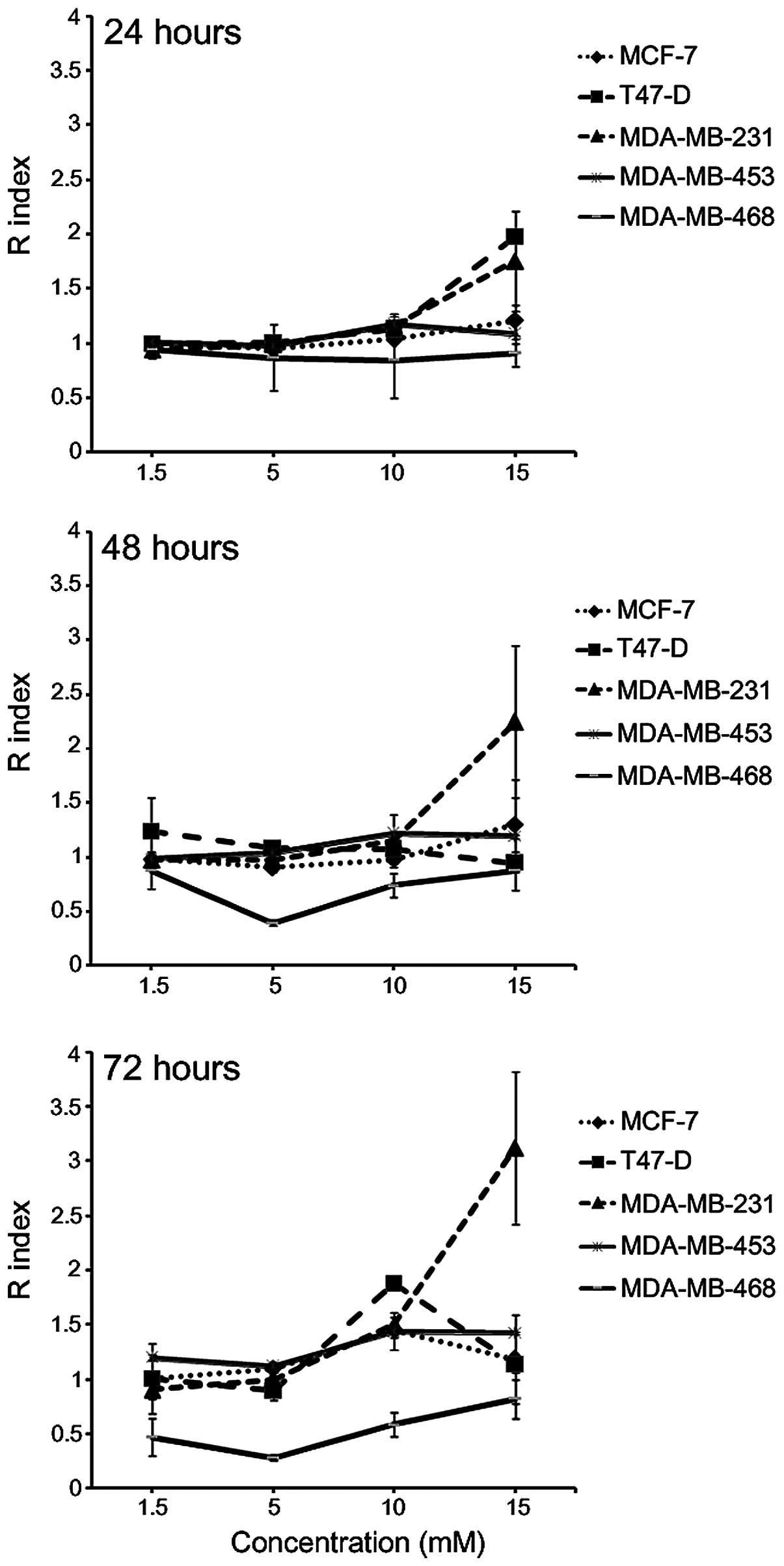
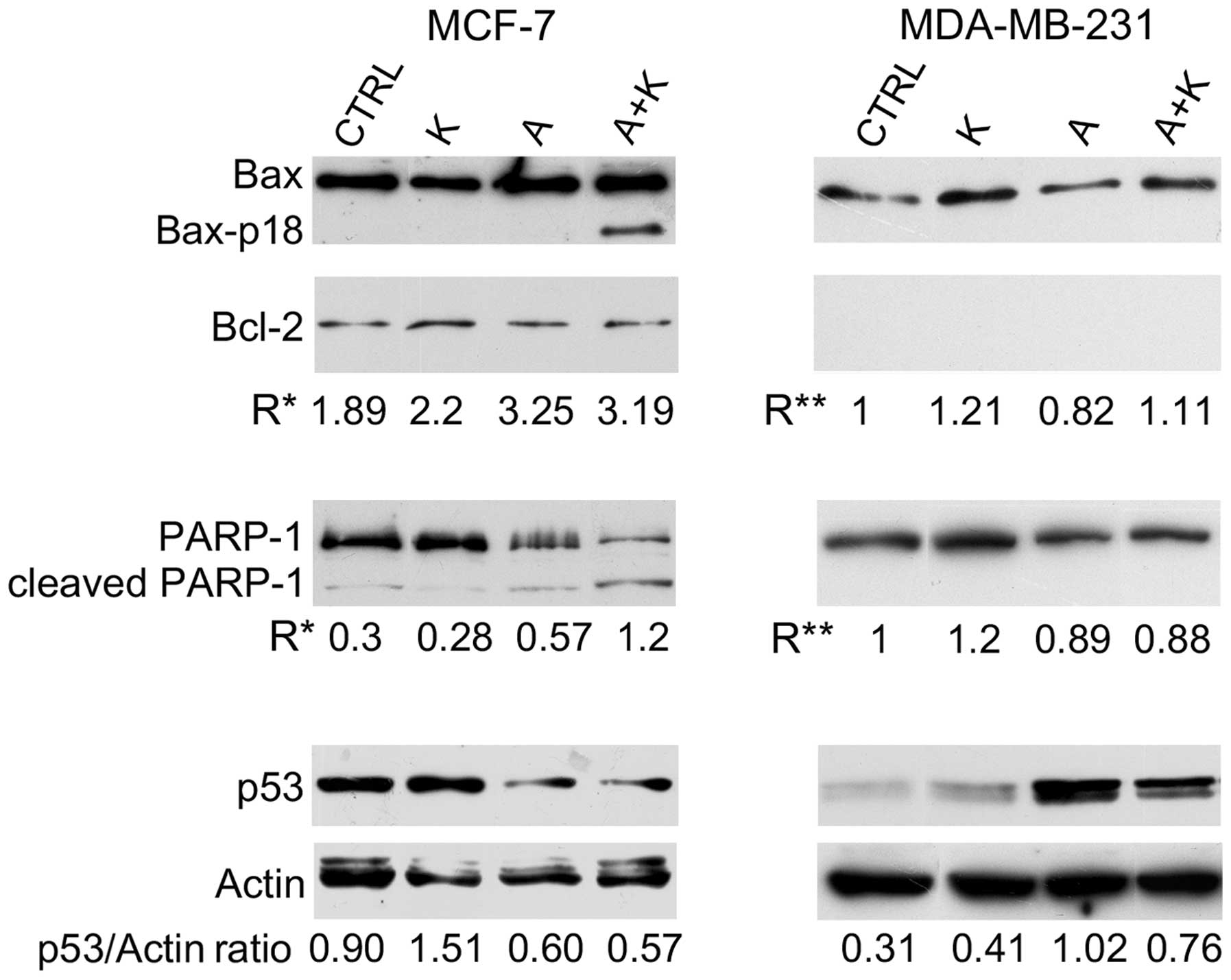
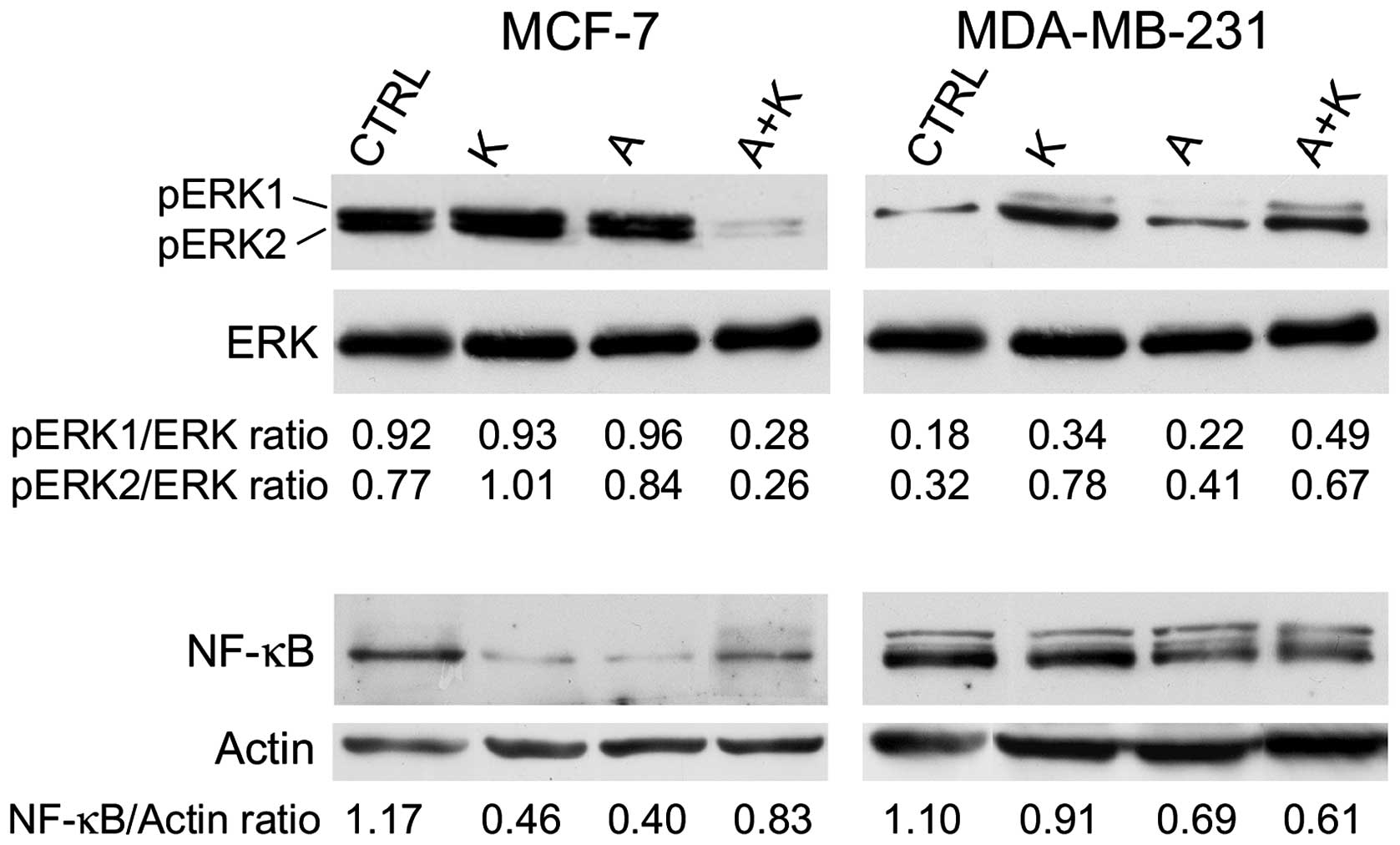
|
1.
|
Khaw KT, Bingham S, Welch A, Luben R,
Wareham N, Oakes S and Day N: Relation between plasma ascorbic acid
and mortality in men and women in EPIC-Norfolk prospective study: A
prospective population study. European Prospective Investigation
into Cancer and Nutrition. Lancet. 357:657–663. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Block G: Epidemiologic evidence regarding
vitamin C and cancer. Am J Clin Nutr. 54(Suppl 6): 1310S–1314S.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Cameron E and Pauling L: The
orthomolecular treatment of cancer. I. The role of ascorbic acid in
host resistance. Chem Biol Interact. 9:273–283. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Creagan ET, Moertel CG, O'Fallon JR,
Schutt AJ, O'Connell MJ, Rubin J and Frytak S: Failure of high-dose
vitamin C (ascorbic acid) therapy to benefit patients with advanced
cancer. A controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 301:687–690. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Ohno S, Ohno Y, Suzuki N, Soma G and Inoue
M: High-dose vitamin C (ascorbic acid) therapy in the treatment of
patients with advanced cancer. Anticancer Res. 29:809–815.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Levine M, Conry-Cantilena C, Wang Y, Welch
RW, Washko PW, Dhariwal KR, Park JB, Lazarev A, Graumlich JF, King
J and Cantilena LR: Vitamin C pharmacokinetics in healthy
volunteers: Evidence for a recommended dietary allowance. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:3704–3709. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Levine M, Wang Y, Padayatty SJ and Morrow
J: A new recommended dietary allowance of vitamin C for healthy
young women. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:9842–9846. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Padayatty SJ, Sun H, Wang Y, Riordan HD,
Hewitt SM, Katz A, Wesley RA and Levine M: Vitamin C
pharmacokinetics: Implications for oral and intravenous use. Ann
Intern Med. 140:533–537. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Hoffer LJ, Levine M, Assouline S,
Melnychuk D, Padayatty SJ, Rosadiuk K, Rousseau C, Robitaille L and
Miller WH Jr: Phase I clinical trial of i.v. ascorbic acid in
advanced malignancy. Ann Oncol. 19:1969–1974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Parrow NL, Leshin JA and Levine M:
Parenteral ascorbate as a cancer therapeutic: A reassessment based
on pharmacokinetics. Antioxid Redox Signal. 19:2141–2156. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ma Y, Chapman J, Levine M, Polireddy K,
Drisko J and Chen Q: High-dose parenteral ascorbate enhanced
chemosensitivity of ovarian cancer and reduced toxicity of
chemotherapy. Sci Transl Med. 6:222ra182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Cone CD Jr: Unified theory on the basic
mechanism of normal mitotic control and oncogenesis. J Theor Biol.
30:151–181. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Hughes FM Jr and Cidlowski JA: Potassium
is a critical regulator of apoptotic enzymes in vitro and in vivo.
Adv Enzyme Regul. 39:157–171. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Wang Z: Roles of K+ channels in
regulating tumour cell proliferation and apoptosis. Pflugers Arch.
448:274–286. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
DeCoursey TE, Chandy KG, Gupta S and
Cahalan MD: Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T
lymphocytes: A role in mitogenesis? Nature. 307:465–468. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Pardo LA: Voltage-gated potassium channels
in cell proliferation. Physiology (Bethesda). 19:285–292. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Wonderlin WF and Strobl JS: Potassium
channels, proliferation and G1 progression. J Membr Biol.
154:91–107. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Boros LG, Lee PW, Brandes JL, Cascante M,
Muscarella P, Schirmer WJ, Melvin WS and Ellison EC: Nonoxidative
pentose phosphate pathways and their direct role in ribose
synthesis in tumors: Is cancer a disease of cellular glucose
metabolism? Med Hypotheses. 50:55–59. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Smith NK, Stabler SB, Cameron IL and
Medina D: X-Ray microanalysis of electrolyte content of normal,
preneoplastic, and neoplastic mouse mammary tissue. Cancer Res.
41:3877–3880. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Arrebola F, Fernández-Segura E, Campos A,
Crespo PV, Skepper JN and Warley A: Changes in intracellular
electrolyte concentrations during apoptosis induced by UV
irradiation of human myeloblastic cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
290:C638–C649. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Mobasheri A, Fox R, Evans I, Cullingham F,
Martín-Vasallo P and Foster CS: Epithelial Na, K-ATPase expression
is down-regulated in canine prostate cancer; a possible consequence
of metabolic transformation in the process of prostate malignancy.
Cancer Cell Int. 3:82003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Chen JQ, Contreras RG, Wang R, Fernandez
SV, Shoshani L, Russo IH, Cereijido M and Russo J: Sodium/potassium
ATPase (Na+, K+-ATPase) and ouabain/related
cardiac glycosides: A new paradigm for development of anti-breast
cancer drugs? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 96:1–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Parkinson GN, Lee MP and Neidle S: Crystal
structure of parallel quadruplexes from human telomeric DNA.
Nature. 417:876–880. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Salvati E, Rizzo A, Iachettini S, Zizza P,
Cingolani C, D'Angelo C, Porru M, Mondello C, Aiello A, Farsetti A,
et al: A basal level of DNA damage and telomere deprotection
increases the sensitivity of cancer cells to G-quadruplex
interactive compounds. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:1759–1769. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Dai J, Carver M and Yang D: Polymorphism
of human telomeric quadruplex structures. Biochimie. 90:1172–1183.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kelland LR: Overcoming the immortality of
tumour cells by telomere and telomerase based cancer therapeutics -
current status and future prospects. Eur J Cancer. 41:971–979.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Paoli G: The Bio-magnetic nature of cancer
and the role of potassium ascorbate and ribose against cellar
degeneration. J Nucl Energy. 7:114–119. 2003.
|
|
28.
|
Croci S, Pedrazzi G, Passeri G, Delsignore
R and Ortalli I: Red cell Hb oxidation of healthy subjects compared
to breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 22:2903–2906.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Croci S, Pedrazzi G, Passeri G, Piccolo P
and Ortalli I: Acetylphenylhydrazine induced haemoglobin oxidation
in erythrocytes studied by Mössbauer spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1568:99–104. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Croci S, Bruni L, Bussolati S, Castaldo M
and Dondi M: Potassium bicarbonate and D-ribose effects on A72
canine and HTB-126 human cancer cell line proliferation in vitro.
Cancer Cell Int. 11:302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Masuelli L, Marzocchella L, Quaranta A,
Palumbo C, Pompa G, Izzi V, Canini A, Modesti A, Galvano F and Bei
R: Apigenin induces apoptosis and impairs head and neck carcinomas
EGFR/ErbB2 signaling. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:1060–1068.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Masuelli L, Marzocchella L, Focaccetti C,
Tresoldi I, Palumbo C, Izzi V, Benvenuto M, Fantini M, Lista F,
Tarantino U, et al: Resveratrol and diallyl disulfide enhance
curcumin-induced sarcoma cell apoptosis. Front Biosci (Landmark
Ed). 17:498–508. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Bei R, Masuelli L, Moriconi E, Visco V,
Moretti A, Kraus MH and Muraro R: Immune responses to all ErbB
family receptors detectable in serum of cancer patients. Oncogene.
18:1267–1275. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Bei R, Budillon A, Masuelli L, Cereda V,
Vitolo D, Di Gennaro E, Ripavecchia V, Palumbo C, Ionna F, Losito
S, et al: Frequent overexpression of multiple ErbB receptors by
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma contrasts with rare antibody
immunity in patients. J Pathol. 204:317–325. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Faggioni G, Pomponi A, De Santis R,
Masuelli L, Ciammaruconi A, Monaco F, Di Gennaro A, Marzocchella L,
Sambri V, Lelli R, et al: West Nile alternative open reading frame
(N-NS4B/WARF4) is produced in infected West Nile Virus (WNV) cells
and induces humoral response in WNV infected individuals. Virol J.
9:2832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Masuelli L, Budillon A, Marzocchella L,
Mrozek MA, Vitolo D, Di Gennaro E, Losito S, Sale P, Longo F, Ionna
F, et al: Caveolin-1 overexpression is associated with simultaneous
abnormal expression of the E-cadherin/α-β catenins complex and
multiple ErbB receptors and with lymph nodes metastasis in head and
neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Cell Physiol. 227:3344–3353. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Masuelli L, Bei R, Sacchetti P,
Scappaticci I, Francalanci P, Albonici L, Coletti A, Palumbo C,
Minieri M, Fiaccavento R, et al: Beta-catenin accumulates in
intercalated disks of hypertrophic cardiomyopathic hearts.
Cardiovasc Res. 60:376–387. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Masuelli L, Pompa G, Fabrizi M, Quaranta
A, Vozza I, Piccoli L, Antonelli A, Marzocchella L, Di Carlo S,
Perrotti V, et al: Patients with peri-implantitis, unlike those
with a healthy periimplant microenvironment, display antibodies to
more than one heat shock protein (HSP 27, HSP 65 and HSP 90) linear
epitope. Eur J Inflamm. 9:257–267. 2011.
|
|
39.
|
Ingrosso G, Fantini M, Nardi A, Benvenuto
M, Sacchetti P, Masuelli L, Ponti E, Frajese GV, Lista F, Schillaci
O, et al: Local radiotherapy increases the level of autoantibodies
to ribosomal P0 protein but not to heat shock proteins,
extracellular matrix molecules and EGFR/ErbB2 receptors in prostate
cancer patients. Oncol Rep. 29:1167–1174. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Palumbo C, Albonici L, Bei R, Bocci C,
Scarpa S, Di Nardo P and Modesti A: HMBA induces cell death and
potentiates doxorubicin toxicity in malignant mesothelioma cells.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 54:398–406. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Toyota H, Yanase N, Yoshimoto T, Moriyama
M, Sudo T and Mizuguchi J: Calpain-induced Bax-cleavage product is
a more potent inducer of apoptotic cell death than wild-type Bax.
Cancer Lett. 189:221–230. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Du J, Cullen JJ and Buettner GR: Ascorbic
acid: Chemistry, biology and the treatment of cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1826:443–457. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Chen Q, Espey MG, Krishna MC, Mitchell JB,
Corpe CP, Buettner GR, Shacter E and Levine M: Pharmacologic
ascorbic acid concentrations selectively kill cancer cells: Action
as a pro-drug to deliver hydrogen peroxide to tissues. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13604–13609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Du J, Martin SM, Levine M, Wagner BA,
Buettner GR, Wang SH, Taghiyev AF, Du C, Knudson CM and Cullen JJ:
Mechanisms of ascorbate-induced cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:509–520. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Chen P, Yu J, Chalmers B, Drisko J, Yang
J, Li B and Chen Q: Pharmacological ascorbate induces cytotoxicity
in prostate cancer cells through ATP depletion and induction of
autophagy. Anticancer Drugs. 23:437–444. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Martinovich GG, Golubeva EN, Martinovich
IV and Cherenkevich SN: Redox regulation of calcium signaling in
cancer cells by ascorbic acid involving the mitochondrial electron
transport chain. J Biophys. 2012:9216532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Han SS, Kim K, Hahm ER, Lee SJ, Surh YJ,
Park HK, Kim WS, Jung CW, Lee MH, Park K, et al: L-ascorbic acid
represses constitutive activation of NF-kappaB and COX-2 expression
in human acute myeloid leukemia, HL-60. J Cell Biochem. 93:257–270.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Park S, Ahn ES, Lee S, Jung M, Park JH, Yi
SY and Yeom CH: Proteomic analysis reveals upregulation of RKIP in
S-180 implanted BALB/C mouse after treatment with ascorbic acid. J
Cell Biochem. 106:1136–1145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Ranzato E, Biffo S and Burlando B:
Selective ascorbate toxicity in malignant mesothelioma: A redox
Trojan mechanism. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 44:108–117. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Chen Q, Espey MG, Sun AY, Lee JH, Krishna
MC, Shacter E, Choyke PL, Pooput C, Kirk KL, Buettner GR and Levine
M: Ascorbate in pharmacologic concentrations selectively generates
ascorbate radical and hydrogen peroxide in extracellular fluid in
vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:8749–8754. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51.
|
Cha J, Roomi MW, Ivanov V, Kalinovsky T,
Niedzwiecki A and Rath M: Ascorbate supplementation inhibits growth
and metastasis of B16FO melanoma and 4T1 breast cancer cells in
vitamin C-deficient mice. Int J Oncol. 42:55–64. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52.
|
Kim JE, Cho HS, Yang HS, Jung DJ, Hong SW,
Hung CF, Lee WJ and Kim D: Depletion of ascorbic acid impairs NK
cell activity against ovarian cancer in a mouse model.
Immunobiology. 217:873–881. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53.
|
Riordan HD, Riordan NH, Jackson JA,
Casciari JJ, Hunninghake R, González MJ, Mora EM, Miranda-Massari
JR, Rosario N and Rivera A: Intravenous vitamin C as a chemotherapy
agent: A report on clinical cases. P R Health Sci J. 23:115–118.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54.
|
Shimpo K, Nagatsu T, Yamada K, Sato T,
Niimi H, Shamoto M, Takeuchi T, Umezawa H and Fujita K: Ascorbic
acid and adriamycin toxicity. Am J Clin Nutr. 54(Suppl 6):
1298S–1301S. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55.
|
Vollbracht C, Schneider B, Leendert V,
Weiss G, Auerbach L and Beuth J: Intravenous vitamin C
administration improves quality of life in breast cancer patients
during chemo-/radiotherapy and aftercare: Results of a
retrospective, multicentre, epidemiological cohort study in
Germany. In Vivo. 25:983–990. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56.
|
L'Allemain G, Paris S and Pouysségur J:
Growth factor action and intracellular pH regulation in
fibroblasts. Evidence for a major role of the
Na+/H+ antiport. J Biol Chem. 259:5809–5815.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57.
|
Gerson DF, Kiefer H and Eufe W:
Intracellular pH of mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes. Science.
216:1009–1010. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58.
|
Bruni L, Babarinde AA, Ortalli I and Croci
S: K-D:rib dampens Hs 578T cancer cell chemoinvasion and
proliferation. Cancer Cell Int. 14:772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59.
|
Lacroix M, Toillon RA and Leclercq G: p53
and breast cancer, an update. Endocr Relat Cancer. 13:293–325.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60.
|
Subik K, Lee JF, Baxter L, Strzepek T,
Costello D, Crowley P, Xing L, Hung MC, Bonfiglio T, Hicks DG and
Tang P: The expression patterns of ER, PR, HER2, CK5/6, EGFR, Ki-67
and AR by immunohistochemical analysis in breast cancer cell lines.
Breast Cancer (Auckl). 4:35–41. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61.
|
Sun D, Lopez-Guajardo CC, Quada J, Hurley
LH and Von Hoff DD: Regulation of catalytic activity and
processivity of human telomerase. Biochemistry. 38:4037–4044. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62.
|
Harley CB, Futcher AB and Greider CW:
Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature.
345:458–460. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63.
|
Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley
CB, West MD, Ho PL, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL and Shay
JW: Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal
cells and cancer. Science. 266:2011–2015. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64.
|
Zahler AM, Williamson JR, Cech TR and
Prescott DM: Inhibition of telomerase by G-quartet DNA structures.
Nature. 350:718–720. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65.
|
Hurley LH: DNA and its associated
processes as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:188–200.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66.
|
Neidle S and Parkinson G: Telomere
maintenance as a target for anticancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 1:383–393. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67.
|
Hurley LH, Wheelhouse RT, Sun D, Kerwin
SM, Salazar M, Fedoroff OY, Han FX, Han H, Izbicka E and Von Hoff
DD: G-quadruplexes as targets for drug design. Pharmacol Ther.
85:141–158. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68.
|
Redon S, Bombard S, Elizondo-Riojas MA and
Chottard JC: Platinum cross-linking of adenines and guanines on the
quadruplex structures of the
AG3(T2AG3)3 and
(T2AG3)4 human telomere sequences
in Na+ and K+ solutions. Nucleic Acids Res.
31:1605–1613. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69.
|
Phan AT and Patel DJ: Two-repeat human
telomeric d(TAGGGTTAGGGT) sequence forms interconverting parallel
and antiparallel G-quadruplexes in solution: Distinct topologies,
thermodynamic properties, and folding/unfolding kinetics. J Am Chem
Soc. 125:15021–15027. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70.
|
Li J, Correia JJ, Wang L, Trent JO and
Chaires JB: Not so crystal clear: The structure of the human
telomere G-quadruplex in solution differs from that present in a
crystal. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:4649–4659. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71.
|
Włodarczyk A, Grzybowski P, Patkowski A
and Dobek A: Effect of ions on the polymorphism, effective charge,
and stability of human telomeric DNA. Photon correlation
spectroscopy and circular dichroism studies. J Phys Chem B.
109:3594–3605. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72.
|
Ambrus A, Chen D, Dai J, Bialis T, Jones
RA and Yang D: Human telomeric sequence forms a hybrid-type
intramolecular G-quadruplex structure with mixed
parallel/antiparallel strands in potassium solution. Nucleic Acids
Res. 34:2723–2735. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73.
|
Dai J, Carver M, Punchihewa C, Jones RA
and Yang D: Structure of the Hybrid-2 type intramolecular human
telomeric G-quadruplex in K+ solution: Insights into
structure polymorphism of the human telomeric sequence. Nucleic
Acids Res. 35:4927–4940. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74.
|
Hadi SM, Ullah MF, Shamim U, Bhatt SH and
Azmi AS: Catalytic therapy of cancer by ascorbic acid involves
redox cycling of exogenous/endogenous copper ions and generation of
reactive oxygen species. Chemotherapy. 56:280–284. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|