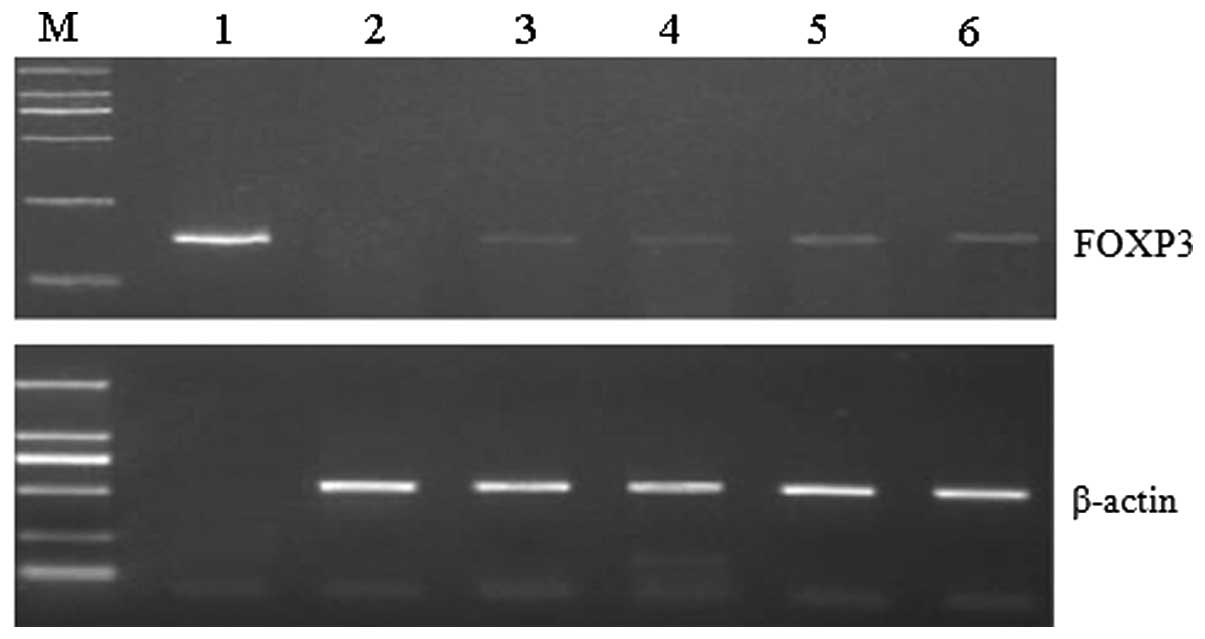
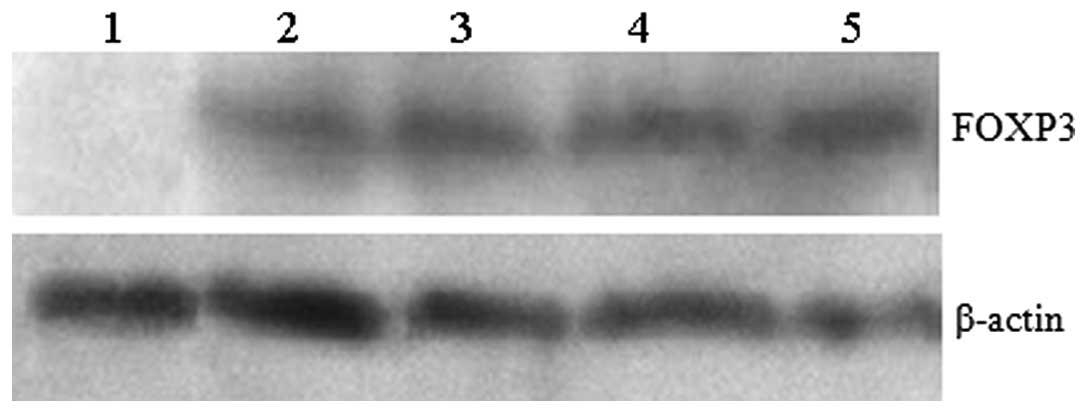
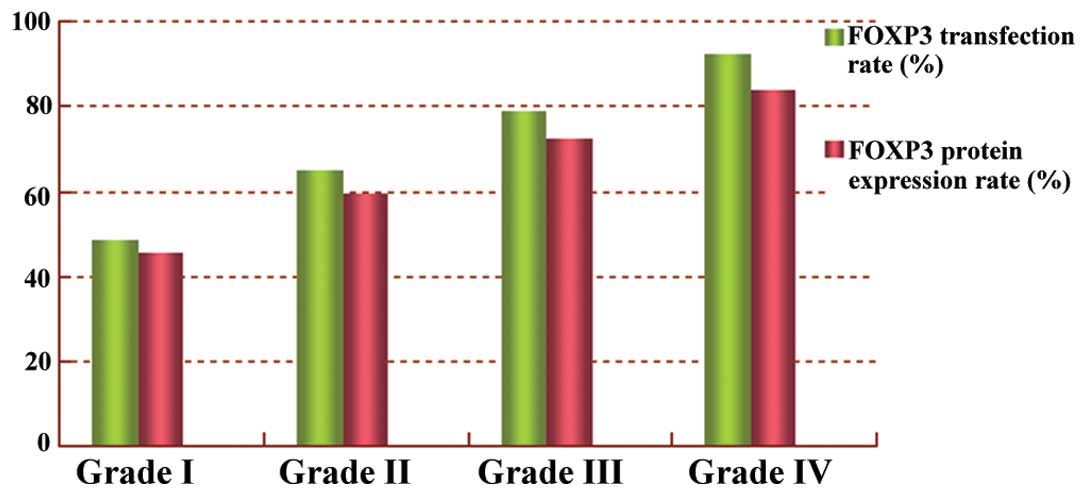
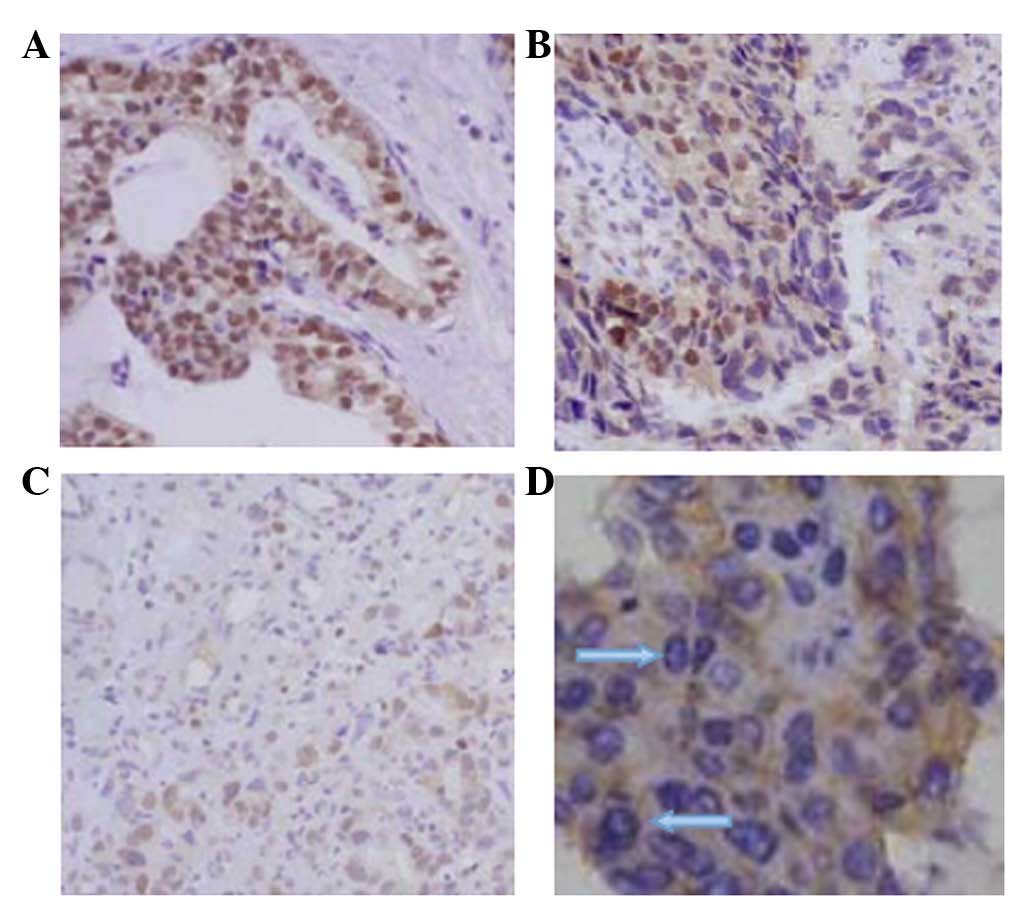
|
1
|
Sugano K: Screening of gastric cancer in
Asia. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 29:895–905. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smid D, Skalicky T, Dolezal J, Kubackova D
and Fichtl J: Surgical treatment of gastric cancer. Bratisl Lek
Listy. 116:666–670. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Reuver PR, Mehta S, Gill P, Andrici J,
D'Urso L, Clarkson A, Mittal A, Hugh TJ, Samra JS and Gill AJ:
Immunoregulatory forkhead box protein p3-positive lymphocytes are
associated with overall survival in patients with pancreatic
neuroendocrine tumors. J Am Coll Surg. 222:281–287. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kasprowicz DJ, Smallwood PS, Tyznik AJ and
Ziegler SF: Scurfin (FoxP3) controls T-dependent immune responses
in vivo through regulation of CD4+ T cell effector function. J
Immunol. 171:1216–1223. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gambineri E, Torgerson TR and Ochs HD:
Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, and X-linked
inheritance (IPEX), a syndrome of systemic autoimmunity caused by
mutations of FOXP3, a critical regulator of T cell homeostasis.
Curr Opin Rheumatol. 15:430–435. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lopes JE, Torgerson TR, Schubert LA,
Anover SD, Ocheltree EL, Ochs HD and Ziegler SF: Analysis of FOXP3
reveals multiple domains required for its function as a
transcriptional repressor. J Immunol. 177:3133–3142. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Buckner JH and Ziegler SF: Functional
analysis of FOXP3. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1143:151–169. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng L, Wang X, Xu L, Wang N, Cai P,
Liang T and Hu L: Foxp3 gene polymorphisms and haplotypes associate
with susceptibility of Graves' disease in Chinese Han population.
Int Immunopharmacol. 25:425–431. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Safinia N, Scotta C, Vaikunthanathan T,
Lechler RI and Lombardi G: Regulatory T cells: Serious contenders
in the promise for immunological tolerance in transplantation.
Front Immunol. 6:4382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bettelli E, Dastrange M and Oukka M: Foxp3
interacts with nuclear factor of activated T cells and NF-kappa B
to repress cytokine gene expression and effector functions of T
helper cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:5138–5143. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Klabusay M: The role of regulatory T-cells
in antitumor immune response. Klin Onkol. 28(Suppl 4): 4S23–4S27.
2015.(In Czech). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hou J, Yu Z, Xiang R, Li C and Wang L,
Chen S, Li Q, Chen M and Wang L: Correlation between infiltration
of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells and expression of B7-H1 in the tumor
tissues of gastric cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. 96:284–291. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li B, Samanta A, Song X, Iacono KT, Bembas
K, Tao R, Basu S, Riley JL, Hancock WW, Shen Y, et al: FOXP3
interactions with histone acetyltransferase and class II histone
deacetylases are required for repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:4571–4576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuan XL, Shen DF, Lu J, Dong P, Wang J, Li
MX and Shen LS: The populations, distribution of regulatory T
cells, Foxp3 mRNA expression gastric cancer patients and the
association with malignant stage. Chinese Journal of Laboratory
Medicine. 31:378–383. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Mühler MR, Clément O, Salomon LJ, Balvay
D, Autret G, Vayssettes C, Cuénod CA and Siauve N: Maternofetal
pharmacokinetics of a gadolinium chelate contrast agent in mice.
Radiology. 258:455–460. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen BB, Liang PC, Liu KL, Hsiao JK, Huang
JC, Wong JM, Lee PH, Shun CT and Ming-Tsang Y: Preoperative
diagnosis of gastric tumors by three-dimensional multidetector row
CT and double contrast barium meal study: Correlation with surgical
and histologic results. J Formos Med Assoc. 106:943–952. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stengel A, Goebel M, Wang L, Rivier J,
Kobelt P, Mönnikes H, Lambrecht NW and Taché Y: Central nesfatin-1
reduces dark-phase food intake and gastric emptying in rats:
Differential role of corticotropin-releasing factor2 receptor.
Endocrinology. 150:4911–4919. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiong Y, Svingen PA, Sarmento OO, Smyrk
TC, Dave M, Khanna S, Lomberk GA, Urrutia RA and Faubion WA Jr:
Differential coupling of KLF10 to Sin3-HDAC and PCAF regulates the
inducibility of the FOXP3 gene. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol. 307:R608–R620. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Merchant SJ, Kim J, Choi AH, Sun V, Chao J
and Nelson R: A rising trend in the incidence of advanced gastric
cancer in young Hispanic men. Gastric Cancer. Feb 29–2016.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hacker U and Lordick F: Current standards
in the treatment of gastric cancer. Dtsch Med Wochenschr.
140:1202–1205. 2015.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kohno D, Nakata M, Maejima Y, Shimizu H,
Sedbazar U, Yoshida N, Dezaki K, Onaka T, Mori M and Yada T:
Nesfatin1 neurons in paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the
rat hypothalamus coexpress oxytocin and vasopressin and are
activated by refeeding. Endocrinology. 149:1295–1301. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yanai H, Matsumoto Y, Harada T, Nishiaki
M, Tokiyama H, Shigemitsu T, Tada M and Okita K: Endoscopic
ultrasonography and endoscopy for staging depth of invasion in
early gastric cancer: A pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc.
46:212–216. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Levi E, Sochacki P, Khoury N, Patel BB and
Majumdar AP: Cancer stem cells in Helicobacter pylori infection and
aging: Implications for gastric carcinogenesis. World J
Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 5:366–372. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ke X, Wang J, Li L, Chen IH, Wang H and
Yang XF: Roles of CD4+CD25 (high) FOXP3+ Tregs in lymphomas and
tumors are complex. Front Biosci. 13:3986–4001. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kakinuma T, Nadiminti H, Lonsdorf AS,
Murakami T, Perez BA, Kobayashi H, Finkelstein SE, Pothiawala G,
Belkaid Y and Hwang ST: Small numbers of residual tumor cells at
the site of primary inoculation are critical for anti-tumor
immunity following challenge at a secondary location. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 56:1119–1131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hao Q, Zhang C, Gao Y, Wang S, Li J, Li M,
Xue X, Li W, Zhang W and Zhang Y: FOXP3 inhibits NF-κB activity and
hence COX2 expression in gastric cancer cells. Cell Signal.
26:564–569. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou Z, Song X, Li B and Greene MI: FOXP3
and its partners: Structural and biochemical insights into the
regulation of FOXP3 activity. Immunol Res. 42:19–28. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mizukami Y, Kono K, Kawaguchi Y, Akaike H,
Kamimura K, Sugai H and Fujii H: Localisation pattern of Foxp3+
regulatory T cells is associated with clinical behaviour in gastric
cancer. Br J Cancer. 98:148–153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Allan SE, Passerini L, Bacchetta R,
Crellin N, Dai M, Orban PC, Ziegler SF, Roncarolo MG and Levings
MK: The role of 2 FOXP3 isoforms in the generation of human CD4+
Tregs. J Clin Invest. 115:3276–3284. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karanikas V, Speletas M, Zamanakou M,
Kalala F, Loules G, Kerenidi T, Barda AK, Gourgoulianis KI and
Germenis AE: Foxp3 expression in human cancer cells. J Transl Med.
6:192008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zuo T, Wang L, Morrison C, Chang X, Zhang
H, Li W, Liu Y, Wang Y, Liu X, Chan MW, et al: FOXP3 is an X-linked
breast cancer suppressor gene and an important repressor of the
HER-2/ErbB2 oncogene. Cell. 129:1275–1286. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Durães C, Almeida GM, Seruca R, Oliveira C
and Carneiro F: Biomarkers for gastric cancer: Prognostic,
predictive or targets of therapy? Virchows Arch. 464:367–378. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zheng Y, Josefowicz SZ, Kas A, Chu TT,
Gavin MA and Rudensky AY: Genome-wide analysis of Foxp3 target
genes in developing and mature regulatory T cells. Nature.
445:936–940. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|