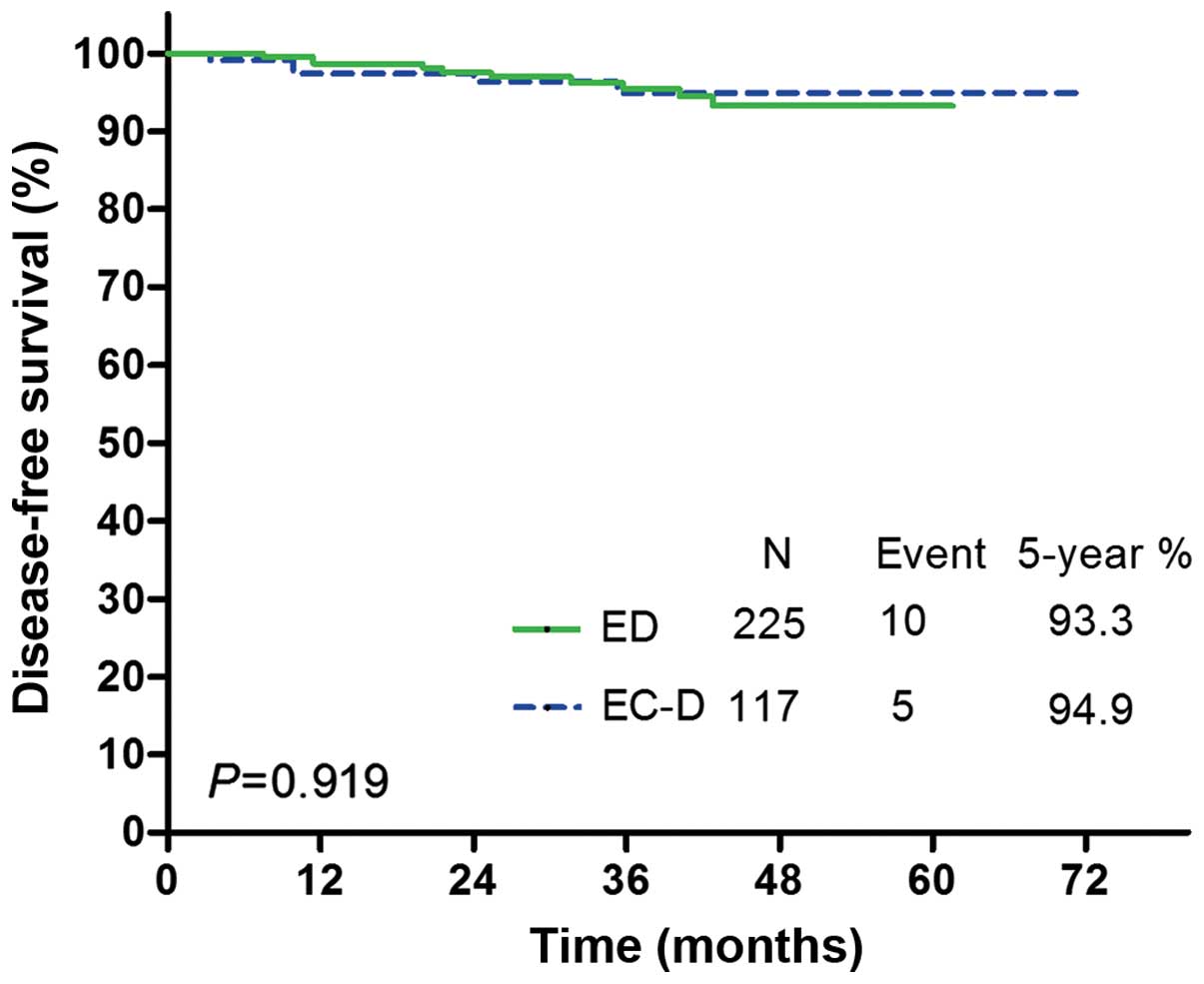
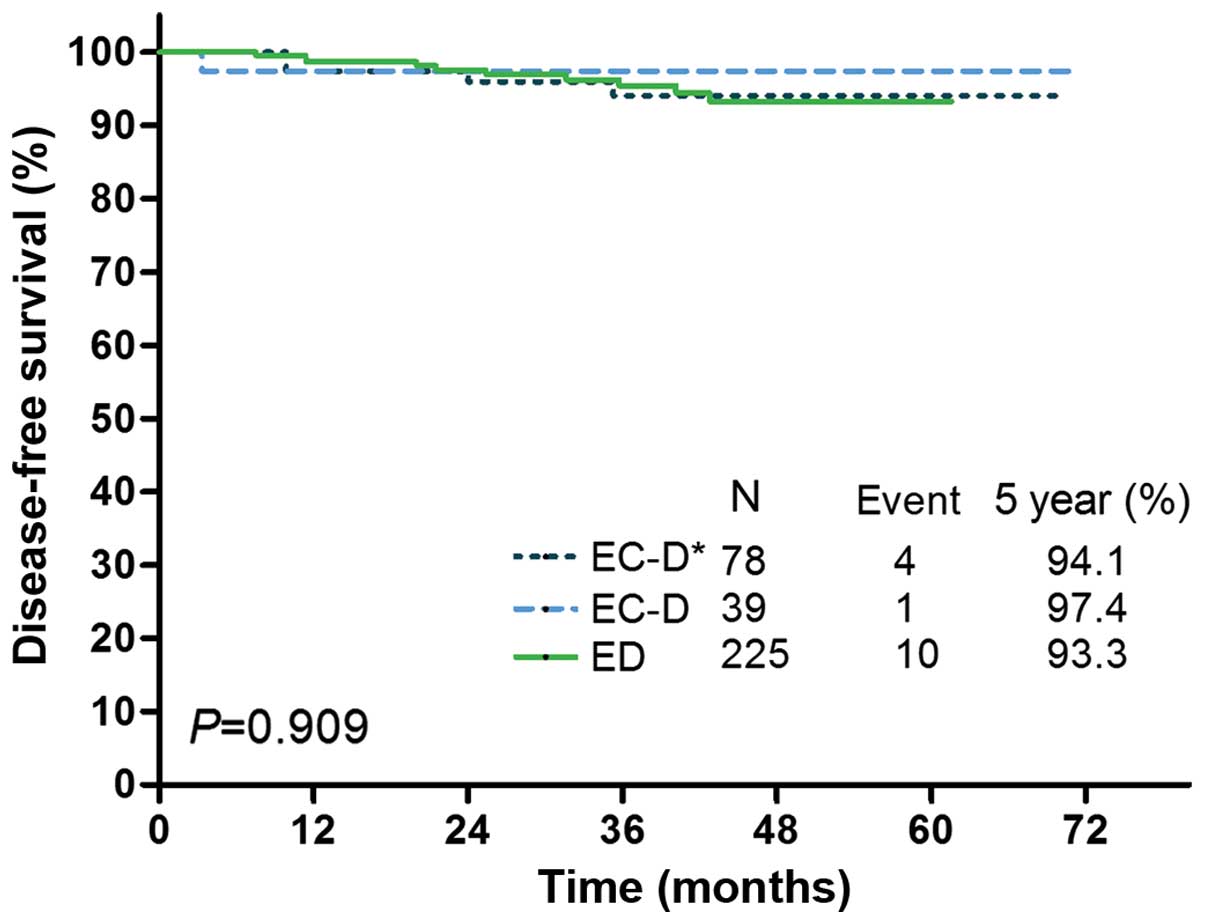
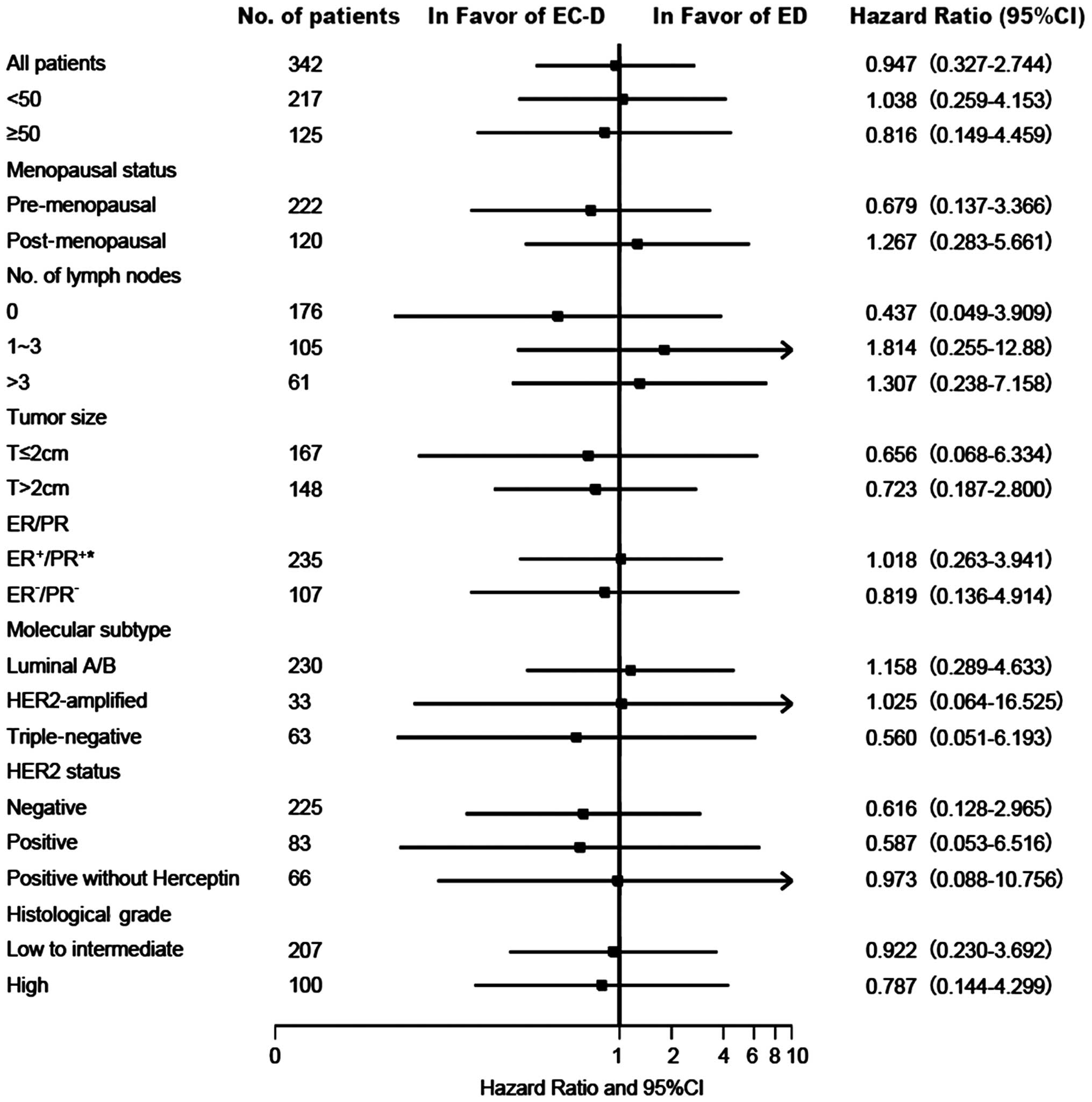
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Forman
D, Bray F, Dikshit R, Elser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M and Parkin DM:
GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC
CancerBase No. 11 (Internet). International Agency for Research on
Cancer (Lyon, France). 2013.http://globocan.iarc.frAccessed. May 07–2015
|
|
2
|
Fan L, Zheng Y, Yu KD, Liu GY, Wu J, Lu
JS, Shen KW, Shen ZZ and Shao ZM: Breast cancer in a transitional
society over 18 years: Trends and present status in Shanghai,
China. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 117:409–416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Porter P: ‘Westernizing’ women's risks?
Breast cancer in lower-income countries. N Engl J Med. 358:213–216.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Early Breast Cancer Trialists'
Collaborative Group (EBCTCG): Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal
therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival:
An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 365:1687–1717. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yuan XM, Wang N, Ouyang T, Yang L, Song
MY, Lin BY, Xie YT, Li JF, Pan KF, You WC, et al: Current status of
diagnosis and treatment of primary breast cancer in beijing, 2008.
Chin J Cancer Res. 23:38–42. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nabholtz JM, Falkson C, Campos D, Szanto
J, Martin M, Chan S, Pienkowski T, Zaluski J, Pinter T, Krzakowski
M, et al: TAX 306 Study Group: Docetaxel and doxorubicin compared
with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide as first-line chemotherapy
for metastatic breast cancer: Results of a randomized, multicenter,
phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 21:968–975. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Steger GG, Galid A, Gnant M, Mlineritsch
B, Lang A, Tausch C, Rudas M, Greil R, Wenzel C, Singer CF, et al:
ABCSG-14: Pathologic complete response with six compared with three
cycles of neoadjuvant epirubicin plus docetaxel and granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor in operable breast cancer: Results of
ABCSG-14. J Clin Oncol. 25:2012–2018. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shao N, Wang S, Yao C, Xu X, Zhang Y,
Zhang Y and Lin Y: Sequential versus concurrent anthracyclines and
taxanes as adjuvant chemotherapy of early breast cancer: A
meta-analysis of phase III randomized control trials. Breast.
21:389–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Eiermann W, Pienkowski T, Crown J, Sadeghi
S, Martin M, Chan A, Saleh M, Sehdev S, Provencher L, Semiglazov V,
et al: Phase III study of doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide with
concomitant versus sequential docetaxel as adjuvant treatment in
patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-normal,
node-positive breast cancer: BCIRG-005 trial. J Clin Oncol.
29:3877–3884. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Francis P, Crown J, Di Leo A, Buyse M,
Balil A, Andersson M, Nordenskjöld B, Lang I, Jakesz R, Vorobiof D,
et al: BIG 02–98 Collaborative Group: Adjuvant chemotherapy with
sequential or concurrent anthracycline and docetaxel: Breast
International Group 02–98 randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:121–133. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Laurentiis M, Cancello G, D'Agostino D,
Giuliano M, Giordano A, Montagna E, Lauria R, Forestieri V,
Esposito A, Silvestro L, et al: Taxane-based combinations as
adjuvant chemotherapy of early breast cancer: A meta-analysis of
randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 26:44–53. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Goldstein LJ, O'Neill A, Sparano JA, Perez
EA, Shulman LN, Martino S and Davidson NE: Concurrent doxorubicin
plus docetaxel is not more effective than concurrent doxorubicin
plus cyclophosphamide in operable breast cancer with 0 to 3
positive axillary nodes: North American Breast Cancer Intergroup
Trial E 2197. J Clin Oncol. 26:4092–4099. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Swain SM, Jeong JH, Geyer CE Jr,
Costantino JP, Pajon ER, Fehrenbacher L, Atkins JN, Polikoff J,
Vogel VG, Erban JK, et al: Longer therapy, iatrogenic amenorrhea,
and survival in early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 362:2053–2065.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Harvey V, Mouridsen H, Semiglazov V,
Jakobsen E, Voznyi E, Robinson BA, Groult V, Murawsky M and Cold S:
Phase III trial comparing three doses of docetaxel for second-line
treatment of advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 24:4963–4970.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan P, Wang J, Ma F, Fan Y, Luo Y, Cai R,
Zhang P, Li Q and Xu B: Comparison of six cycles of epirubicin and
paclitaxel (ET) versus four cycles of epirubicin and
cyclophosphamide, followed by four cycles of paclitaxel (EC-T) as
adjuvant therapy for operable breast cancer in women with positive
axillary nodes. J Clin Oncol. 32(Suppl; abstr 1042): 5s2014.
|
|
16
|
Hong WS, Jeon JY, Kang SY, Jung YS, Kim
JY, Ahn MS, Kang DK, Kim TH, Yim HE, An YS, et al: Comparison of
neoadjuvant adriamycin and docetaxel versus adriamycin,
cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel in patients with operable
breast cancer. J Korean Surg Soc. 85:7–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Smith TJ, Khatcheressian J, Lyman GH, Ozer
H, Armitage JO, Balducci L, Bennett CL, Cantor SB, Crawford J,
Cross SJ, et al: 2006 update of recommendations for the use of
white blood cell growth factors: An evidence-based clinical
practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 24:3187–3205. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sparano JA, Wang M, Martino S, Jones V,
Perez EA, Saphner T, Wolff AC, Sledge GW Jr, Wood WC and Davidson
NE: Weekly paclitaxel in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer. N
Engl J Med. 358:1663–1671. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|