Article
Human wings apart-like gene is specifically overexpressed in cervical cancer
- Authors:
- Xiaoqin Lu
- Jinquan Cui
- Meizhou Fu
- Wuliang Wang
-
View Affiliations / Copyright
Affiliations:
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan 450014, P.R. China, Department of Intensive Care Unit, Henan Provincial People's Hospital, Zhengzhou, Henan 450000, P.R. China
-
Pages:
171-176
|
Published online on:
May 13, 2016
https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.4563
- Expand metrics +
Metrics:
Total
Views: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
Metrics:
Total PDF Downloads: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
Cervical cancer is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in women. The human wings apart‑like (hWAPL) gene, which is 30,793 bp long and located on 10q23.2., is a human homologue of the WAPL gene in Drosophila melanogaster. hWAPL has the characteristics of an oncogene in uterine cervical cancer. The present study investigated the expression of the hWAPL gene in tissues, including 9 common cancers, consisting of cervical, gastric and lung cancers, liver, bladder, esophageal, endometrial, renal and rectal carcinomas, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and benign squamous epithelia. The immunohistochemical analysis was conducted using paraffin-embedded tissues obtained from 413 patients, consisting of 27 benign squamous epithelial tissue samples, and 47 cervical cancer, 30 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)I, 33 CINII, 38 CINIII, 29 gastric cancer, 28 liver carcinoma, 26 bladder carcinoma, 35 esophageal carcinoma, 25 endometrial, 26 renal carcinoma, 36 rectal carcinoma and 33 lung cancer tissues. The expression of hWAPL mRNA was evaluated by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction in 8 benign squamous epithelia and 11 cervical cancer tissues. Compared to benign squamous epithelia and the 8 other cancers, hWAPL protein was significantly increased in cervical cancer (P<0.001). The expression of the hWAPL protein in cervical cancer and CINIII tissues was markedly increased compared to the expression in CINI and CINII tissues (P<0.001). Despite the significant difference in the staining scores (P<0.001), no significant difference was observed in the percentage of tissues expressing hWAPL (P=0.102) between cervical cancer and CINIII. The hWAPL gene may therefore be specifically overexpressed in cervical cancer. The overexpression of hWAPL may play an important role in occurrence and development of cervical cancer.
View Figures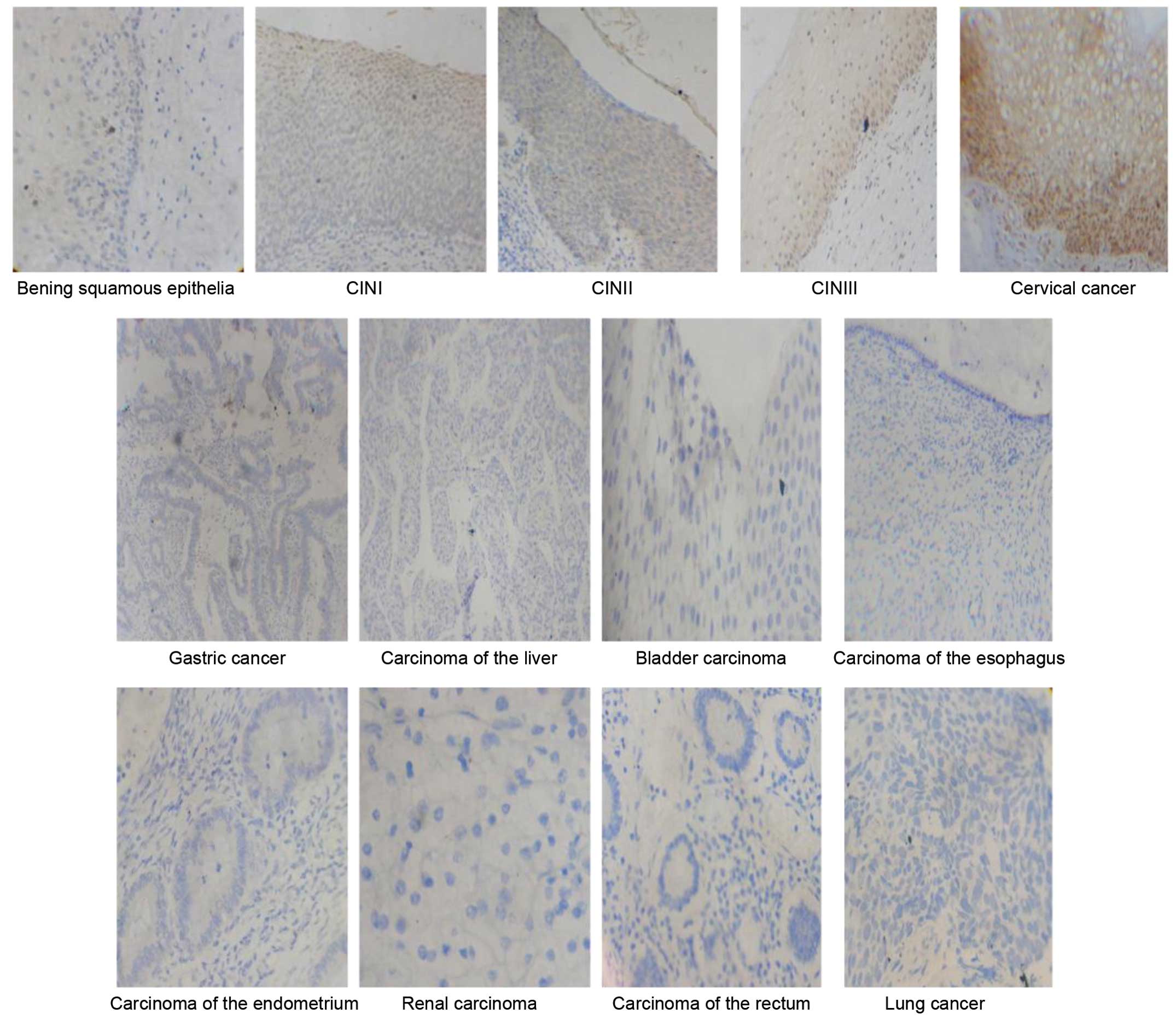 |
Figure 1
|
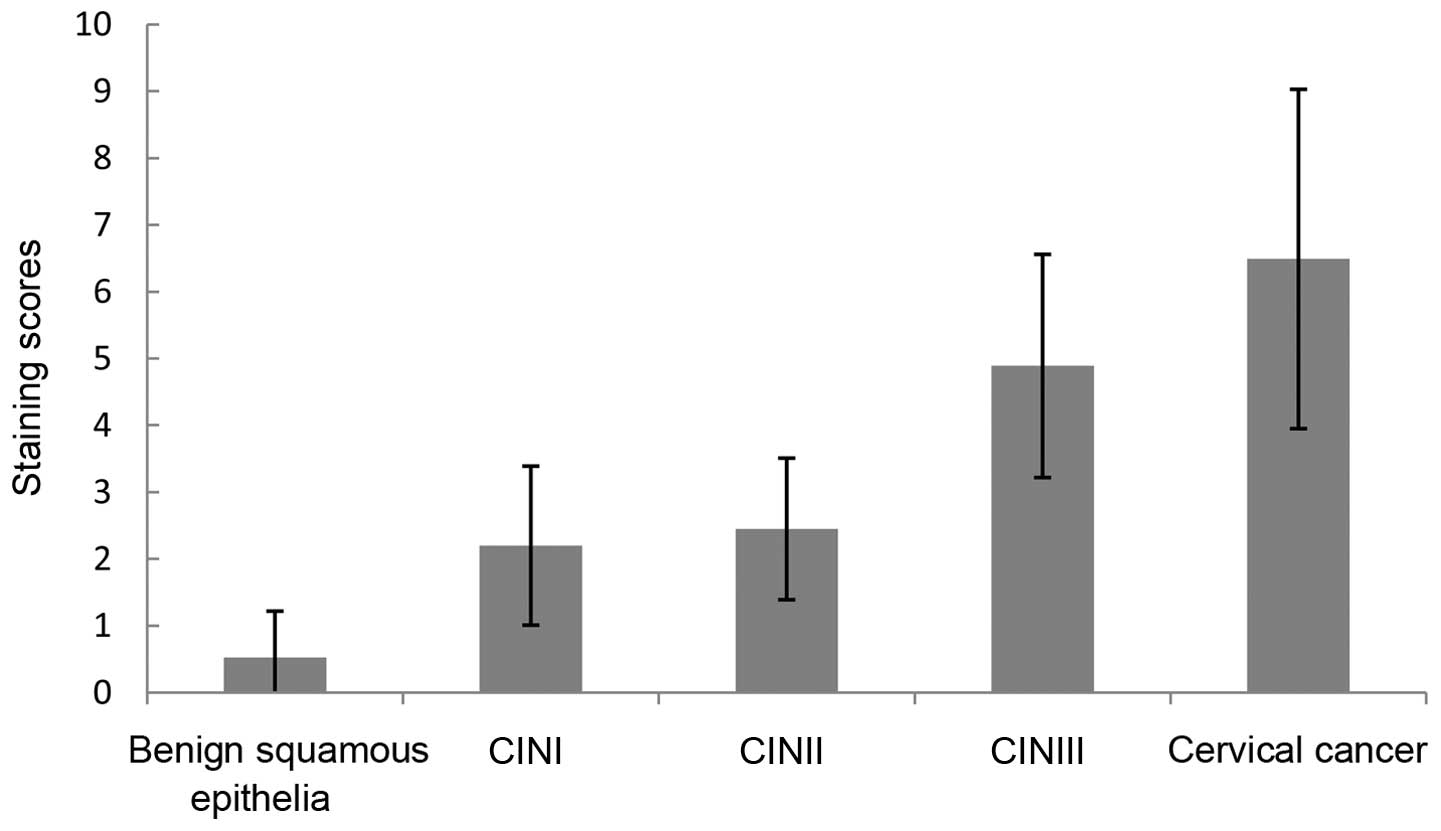 |
Figure 2
|
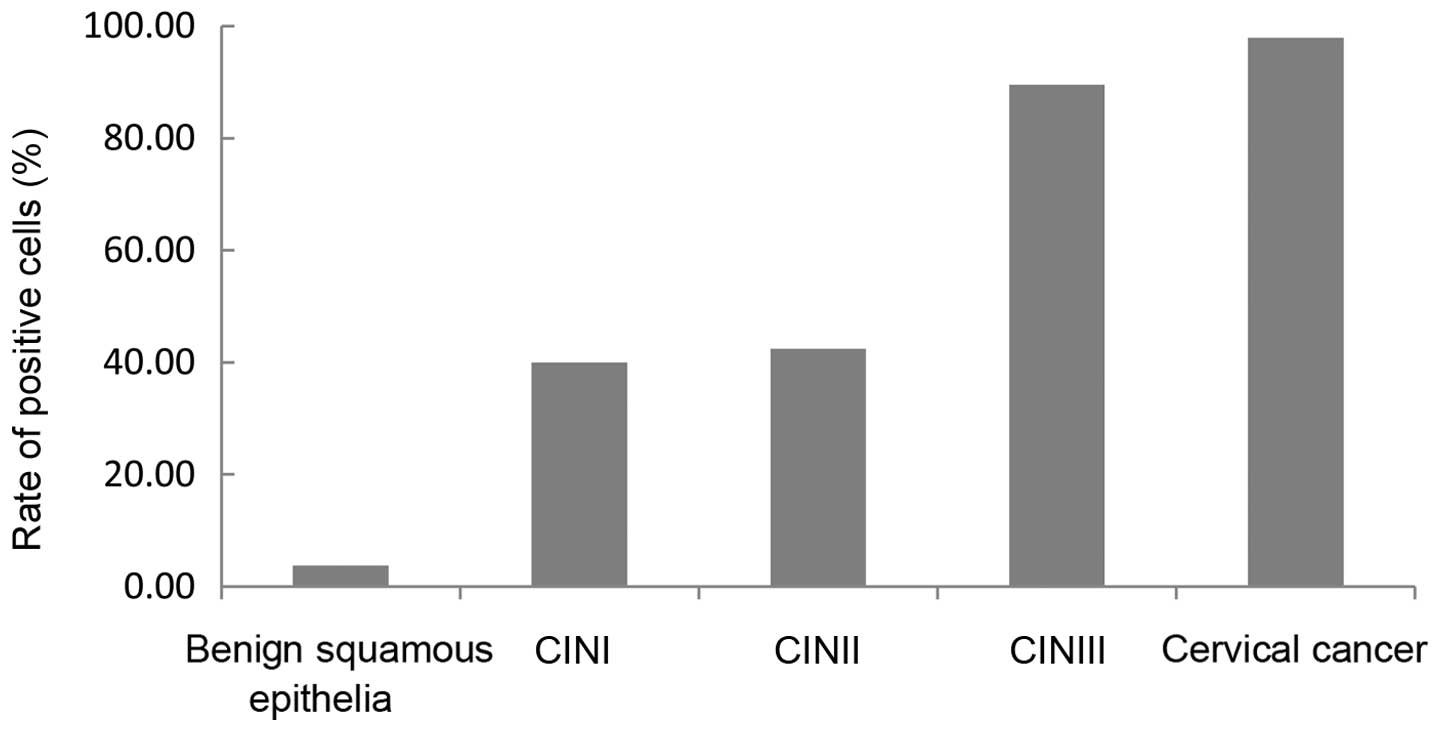 |
Figure 3
|
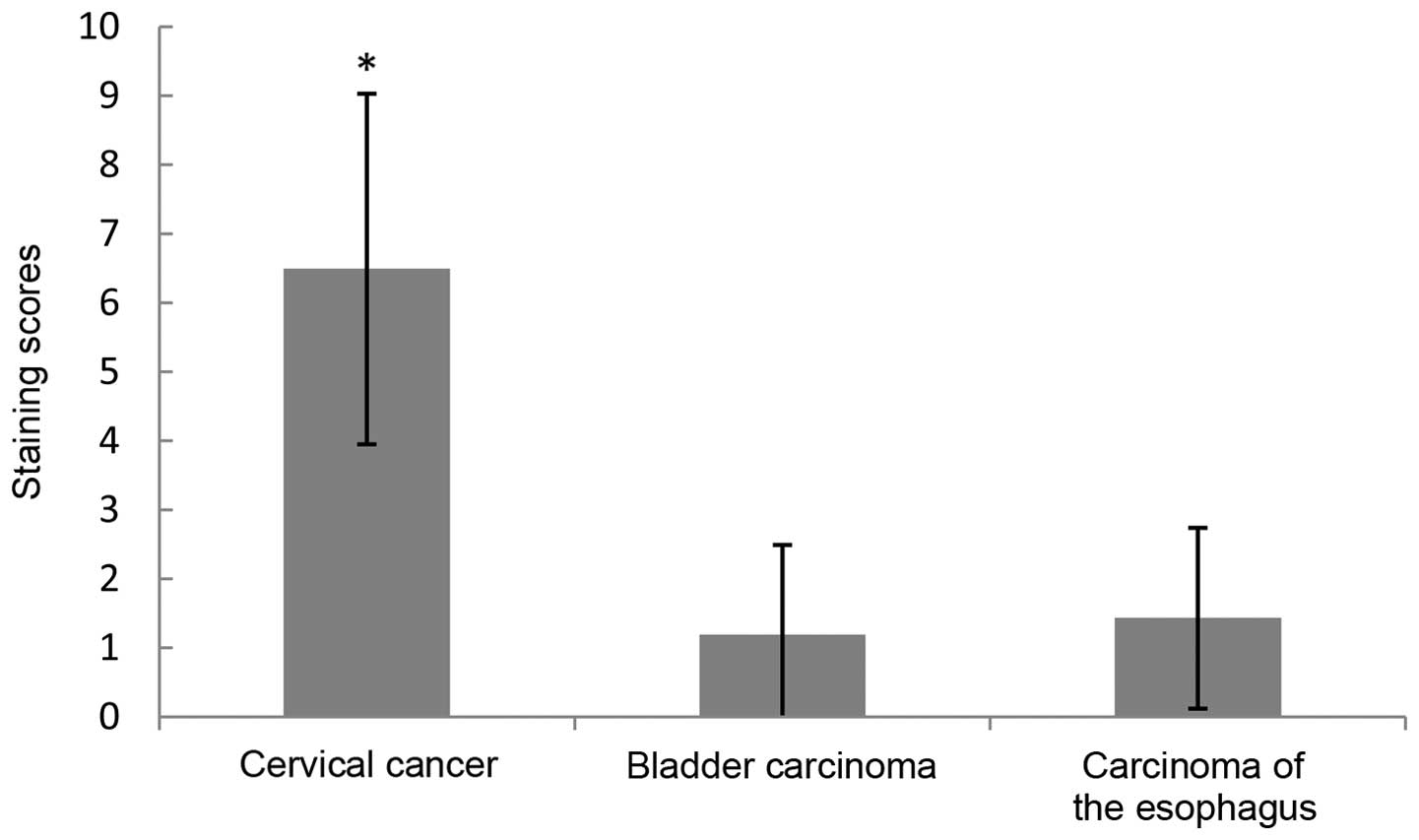 |
Figure 4
|
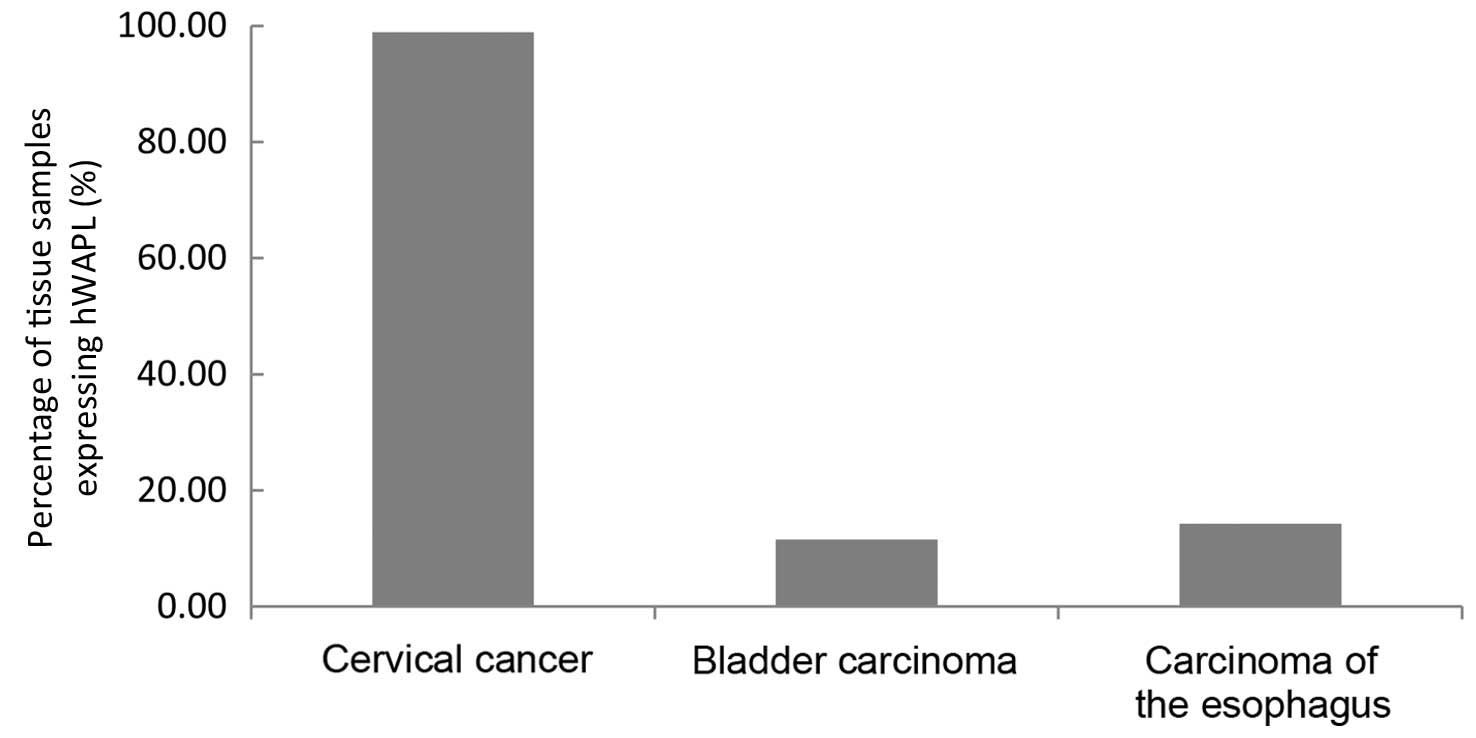 |
Figure 5
|
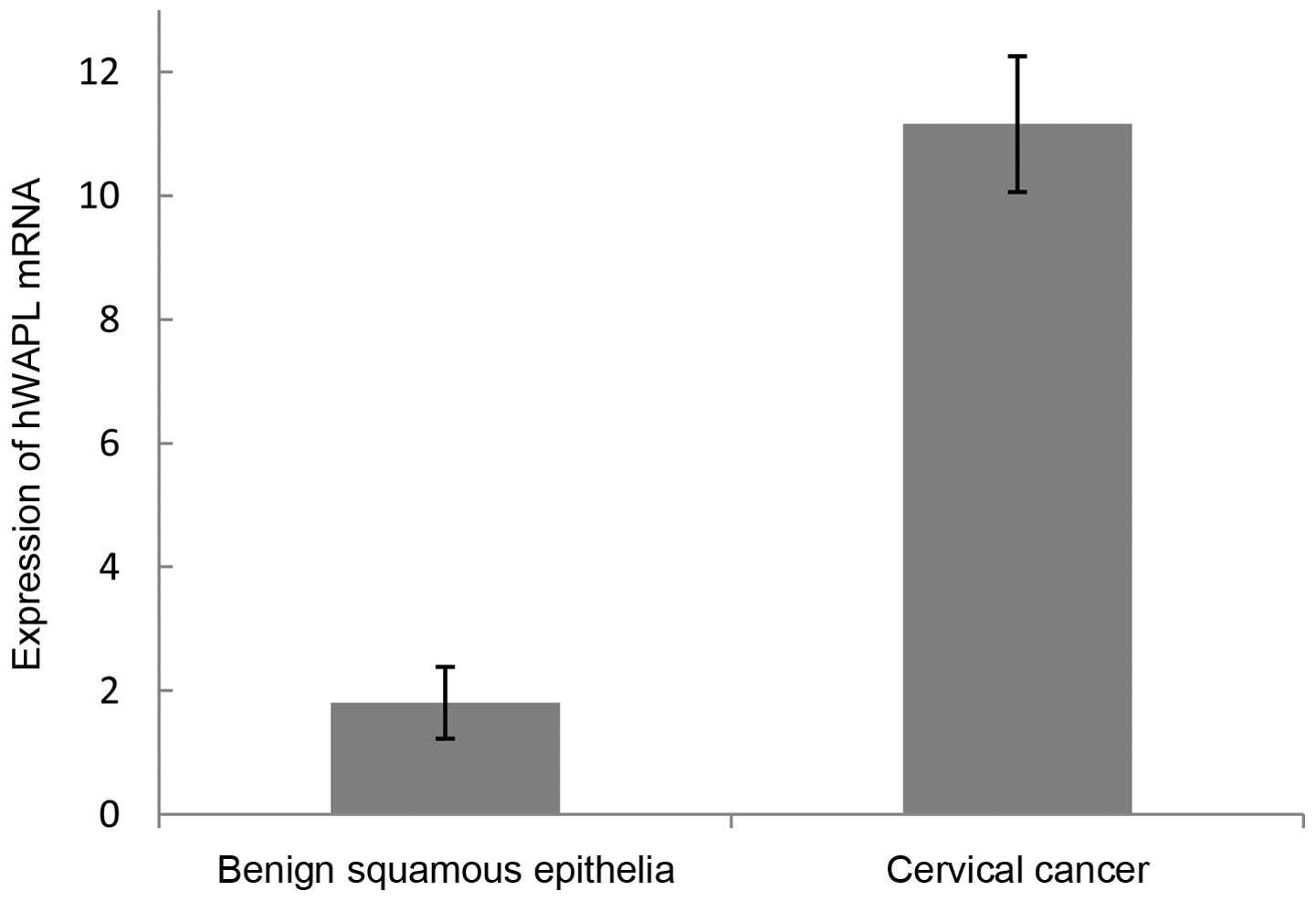 |
Figure 6
|
View References
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan Z, Li J, Pan X, Chen S, Wang Z, Li F,
Qu S and Shao R: Methylation of the RASSF1A gene promoter in Uigur
women with cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Tumori. 95:76–80.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dueñas-González A, Lizano M, Candelaria M,
Cetina L, Arce C and Cervera E: Epigenetics of cervical cancer. An
overview and therapeutic perspectives. Mol Cancer. 4:382005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Verní F, Gandhi R, Goldberg ML and Gatti
M: Genetic and molecular analysis of wings apart-like (WAPL), a
gene controlling heterochromatin organization in drosophila
melanogaster. Genetics. 154:1693–1710. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dobie KW, Kennedy CD, Velasco VM, McGrath
TL, Weko J, Patterson RW and Karpen GH: Identification of
chromosome inheritance modifiers in drosophila melanogaster.
Genetics. 157:1623–1637. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gandhi R, Gillespie PJ and Hirano T: Human
Wapl is a cohesin-binding protein that promotes sister-chromatid
resolution in mitotic prophase. Curr Biol. 16:2406–2417. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oikawa K, Ohbayashi T, Kiyono T, Nishi H,
Isaka K, Umezawa A, Kuroda M and Mukai K: Expression of a novel
human gene, human wings apart-like (hWAPL), is associated with
cervical carcinogenesis an tumor progression. Cancer Res.
64:3545–3549. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Adersson S, Rylander E, Larsson B, Strand
A, Silfversvärd C and Wilander E: The role of human papillomavirus
in cervical adenocarcinoma carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer.
37:246–250. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Muñoz N, Bosch FX, de Sanjosé S, Herrero
R, Castellsagué X, Shah KV, Snijders PJ and Meijer CJ:
International Agency for Research on Cancer Multicenter Cervical
Cancer Study Group: Epidemiologic classification of human
papillomavirus types associated with cervical caner. N Engl J Med.
348:518–527. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Doorbar J, Quint W, Banks L, Bravo IG,
Stoler M, Broker TR and Stanley MA: The biology and life-cycle of
human papillomaviruses. Vaccine. 30(Suppl 5): F55–F70. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuroda M, Kiyono T, Oikawa K, Yoshida K
and Mukai K: The human papillomavirus E6 and E7 inducible oncogene,
hWAPL, exhibits potential as a therapeutic target. Br J Cancer.
92:290–293. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|




















