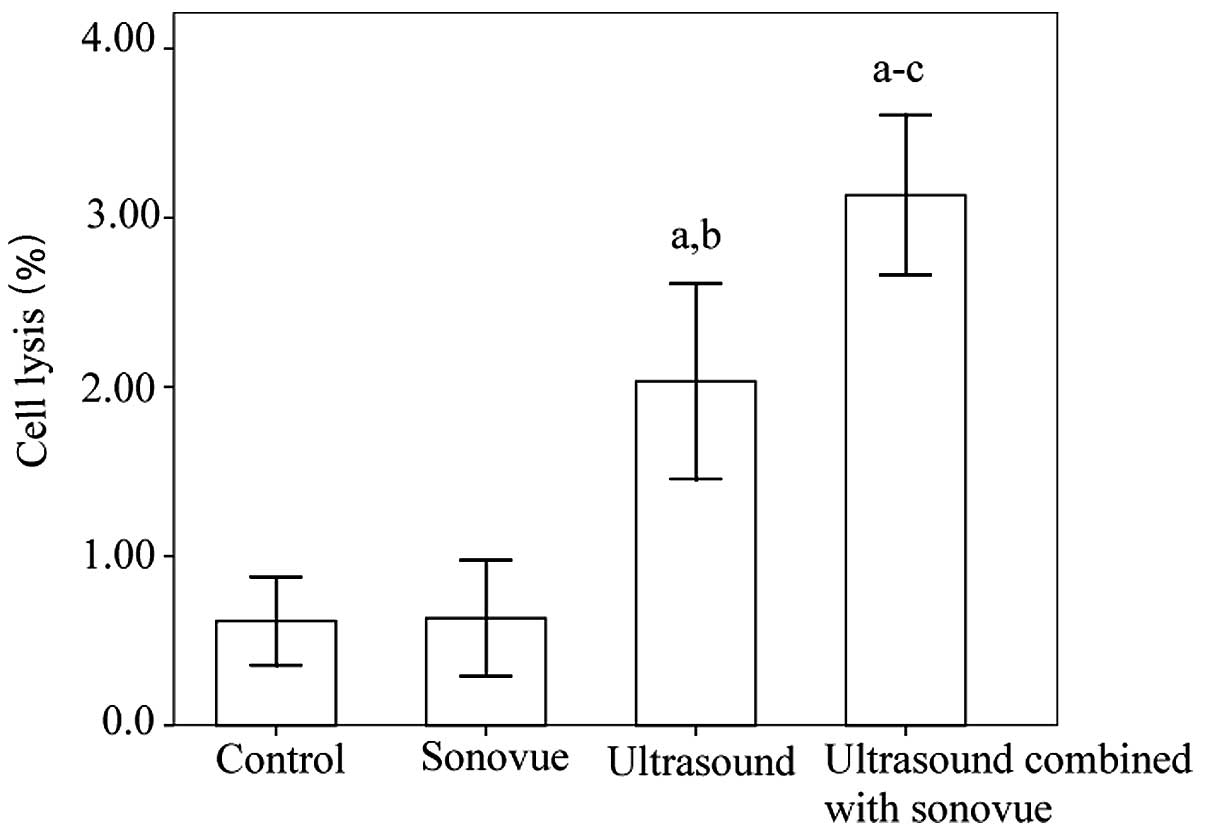
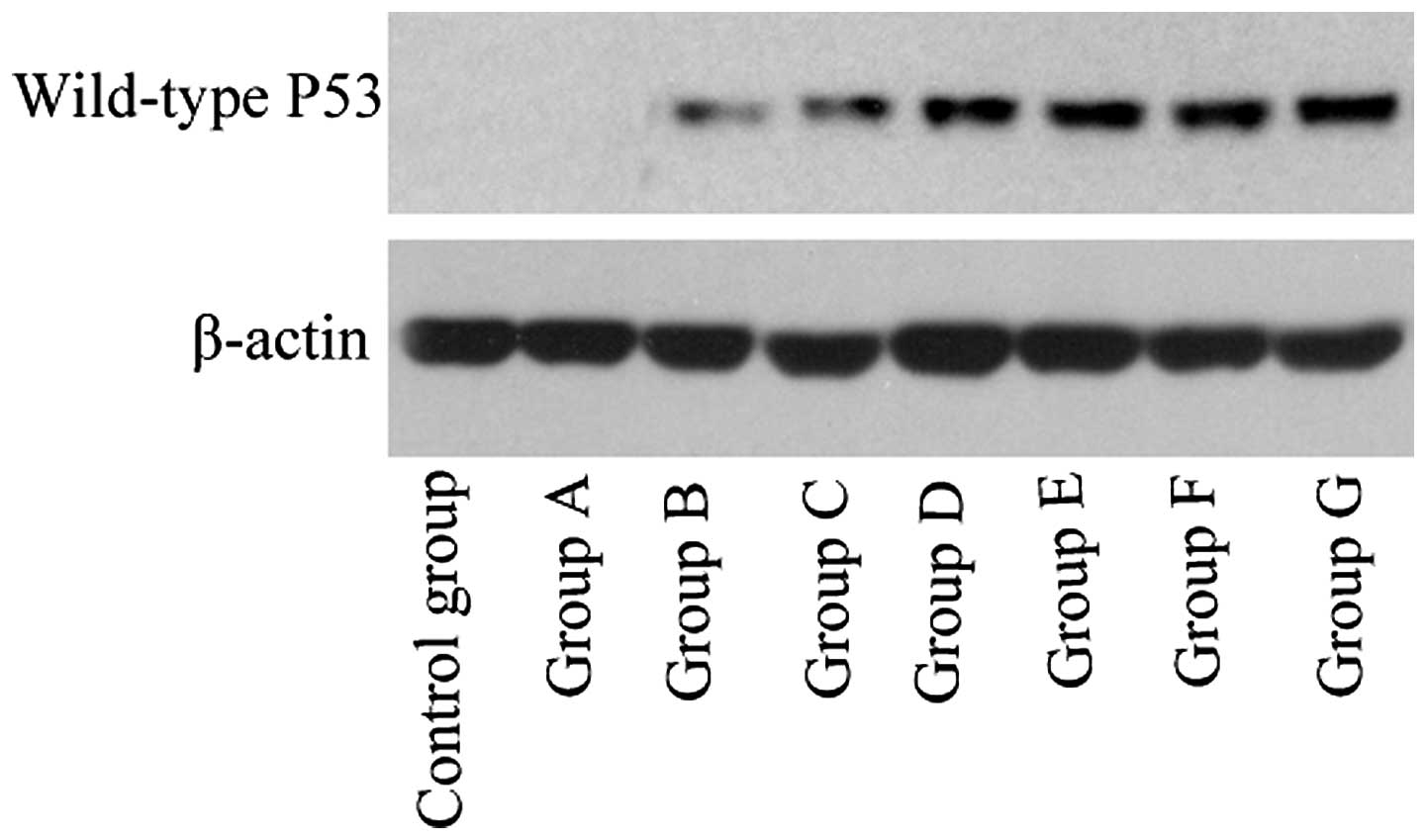
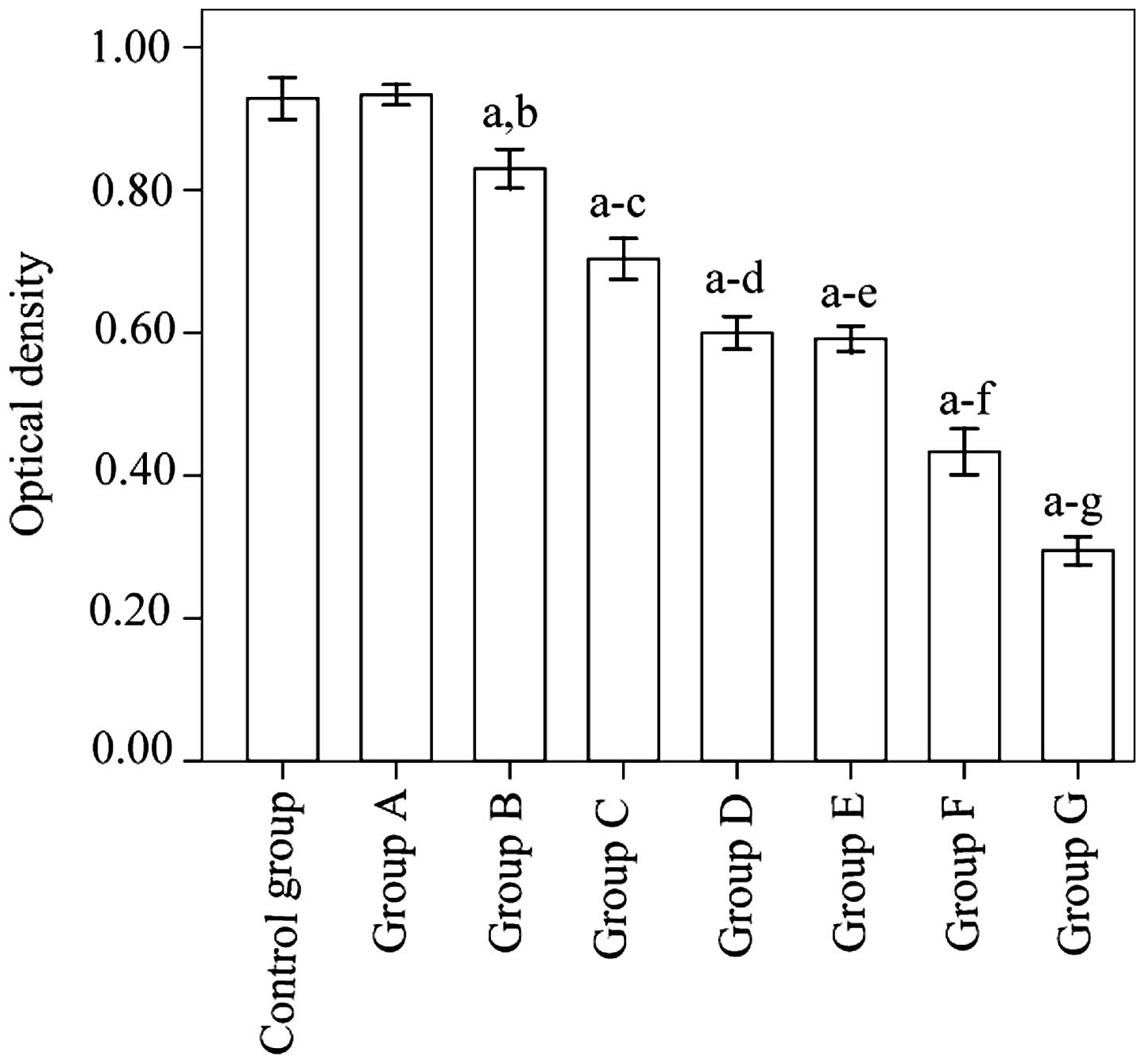
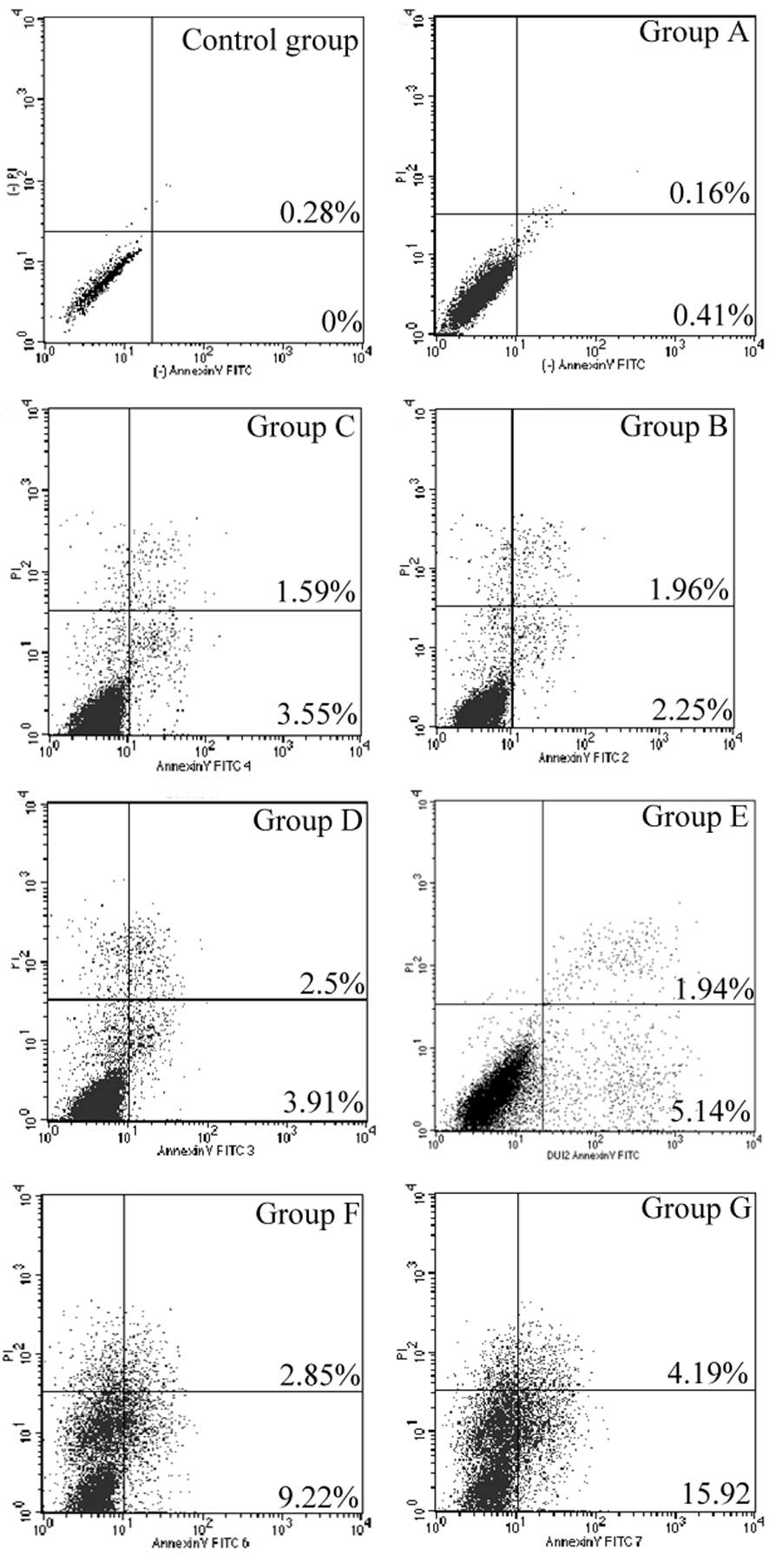
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu AH, Hu ZM, Qu JB, Liu SM, Syed AK, Yuan
HQ and Lou HX: Cyclic bisbibenzyls induce growth arrest and
apoptosis of human prostate cancer PC3 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
31:609–615. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mangar SA, Huddart RA, Parker CC,
Dearnaley DP, Khoo VS and Horwich A: Technological advances in
radiotherapy for the treatment of localised prostate cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 41:908–921. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanaka G, Hirata Y, Goldenberg SL,
Bruchovsky N and Aihara K: Mathematical modelling of prostate
cancer growth and its application to hormone therapy. Philos Trans
A Math Phys Eng Sci. 368:5029–5044. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lecornet E, Ahmed HU, Moore C and Emberton
M: Focal therapy for prostate cancer: A potential strategy to
address the problem of overtreatment. Arch Esp Urol. 63:845–852.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baumert H: Salvage treatments for
prostatic radiation failure. Cancer Radiother. 14:442–445. 2010.(In
French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Verma IM and Somia N: Gene
therapy-promises, problems and prospects. Nature. 389:239–242.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wyber JA, Andrews J and D'Emanuele A: The
use of sonication for the efficient delivery of plasmid DNA into
cells. Pharm Res. 14:750–756. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Whelan J: Electroporation and ultrasound
for gene and drug delivery. Drug Delivery Today. 11:585–586. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Danialou G, Comtois AS, Dudley RW,
Nalbantoglu J, Gilbert R, Karpati G, Jones DH and Petrof BJ:
Ultrasound increase plasmid-mediated gene transfer to dystrophic
muscles without collateral damage. Mol Ther. 5:687–693. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Negishi Y, Omata D, Iijima H, Takabayashi
Y, Suzuki K, Endo Y, Suzuki R, Maruyama K, Nomizu M and Aramaki Y:
Enhanced laminin-derived peptide AG73-mediated liposomal gene
transfer by bubble liposomes and ultrasound. Mol Pharm. 7:217–226.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Audouy SA, de Leij LF, Hoekstra D and
Molema G: In vivo characteristics of cationic liposomes as delivery
vectors for gene therapy. Pharm Res. 19:1599–1605. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hirko A, Tang F and Hughes JA: Cationic
lipid vectors for plasmid DNA delivery. Curr Med Chem.
10:1185–1193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin VC, Huang CY, Lee YC, Yu CC, Chang TY,
Lu TL, Huang SP and Bao BY: Genetic variations in TP53 binding
sites are predictors of clinical outcomes in prostate cancer
patients. Arch Toxicol. 88:901–911. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han L, Zhao J, Liu J, Duan XL, Li LH, Wei
XF, Wei Y and Liang XJ: A universal gene carrier platform for
treatment of human prostatic carcinoma by p53 transfection.
Biomaterials. 35:3110–3120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wan C, Qian J, Li F and Li H:
Ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction enhances
polyethylenimine-mediated gene transfection in vitro in human
retinal pigment epithelial cells and in vivo in rat retina. Mol Med
Rep. 12:2835–2841. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sugano M, Negishi Y, Endo-Takahashi Y,
Hamano N, Usui M, Suzuki R, Maruyama K, Aramaki Y and Yamamoto M:
Gene delivery to periodontal tissue using Bubble liposomes and
ultrasound. J Periodontal Res. 49:398–404. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen Z, Xie M, Wang X, Lv Q and Ding S:
Efficient gene delivery to myocardium with ultrasound targeted
microbubble destruction and polyethylenimine. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 28:613–617. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zolochevska O, Xia X, Williams BJ, Ramsay
A, Li S and Figueiredo ML: Sonoporation delivery of interleukin-27
gene therapy efficiently reduces prostate tumor cell growth in
vivo. Hum Gene Ther. 22:1537–1550. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tachibana K and Tachibana S: Transdermal
delivery of insulin by ultrasonic vibration. J Pharm Pharmacol.
43:270–271. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Newman CM and Bettinger T: Gene therapy
progress and prospects: Ultrasound for gene transfer. Gene Ther.
14:465–475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang G, Zhuo Z, Xia H, Zhang Y, He Y, Tan
W and Gao Y: Investigation into the impact of diagnostic ultrasound
with microbubbles on the capillary permeability of rat hepatomas.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 39:628–637. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tomizawa M, Shinozaki F, Motoyoshi Y,
Sugiyama T, Yamamoto S and Sueishi M: Sonoporation: Gene transfer
using ultrasound. World J Methodol. 3:39–44. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marentis TC, Kusler B, Yaralioglu GG, Liu
S, Haeggström EO and Khuri-Yakub BT: Microfluidic sonicator for
real-time disruption of eukaryotic cells and bacterial spores for
DNA analysis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 31:1265–1277. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bai WK, Wu ZH, Shen E, Zhang JZ and Hu B:
The improvement of liposome-mediated transfection of pEGFP DNA into
human prostate cancer cells by combining low-frequency and
low-energy ultrasound with microbubbles. Oncol Rep. 27:475–480.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scott SL, Earle JD and Gumerlock PH:
Functional p53 increases prostate cancer cell survival after
exposure to fractionated doses of ionizing radiation. Cancer Res.
63:7190–7196. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sicklick JK, Li YX, Jayaraman A, Kannangai
R, Qi Y, Vivekanandan P, Ludlow JW, Owzar K, Chen W, Torbenson MS
and Diehl AM: Dysregulation of the Hedgehog pathway in human
hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 27:748–757. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang XB, Liu QH, Wang P, Zhang K, Tang W
and Wang BL: Enhancement of apoptosis by sonodynamic therapy with
protoporphyrin IX in isolate sarcoma 180 cells. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 23:238–246. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fang HY, Tsai KC, Cheng WH, Shieh MJ, Lou
PJ, Lin WL and Chen WS: The effects of power on-off durations of
pulsed ultrasound on the destruction of cancer cells. Int J
Hyperthermia. 23:371–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kodama T, Tomita Y, Koshiyama K and
Blomley MJ: Transfection effect of microbubbles on cells in
superposed ultrasound waves and behavior of cavitation bubble.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 32:905–914. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ecke TH, Schlechte HH, Hübsch A, Lenk SV,
Schiemenz K, Rudolph BD and Miller K: TP53 mutation in prostate
needle biopsies-comparison with patients follow-up. Anticancer Res.
27:4143–4148. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gupta K, Thakur VS, Bhaskaran N, Nawab A,
Babcook MA, Jackson MW and Gupta S: Green tea polyphenols induce
p53-dependent and p53-independent apoptosis in prostate cancer
cells through two distinct mechanisms. PLoS One. 7:e525722012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li X, Li Y, Hu J, Wang B, Zhao L, Ji K,
Guo B, Yin D, Du Y, Kopecko DJ, et al: Plasmid-based E6-specific
siRNA and co-expression of wild-type p53 suppresses the growth of
cervical cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 335:242–250.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang JF, Wu CJ, Zhang CM, Qiu QY and Zheng
M: Ultrasound-mediated microbubble destruction facilitates gene
transfection in rat C6 glioma cells. Mol Biol Rep. 36:1263–1267.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Manome Y, Nakayama N, Nakayama K and
Furuhata H: Insonation facilitates plasmid DNA transfection into
the central nervous system and microbubbles enhance the effect.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 31:693–702. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|