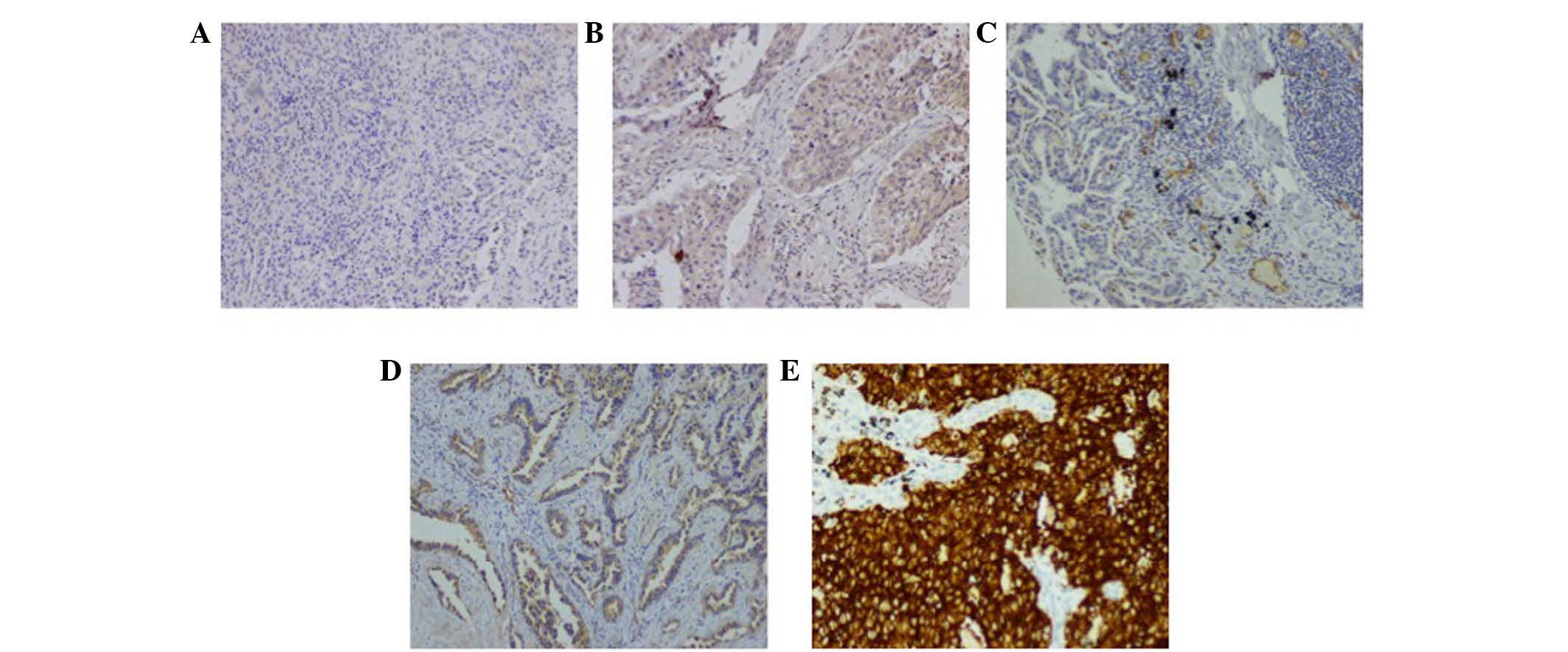
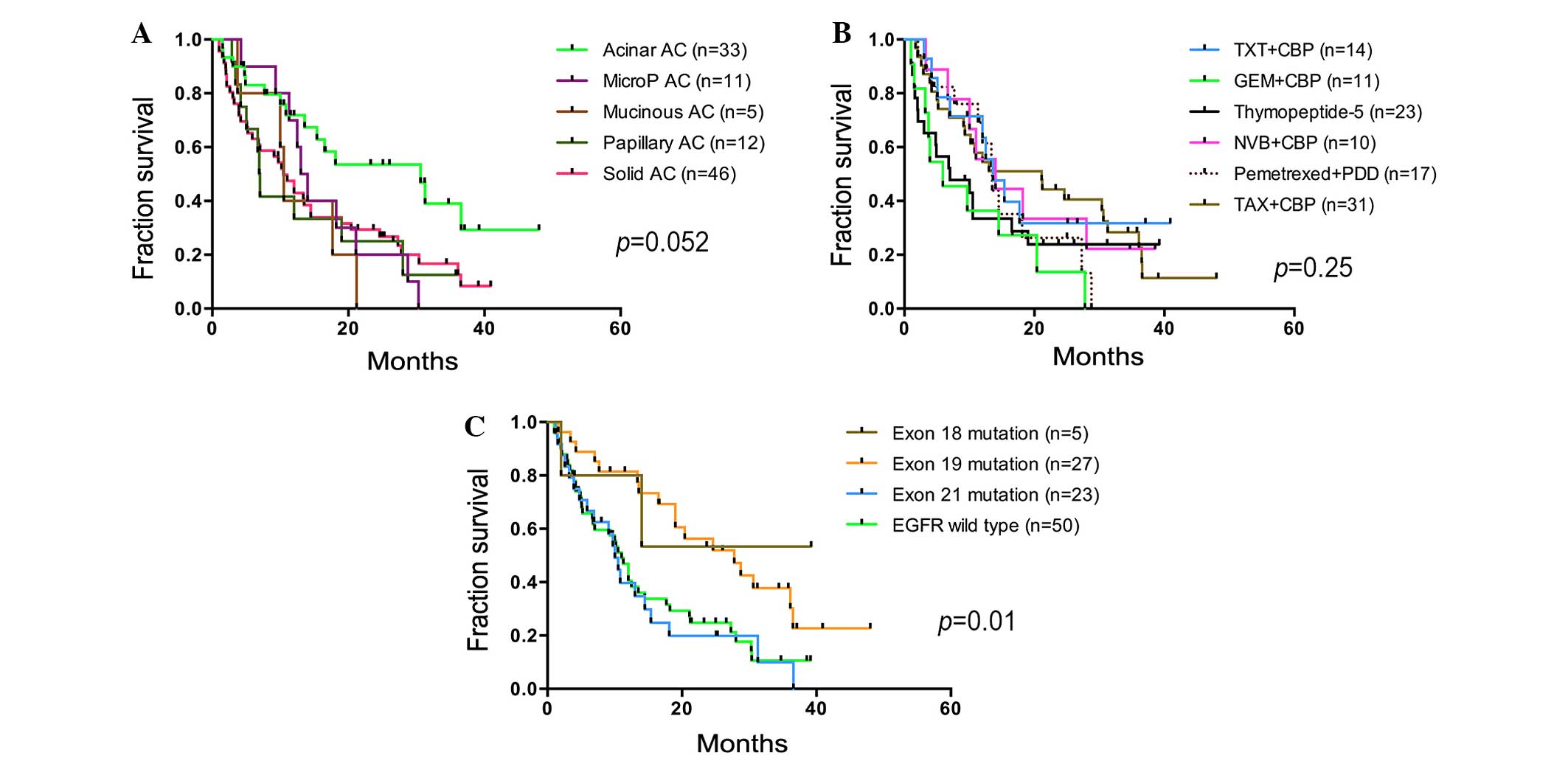
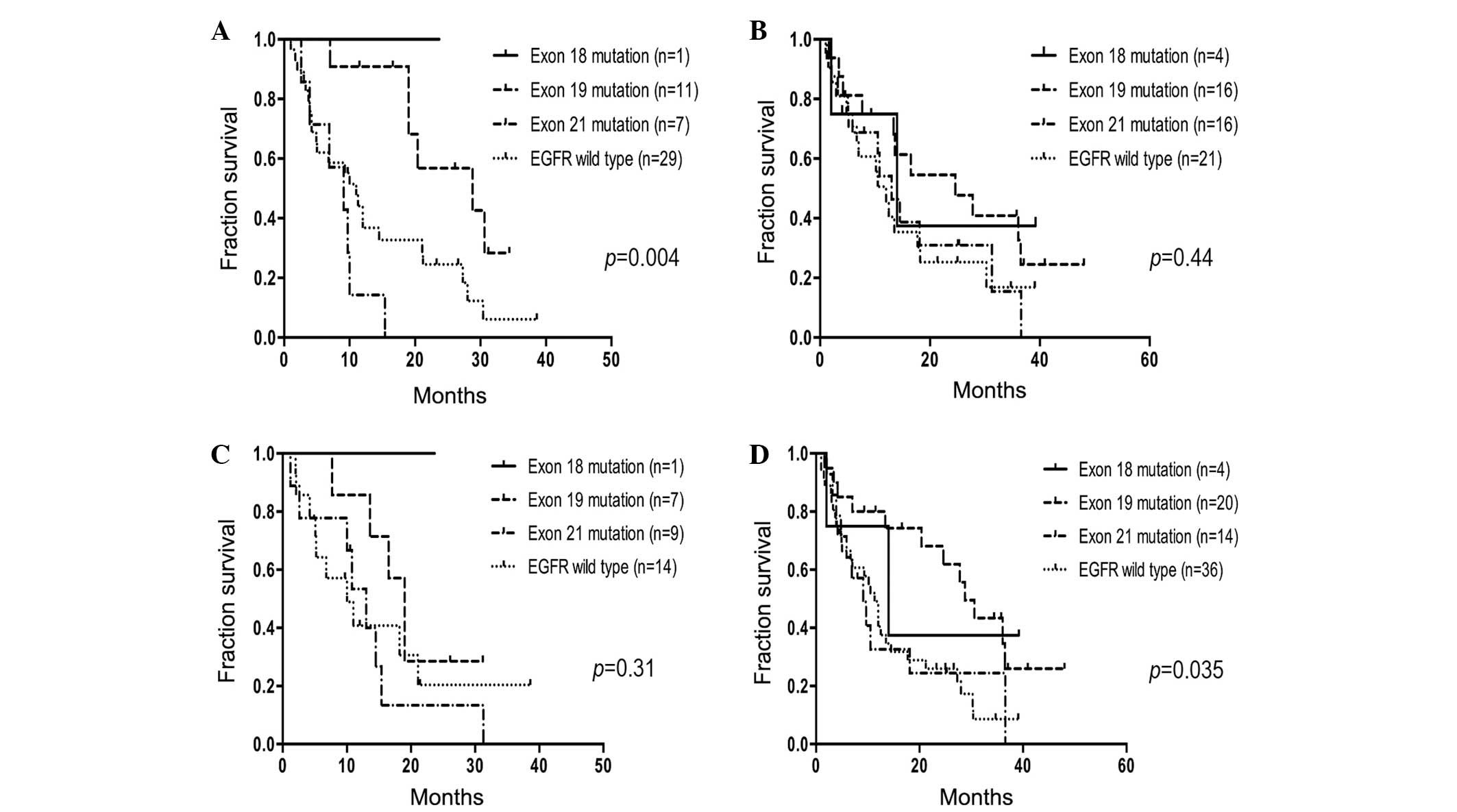
|
1
|
Curado MP, Edwards B, Shin HR, Storm H,
Ferlay J, Heanue M and Boyle P: Cancer Incidence in Five
Continents. IARC Scientific Publications; Lyon: 2007
|
|
2
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Müller-Hermelink
HK and Harris CC: World Health Organization Classification of
TumoursPathology & Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura,
Thymus and Heart. IARC Press; Lyon: 2004
|
|
3
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M,
Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ,
Van Schil PE, et al: International association for the study of
lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society
international multidisciplinary classification of lung
adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 6:244–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Müller-Hermelink
HK and Harris CC: Pathology and Genetics: Tumours of the Lung,
Pleura, Thymus and Heart. IARC Press; Lyon, France: 2004,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, Shimosato Y
and Brambilla E: Histological Typing of Lung and Pleural Tumors.
Springer; Berlin: 1999, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yanagawa N, Shiono S, Abiko M, Ogata SY,
Sato T and Tamura G: The correlation of the international
association for the study of lung cancer (IASLC)/American Thoracic
Society (ATS)/European Respiratory Society (ERS) classification
with prognosis and EGFR mutation in lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Thorac
Surg. 98:453–458. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoshizawa A, Sumiyoshi S, Sonobe M,
Kobayashi M, Fujimoto M, Kawakami F, Tsuruyama T, Travis WD, Date H
and Haga H: Validation of the IASLC/ATS/ERS lung adenocarcinoma
classification for prognosis and association with EGFR and KRAS
gene mutations: Analysis of 440 Japanese patients. J Thorac Oncol.
8:52–61. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R,
Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat
SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al: Activating mutations in the
epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of
non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med.
350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Riely GJ, Politi KA, Miller VA and Pao W:
Update on epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:7232–7241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sakai K, Arao T, Shimoyama T, Murofushi K,
Sekijima M, Kaji N, Tamura T, Saijo N and Nishio K: Dimerization
and the signal transduction pathway of a small in-frame deletion in
the epidermal growth factor receptor. FASEB J. 20:311–313.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun Y, Yu X, Shi X, Hong W, Zhao J and Shi
L: Correlation of survival and EGFR mutation with predominant
histologic subtype according to the new lung adenocarcinoma
classification in stage IB patients. World J Surg Oncol.
12:1482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S,
Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara S, Watanabe H, Kurashina K,
Hatanaka H, et al: Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK
fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 448:561–566.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT,
Solomon B, Maki RG, Ou SH, Dezube BJ, Jänne PA, Costa DB, et al:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1693–1703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gandhi L and Jänne PA: Crizotinib for
ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: A new targeted therapy
for a new target. Clin Cancer Res. 18:3737–3742. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rodig SJ, Mino-Kenudson M, Dacic S, Yeap
BY, Shaw A, Barletta JA, Stubbs H, Law K, Lindeman N, Mark E, et
al: Unique clinicopathologic features characterize ALK-rearranged
lung adenocarcinoma in the western population. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5216–5223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mino-Kenudson M, Chirieac LR, Law K,
Hornick JL, Lindeman N, Mark EJ, Cohen DW, Johnson BE, Jänne PA,
Iafrate AJ and Rodig SJ: A novel, highly sensitive antibody allows
for the routine detection of ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinomas by
standard immunohistochemistry. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1561–1571. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ying J, Guo L, Qiu T, Shan L, Ling Y, Liu
X and Lu N: Diagnostic value of a novel fully automated
immunochemistry assay for detection of ALK rearrangement in primary
lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Oncol. 24:2589–2593. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
ten Hoeve J, Kaartinen V, Fioretos T,
Haataja L, Voncken JW, Heisterkamp N and Groffen J: Cellular
interactions of CRKL and SH2-SH3 adaptor protein. Cancer Res.
54:2563–2567. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Senechal K, Halpern J and Sawyers CL: The
CRKL adaptor protein transforms fibroblasts and functions in
transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene. J Biol Chem.
271:23255–23261. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hafizi S and Dahlbäck B: Signalling and
functional diversity within the Axl subfamily of receptor tyrosine
kinases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:295–304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Goruppi S, Ruaro E, Varnum B and Schneider
C: Requirement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway
and Src for Gas6-Axl mitogenic and survival activities in NIH 3T3
fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 17:4442–4453. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hector A, Montgomery EA, Karikari C, Canto
M, Dunbar KB, Wang JS, Feldmann G, Hong SM, Haffner MC, Meeker AK,
et al: The Axl receptor tyrosine kinase is an adverse prognostic
factor and a therapeutic target in esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Biol Ther. 10:1009–1018. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Lee JC, Lin L, Olivas V, Au V,
LaFramboise T, Abdel-Rahman M, Wang X, Levine AD, Rho JK, et al:
Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted
therapy in lung cancer. Nat Genet. 44:852–860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paccez JD, Vasques GJ, Correa RG,
Vasconcellos JF, Duncan K, Gu X, Bhasin M, Libermann TA and Zerbini
LF: The receptor tyrosine kinase Axl is an essential regulator of
prostate cancer proliferation and tumor growth and represents a new
therapeutic target. Oncogene. 32:689–698. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M,
Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ,
Van Schil PE, et al: International association for the study of
lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society
international multidisciplinary classification of lung
adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 6:244–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. 7th. Wiley-Blackwell;
Hoboken, NJ: 2009
|
|
27
|
Cai YR, Zhang HQ, Qu Y, Mu J, Zhao D, Zhou
LJ, Yan H, Ye JW and Liu Y: Expression of MET and SOX2 genes in
non-small cell lung carcinoma with EGFR mutation. Oncol Rep.
26:877–885. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et
al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Minca EC, Portier BP, Wang Z, Lanigan C,
Farver CF, Feng Y, Ma PC, Arrossi VA, Pennell NA and Tubbs RR: ALK
status testing in non-small cell lung carcinoma: Correlation
between ultrasensitive IHC and FISH. J Mol Diagn. 15:341–346. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Motoi N, Szoke J, Riely GJ, Seshan VE,
Kris MG, Rusch VW, Gerald WL and Travis WD: Lung adenocarcinoma:
Modification of the 2004 WHO mixed subtype to include the major
histologic subtype suggests correlations between papillary and
micropapillary adenocarcinoma subtypes, EGFR mutations and gene
expression analysis. Am J Surg Pathol. 32:810–827. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sica G, Yoshizawa A, Sima CS, Azzoli CG,
Downey RJ, Rusch VW, Travis WD and Moreira AL: A grading system of
lung adenocarcinomas based on histologic pattern is predictive of
disease recurrence in stage I tumors. Am J Surg Pathol.
34:1155–1162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
De Oliveira Duarte Achcar R, Nikiforova MN
and Yousem SA: Micropapillary lung adenocarcinoma: EGFR, K-ras and
BRAF mutational profile. Am J Clin Pathol. 131:694–700. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim YH, Ishii G, Goto K, Nagai K, Tsuta K,
Shiono S, Nitadori J, Kodama T, Nishiwaki Y and Ochiai A: Dominant
papillary subtype is a significant predictor of the response to
gefitinib in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clin Cancer Res.
10:7311–7317. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ding L, Getz G, Wheeler DA, Mardis ER,
McLellan MD, Cibulskis K, Sougnez C, Greulich H, Muzny DM, Morgan
MB, et al: Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung
adenocarcinoma. Nature. 455:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Taniguchi K, Okami J, Kodama K,
Higashiyama M and Kato K: Intratumor heterogeneity of epidermal
growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer and its correlation
to the response to gefitinib. Cancer Sci. 99:929–935. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang J, Fujimoto J, Zhang J, Wedge DC,
Song X, Zhang J, Seth S, Chow CW, Cao Y, Gumbs C, et al: Intratumor
heterogeneity in localized lung adenocarcinomas delineated by
multiregion sequencing. Science 346(6206). 256–259. 2014.
|
|
37
|
Tsutsumida H, Nomoto M, Goto M, Kitajima
S, Kubota I, Hirotsu Y, Wakimoto J, Hollingsworth MA and Yonezawa
S: A micropapillary pattern is predictive of a poor prognosis in
lung adenocarcinoma and reduced surfactant apoprotein A expression
in the micropapillary pattern is an excellent indicator of a poor
prognosis. Mod Pathol. 20:638–647. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yoshizawa A, Motoi N, Riely GJ, Sima CS,
Gerald WL, Kris MG, Park BJ, Rusch VW and Travis WD: Impact of
proposed IASLC/ATS/ERS classification of lung adenocarcinoma:
Prognostic subgroups and implications for further revision of
staging based on analysis of 514 stage I cases. Mod Pathol.
24:653–664. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Akamatsu H, Kaira K, Murakami H, Serizawa
M, Koh Y, Ono A, Shukuya T, Tsuya A, Nakamura Y, Kenmotsu H, et al:
The impact of clinical outcomes according to EGFR mutation status
in patients with locally advanced lung adenocarcinoma who recieved
concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol. 37:144–147. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J,
Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singh B, Heelan R, Rusch V, Fulton L, et al:
EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from ‘never
smokers’ and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib
and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:13306–13311. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Finberg KE, Sequist LV, Joshi VA,
Muzikansky A, Miller JM, Han M, Beheshti J, Chirieac LR, Mark EJ
and Iafrate AJ: Mucinous differentiation correlates with absence of
EGFR mutation and presence of KRAS mutation in lung adenocarcinomas
with bronchioloalveolar features. J Mol Diagn. 9:320–326. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Honegger AM, Dull TJ, Felder S, Van
Obberghen E, Bellot F, Szapary D, Schmidt A, Ullrich A and
Schlessinger J: Point mutation at the ATP binding site of EGF
receptor abolishes protein-tyrosine kinase activity and alters
cellular routing. Cell. 51:199–209. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huse M and Kuriyan J: The conformational
plasticity of protein kinases. Cell. 109:275–282. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gazdar AF, Shigematsu H, Herz J and Minna
JD: Mutations and addiction to EGFR: The Achilles ‘heal’ of lung
cancers? Trends Mol Med. 10:481–486. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Togashi Y, Soda M, Sakata S, Sugawara E,
Hatano S, Asaka R, Nakajima T, Mano H and Takeuchi K: KLC1-ALK: A
novel fusion in lung cancer identified using a formalin-fixed
paraffin-embedded tissue only. PLoS One. 7:e313232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Takeuchi K, Choi YL, Togashi Y, Soda M,
Hatano S, Inamura K, Takada S, Ueno T, Yamashita Y, Satoh Y, et al:
KIF5B-ALK, a novel fusion oncokinase identified by an
immunohistochemistry-based diagnostic system for ALK-positive lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:3143–3149. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Boland JM, Erdogan S, Vasmatzis G, Yang P,
Tillmans LS, Johnson MR, Wang X, Peterson LM, Halling KC, Oliveira
AM, et al: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase immunoreactivity correlates
with ALK gene rearrangement and transcriptional up-regulation in
non-small cell lung carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 40:1152–1158. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crinó
L, Ahn MJ, De Pas T, Besse B, Solomon BJ, Blackhall F, et al:
Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 368:2385–2394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wu SG, Kuo YW, Chang YL, Shih JY, Chen YH,
Tsai MF, Yu CJ, Yang CH and Yang PC: EML4-ALK translocation
predicts better outcome in lung adenocarcinoma patients with
wild-type EGFR. J Thorac Oncol. 7:98–104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shaw AT, Yeap BY, Mino-Kenudson M,
Digumarthy SR, Costa DB, Heist RS, Solomon B, Stubbs H, Admane S,
McDermott U, et al: Clinical features and outcome of patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer who harbor EML4-ALK. J Clin Oncol.
27:4247–4253. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Takahashi T, Sonobe M, Kobayashi M,
Yoshizawa A, Menju T, Nakayama E, Mino N, Iwakiri S, Sato K,
Miyahara R, et al: Clinicopathologic features of non-small-cell
lung cancer with EML4-ALK fusion gene. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:889–897.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Verma A, Warner SL, Vankayalapati H,
Bearss DJ and Sharma S: Targeting Axl and Mer kinases in cancer.
Mol Cancer Ther. 10:1763–1773. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ishikawa M, Sonobe M, Nakayama E,
Kobayashi M, Kikuchi R, Kitamura J, Imamura N and Date H: Higher
expression of receptor tyrosine kinase Axl, and differential
expression of its ligand, Gas6, predict poor survival in lung
adenocarcinoma patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 20(Suppl 3): S467–S476.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Stommel JM, Kimmelman AC, Ying H,
Nabioullin R, Ponugoti AH, Wiedemeyer R, Stegh AH, Bradner JE,
Ligon KL, Brennan C, et al: Coactivation of receptor tyrosine
kinases affects the response of tumor cells to targeted therapies.
Science. 318:287–290. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Eder JP, Shapiro GI, Appleman LJ, Zhu AX,
Miles D, Keer H, Cancilla B, Chu F, Hitchcock-Bryan S, Sherman L,
et al: A phase I study of foretinib, a multi-targeted inhibitor of
c-Met and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:3507–3516. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang Y, Dong QZ, Fu L, Stoecker M, Wang E
and Wang EH: Overexpression of CRKL correlates with poor prognosis
and cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog.
52:890–899. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cheung HW, Du J, Boehm JS, He F, Weir BA,
Wang X, Butaney M, Sequist LV, Luo B, Engelman JA, et al:
Amplification of CRKL induces transformation and epidermal growth
factor receptor inhibitor resistance in human non-small cell lung
cancers. Cancer Discov. 1:608–625. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ladanyi M and Pao W: Lung adenocarcinoma:
Guiding EGFR-targeted therapy and beyond. Mod Pathol. 21(Suppl 2):
S16–S22. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kwei KA, Kim YH, Girard L, Kao J,
Pacyna-Gengelbach M, Salari K, Lee J, Choi YL, Sato M, Wang P, et
al: Genomic profiling identifies TITF1 as a lineage-specific
oncogene amplified in lung cancer. Oncogene. 27:3635–3640. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sun S, Schiller JH, Spinola M and Minna
JD: New molecularly targeted therapies for lung cancer. J Clin
Invest. 117:2740–2750. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Marks JL, McLellan MD, Zakowski MF, Lash
AE, Kasai Y, Broderick S, Sarkaria IS, Pham D, Singh B, Miner TL,
et al: Mutational analysis of EGFR and related signaling pathway
genes in lung adenocarcinomas identifies a novel somatic kinase
domain mutation in FGFR4. PLoS One. 2:e4262007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kendall J, Liu Q, Bakleh A, Krasnitz A,
Nguyen KC, Lakshmi B, Gerald WL, Powers S and Mu D: Oncogenic
cooperation and coamplification of developmental transcription
factor genes in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:16663–16668. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Eberhard DA, Johnson BE, Amler LC, Goddard
AD, Heldens SL, Herbst RS, Ince WL, Jänne PA, Januario T, Johnson
DH, et al: Mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor and in
KRAS are predictive and prognostic indicators in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy alone and in
combination with erlotinib. J Clin Oncol. 23:5900–5909. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sell S: Stem cell origin of cancer and
differentiation therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 51:1–28. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ninomiya H, Hiramatsu M, Inamura K, Nomura
K, Okui M, Miyoshi T, Okumura S, Satoh Y, Nakagawa K, Nishio M, et
al: Correlation between morphology and EGFR mutations in lung
adenocarcinomas. Significance of the micropapillary pattern and the
hobnail cell type. Lung Cancer. 63:235–240. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tsuta K, Kawago M, Yoshida A, Sekine S,
Asamura H, Furuta K and Kushima R: Primary lung adenocarcinoma with
morule-like components: A unique histologic hallmark of aggressive
behavior and EGFR mutation. Lung Cancer. 85:12–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Blons H, Côté JF, Le Corre D, Riquet M,
Fabre-Guilevin E, Laurent-Puig P and Danel C: Epidermal growth
factor receptor mutation in lung cancer are linked to
bronchioloalveolar differentiation. Am J Surg Pathol. 30:1309–1315.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sakuma Y, Matsukuma S, Yoshihara M,
Nakamura Y, Noda K, Nakayama H, Kameda Y, Tsuchiya E and Miyagi Y:
Distinctive evaluation of nonmucinous and mucinous subtypes of
bronchioloalveolar carcinomas in EGFR and K-ras gene-mutation
analyses for Japanese lung adenocarcinomas: Confirmation of the
correlations with histologic subtypes and gene mutations. Am J Clin
Pathol. 128:100–108. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Miller VA, Riely GJ, Zakowski MF, Li AR,
Patel JD, Heelan RT, Kris MG, Sandler AB, Carbone DP, Tsao A, et
al: Molecular characteristics of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and
adenocarcinoma, bronchioloalveolar carcinoma subtype, predict
response to erlotinib. J Clin Oncol. 26:1472–1478. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shim HS, Lee DH, Park EJ and Kim SH:
Histopathologic characteristics of lung adenocarcinomas with
epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in the International
Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic
Society/European Respiratory Society lung adenocarcinoma
classification. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 135:1329–1334. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wu SG, Chang YL, Hsu YC, Wu JY, Yang CH,
Yu CJ, Tsai MF, Shih JY and Yang PC: Good response to gefitinib in
lung adenocarcinoma of complex epidermal growth factor receptor
(EGFR) mutations with the classical mutation pattern. Oncologist.
13:1276–1284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yoshida T, Ishii G, Goto K, Yoh K, Niho S,
Umemura S, Matsumoto S, Ohmatsu H, Nagai K, Ohe Y and Ochiai A:
Solid predominant histology predicts EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor
response in patients with EGFR mutation-positive lung
adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 139:1691–1700. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|