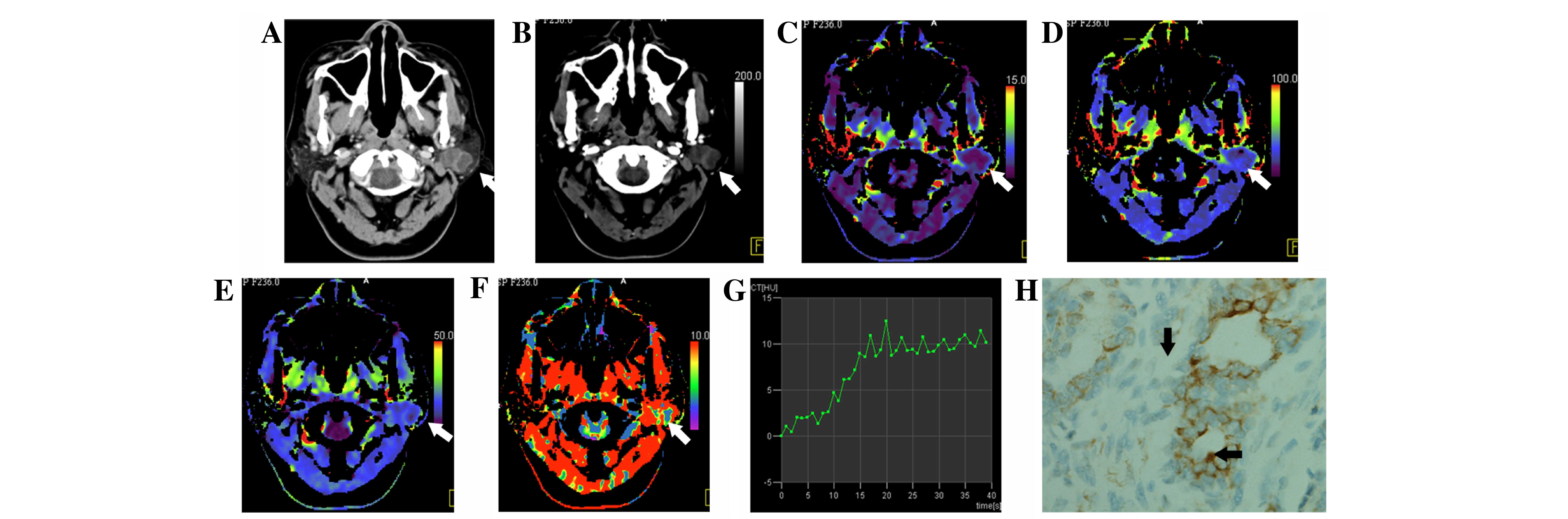
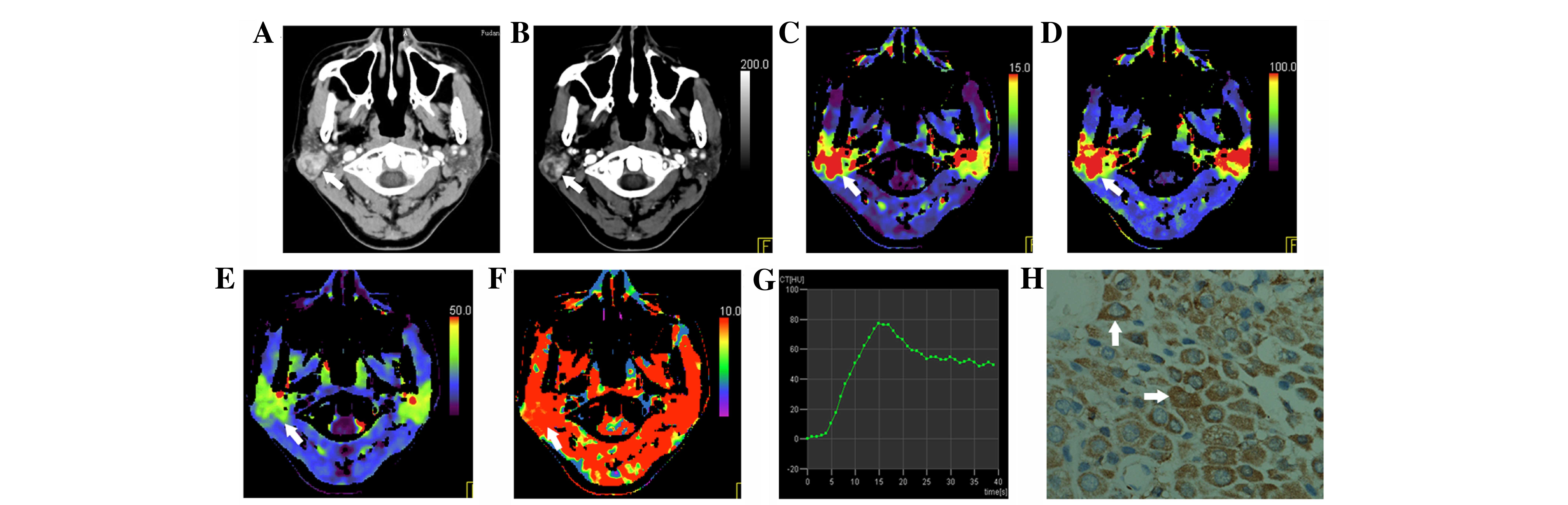
|
1
|
Lee TY, Purdie TG and Stewart E: CT
imaging of angiogenesis. Q J Nucl Med. 47:171–187. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li C, Fan J, Song X, Zhang B, Chen Y, Li
C, Mi K, Ma H, Song Y, Tao X and Li G: Expression of angiopoietin-2
and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 correlates with
lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis and affects survival of oral
squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e753882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dai W, Li Y, Zhou Q, Xu Z, Sun C, Tan X
and Lu L: Cetuximab inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma invasion
and metastasis via degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor.
J Oral Pathol Med. 43:250–257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
de Oliveira MV, Pereira Gomes EP, Pereira
CS, de Souza LR, Barros LO, Mendes DC, Guimarães AL and De Paula
AM: Prognostic value of microvessel density and p53 expression on
the locoregional metastasis and survival of the patients with head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol.
21:444–451. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen TW, Yang ZG, Chen HJ, Li Y, Tang SS,
Yao J, Dong ZH and He D: Quantitative assessment of first-pass s
using a low-dose method at multidetector CT in oesophageal squamous
cell carcinoma: Correlation with VEGF expression. Clin Radiol.
67:746–753. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ling S, Deng D, Mo Y, Zhang X, Guan X and
Wei Q: Correlations between CT perfusion parameters and vascular
endothelial growth factor expression and microvessel density in
implanted VX2 lung tumors. Cell Biochem Biophys. 70:629–633. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Choi JY, Jang KT, Shim YM, Kim K, Ahn G,
Lee KH, Choi Y, Choe YS and Kim BT: Prognostic significance of
vascular endothelial growth factor expression and microvessel
density in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Comparison with
positron emission tomography. Ann Surg Oncol. 13:1054–1062. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kleespies A, Guba M, Jauch KW and Bruns
CJ: Vascular endothelial growth factor in esophageal cancer. J Surg
Oncol. 87:95–104. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meijerink MR, van Waesberghe JH, van der
Weide L, van den Tol P, Meijer S and van Kuijk C:
Total-liver-volume perfusion CT using 3-D image fusion to improve
detection and characterization of liver metastases. Eur Radiol.
18:2345–2354. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yi CA, Lee KS, Kim EA, Han J, Kim H, Kwon
OJ, Jeong YJ and Kim S: Solitary pulmonary nodules: Dynamic
enhanced multi-detector row CT study and comparison with vascular
endothelial growth factor and microvessel density. Radiology.
233:191–199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Trojanowska A, Trojanowski P, Drop A,
Jargiełło T and Klatka J: Head and neck cancer: Value of perfusion
CT in depicting primary tumor spread. Med Sci Monit.
18:CR112–CR118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miles KA: Tumour angiogenesis and its
relation to contrast enhancement on computed tomography: A review.
Eur J Radiol. 30:198–205. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bisdas S, Baghi M, Wagenblast J, Knecht R,
Thng CH, Koh TS and Vogl TJ: Differentiation of benign and
malignant parotid tumours using deconvolution-based perfusion CT
imaging: Feasibility of the method and initial results. Eur J
Radiol. 64:258–265. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
George ML, Dzik-Jurasz AS, Padhani AR,
Brown G, Tait DM, Eccles SA and Swift RI: Non-invasive methods of
assessing angiogenesis and their value in predicting response to
treatment in colorectal cancer. Br J Surg. 88:1628–1636. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Hamberg LM, Hahn PF,
Willett CG, Saini S, Mueller PR and Lee TY: Assessing tumour
perfusion and treatment response in rectal cancer with multisection
CT: Initial observations. Radiology. 234:785–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rumboldt Z, Al-Okaili R and Deveikis JP:
Perfusion CT for head and neck tumours: Pilot study. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 26:1178–1185. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang ZY, Meng QF, Xu QL, Li SR, Yan CG,
Xie HB, Yang XF, Peng Q and Lai YR: Correlation between CT
perfusion and vascular endothelial growth factor in neoplasm of
head and neck. Zhonghua Fang She Xue Za Zhi. 41:900–906. 2007.(In
Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Schmid-Tannwald C, Thomas S, Ivancevic MK,
Dahi F, Rist C, Sethi I and Oto A: Diffusion-weighted MRI of
metastatic liver lesions: Is there a difference between
hypervascular and hypovascular metastases? Acta Radiol. 55:515–523.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Spira D, Neumeister H, Spira SM, Hetzel J,
Spengler W and von Weyhern CH: Assessment of tumor vascularity in
lung cancer using volume perfusion CT (VPCT) with histopathologic
comparison: A further step toward an individualized tumor
characterization. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 37:15–21. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reiner CS, Roessle M, Thiesler T, Eberli
D, Klotz E and Frauenfelder T: Computed tomography perfusion
imaging of renal cell carcinoma: Systematic comparison with
histopathological angiogenic and prognostic markers. Invest Radiol.
48:183–191. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
d'Assignies G, Couvelard A, Bahrami S,
Vullierme MP, Hammel P, Hentic O, Sauvanet A, Bedossa P,
Ruszniewski P and Vilgrain V: Pancreatic endocrine tumours: Tumour
blood flow assessed with perfusion CT reflects angiogenesis and
correlates with prognostic factors. Radiology. 250:407–416. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Volm M, Koomägi R and Mattern J:
Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor and its
receptor Flt-1 in squamous cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
74:64–68. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dong Y, Lei GW, Wang SW, Zheng SW, Ge Y
and Wei FC: Diagnostic value of CT perfusion imaging for parotid
lesions. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 43:201302372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Woo SH, Choi DS, Kim JP, Park JJ, Joo YH,
Chung PS, Kim BY, Ko YH, Jeong HS and Kim HJ: Two-phase computed
tomography study of warthin tumor of parotid gland: Differentiation
from other parotid gland tumors and its pathologic explanation. J
Comput Assist Tomogr. 37:518–524. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
O'Byrne KJ, Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki
A, Cox G, Turley H, Steward WP, Gatter K and Harris AL: Vascular
endothelial growth factor, platelet-derived endothelial cell growth
factor and angiogenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer.
82:1427–1432. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ng QS, Goh V, Milner J, Stratford MR,
Folkes LK, Tozer GM, Saunders MI and Hoskin PJ: Effect of nitric
oxide synthesis on tumour blood volume and vascular activity: A
phase I study. Lancet Oncol. 8:111–118. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Wang R, Lou H, Zou Y and Zhang M:
Functional computed tomographic quantification of angiogenesis in
rabbit VX2 soft-tissue tumour before and after interventional
therapy. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 32:697–705. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Goh V, Halligan S, Daley F, Wellsted DM,
Guenther T and Bartram CI: Colorectal tumour vascularity:
Quantitative assessment with multidetector CT-do tumour perfusion
measurements reflect angiogenesis? Radiology. 249:510–517. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yao J, Yang ZG, Chen HJ, Chen TW and Huang
J: Gastric adenocarcinoma: Can perfusion CT help to noninvasively
evaluate tumour angiogenesis? Abdom Imaging. 36:15–21. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Y, Zhang J, Dai J, Feng X, Lu H and
Zhou C: Angiogenesis of renal cell carcinoma: Perfusion CT
findings. Abdom Imaging. 35:622–628. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Reinmuth N, Parikh AA, Ahmad SA, Liu W,
Stoeltzing O, Fan F, Takeda A, Akagi M and Ellis LM: Biology of
angiogenesis in tumours of the gastrointestinal tract. Microsc Res
Tech. 60:199–207. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|