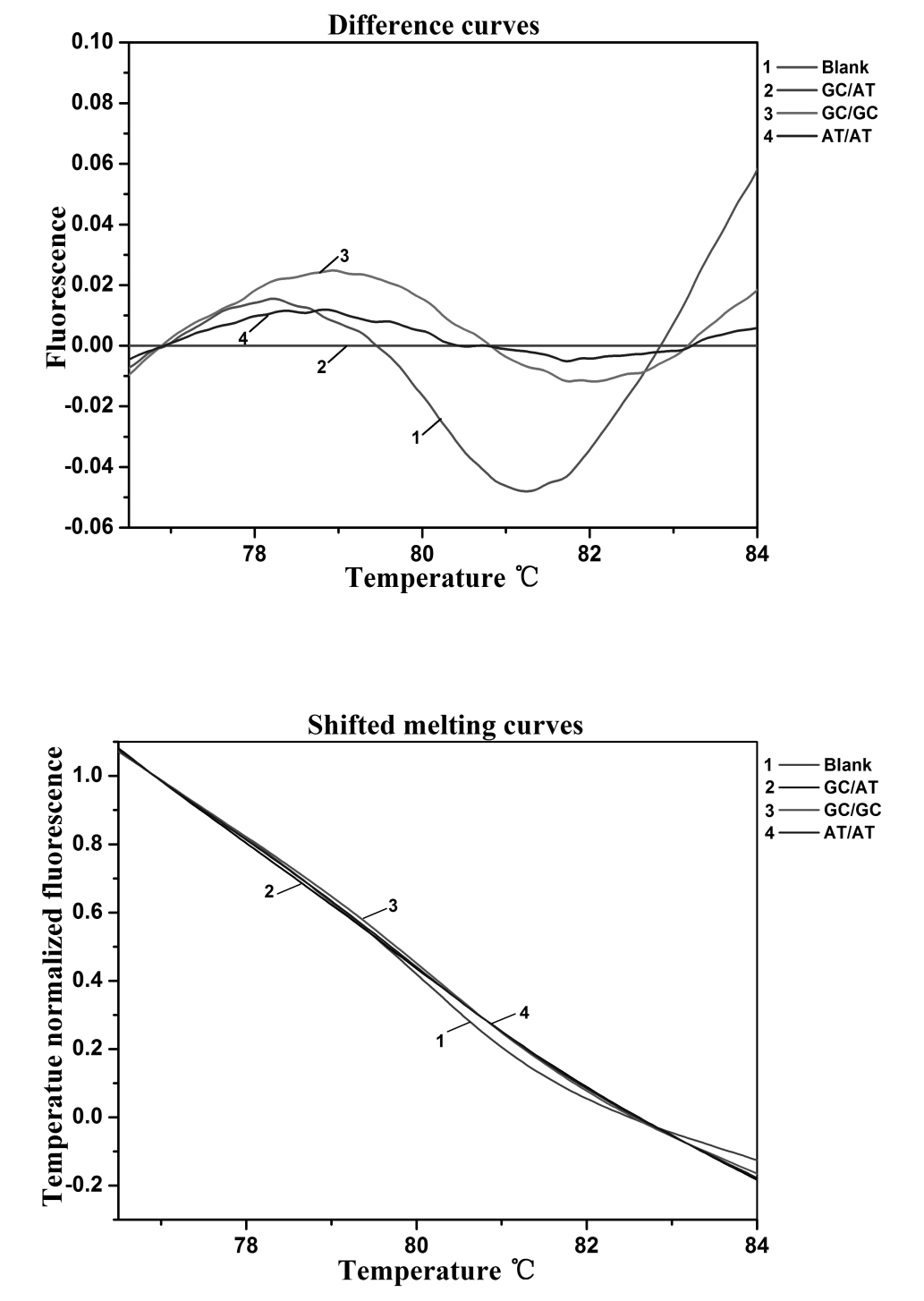
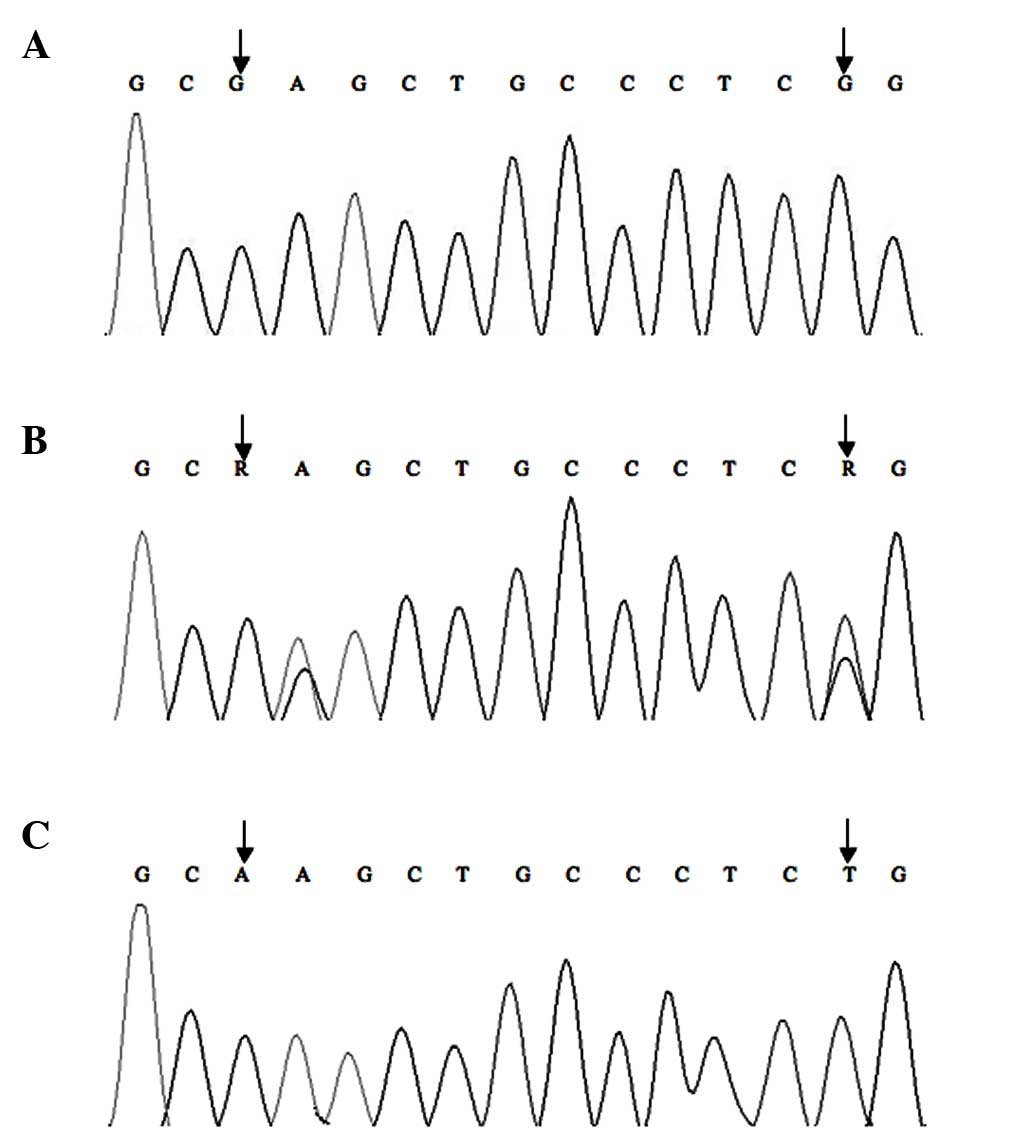
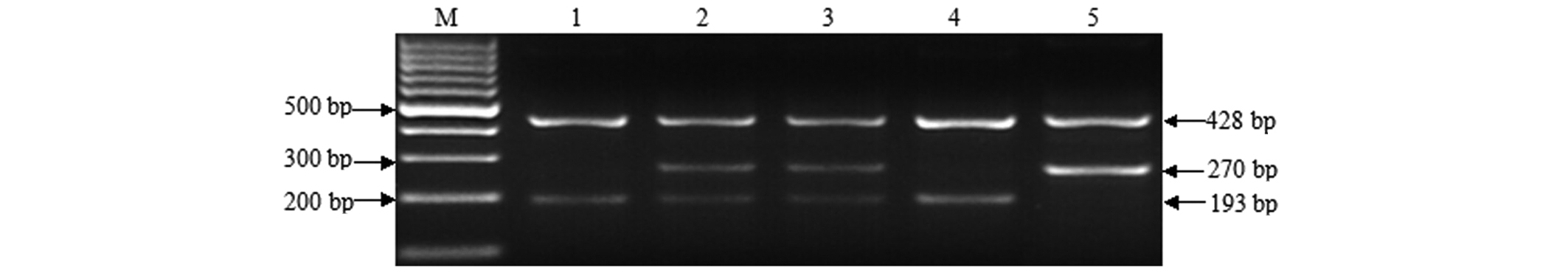
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akinyemiju TF: Socio-economic and health
access determinants of breast and cervical cancer screening in
low-income countries: Analysis of the world health survey. PLoS
One. 7:e488342012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ginsberg GM, Lauer JA, Zelle S, Baeten S
and Baltussen R: Cost effectiveness of strategies to combat breast,
cervical, and colorectal cancer in sub-Saharan Africa and South
East Asia: Mathematical modelling study. BMJ. 344:e6142012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shuai HL, Luo X, Yan RL, Li J and Chen DL:
XRCC1 polymorphisms are associated with cervical cancer risk and
response to chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:6423–6427. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gocze K, Gombos K, Juhasz K, Kovacs K,
Kajtar B, Benczik M, Gocze P, Patczai B, Arany I and Ember I:
Unique microRNA expression profiles in cervical cancer. Anticancer
Res. 33:2561–2567. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moore EE, Wark JD, Hopper JL, Erbas B and
Garland SM: CeCaGeEn Study Group: The roles of genetic and
environmental factors on risk of cervical cancer: A review of
classical twin studies. Twin Res Hum Genet. 15:79–86. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Atalah E, Urteaga C, Rebolledo A, Villegas
RA, Medina E and Csendes A: Diet, smoking and reproductive history
as risk factor for cervical cancer. Rev Med Chile. 129:597–603.
2001.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bayo S, Bosch FX, De SS, Munoz N, Combita
AL, Coursaget P, Diaz M, Dolo A, van den Brule AJ and Meijer CJ:
Risk factors of invasive cervical cancer in Mali. Int J Epidemiol.
31:202–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vaccarella S, Lortet-Tieulent J, Plummer
M, Franceschi S and Bray F: Worldwide trends in cervical cancer
incidence: Impact of screening against changes in disease risk
factors. Eur J Cancer. 49:3262–3273. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lippman A, Melnychuk R, Shimmin C and
Boscoe M: Human papillomavirus, vaccines and women's health:
Questions and cautions. CMAJ. 177:484–487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Turati F, Negri E and Vecchia CL: Family
history and the risk of cancer: Genetic factors influencing
multiple cancer sites. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 14:1–4. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Asher G, Tsvetkov P, Kahana C and Shaul Y:
A mechanism of ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation of the
tumor suppressors p53 and p73. Genes Dev. 19:316–321. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ramadan S, Terrinoni A, Catani MV, Sayan
AE, Knight RA, Mueller M, Krammer PH, Melino G and Candi E: p73
induces apoptosis by different mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 331:713–717. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Murray-Zmijewski F, Lane DP and Bourdon
JC: p53/p63/p73 isoforms: An orchestra of isoforms to harmonise
cell differentiation and response to stress. Cell Death Differ.
13:962–972. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zawacka-Pankau J, Kostecka A, Sznarkowska
A, Hedström E and Kawiak A: p73 tumor suppressor protein: A close
relative of p53 not only in structure but also in anti-cancer
approach? Cell Cycle. 9:720–728. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Massagué J: G1 cell-cycle control and
cancer. Nature. 432:298–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moll UM and Slade N: p63 and p73: Roles in
development and tumor formation. Mol Cancer Res. 2:371–386.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tomasini R, Mak TW and Melino G: The
impact of p53 and p73 on aneuploidy and cancer. Trends Cell Biol.
18:244–252. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rufini A, Agostini M, Grespi F, Tomasini
R, Sayan BS, Niklison-Chirou MV, Conforti F, Velletri T, Mastino A,
Mak TW, et al: p73 in Cancer. Genes Cancer. 2:491–502. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ahomadegbe JC, Tourpin S, Kaghad M, Zelek
L, Vayssade M, Mathieu MC, Rochard F, Spielmann M, Tursz T, Caput
D, et al: Loss of heterozygosity, allele silencing and decreased
expression of p73 gene in breast cancers: Prevalence of alterations
in inflammatory breast cancers. Oncogene. 19:5413–5418. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schabath MB, Wu X, Wei Q, Li G, Gu J and
Spitz MR: Combined effects of the p53 and p73 polymorphisms on lung
cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:158–161. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L,
Biscan JC, Valent A, Minty A, Chalon P, Lelias JM, Dumont X, et al:
Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at lp36, a region
frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell.
90:809–819. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu Y, Dong W, Mou Q, Leng Y, Zhang L and
Duan L: Impact of p73 gene polymorphism on cancer susceptibility: A
meta analysis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:6820–6825. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng B, Liu F, Wei Y, Luo L, Chen X, Yan L
and Li B: Association of a p73 exon 2 G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism
with risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population.
Tumour Biol. 34:293–299. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yuan P, Miao XP, Zhang XM, Wang ZH, Tan W,
Zhang XR, Sun Y, Xu BH and Lin DX: Association of the
responsiveness of advanced non-small cell lung cancer to
platinum-based chemotherapy with p53 and p73 polymorphisms.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 28:107–110. 2006.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang S, Wang DJ, Li WS, Wang N, Zhou RM,
Sun DL, Duan YN, Li SZ, Li XF and Li Y: Association of p73 and MDM2
polymorphisms with the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer in Chinese
women. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 19:572–577. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou X and Wu C: Association of p73
G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphisms with genetic susceptibilities to
breast cancer: A case-control study. Med Oncol. 29:3216–3221. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang SS, Guo HY, Dong LL, Zhu XQ, Ma L, Li
W and Tang JX: Association between a p73 gene polymorphism and
genetic susceptibility to non-small cell lung cancer in the south
of China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:10387–10391. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang HQ, Lu SJ, Tang MX, Chen LQ, Liu SH,
Guo CF, Wang XY, Chen J and Xie L: Association of estrogen receptor
beta gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 34:760–764. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
De Feo E, Simone B, Kamgaing RS, Gallì P,
Hamajima N, Hu Z, Li G, Li Y, Matsuo K, Park JY, et al: p73
G4C14-to-A4T14 gene polymorphism and interaction with p53 exon 4
Arg72Pro on cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis of the
literature. Mutagenesis. 27:267–273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xia S, Fang L, Zhao Z, Xie F and Li H:
Genetic association between p73 G4C14-A4T14 polymorphism and risk
of squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Med. 16:49–55. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou X: p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphisms
are positively correlated with triple-negative breast cancer in
southwestern China. Med Oncol. 30:5152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang DJ, Yan LI, Zhou RM, Wang N, Duan Y,
Sun D, Li S, Li X and Kang S: Association of p73 and MDM2
polymorphisms with the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer. Tumor.
29:892–897. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Craveiro R, Bravo I, Catarino R, Teixeira
AL, Sousa H, Pereira D, Pereira H and Medeiros R: The role of p73
G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism in the susceptibility to cervical
cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 31:224–229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Niwa Y, Hamajima N, Atsuta Y, Yamamoto K,
Tamakoshi A, Saito T, Hirose K, Nakanishi T, Nawa A, Kuzuya K and
Tajima K: Genetic polymorphisms of p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 at exon 2 and
p53 Arg72Pro and the risk of cervical cancer in Japanese. Cancer
Lett. 205:55–60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu S, Chan K, Leung R, Tsang P, Wei N and
Ngan H: Genetic polymorphisms of p73 is associated with the risk of
cervical cancer. Cancer Res. 67:34342007.
|
|
38
|
Vossen RH, Aten E, Roos A and den Dunnen
JT: High-resolution melting analysis (HRMA): More than just
sequence variant screening. Hum Mutat. 30:860–866. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|