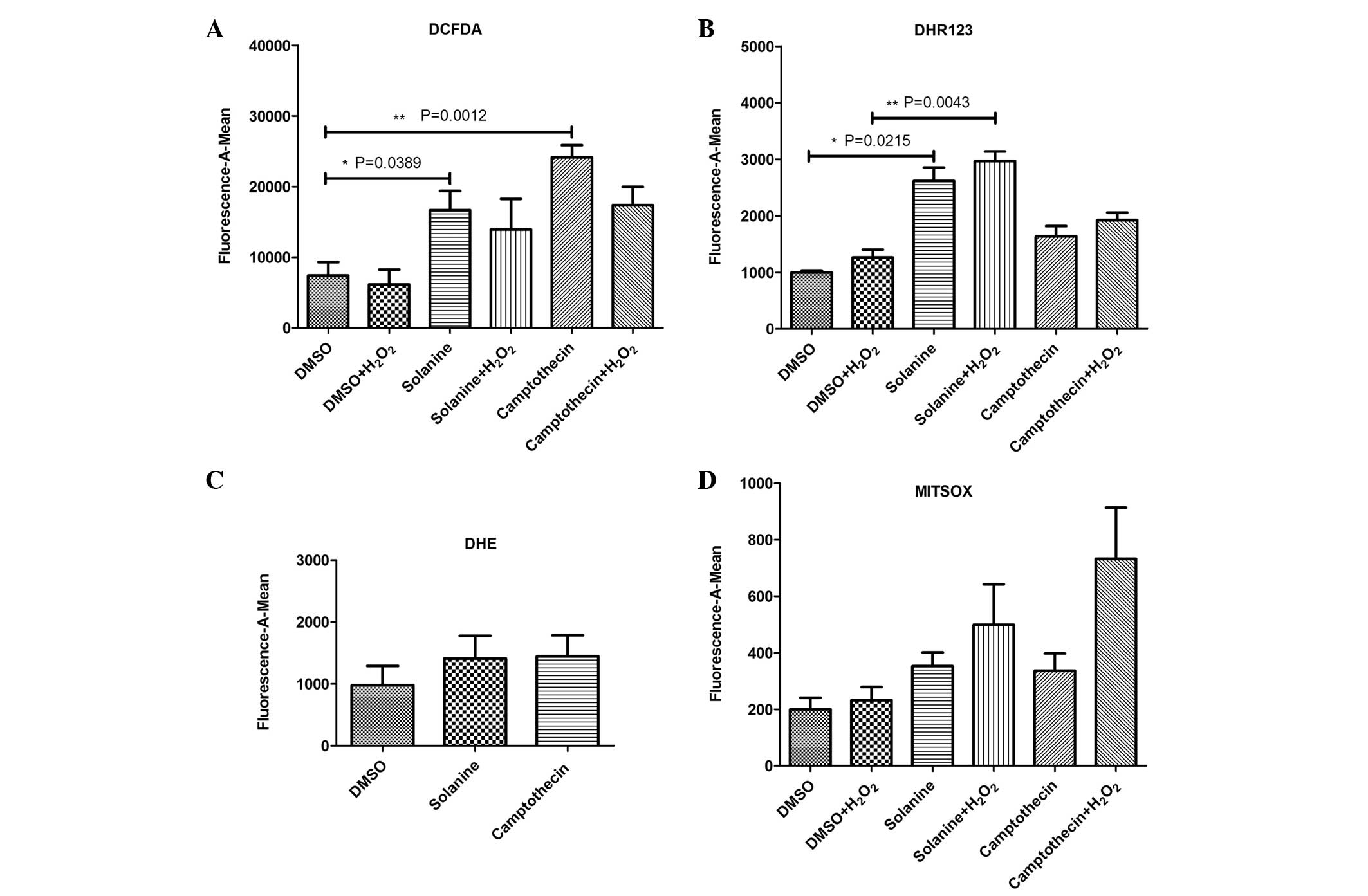
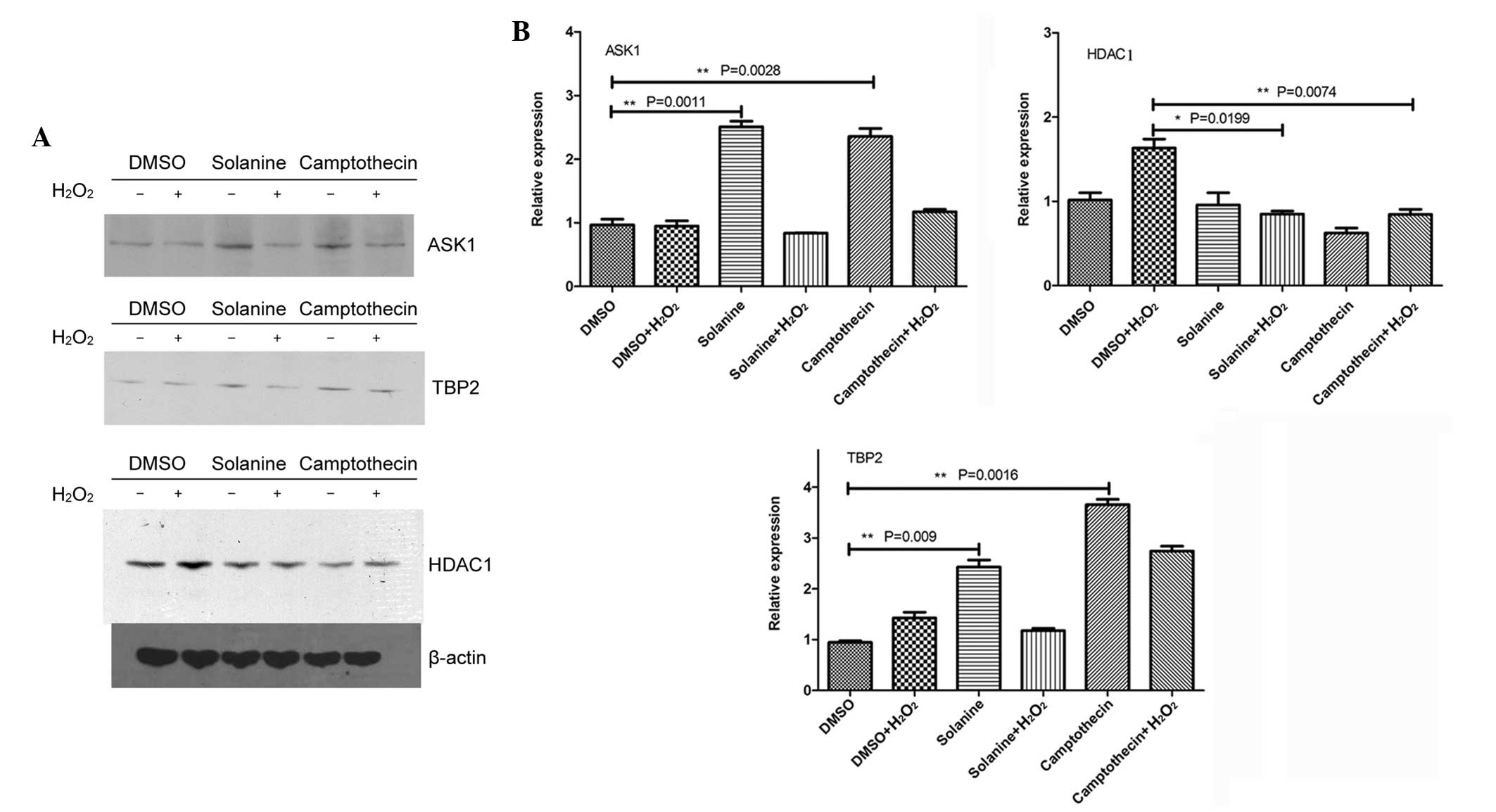
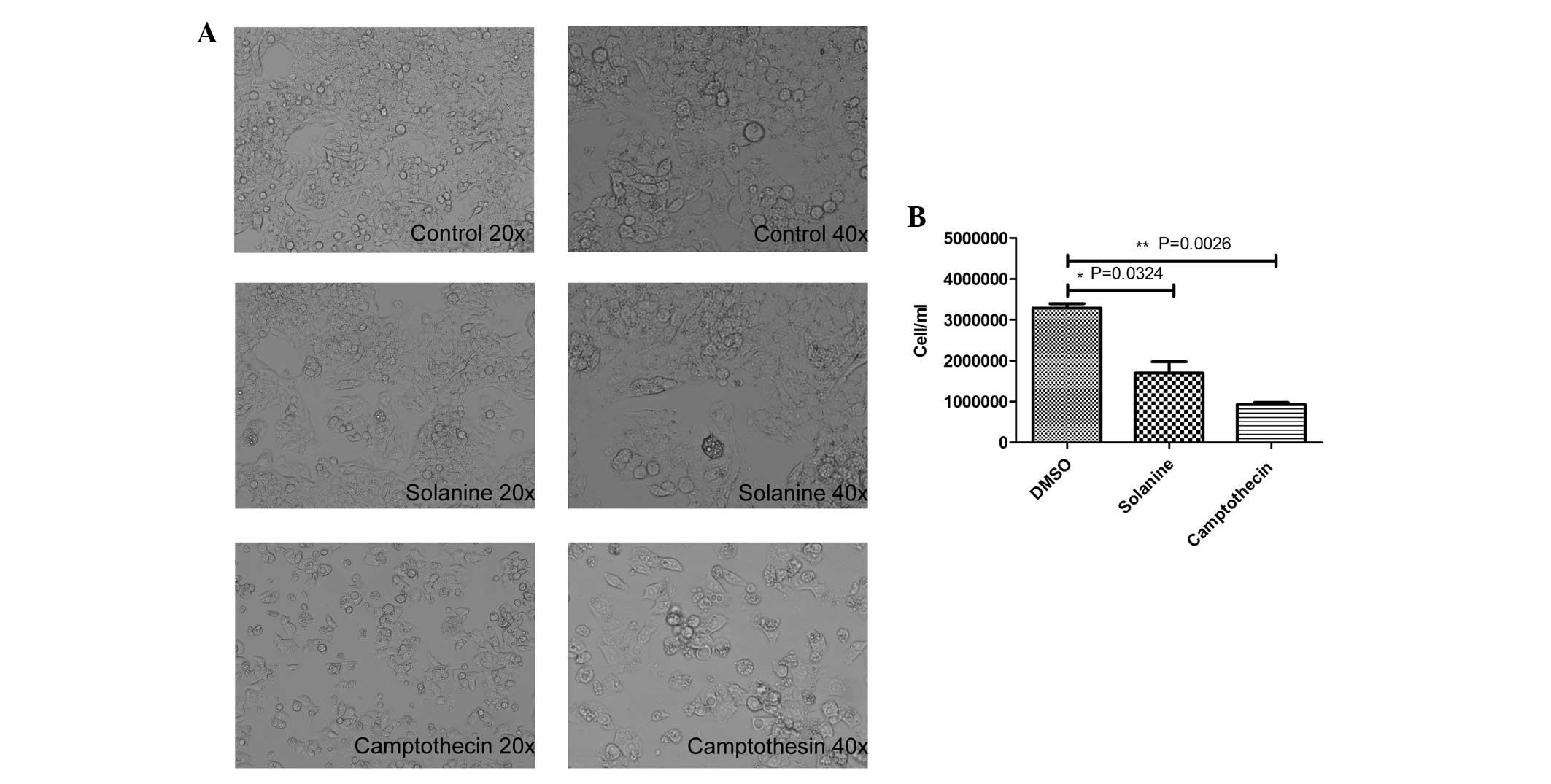
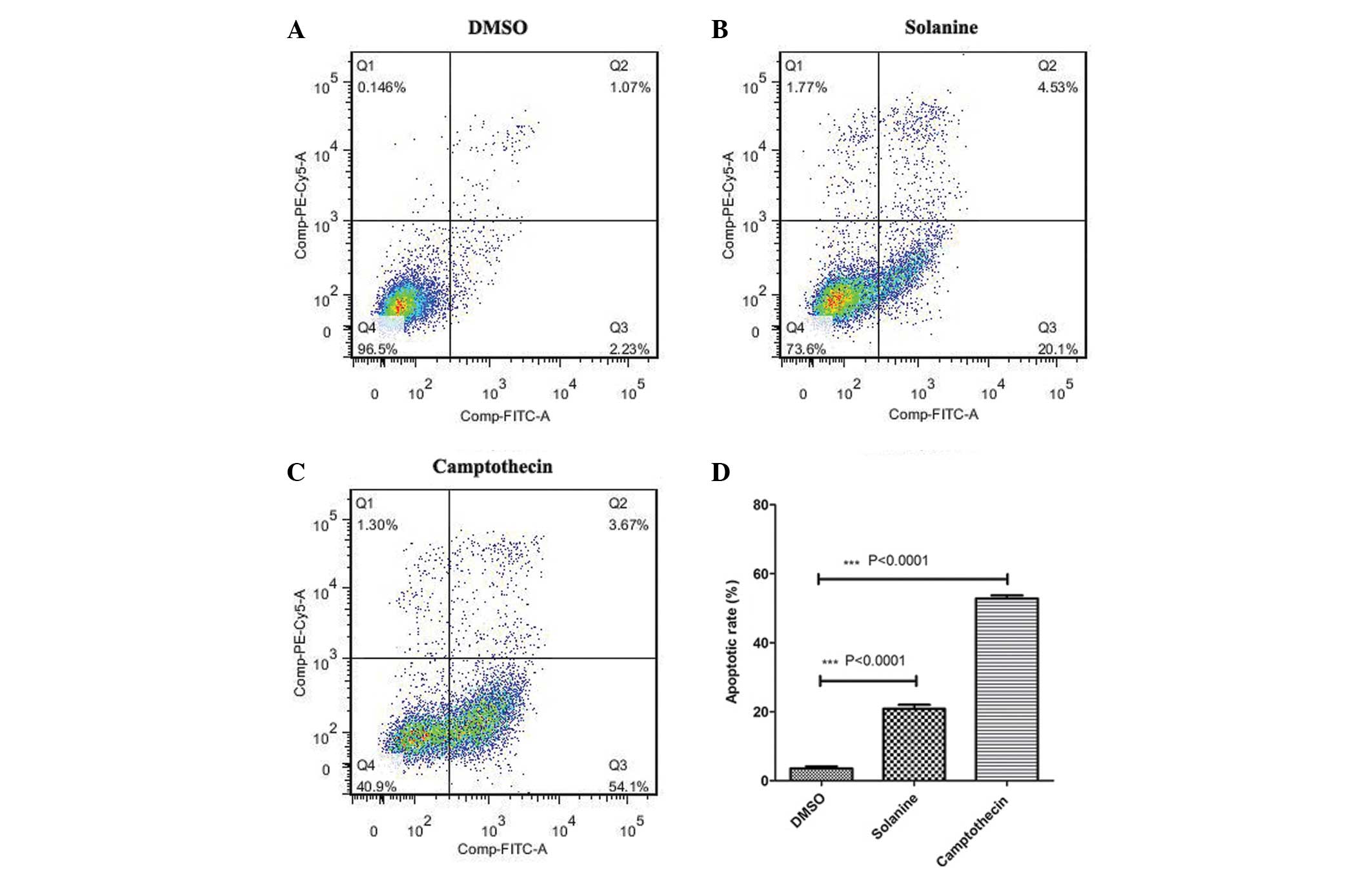
|
1
|
Shariff MI, Cox IJ, Gomaa AI, Khan SA,
Gedroyc W and Taylor-Robinson SD: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current
trends in worldwide epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and
therapeutics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:353–367. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA and Reichman ME:
Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends
in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 27:1485–1491.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rampone B, Schiavone B, Martino A, Viviano
C and Confuorto G: Current management strategy of hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 15:3210–3216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stefaniuk P, Cianciara J and
Wiercinska-Drapalo A: Present and future possibilities for early
diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
16:418–424. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang X, Wang N, Cheung F, Lao L, Li C and
Feng Y: Chinese medicines for prevention and treatment of human
hepatocellular carcinoma: Current progress on pharmacological
actions and mechanisms. J Integr Med. 13:142–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kodamatani H, Saito K, Niina N, Yamazaki S
and Tanaka Y: Simple and sensitive method for determination of
glycoalkaloids in potato tubers by high-performance liquid
chromatography with chemiluminescence detection. J Chromatogr A.
1100:26–31. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Friedman M: Potato glycoalkaloids and
metabolites: Roles in the plant and in the diet. J Agric Food Chem.
54:8655–8681. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bodart P and Noirfalise A: Glycoalkaloids
in potatoes. Rev Med Liege. 58:25–32. 2003.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shindo T, Ushiyama H, Kan K, Yasuda K and
Saito K: Contents and its change during storage of alpha-solanine
and alpha-chaconine in potatoes. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi.
45:277–282. 2004.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zywicki B, Catchpole G, Draper J and Fiehn
O: Comparison of rapid liquid chromatography-electrospray
ionization-tandem mass spectrometry methods for determination of
glycoalkaloids in transgenic field-grown potatoes. Anal Biochem.
336:178–186. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Korpan YI, Nazarenko EA, Skryshevskaya IV,
Martelet C, Jaffrezic-Renault N and El'skaya AV: Potato
glycoalkaloids: True safety or false sense of security? Trends
Biotechnol. 22:147–151. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Glossman-Mitnik D: CHIH-DFT determination
of the molecular structure and infrared and ultraviolet spectra of
gamma-solanine. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc.
66:208–211. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stobiecki M, Matysiak-Kata I, Frański R,
Skała J and Szopa J: Monitoring changes in anthocyanin and steroid
alkaloid glycoside content in lines of transgenic potato plants
using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry.
62:959–969. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang S, Panter KE, Gaffield W, Evans RC
and Bunch TD: Effects of steroidal glycoalkaloids from potatoes
(Solanum tuberosum) on in vitro bovine embryo development.
Anim Reprod Sci. 85:243–250. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ji YB: Antitumor effects in traditional
Chinese medicine. Pharmacological Action, Application of Available
Composition of Traditional Chinese Medicine (1st). (Harbin,
Heilongjiang). Heilongjiang Science and Technology Press.
4331995.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Son YO, Kim J, Lim JC, Chung Y, Chung GH
and Lee JC: Ripe fruit of Solanum nigrum L. inhibits cell
growth and induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. Food Chem Toxicol.
41:1421–1428. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
An L, Tang JT, Liu XM and Gao NN: Research
progress on mechanism of anti-tumor effect of Solanum
nigrum. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 31:1225–1226. 2006.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ji YB, Gao SY, Ji CF and Zou X: Induction
of apoptosis in HepG2 cells by solanine and Bcl-2 protein. J
Ethnopharmacol. 115:194–202. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Macho A, Hirsch T, Marzo I, Marchetti P,
Dallaporta B, Susin SA, Zamzami N and Kroemer G: Glutathione
depletion is an early and calcium elevation is a late event of
thymocyte apoptosis. J Immunol. 158:4612–4619. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao SY, Wang QJ and Ji YB: Effect of
solanine on the membrane potential of mitochondria in HepG2 cells
and [Ca2+]i in the cells. WorId J Gastroenterol. 12:3359–3367.
2006.
|
|
21
|
Eom KS, Kim HJ, So HS, Park R and Kim TY:
Berberine-induced apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G cells is
mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress accompanying reactive
oxygen species and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biol Pharm Bull.
33:1644–1649. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB and Sil PC:
Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and
mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol.
87:1157–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hashiguchi K, Tsuchiya H, Tomita A, Ueda
C, Akechi Y, Sakabe T, Kurimasa A, Nozaki M, Yamada T, Tsuchida S
and Shiota G: Involvement of ETS1 in thioredoxin-binding protein 2
transcription induced by a synthetic retinoid CD437 in human
osteosarcoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 391:621–626. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bouchain G and Delorme D: Novel
hydroxamate and anilide derivatives as potent histone deacetylase
inhibitors: Synthesis and antiproliferative evaluation. Curr Med
Chem. 10:2359–2372. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Phi DK, Mühlbauer E and Phi-van L:
Histone deacetylase HDAC1 downregulates transcription of the
serotonin transporter (5-HTT) gene in tumor cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1849:909–918. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee WL, Huang JY and Shyur LF: Phytoagents
for cancer management: Regulation of nucleic acid oxidation, ROS
and related mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:9258042013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zou Y, Yang J, Liu X and Yuan J:
Relationship between reactive oxygen species and apoptosis in HepG2
cells induced by sodium selenite. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 36:272–274.
2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu XD, Jin ZX, Wan CL and Jin R: Effect of
herba agrimoniae in apoptosis of human hepatoma cell line HepG2
cells research. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yao Zi Xun. 2:82010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Chen WQ, Shen W and Shen DM: The changes
of ROS and mitochondria membrane potential in HepG2 cells on the
pressure of cisplatin. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 13:531–533.
2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu YZ, Dong YG, Zhai YF, Lu JH, Wu MX,
Zhou Y and He ZY: Effect of simvastatin on homocysteine - induced
endothelial dysfunction and inflammatory response and its molecular
mechanisms. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 8:1594–1598. 2005.(In
Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Djordjević VB: Free radicals in cell
biology. Int Rev Cytol. 237:57–89. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Closa D and Folch-Puy E: Oxygen free
radicals and the systemic inflammatory response. IUBMB Life.
56:185–191. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao XQ: Solanum nigrum compound
syrup-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in murine I-122 mechanism.
Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi. 9:974–975. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Lu MK, Shih YW, Chien Chang TT, Fang LH,
Huang HC and Chen PS: α-Solanine inhibits human melanoma cell
migration and invasion by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-2/9
activities. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:1685–1691. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lu MK, Chen PH, Shih YW, Chang YT, Huang
ET, Liu CR and Chen PS: Alpha-chaconine inhibits angiogenesis in
vitro by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-2. Biol Pharm Bull.
33:622–630. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lépine S, Sulpice JC and Giraud F:
Signaling pathways involved in glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of
thymocytes. Crit Rev Immunol. 25:263–288. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tang B, Du J, Wang J, Tan G, Gao Z, Wang Z
and Wang L: Alpinetin suppresses proliferation of human hepatoma
cells by the activation of MKK7 and elevates sensitization to
cis-diammined dichloridoplatium. Oncol Rep. 27:1090–1096.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Al-Qubaisi M, Rozita R, Yeap SK, Omar AR,
Ali AM and Alitheen NB: Selective cytotoxicity of goniothalamin
against hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells. Molecules. 16:2944–2959. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|