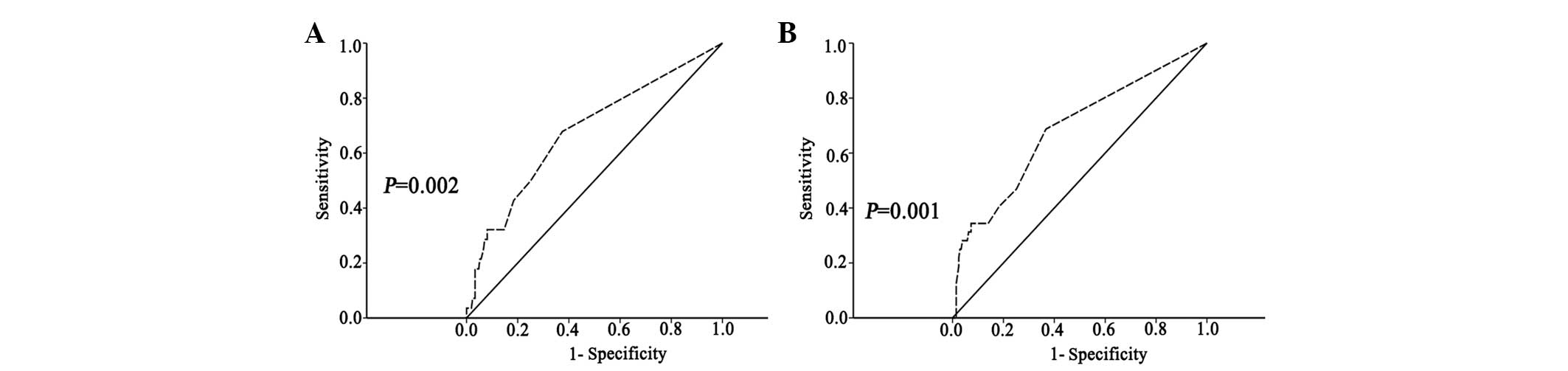
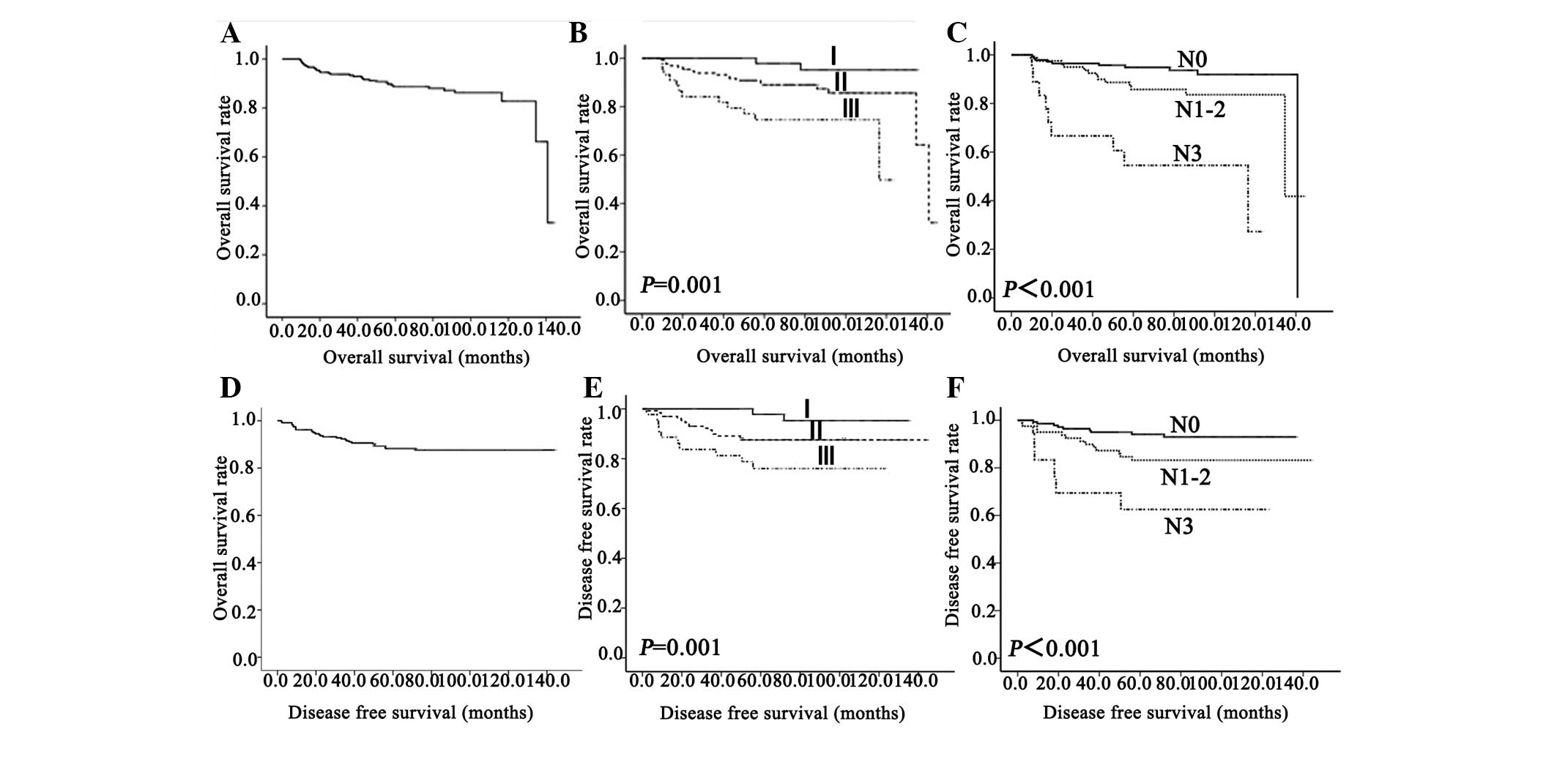
|
1
|
Alkis N, Durnali AG, Arslan UY, Kocer M,
Onder FO, Tokluoglu S, Celenkoglu G, Muallaoglu S, Utkan G, Ulas A,
et al: Optimal timing of adjuvant treatment in patients with early
breast cancer. Med Oncol. 28:1255–1259. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ono M, Tsuda H, Shimizu C, Yamamoto S,
Shibata T, Yamamoto H, Hirata T, Yonemori K, Ando M, Tamura K, et
al: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are correlated with response to
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 132:793–805. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abd El-Rehim DM, Pinder SE, Paish CE, Bell
J, Blamey RW, Robertson JF, Nicholson RI and Ellis IO: Expression
of luminal and basal cytokeratins in human breast carcinoma. J
Pathol. 203:661–671. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler
LG, Cowan D, Conway K, Karaca G, Troester MA, Tse CK, Edmiston S,
et al: Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina
Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 295:2492–2502. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M,
Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler
L, et al: Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the
basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5367–5374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Prat A and Perou CM: Deconstructing the
molecular portraits of breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 5:5–23. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dawson SJ, Provenzano E and Caldas C:
Triple negative breast cancers: Clinical and prognostic
implications. Eur J Cancer. 45(Suppl 1): 27–40. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bauer KR, Brown M, Cress RD, Parise CA and
Caggiano V: Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor
(ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and
HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative
phenotype: A population-based study from the California cancer
Registry. Cancer. 109:1721–1728. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Irvin WJ Jr and Carey LA: What is
triple-negative breast cancer? Eur J Cancer. 44:2799–2805. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pal SK, Childs BH and Pegram M: Triple
negative breast cancer: Unmet medical needs. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 125:627–636. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Metzger-Filho O, Tutt A, de Azambuja E,
Saini KS, Viale G, Loi S, Bradbury I, Bliss JM, Azim HA Jr, Ellis
P, et al: Dissecting the heterogeneity of triple-negative breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 30:1879–1887. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gucalp A and Traina TA: Triple-negative
breast cancer: Adjuvant therapeutic options. Chemother Res Pract.
2011:6962082011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Laurentiis M, Cianniello D, Caputo R,
Stanzione B, Arpino G, Cinieri S, Lorusso V and De Placido S:
Treatment of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC): Current options
and future perspectives. Cancer Treat Rev. 36(Suppl 3): S80–S86.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Silver DP, Richardson AL, Eklund AC, Wang
ZC, Szallasi Z, Li Q, Juul N, Leong CO, Calogrias D, Buraimoh A, et
al: Efficacy of neoadjuvant Cisplatin in triple-negative breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:1145–1153. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH,
Robertson JF and Ellis IO: Prognostic markers in triple-negative
breast cancer. Cancer. 109:25–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Calza S, Hall P, Auer G, Bjöhle J, Klaar
S, Kronenwett U, Liu ET, Miller L, Ploner A, Smeds J, et al:
Intrinsic molecular signature of breast cancer in a
population-based cohort of 412 patients. Breast Cancer Res.
8:R342006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mersin H, Yildirim E, Berberoglu U and
Gülben K: The prognostic importance of triple negative breast
carcinoma. Breast. 17:341–346. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Sarrió D, Honrado E,
Hardisson D, Calero F, Benitez J and Palacios J: Prognostic
significance of basal-like phenotype and fascin expression in
node-negative invasive breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res.
12:1533–1539. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Sarrió D, Honrado E,
Moreno-Bueno G, Hardisson D, Calero F, Benítez J and Palacios J:
Vimentin and laminin expression is associated with basal-like
phenotype in both sporadic and BRCA1-associated breast carcinomas.
J Clin Pathol. 60:1006–1012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reis-Filho JS, Milanezi F, Steele D,
Savage K, Simpson PT, Nesland JM, Pereira EM, Lakhani SR and
Schmitt FC: Metaplastic breast carcinomas are basal-like tumours.
Histopathology. 49:10–21. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abdulkarim BS, Cuartero J, Hanson J,
Deschênes J, Lesniak D and Sabri S: Increased risk of locoregional
recurrence for women with T1-2N0 triple-negative breast cancer
treated with modified radical mastectomy without adjuvant radiation
therapy compared with breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol.
29:2852–2858. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hernandez-Aya LF, Chavez-Macgregor M, Lei
X, Meric-Bernstam F, Buchholz TA, Hsu L, Sahin AA, Do KA, Valero V,
Hortobagyi GN, et al: Nodal status and clinical outcomes in a large
cohort of patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 29:2628–2634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu
W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL and Massagué J: Genes
that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature. 436:518–524.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bertucci F, Finetti P, Cervera N,
Charafe-Jauffret E, Mamessier E, Adélaïde J, Debono S, Houvenaeghel
G, Maraninchi D, Viens P, et al: Gene expression profiling shows
medullary breast cancer is a subgroup of basal breast cancers.
Cancer Res. 66:4636–4644. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fadare O, Wang SA and Hileeto D: The
expression of cytokeratin 5/6 in invasive lobular carcinoma of the
breast: Evidence of a basal-like subset? Hum Pathol. 39:331–336.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oakman C, Viale G and Di Leo A: Management
of triple negative breast cancer. Breast. 19:312–321. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sihto H, Lundin J, Lundin M, Lehtimäki T,
Ristimäki A, Holli K, Sailas L, Kataja V, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T,
Isola J, et al: Breast cancer biological subtypes and protein
expression predict for the preferential distant metastasis sites: A
nationwide cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 13:R872011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang
MC, Voduc D, Speers CH, Nielsen TO and Gelmon K: Metastatic
behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 28:3271–3277.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Colleoni M, Cole BF, Viale G, Regan MM,
Price KN, Maiorano E, Mastropasqua MG, Crivellari D, Gelber RD,
Goldhirsch A, et al: Classical cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and
fluorouracil chemotherapy is more effective in triple-negative,
node-negative breast cancer: Results from two randomized trials of
adjuvant chemoendocrine therapy for node-negative breast cancer. J
Clin Oncol. 28:2966–2973. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cheang MC, Voduc KD, Tu D, Jiang S, Leung
S, Chia SK, Shepherd LE, Levine MN, Pritchard KI, Davies S, et al:
Responsiveness of intrinsic subtypes to adjuvant anthracycline
substitution in the NCIC.CTG MA.5 randomized trial. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:2402–2412. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hugh J, Hanson J, Cheang MC, Nielsen TO,
Perou CM, Dumontet C, Reed J, Krajewska M, Treilleux I, Rupin M, et
al: Breast cancer subtypes and response to docetaxel in
node-positive breast cancer: Use of an immunohistochemical
definition in the BCIRG 001 trial. J Clin Oncol. 27:1168–1176.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bhatti AB, Khan AI, Siddiqui N, Muzaffar
N, Syed AA, Shah MA and Jamshed A: Outcomes of triple-negative
versus non-triple-negative breast cancers managed with
breast-conserving therapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2577–2581.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T,
Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, Harris L, Hait W and Toppmeyer D:
Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively
managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
24:5652–5657. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang L, Hao C, Dong G and Tong Z:
Analysis of Clinical Features and Outcome of 356 Triple-Negative
Breast Cancer Patients in China. Breast Care (Basel). 7:13–17.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tischkowitz M, Brunet JS, Bégin LR,
Huntsman DG, Cheang MC, Akslen LA, Nielsen TO and Foulkes WD: Use
of immunohistochemical markers can refine prognosis in triple
negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 7:1342007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kandel MJ, Stadler Z, Masciari S, Collins
L, Schnitt S, Harris L, Miron A, Richardson A and Garber JE:
Prevalence of BRCA1 mutations in triple negative breast cancer
(BC). J Clin Oncol. 24(Suppl 18): 5082006.
|
|
40
|
Carey LA, Dees EC, Sawyer L, Gatti L,
Moore DT, Collichio F, Ollila DW, Sartor CI, Graham ML and Perou
CM: The triple negative paradox: Primary tumor chemosensitivity of
breast cancer subtypes. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2329–2334. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kaplan HG, Malmgren JA and Atwood M: T1N0
triple negative breast cancer: Risk of recurrence and adjuvant
chemotherapy. Breast J. 15:454–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|