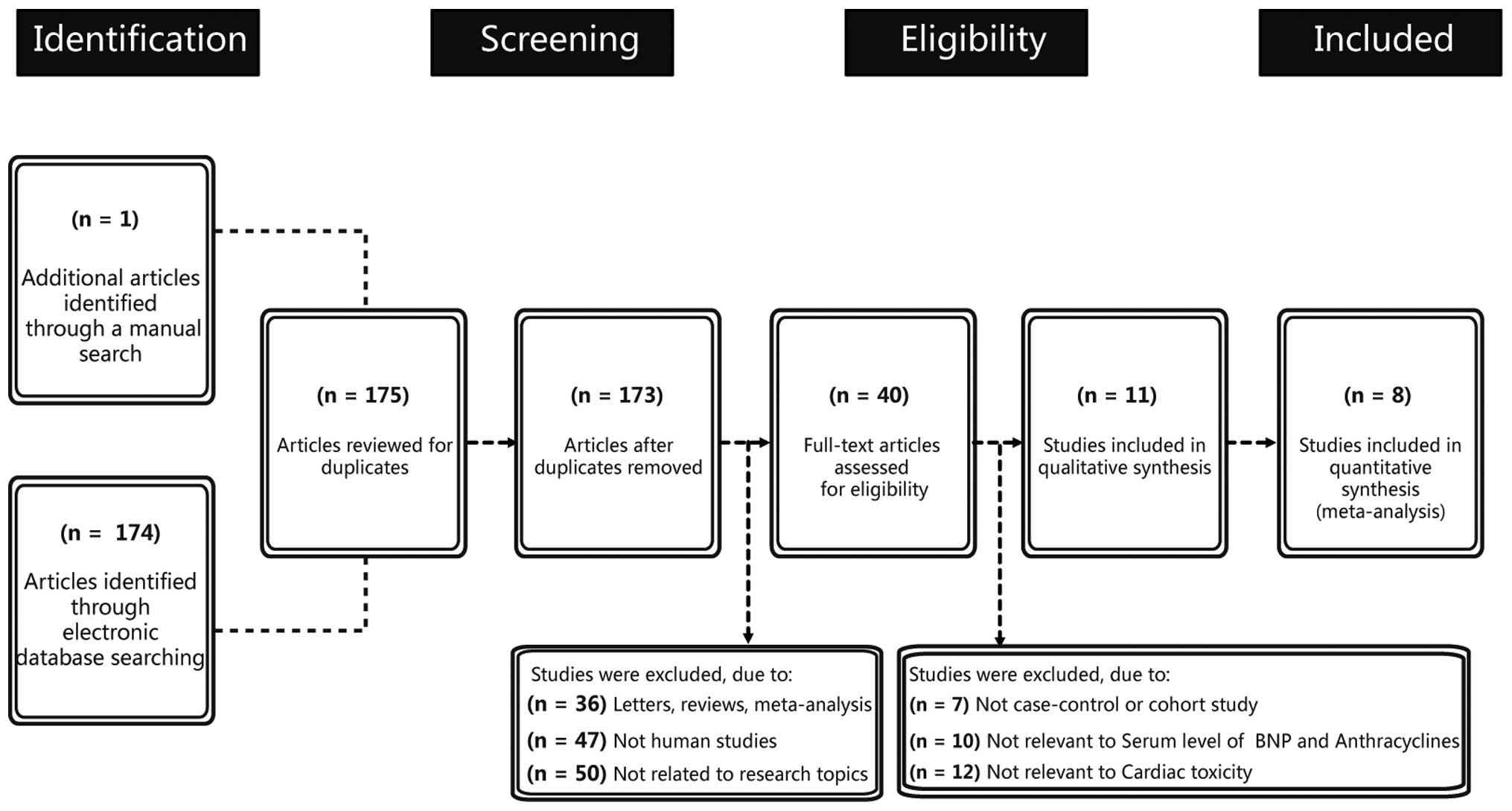
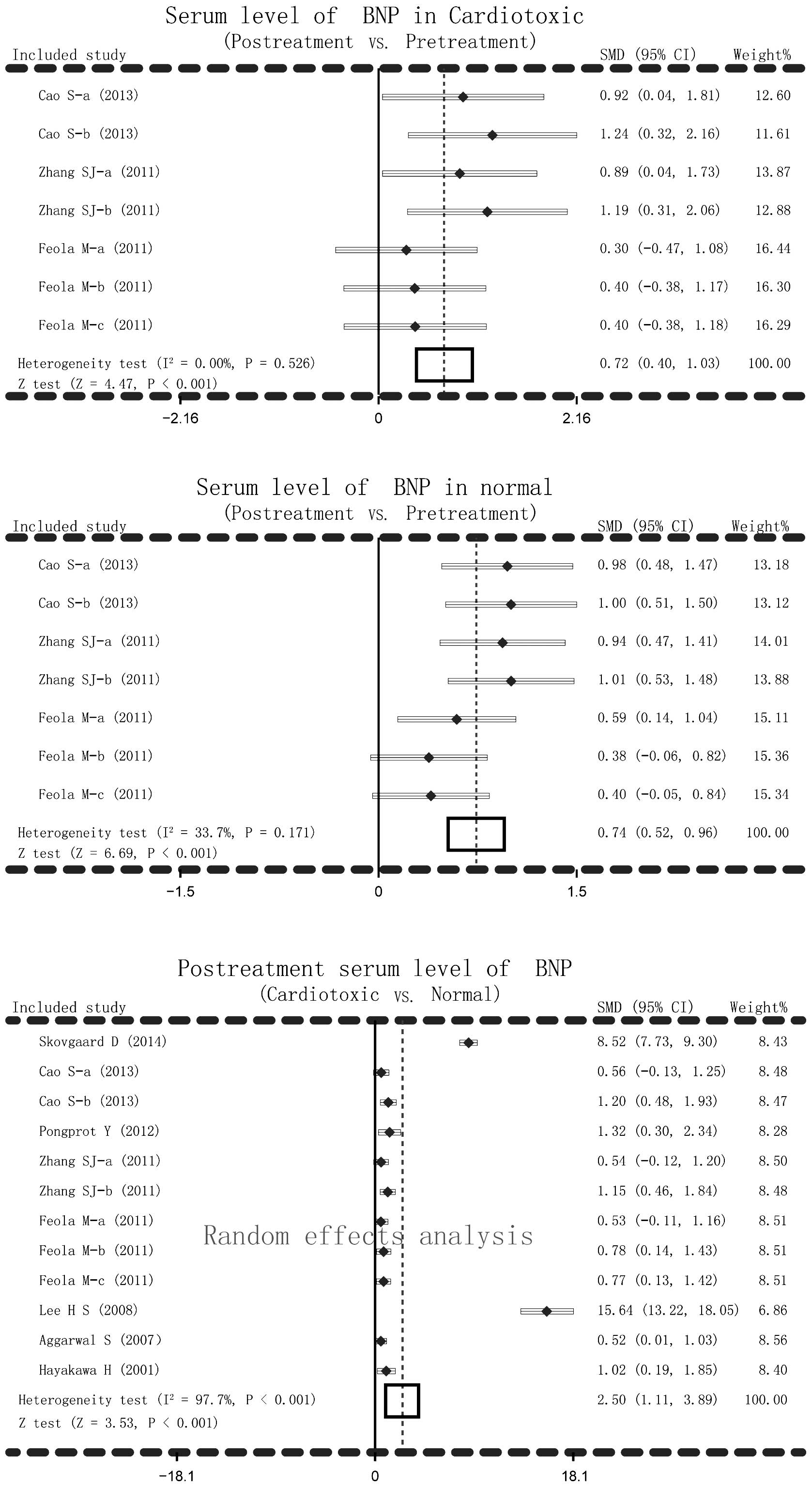
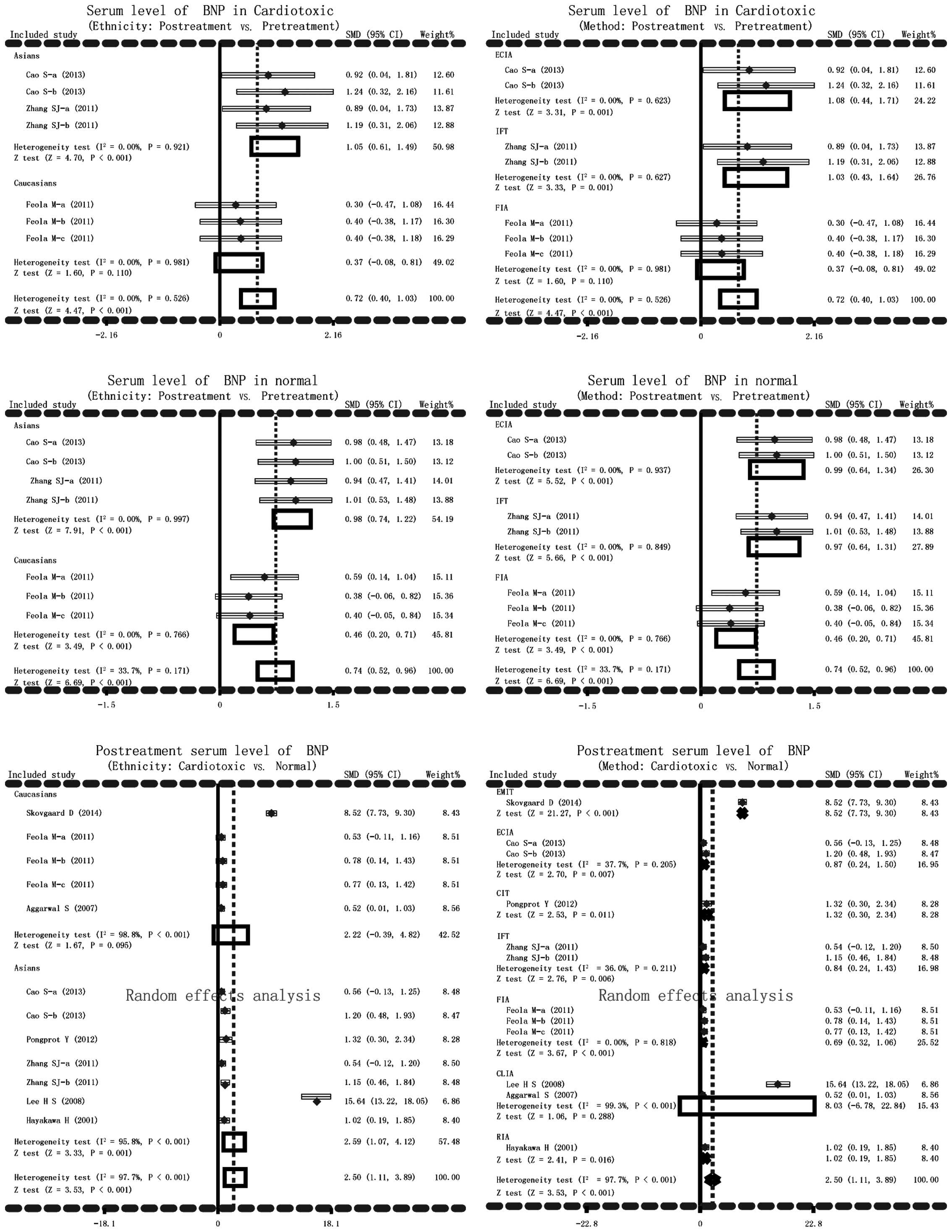
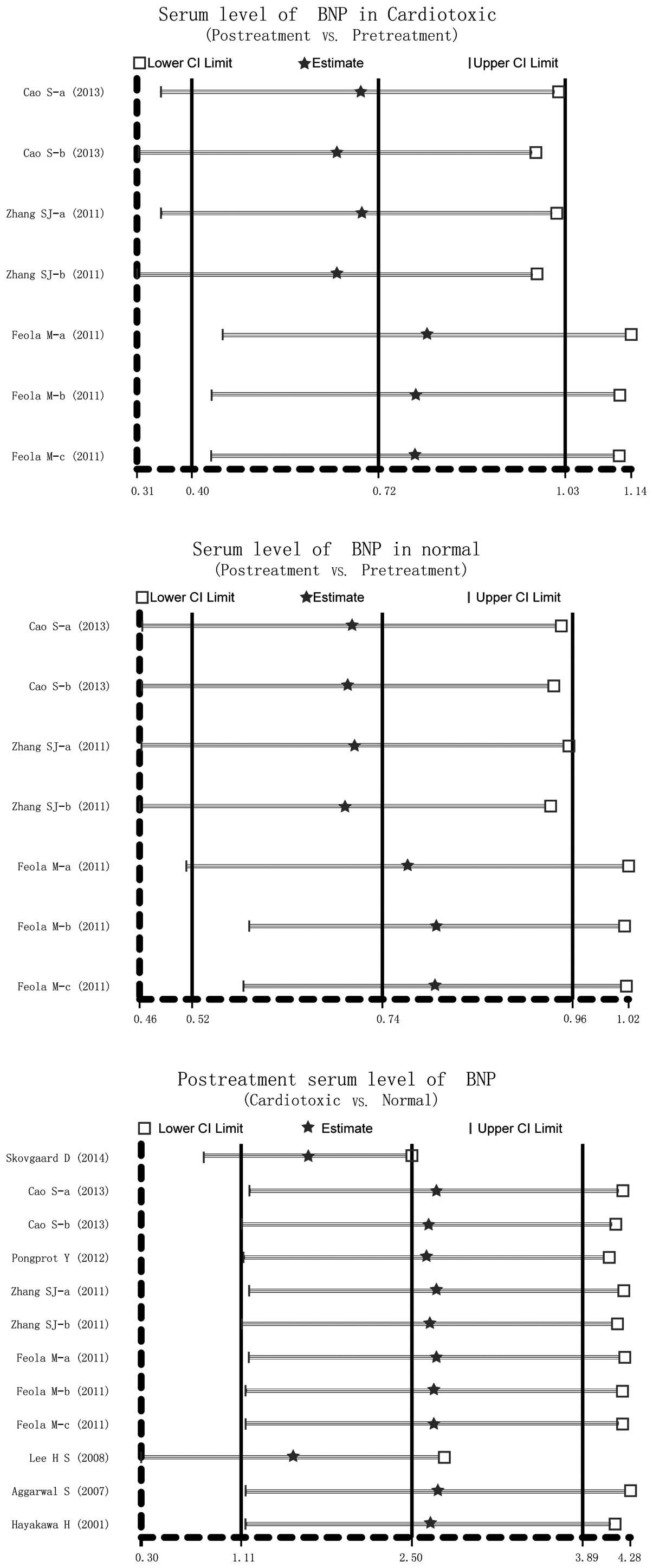
|
1
|
Lee HS, Son CB, Shin SH and Kim YS:
Clinical correlation between brain natriutetic peptide and
anthracyclin-induced cardiac toxicity. Cancer Res Treat.
40:121–126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aapro M, Bernard-Marty C, Brain EG, Batist
G, Erdkamp F, Krzemieniecki K, Leonard R, Lluch A, Monfardini S,
Ryberg M, et al: Anthracycline cardiotoxicity in the elderly cancer
patient: A SIOG expert position paper. Ann Oncol. 22:257–267. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Visscher H, Ross CJ, Rassekh SR, Barhdadi
A, Dubé MP, Al-Saloos H, Sandor GS, Caron HN, van Dalen EC, Kremer
LC, et al: Pharmacogenomic prediction of anthracycline-induced
cardiotoxicity in children. J Clin Oncol. 30:1422–1428. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lipshultz SE, Alvarez JA and Scully RE:
Anthracycline associated cardiotoxicity in survivors of childhood
cancer. Heart. 94:525–533. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ewer MS and Lenihan DJ: Left ventricular
ejection fraction and cardiotoxicity: Is our ear really to the
ground? J Clin Oncol. 26:1201–1203. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
van der Pal HJ, van Dalen EC, Hauptmann M,
Kok WE, Caron HN, van den Bos C, Oldenburger F, Koning CC, van
Leeuwen FE and Kremer LC: Cardiac function in 5-year survivors of
childhood cancer: A long-term follow-up study. Arch Intern Med.
170:1247–1255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kremer LC, van der Pal HJ, Offringa M, van
Dalen EC and Voûte PA: Frequency and risk factors of subclinical
cardiotoxicity after anthracycline therapy in children: A
systematic review. Ann Oncol. 13:819–829. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feola M, Garrone O, Occelli M, Francini A,
Biggi A, Visconti G, Albrile F, Bobbio M and Merlano M:
Cardiotoxicity after anthracycline chemotherapy in breast
carcinoma: Effects on left ventricular ejection fraction, troponin
I and brain natriuretic peptide. Int J Cardiol. 148:194–198. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pongprot Y, Sittiwangkul R, Charoenkwan P
and Silvilairat S: Use of cardiac markers for monitoring of
doxorubixin-induced cardiotoxicity in children with cancer. J
Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 34:589–595. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hayakawa H, Komada Y, Hirayama M, Hori H,
Ito M and Sakurai M: Plasma levels of natriuretic peptides in
relation to doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and cardiac function
in children with cancer. Med Pediatr Oncol. 37:4–9. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Skovgaard D, Hasbak P and Kjaer A: BNP
predicts chemotherapy-related cardiotoxicity and death: Comparison
with gated equilibrium radionuclide ventriculography. PLoS One.
9:e967362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Beleigoli AM, Boersma E, de Diniz MF,
Vidigal PG, Lima-Costa MF and Ribeiro AL: C-reactive protein and
B-type natriuretic peptide yield either a non-significant or a
modest incremental value to traditional risk factors in predicting
long-term overall mortality in older adults. PLoS One.
8:e758092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Khalaf MA, Abdelrahman TM and Abbas MF:
Values of using QTc and N-terminal fragment of B-type natriuretic
peptide as markers for early detection of acute antipsychotic
drugs-induced cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 11:10–17. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM,
McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P, Omland T, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Wu
AH, et al: Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the
emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 347:161–167.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Troughton RW, Frampton CM, Yandle TG,
Espiner EA, Nicholls MG and Richards AM: Treatment of heart failure
guided by plasma aminoterminal brain natriuretic peptide (N-BNP)
concentrations. Lancet. 355:1126–1130. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Geske JB, McKie PM, Ommen SR and Sorajja
P: B-type natriuretic peptide and survival in hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 61:2456–2460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gerber IL, Stewart RA, Legget ME, West TM,
French RL, Sutton TM, Yandle TG, French JK, Richards AM and White
HD: Increased plasma natriuretic peptide levels reflect symptom
onset in aortic stenosis. Circulation. 107:1884–1890. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morrow DA, de Lemos JA, Sabatine MS,
Murphy SA, Demopoulos LA, Di Battiste PM, McCabe CH, Gibson CM,
Cannon CP and Braunwald E: Evaluation of B-type natriuretic peptide
for risk assessment in unstable angina/non-ST-elevation myocardial
infarction: B-type natriuretic peptide and prognosis in
TACTICS-TIMI 18. J Am Coll Cardiol. 41:1264–1272. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Berger R, Huelsman M, Strecker K, Bojic A,
Moser P, Stanek B and Pacher R: B-type natriuretic peptide predicts
sudden death in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation.
105:2392–2397. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Daniels LB and Maisel AS: Natriuretic
peptides. J Am Coll Cardiol. 50:2357–2368. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Costa VN, Nomura RM, Miyadahira S, Vieira
Francisco RP and Zugaib M: Cord blood B-type natriuretic peptide
levels in placental insufficiency: Correlation with fetal Doppler
and pH at birth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 171:231–234.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Esteves WA, Lodi-Junqueira L, Neto CP, Tan
TC, Nascimento BR, Mehrotra P, Barbosa MM, Ribeiro AL and Nunes MC:
The impact of right ventricular stroke work on B-type natriuretic
peptide levels in patients with mitral stenosis undergoing
percutaneous mitral valvuloplasty. J Interv Cardiol. 26:501–508.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jan SL, Lin SJ, Fu YC, Lin MC, Chan SC and
Hwang B: Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide study in children with
severe enterovirus 71 infection: A pilot study. Int J Infect Dis.
17:e1166–e1171. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vila G, Resl M, Stelzeneder D, Struck J,
Maier C, Riedl M, Hülsmann M, Pacher R, Luger A and Clodi M: Plasma
NT-proBNP increases in response to LPS administration in healthy
men. J Appl Physiol (1985). 105:1741–1745. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Clerico A, Giannoni A, Vittorini S and
Passino C: Thirty years of the heart as an endocrine organ:
Physiological role and clinical utility of cardiac natriuretic
hormones. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 301:H12–H20. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hequet O, Le QH, Moullet I, Pauli E,
Salles G, Espinouse D, Dumontet C, Thieblemont C, Arnaud P, Antal
D, et al: Subclinical late cardiomyopathy after doxorubicin therapy
for lymphoma in adults. J Clin Oncol. 22:1864–1871. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zintzaras E and Ioannidis JP: HEGESMA:
Genome search meta-analysis and heterogeneity testing.
Bioinformatics. 21:3672–3673. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zintzaras E and Ioannidis JP:
Heterogeneity testing in meta-analysis of genome searches. Genet
Epidemiol. 28:123–137. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Song F and Gilbody S: Bias in
meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Increase in
studies of publication bias coincided with increasing use of
meta-analysis. BMJ. 316:4711998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR
and Rushton L: Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias
in meta-analysis. JAMA. 295:676–680. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aggarwal S, Pettersen MD, Bhambhani K,
Gurczynski J, Thomas R and L'Ecuyer T: B-type natriuretic peptide
as a marker for cardiac dysfunction in anthracycline-treated
children. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 49:812–816. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang SJ and Cui YZ: Measurement of brain
natriuretic peptide ring based chemotherapy in patients with
cardiac toxicity in anthracene. Chinese Journal of Difficult and
Complicated Cases. 10:444–445. 2011.
|
|
35
|
Cao S, Pang DM, Duan HB, Lin YD and Li LT:
Application value in the levels of plasma NTproBNP in patients with
cardiac toxicity. Modern Diagnosis & Treatment. 303–304.
2013.
|
|
36
|
Mavinkurve-Groothuis AM, Marcus KA,
Pourier M, Loonen J, Feuth T, Hoogerbrugge PM, de Korte CL and
Kapusta L: Myocardial 2D strain echocardiography and cardiac
biomarkers in children during and shortly after anthracycline
therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL): A prospective
study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 14:562–569. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Krawczuk-Rybak M, Dakowicz L, Hryniewicz
A, Maksymiuk A, Zelazowska-Rutkowska B and Wysocka J: Cardiac
function in survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and
Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Paediatr Child Health. 47:455–459. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|