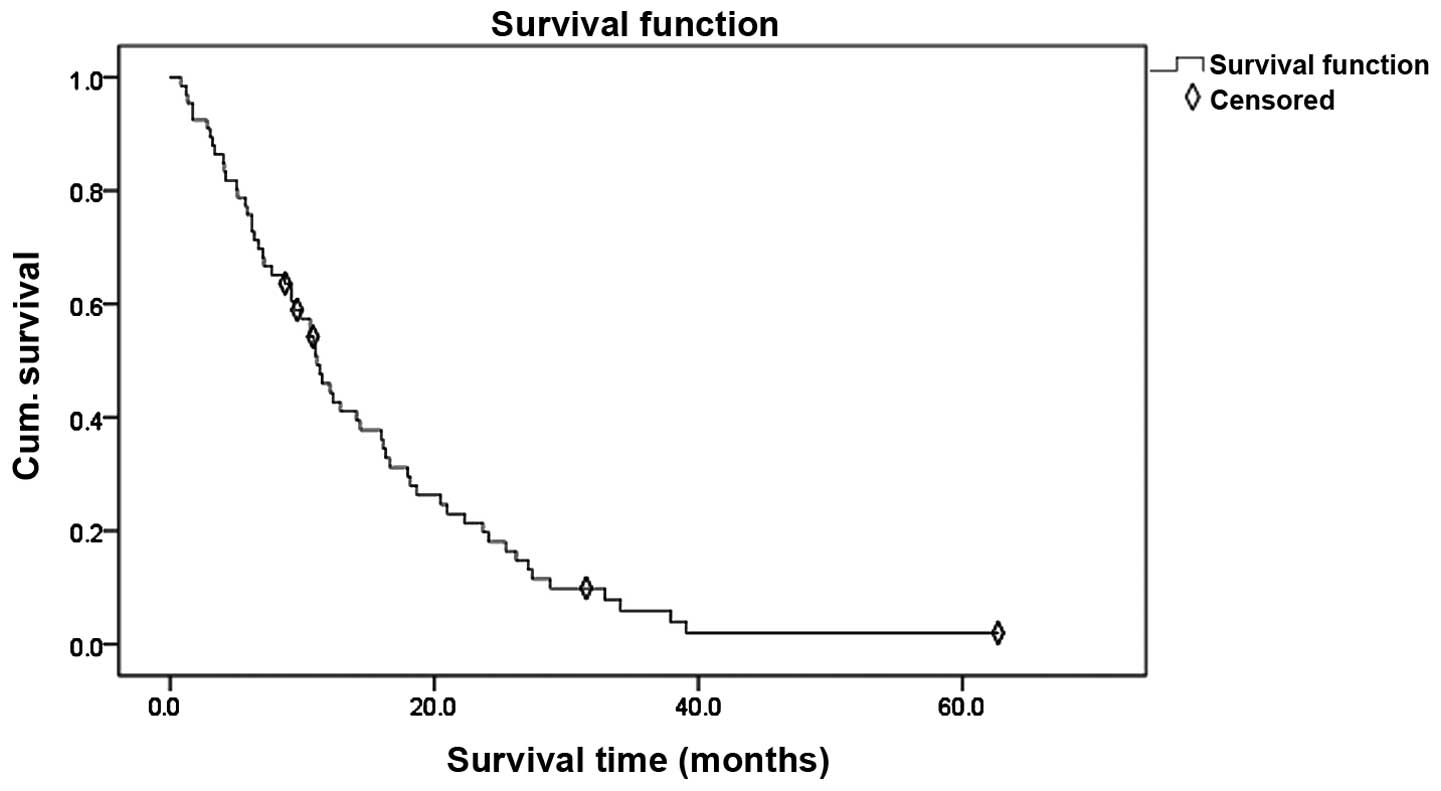
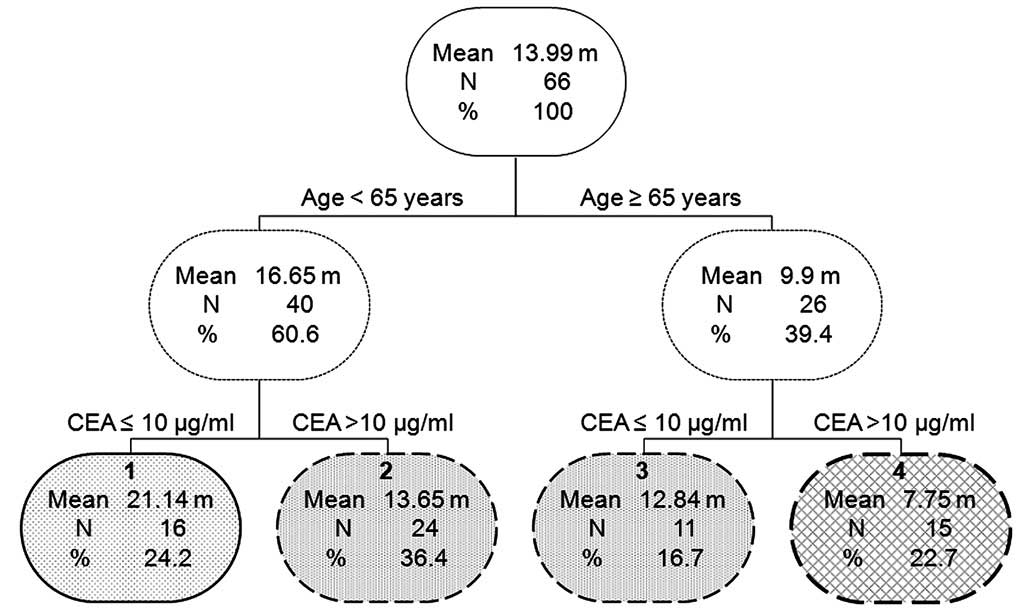
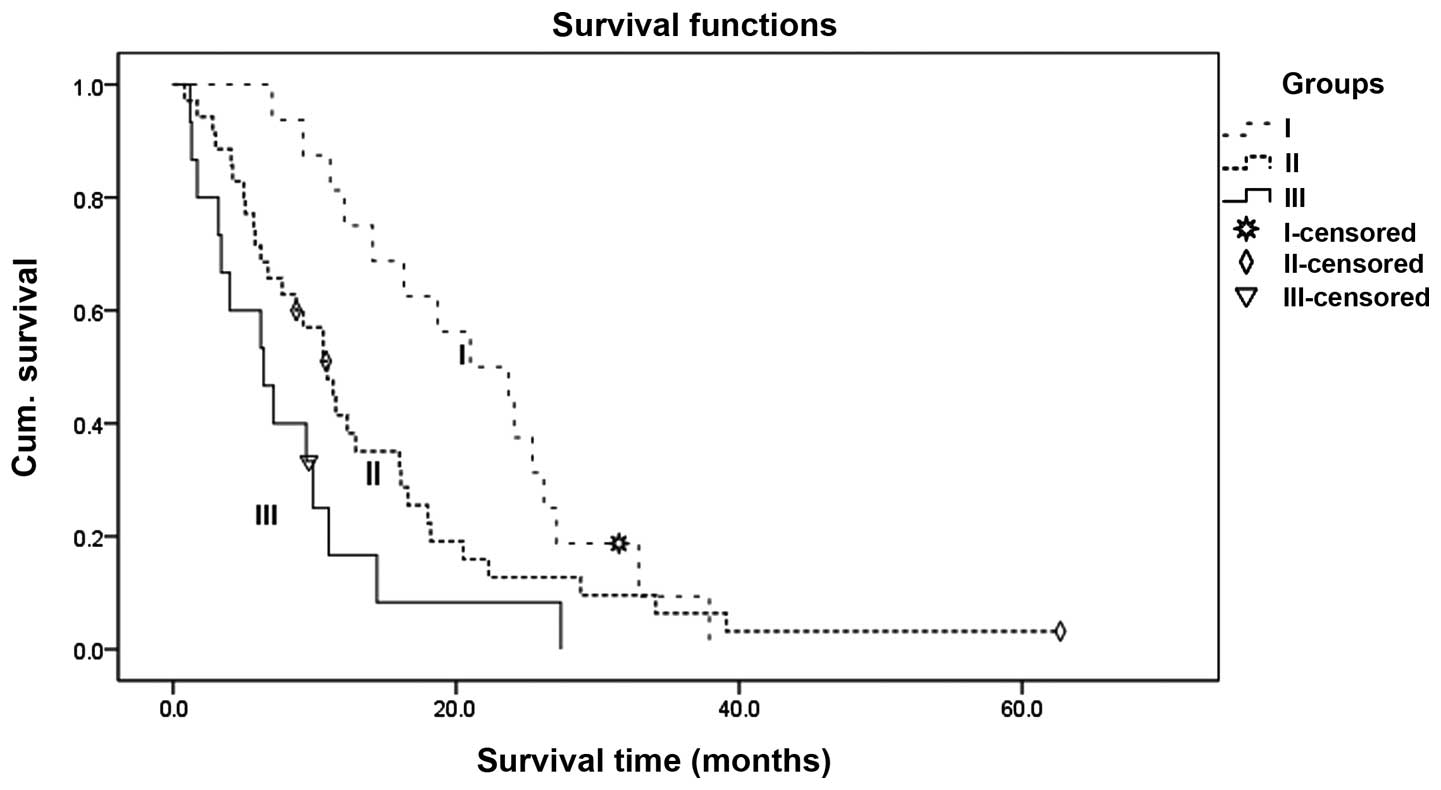
|
1
|
Kong DS, Lee JI, Nam DH and Park K, Kim
JH, Kim JG, Park JO and Park K: Prognosis of non-small cell lung
cancer with synchronous brain metastases treated with gamma knife
radiosurgery. J Korean Med Sci. 21:527–532. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zimm S, Wampler GL, Stablein D, Hazra T
and Young HF: Intracerebral metastases in solid-tumor patients:
Natural history and results of treatment. Cancer. 48:384–394. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang L, Parkin DM, Ferlay J, Li L and Chen
Y: Estimates of cancer incidence in China for 2000 and projections
for 2005. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:243–250.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gaspar L, Scott C, RotmaIl M, Asbell S,
Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG and Byhardt R: Recursive
partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three
radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) brain metastases trials.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 37:745–751. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lagerwaard FJ, Levendag PC, Nowak PJ,
Eijkenboom WM, Hanssens PE and Schmitz PI: Prognostic factors in
patients with brain metastases: A review of 1292 patients. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 43:795–803. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Peng H, Ma M and Han B: Survival analysis
of 1,742 patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer.
Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 14:362–366. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mekhail T, Sombeck M and Sollaccio R:
Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after
radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral
metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. Curr Oncol Rep.
13:255–258. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J,
Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singh B, Heelan R, Rusch V, Fulton L, et al:
EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from ‘never
smokers’ and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib
and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:13306–13311. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nieder N, Bremnes RM and Andratschke NH:
Prognostic scores in patients with brain metastases from non-small
cell lung cancer. Thorac Oncol. 4:1337–1341. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Abacioglu U, Caglar H, Atasoy BM,
Abdulloev T, Akgun Z and Kilic T: Gamma knife radiosurgery in non
small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: Treatment
results and prognostic factors. J BUON. 15:274–280. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu PJ, Chen WG, Feng QL, Chen W, Jiang MJ
and Li ZQ: Association between CYP1B1 gene polymorphisms and risk
factors and susceptibility to laryngeal cancer. Med Sci Monit.
21:239–245. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gass K, Klein M, Sarnat SE, Winquist A,
Darrow LA, Flanders WD, Chang HH, Mulholland JA, Tolbert PE and
Strickland MJ: Associations between ambient air pollutant mixtures
and pediatric asthma emergency department visits in three cities: A
classification and regression tree approach. Environ Health.
14:582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rovlias A, Theodoropoulos S and
Papoutsakis D: Chronic subdural hematoma: Surgical management and
outcome in 986 cases: A classification and regression tree
approach. Surg Neurol Int. 6:1272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kong DS, Lee JI, Nam DH and Park K, Kim
JH, Kim JG, Park JO and Park K: Prognosis of non-small cell lung
cancer with synchronous brain metastases treated with gamma knife
radiosurgery. J Korean Med Sci. 21:527–532. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ebert BL, Niemierko E, Shaffe K and Salgia
R: Use of temozolomide with other cytotoxic chemotherapy in the
treatment of patients with recurrent brain metastases from lung
cancer. Oncologist. 8:69–75. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arrieta O, Villarreal-Garza C, Zamora J,
Blake-Cerda M, de la Mata MD, Zavala DG, Muñiz-Hernández S and de
la Garza J: Long-term survival in patients with non-small cell lung
cancer and synchronous brain metastasis treated with whole-brain
radiotherapy and thoracic chemoradiation. Radiat Oncol. 6:1662011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma S, Xu Y, Deng Q and Yu X: Treatment of
brain metastasis from non-small cell lung with whole brain
radiotherapy and gefitinib in a Chinese population. Lung Cancer.
65:198–203. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lock M, Chow E, Pond GR, Do V, Danjoux C,
Dinniwell R, Lea J and Bezjak A: Prognostic factors in brain
metastases: Can we determine patients who do not benefit from
whole-brain radiotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 16:332–338.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiang Z, Chen J, Zhang H, Shen L and Wei
Q: Whole brain radiotherapy-based combined modality treatment of
brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective
analysis of prognostic factors. Oncol Res Treat. 38:35–40. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S,
Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG and Byhardt R: Recursive
partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three
radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) brain metastases trials.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 37:745–51. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gaspar LE, Scott C, Murray K and Curran W:
Validation of the RTOG recursive partitioning analysis (RPA)
classification for brain metastases. Int J Radiation Oncol Biol
Phys. 47:1001–1006. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gerosa M, Nicolato A, Foroni R, Tomazzoli
L and Bricolo A: Analysis of long-term outcomes and prognostic
factors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer brain
metastases treated by gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg.
102(Suppl): 75–80. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zindler JD, Rodrigues G, Haasbeek CJ, De
Haan PF, Meijer OW, Slotman BJ and Lagerwaard FJ: The clinical
utility of prognostic scoring systems in patients with brain
metastases treated with radiosurgery. Radiother Oncol. 106:370–374.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rotin DL, Paklina OV, Kobiakov GL,
Shishkina LV, Kravchenko ÉV and Stepanian MA: Lung cancer
metastases to the brain: Clinical and morphological prognostic
factors. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 77:24–28. 2013.(In
Russian), discussion 29. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rades D, Schild SE, Lohynska R, Veninga T,
Stalpers LJ and Dunst J: Two radiation regimens and prognostic
factors for brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer
patients. Cancer. 110:1077–1082. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fiala O, Pessek M, Finek J, Benesova L,
MinariK M, Bortlicek Z and Topolcan O: Predictive role of CEA and
CYFRA21-1 in patients with advanced-stage NSCLC treated with
erlotinib. Anticancer Res. 34:3205–3210. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schilling C, Mortimer D, Dalziel K, Heeley
E, Chalmers J and Clarke P: Using Classification and Regression
Trees (CART) to identify prescribing thresholds for cardiovascular
disease. Pharmacoeconomics. Nov 17–2015.(Epub ahead of print).
|