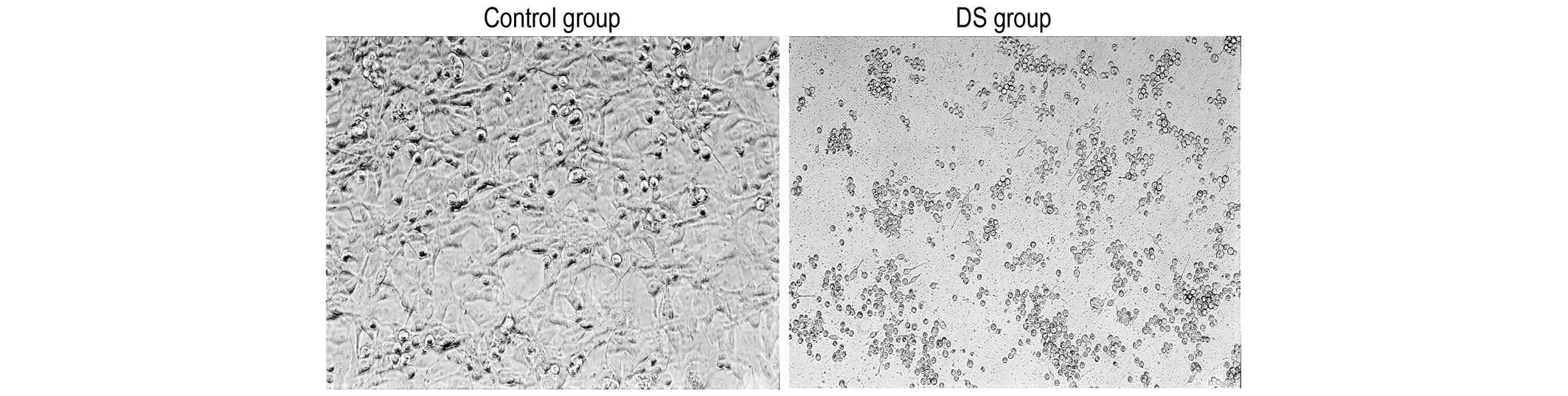
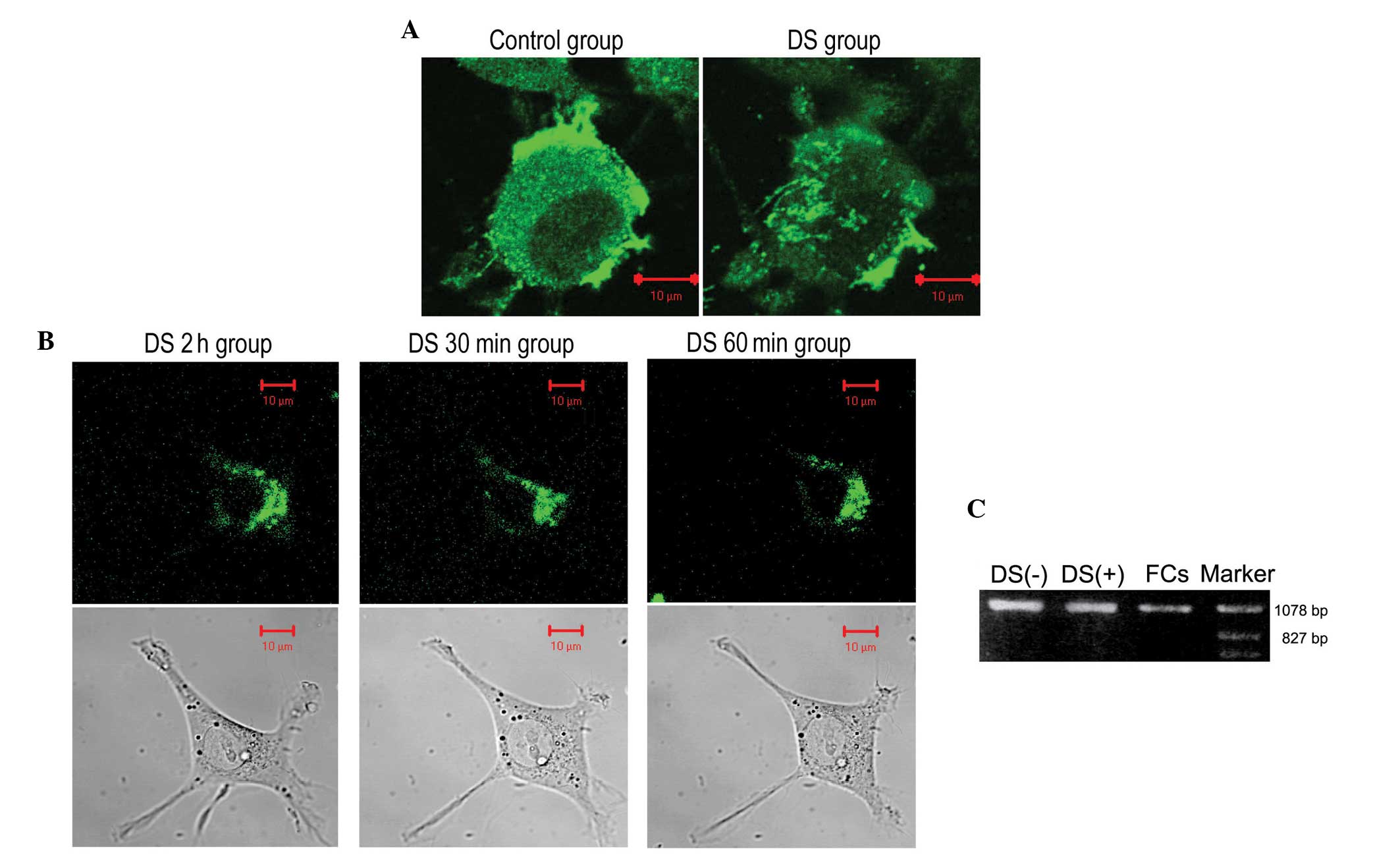
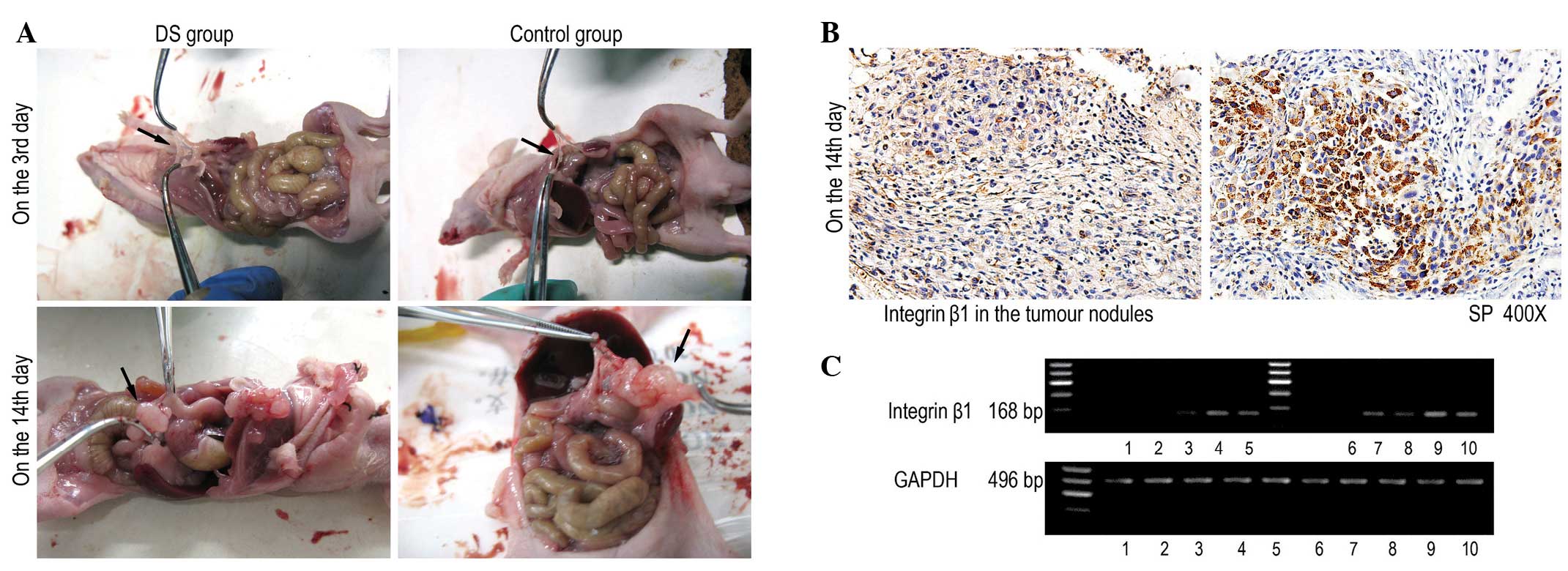
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang J, Yu JC, Kang WM and Ma ZQ:
Treatment strategy for early gastric cancer. Surg Oncol.
21:119–123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu Y: Gastric cancer. Surgery. Wang X and
Wang J: 8:People's Health Publication. (Beijing). 360–365.
2014.
|
|
4
|
Wang Z and Chen L: Present status of
treatment in peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer. Zhonghua Wei
Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 18:194–197. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Broll R, Weschta M, Windhoevel U, Berndt
S, Schwandner O, Roblick U, Schiedeck TH, Schimmelpenning H, Bruch
HP and Duchrow M: Prognostic significance of free gastrointestinal
tumor cells in peritoneal lavage detected by immunocytochemistry
and polymerase chain reaction. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 386:285–292.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maehara Y, Hasuda S, Koga T, Tokunaga E,
Kakeji Y and Sugimache K: Postoperative outcome and sites of
recurrence in patients following curative resection of gastric
cancer. Br J Surg. 87:353–357. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yonemura Y, Bandou E, Kawamura T, Endou Y
and Sasaki T: Quantitative prognostic indicators of peritoneal
dissemination of gastric cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 32:602–606.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Orr AW, Ginsberg MH, Shattil SJ, Deckmyn H
and Schwartz MA: Matrix-specific suppression of integrin activation
in shear stress signalling. Mol Biol Cell. 17:4686–4697. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Niu G and Chen X: Why integrin as a
primary target for imaging and therapy. Theranostics. 1:30–47.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hagiwara A, Sawai K, Sakakura C, Shirasu
M, Ohgaki M, Imanishi T, Yamasaki J, Togawa T and Takahashi T:
Prevention of peritoneal metastasis of cancer with dextran
sulfate-an experimental study in mice. Anticancer Drugs. 8:894–897.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chervoneva I, Li Y, Schulz S, Croker S,
Wilson C, Waldman SA and Hyslop T: Selection of optimal reference
genes for normalization in quantitative RT-PCR. BMC Bioinformatics.
11:2532010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pasechnikov V, Chukov S, Fedorov E,
Kikuste I and Leja M: Gastric cancer: Prevention, screening and
early diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:13842–13862. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh SR: Gastric cancer stem cells: A
novel therapeutic target. Cancer Lett. 338:110–119. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Humphries MJ: Integrin structure. Biochem
Soc Trans. 28:311–339. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Trepet X, Chen Z and Jacobson K: Cell
Migration. Compr Physiol. 2:2369–2392. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Giancotti FG and Ruoslahli E: Integrin
signalling. Science. 285:1028–1032. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zamir E, Katz M, Posen Y, Erez N, Yamada
KM, Katz BZ, Lin S, Lin DC, Bershadsky A, Kam Z and Geiger B:
Dynamics and segregation of cell matrix adhesions in cultured
fibroblasts. Nat Cell Biol. 2:191–196. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yano H, Mazaki Y, Kurokawa K, Hanks SK,
Matsuda M and Sabe H: Roles played by a subset of integrin
signaling molecules in cadherin-based cell-cell adhesion. J Cell
Biol. 166:283–295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Janssen M, Frielink C, Dijkgraf I, Oyen W,
Edwards DS, Liu S, Rajopadhye M, Massuger L, Corstens F and Boerman
O: Improved tumor targeting of radiolabeled RGD peptides using
rapid does fractionation. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 19:399–404.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lynch L, Vodyanik PI, Boettiger D and
Guvakova MA: Insulin-like growth factor I controls adhesion
strength mediated by alpha5 beta l integrins in motile carcinoma
cells. Mol Biol Cell. 16:51–63. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Howe GA and Addison C: β1 integrin: An
emerging player in the modulation of tumorigenesis and response to
therapy. Cell Adh Migr. 6:71–77. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|