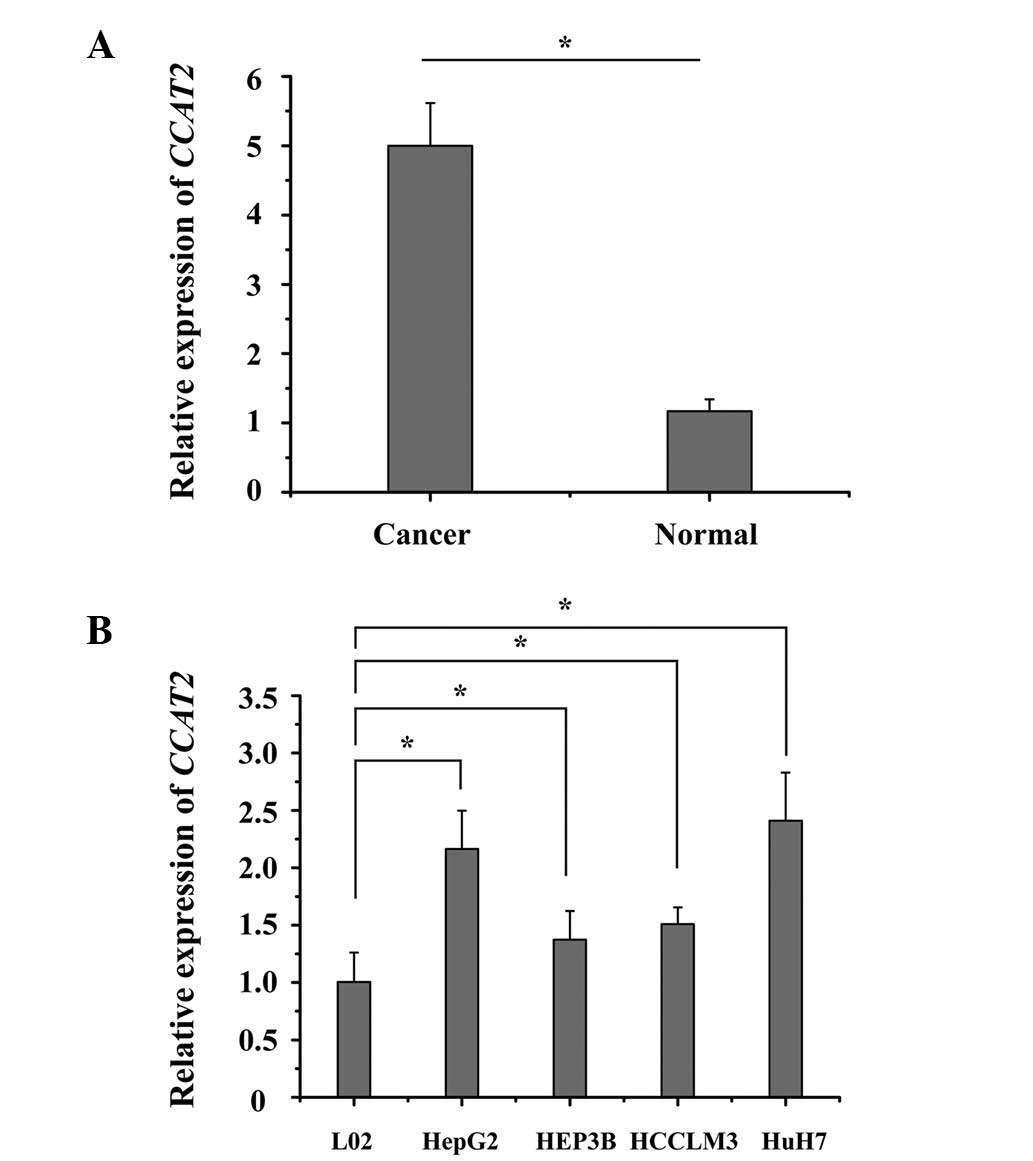
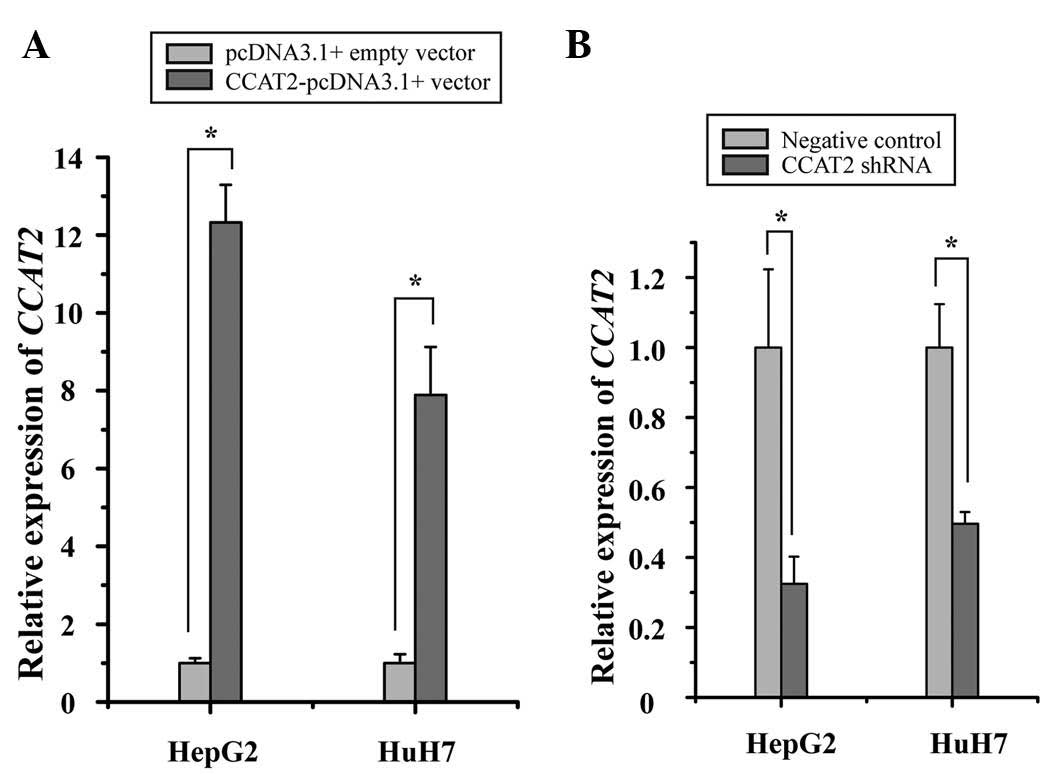
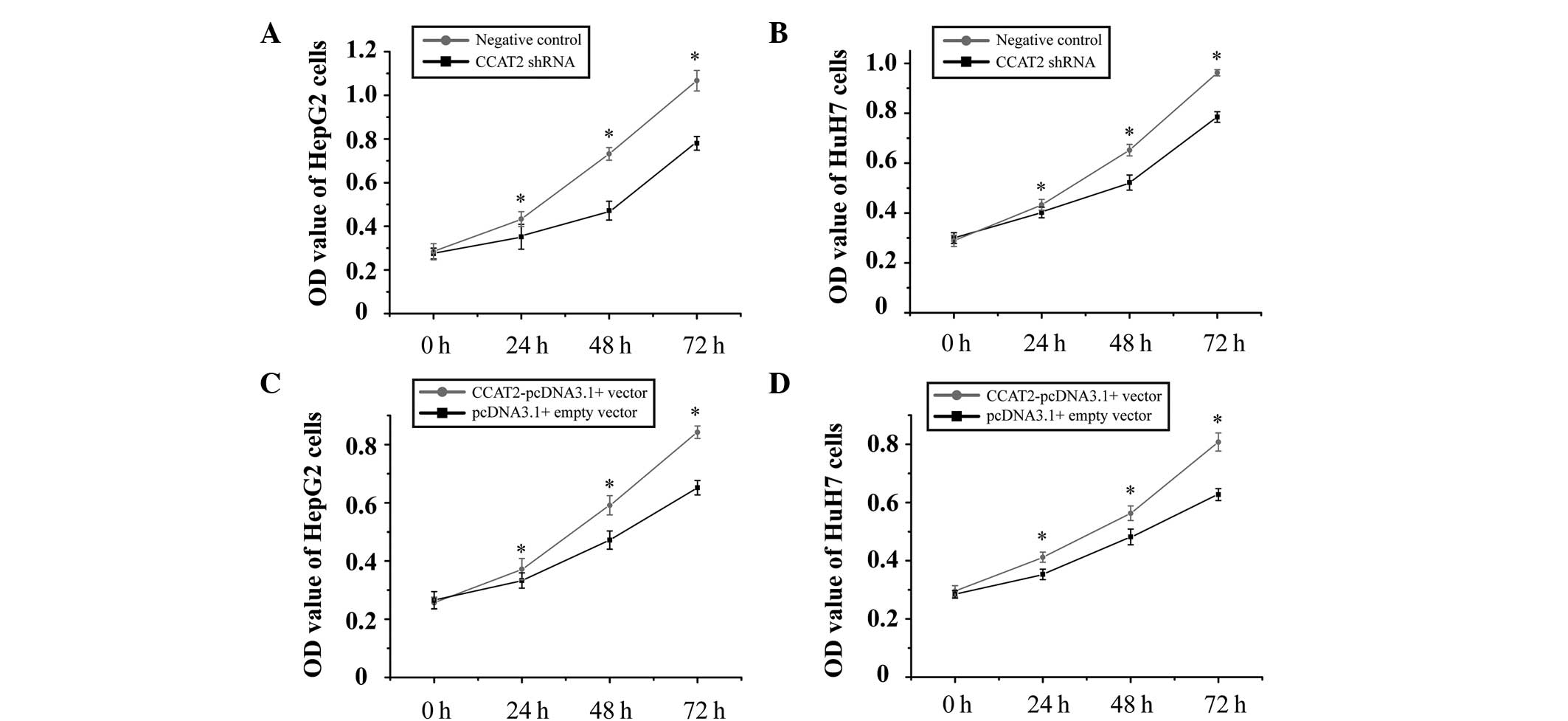
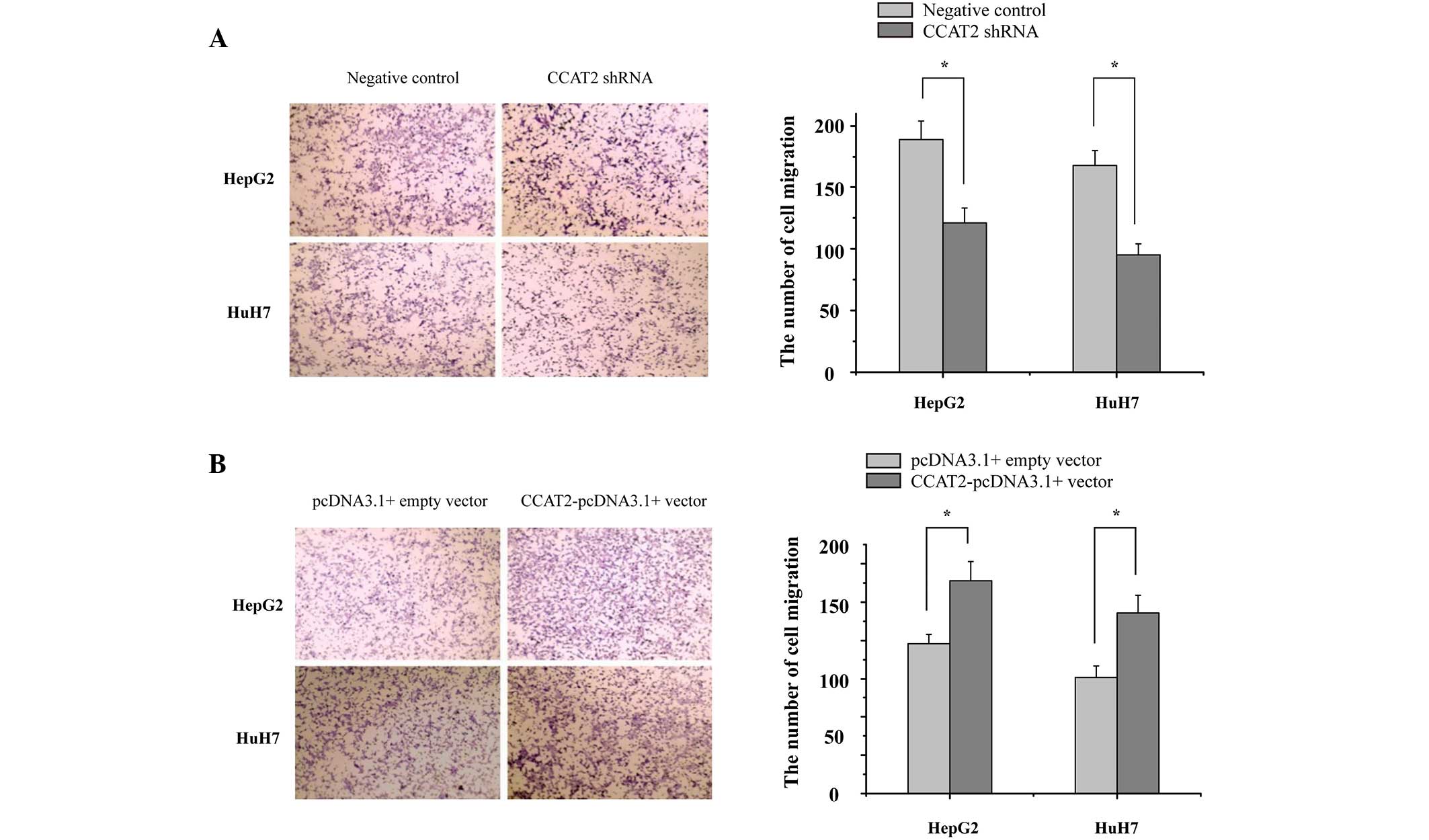
|
1
|
Lin L, Liang H, Wang Y, Yin X, Hu Y, Huang
J, Ren T, Xu H, Zheng L and Chen X: MicroRNA-141 inhibits cell
proliferation and invasion and promotes apoptosis by targeting
hepatocyte nuclear factor-3β in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC
Cancer. 14:8792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Block TM, Mehta AS, Fimmel CJ and Jordan
R: Molecular viral oncology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene.
22:5093–5107. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Braconi C, Valeri N, Kogure T, Gasparini
P, Huang N, Nuovo GJ, Terracciano L, Croce CM and Patel T:
Expression and functional role of a transcribed noncoding RNA with
an ultraconserved element in hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:786–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li G, Zhang H, Wan X, Yang X, Zhu C, Wang
A, He L, Miao R, Chen S and Zhao H: Long noncoding RNA plays a key
role in metastasis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:7805212014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cui M, Zheng M, Sun B, Wang Y, Ye L and
Zhang X: A long noncoding RNA perturbs the circadian rhythm of
hepatoma cells to facilitate hepatocarcinogenesis. Neoplasia.
17:79–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong P, Yu F, Fan X, Lin Z, Chen Y and Li
J: Inhibition of ATIR by shRNA prevents collagen synthesis in
hepatic stellate cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 344:195–202. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gomes AQ, Nolasco S and Soares H:
Non-coding RNAs: Multi-tasking molecules in the cell. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:16010–16039. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao SM, Xing CY, Chen CQ, Lin SS, Dong PH
and Yu FJ: miR-15a and miR-16-1 inhibit the proliferation of
leukemic cells by down-regulating WT1 protein level. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 30:1102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu FJ, Dong PH, Fan XF, Lin Z, Chen YP and
Li J: Down-regulation of angiotensin II by shRNA reduces collagen
synthesis in hepatic stellate cells. Int J Mol Med. 25:801–806.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen SL, Zheng MH, Yang T, Song M and Chen
YP: Disparate profiles of dys-regulated miRNAs in activated hepatic
stellate cells. Hepatology. 57:1285–1286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kitagawa M, Kotake Y and Ohhata T: Long
non-coding RNAs involved in cancer development and cell fate
determination. Curr Drug Targets. 13:1616–1621. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K, Srikantan S, Yang
X, Martindale JL, De S, Huarte M, Zhan M, Becker KG and Gorospe M:
LincRNA-p21 suppresses target mRNA translation. Mol Cell.
47:648–655. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoon JH, Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M:
Posttranscriptional gene regulation by long noncoding RNA. J Mol
Biol. 425:3723–3730. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Yang L and Chen LL: Life without
A tail: New formats of long noncoding RNAs. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 54:338–349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nadal-Ribelles M, Solé C, Xu Z, Steinmetz
LM, de Nadal E and Posas F: Control of Cdc28 CDK1 by a
stress-induced lncRNA. Mol Cell. 53:549–561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang F, Yi F, Han X, Du Q and Liang Z:
MALAT-1 interacts with hnRNP C in cell cycle regulation. FEBS Lett.
587:3175–3181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y and Song Y:
Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human
diseases. Cancer Lett. 339:159–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lai MC, Yang Z, Zhou L, Zhu QQ, Xie HY,
Zhang F, Wu LM, Chen LM and Zheng SS: Long non-coding RNA MALAT-1
overexpression predicts tumor recurrence of hepatocellular
carcinoma after liver transplantation. Med Oncol. 29:1810–1816.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ishibashi M, Kogo R, Shibata K, Sawada G,
Takahashi Y, Kurashige J, Akiyoshi S, Sasaki S, Iwaya T, Sudo T, et
al: Clinical significance of the expression of long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:946–950.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Braconi C, Kogure T, Valeri N, Huang N,
Nuovo G, Costinean S, Negrini M, Miotto E, Croce CM and Patel T:
microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene
MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene. 30:4750–4756. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang CY, Hua L, Yao KH, Chen JT, Zhang JJ
and Hu JH: Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 is up-regulated in gastric
cancer and associated with poor prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:779–785. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiu M, Xu Y, Yang X, Wang J, Hu J, Xu L
and Yin R: CCAT2 is a lung adenocarcinoma-specific long non-coding
RNA and promotes invasion of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour
Biol. 35:5375–5380. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deng R, Liu B, Wang Y, Yan F, Hu S, Wang
H, Wang T, Li B, Deng X, Xiang S, et al: High expression of the
newly found long noncoding RNA Z38 promotes cell proliferation and
oncogenic activity in breast cancer. J Cancer. 7:576–586. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng W, Wang J, Zhang J, Cai J, Bai Z and
Zhang Z: TET2 regulates LncRNA-ANRIL expression and inhibits the
growth of human gastric cancer cells. IUBMB Life. 68:355–364. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Qiu M, Xu Y, Li M, Dong G, Mao Q,
Yin R and Xu L: Long noncoding RNA CCAT2 correlates with smoking in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:5523–5528.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Redis RS, Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Tudoran
O, Ivan C, Spizzo R, Zhang X, de Weerd V, Shimizu M, Ling H, et al:
CCAT2, a novel long non-coding RNA in breast cancer: Expression
study and clinical correlations. Oncotarget. 4:1748–1762. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ling H, Spizzo R, Atlasi Y, Nicoloso M,
Shimizu M, Redis RS, Nishida N, Gafà R, Song J, Guo Z, et al:
CCAT2, a novel noncoding RNA mapping to 8q24, underlies metastatic
progression and chromosomal instability in colon cancer. Genome
Res. 23:1446–1461. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu J, Liu S, Ye F, Shen Y, Tie Y, Zhu J,
Jin Y, Zheng X, Wu Y and Fu H: The long noncoding RNA expression
profile of hepatocellular carcinoma identified by microarray
analysis. PLoS One. 9:e1017072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pan YF, Feng L, Zhang XQ, Song LJ, Liang
HX, Li ZQ and Tao FB: Role of long non-coding RNAs in gene
regulation and oncogenesis. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:2378–2383.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li J, Meng H, Bai Y and Wang K: Regulation
of lncRNA and its role in cancer metastasis. Oncol Res. 23:205–217.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Adams BD, Anastasiadou E, Esteller M, He L
and Slack FJ: The inescapable influence of noncoding RNAs in
cancer. Cancer Res. 75:5206–5210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Faghihi MA, Modarresi F, Khalil AM, Wood
DE, Sahagan BG, Morgan TE, Finch CE, St Laurent G III, Kenny PJ and
Wahlestedt C: Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in
Alzheimer's disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of
beta-secretase. Nat Med. 14:723–730. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Pickard MR, Hedge
VL, Farzaneh F and Williams GT: GAS5, a non-protein-coding RNA,
controls apoptosis and is downregulated in breast cancer. Oncogene.
28:195–208. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuan SX, Yang F, Yang Y, Tao QF, Zhang J,
Huang G, Yang Y, Wang RY, Yang S, Huo XS, et al: Long noncoding RNA
associated with microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma
promotes angiogenesis and serves as a predictor for hepatocellular
carcinoma patients' poor recurrence-free survival after
hepatectomy. Hepatology. 56:2231–2241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Matouk IJ, DeGroot N, Mezan S, Ayesh S,
Abu-lail R, Hochberg A and Galun E: The H19 non-coding RNA is
essential for human tumor growth. PLoS One. 2:e8452007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang F, Zhang L, Huo XS, Yuan JH, Xu D,
Yuan SX, Zhu N, Zhou WP, Yang GS, Wang YZ, et al: Long noncoding
RNA high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma facilitates tumor
growth through enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in humans. Hepatology.
54:1679–1689. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen X, Liu L and Zhu W: Up-regulation of
long non-coding RNA CCAT2 correlates with tumor metastasis and poor
prognosis in cervical squamous cell cancer patients. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:13261–13266. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|