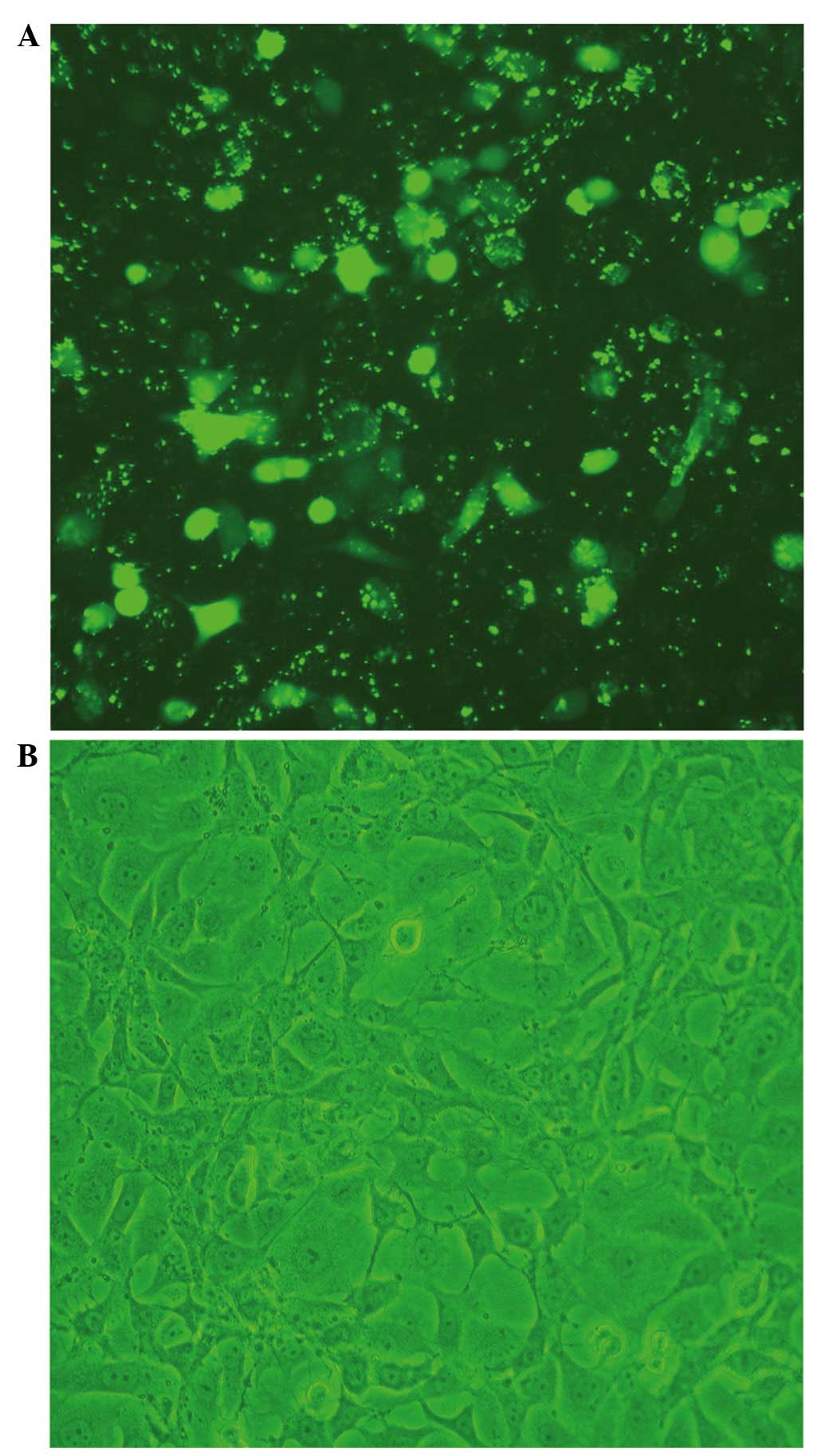
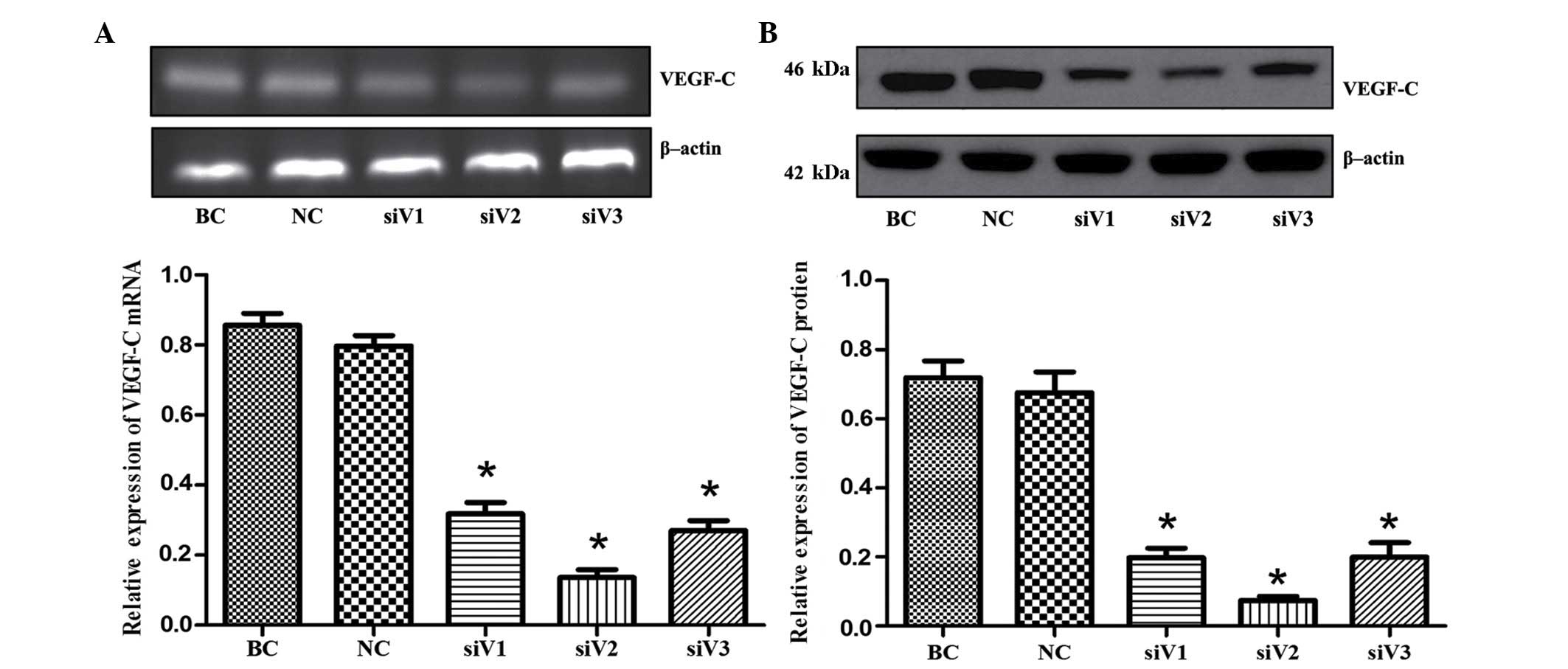
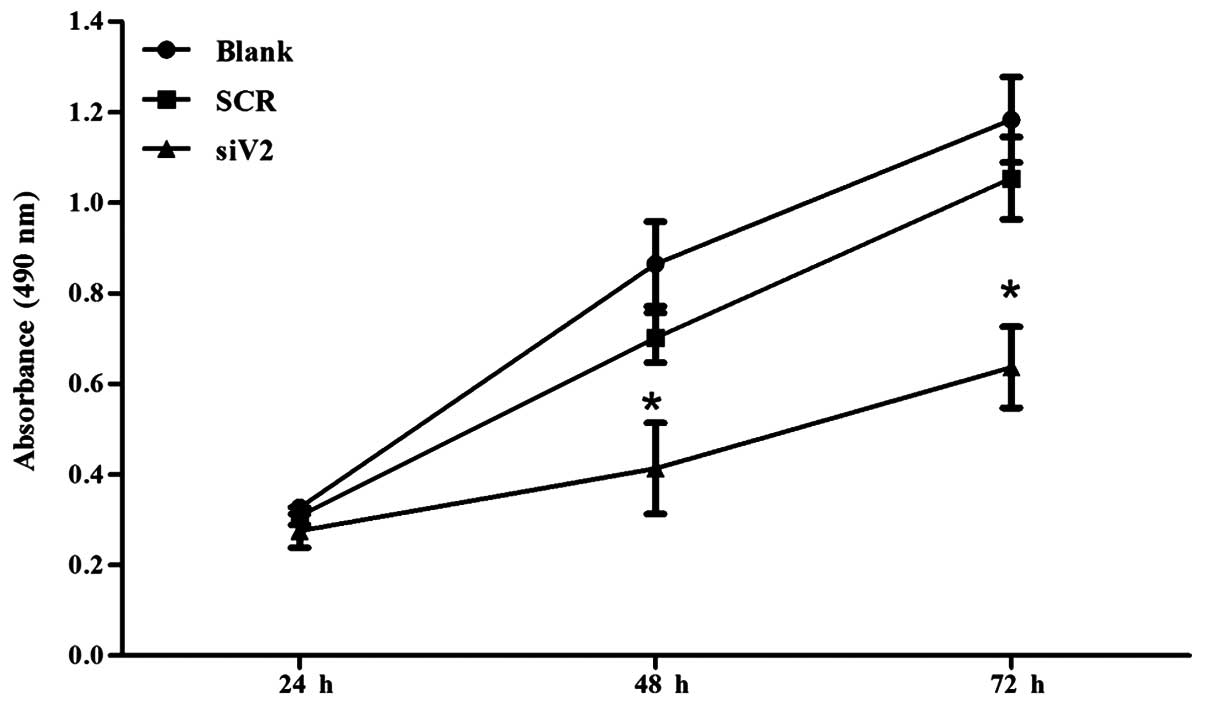
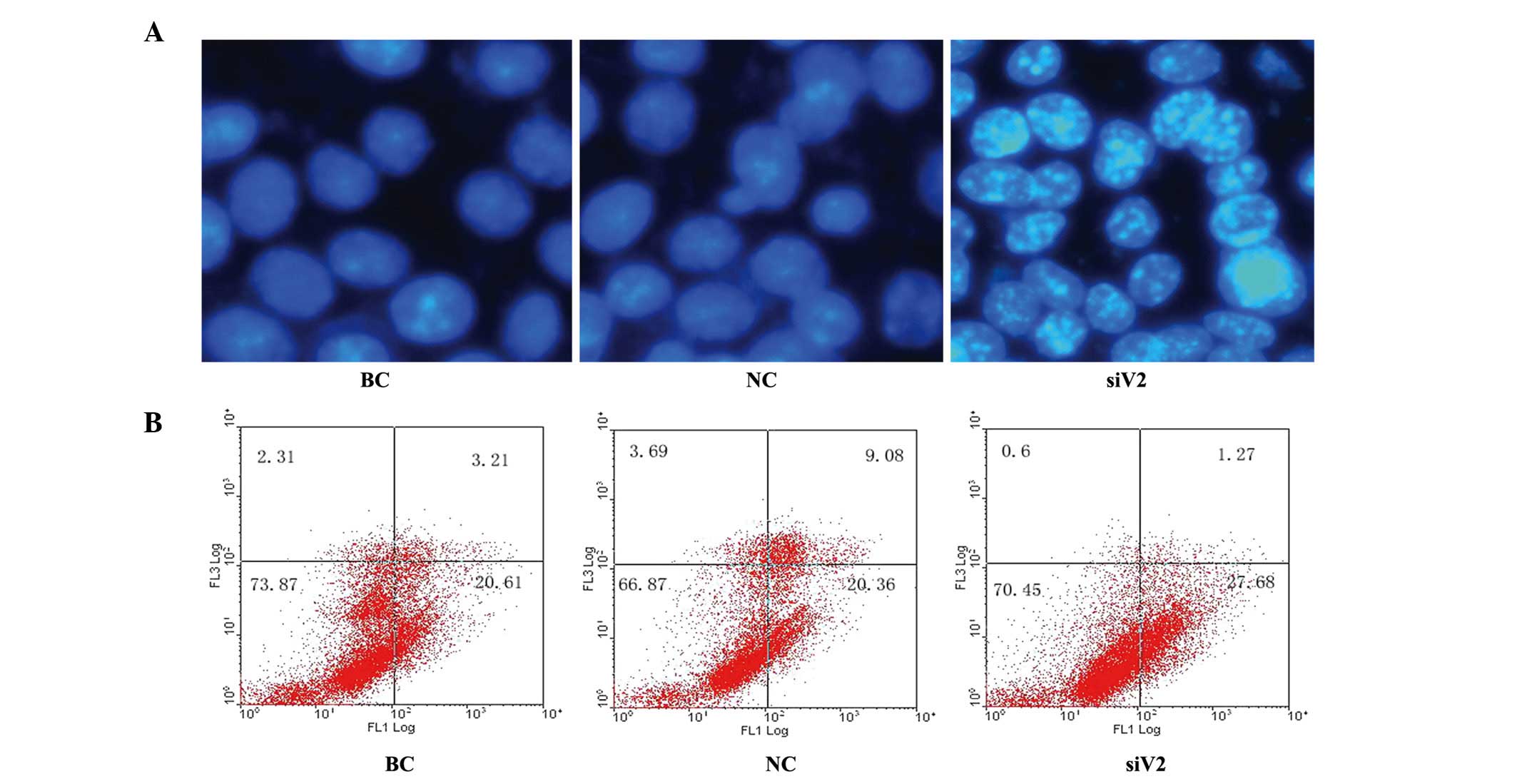
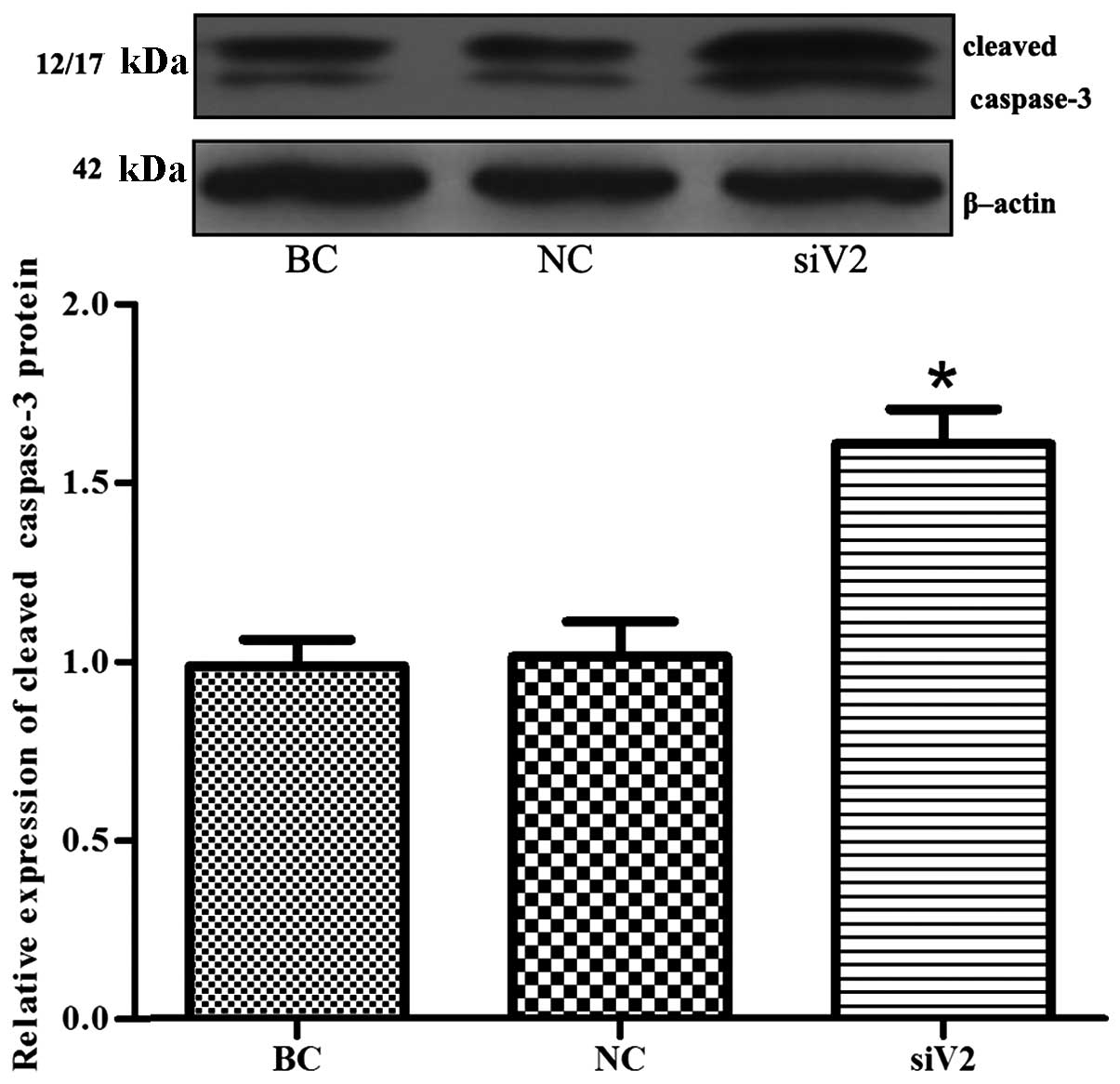
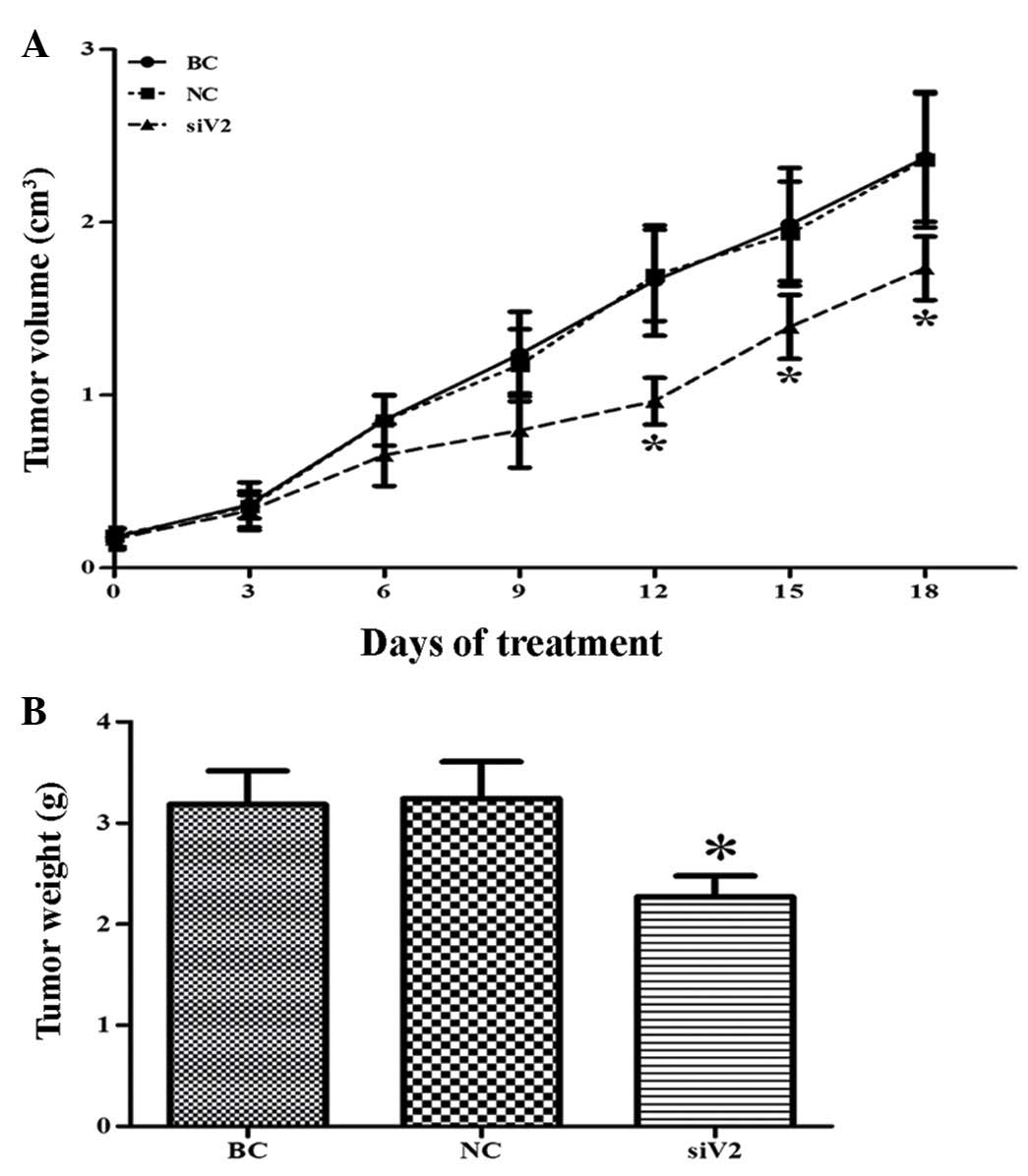
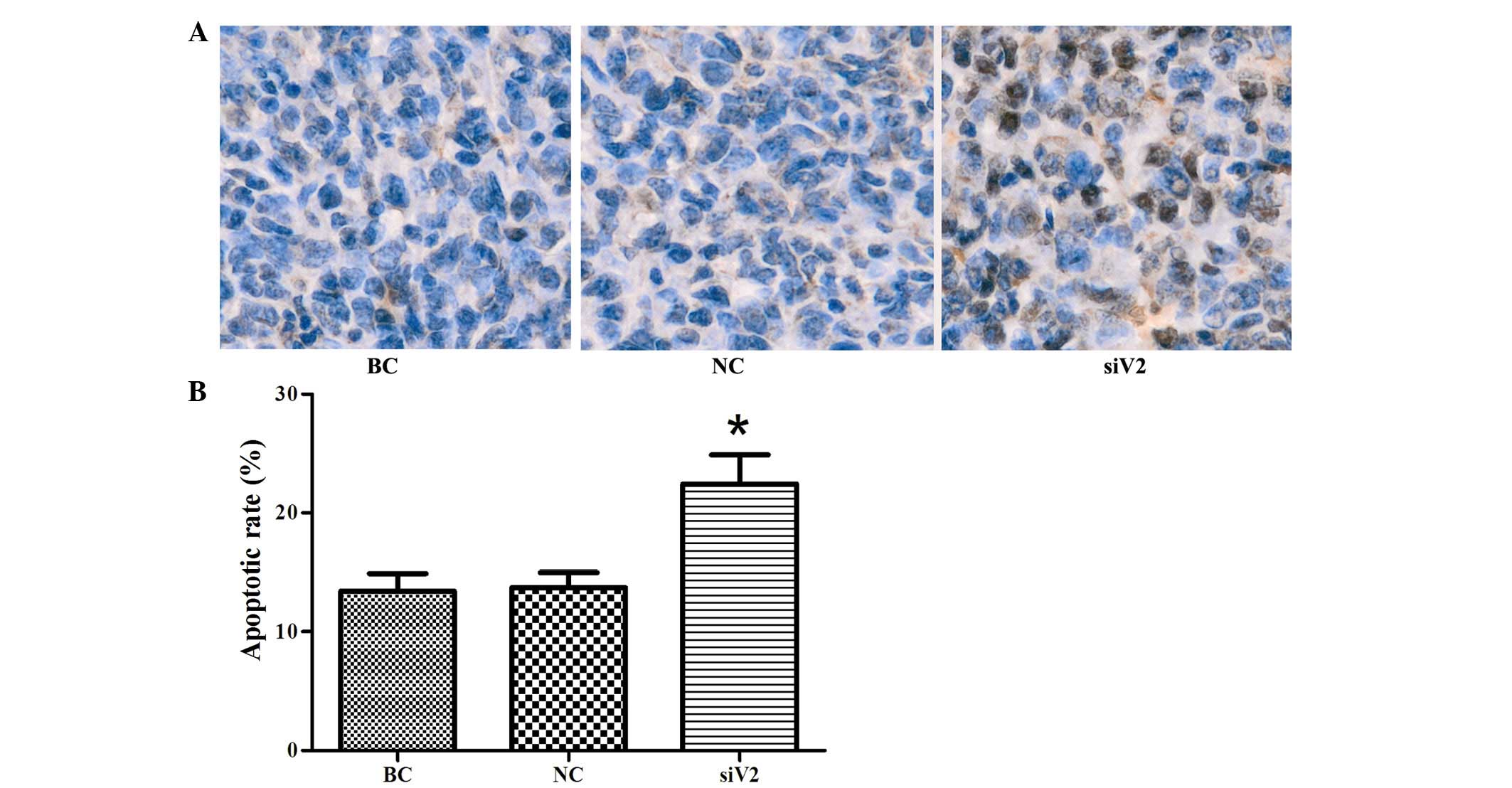
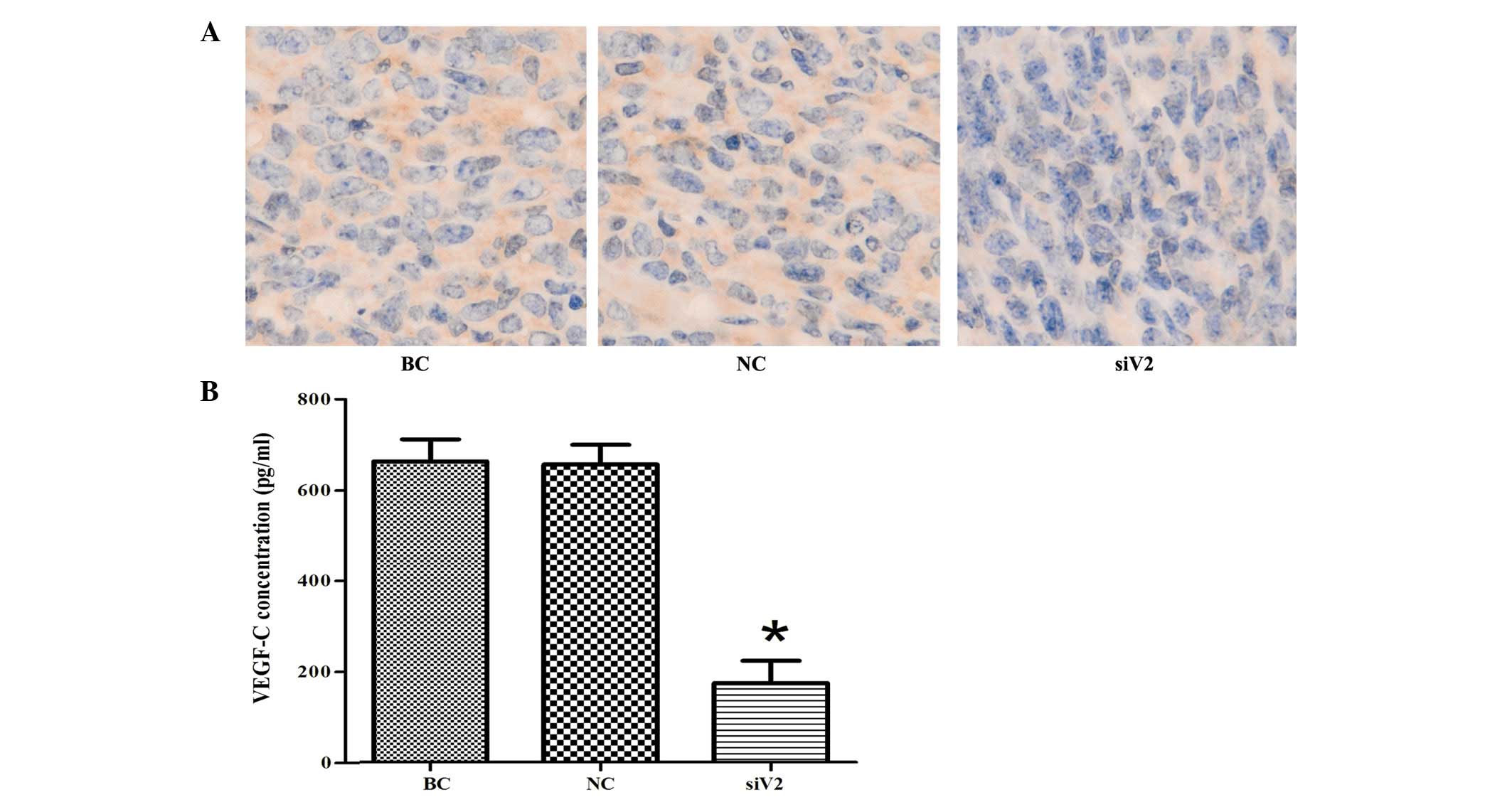
|
1
|
Montazeri A: Health-related quality of
life in breast cancer patients: A bibliographic review of the
literature from 1974 to 2007. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 27:322008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nathanson SD: Insights into the mechanisms
of lymph node metastasis. Cancer. 98:413–423. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ran S, Volk L, Hall K and Flister MJ:
Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer.
Pathophysiology. 17:229–251. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Joukov V, Kaipainen A, Jeltsch M, Pajusola
K, Olofsson B, Kumar V, Eriksson U and Alitalo K: Vascular
endothelial growth factors vegf-b and vegf-c. J Cell Physiol.
173:211–215. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fournier E, Birnbaum D and Borg JP:
Receptors for factors of the vegf (Vascular Endothelial Growth
Family). Bull Cancer. 84:397–405. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Deckers MM, Karperien M, van der Bent C,
Yamashita T, Papapoulos SE and Löwik CW: Expression of vascular
endothelial growth factors and their receptors during osteoblast
differentiation. Endocrinology. 141:1667–1674. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su JL, Yen CJ, Chen PS, Chuang SE, Hong
CC, Kuo IH, Chen HY, Hung MC and Kuo ML: The role of the
VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 axis in cancer progression. Br J Cancer. 96:541–545.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ge YL, Zhang X, Zhang JY, Hou L and Tian
RH: The mechanisms on apoptosis by inhibiting VEGF expression in
human breast cancer cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 9:389–395. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kodama M, Kitadai Y, Tanaka M, Kuwai T,
Tanaka S, Oue N, Yasui W and Chayama K: Vascular endothelial growth
factor c stimulates progression of human gastric cancer via both
autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7205–7214.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun P, Gao J, Liu YL, Wei LW, Wu LP and
Liu ZY: RNA interference (RNAi)-mediated vascular endothelial
growth factor-C (VEGF-C) reduction interferes with
lymphangiogenesis and enhances epirubicin sensitivity of breast
cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 308:161–168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
U.S. National Institutes of Health, .
Laboratory animal welfare: Public Health Service policy on humane
care and use of laboratory animals by awardee institutions; notice.
Fed Regist. 50:19584–19585. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xue M, Ge Y, Zhang J, Liu Y, Wang Q, Hou L
and Zheng Z: Fucoidan inhibited 4T1 mouse breast cancer cell growth
in vivo and in vitro via downregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Nutr Cancer. 65:460–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan Y, Jia L, Zhang J, Liu Y and Bu X:
Effect of recombinant Newcastle disease virus transfection on lung
adenocarcinoma A549 cells in vitro. Oncol Lett. 8:2569–2576.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Elbashir SM, Lendeckel W and Tuschl T: RNA
interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev.
15:188–200. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sioud M: RNA interference: Mechanisms,
technical challenges, and therapeutic opportunities. Methods Mol
Biol. 1218:1–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mansoori B, Shotorbani S Sandoghchian and
Baradaran B: RNA interference and its role in cancer therapy. Adv
Pharm Bull. 4:313–321. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li JP, Cao NX, Jiang RT, He SJ, Huang TM,
Wu B, Chen DF, Ma P, Chen L, Zhou SF, et al: Knockdown of
gcf2/lrrfip1 by rnai causes cell growth inhibition and increased
apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:2753–2758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan XD, Yang ZP, Tang QL, Peng T, Zhang
ZB, Zhou SG, Wang GX, He B and Zang LQ: Expression and function of
GSTA1 in lung cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:8631–8635.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Joukov V, Sorsa T, Kumar V, Jeltsch M,
Claesson-Welsh L, Cao Y, Saksela O, Kalkkinen N and Alitalo K:
Proteolytic processing regulates receptor specificity and activity
of VEGF-C. Embo J. 16:3898–3911. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, Chilov
D, Lahtinen I, Kukk E, Saksela O, Kalkkinen N and Alitalo K: A
novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for
the flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases.
Embo J. 15:290–298. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Alitalo A and Detmar M: Interaction of
tumor cells and lymphatic vessels in cancer progression. Oncogene.
31:4499–4508. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kinoshita J, Kitamura K, Kabashima A,
Saeki H, Tanaka S and Sugimachi K: Clinical significance of
vascular endothelial growth factor-c (vegf-c) in breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 66:159–164. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chambers AF, Groom AC and MacDonald IC:
Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:563–572. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Duffy MJ, McGowan PM and Gallagher WM:
Cancer invasion and metastasis: Changing views. J Pathol.
214:283–293. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu C, Gui Q, Chen W, Wu L, Sun W, Zhang N,
Xu Q, Wang J and Fu X: Small interference RNA targeting tissue
factor inhibits human lung adenocarcinoma growth in vitro and in
vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Decio A, Taraboletti G, Patton V, Alzani
R, Perego P, Fruscio R, Jürgensmeier JM, Giavazzi R and Belotti D:
Vascular endothelial growth factor c promotes ovarian carcinoma
progression through paracrine and autocrine mechanisms. Am J
Pathol. 184:1050–1061. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang HH, Qi F, Shi YR, Miao JG, Zhou M,
He W, Chen MF, Li Y, Zu XB and Qi L: RNA interference-mediated
vascular endothelial growth factor-C reduction suppresses malignant
progression and enhances mitomycin C sensitivity of bladder cancer
T24 cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 27:291–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Muders MH, Zhang H, Wang E, Tindall DJ and
Datta K: Vascular endothelial growth factor-C protects prostate
cancer cells from oxidative stress by the activation of mammalian
target of rapamycin complex-2 and AKT-1. Cancer Res. 69:6042–6048.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Feng Y, Hu J, Ma J, Feng K, Zhang X, Yang
S, Wang W, Zhang J and Zhang Y: RNAi-mediated silencing of VEGF-C
inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by simultaneously
down-regulating the CXCR4, CCR7, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3-dependent
axes-induced ERK, p38 and AKT signalling pathways. Eur J Cancer.
47:2353–2363. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kurenova EV, Hunt DL, He D, Fu AD, Massoll
NA, Golubovskaya VM, Garces CA and Cance WG: Vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor-3 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation,
motility and survival in vitro and tumor formation in vivo. Cell
Cycle. 8:2266–2980. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alison MR and Sarraf CE: Apoptosis: A
gene-directed programme of cell death. J R Coll Physicians Lond.
26:25–35. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Desoize B and Sen S: Apoptosis or
programmed cell death: Concepts, mechanisms and contribution in
oncology. Bull Cancer. 79:413–425. 1992.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Snigdha S, Smith ED, Prieto GA and Cotman
CW: Caspase-3 activation as a bifurcation point between plasticity
and cell death. Neurosci Bull. 28:14–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Aslakson CJ and Miller FR: Selective
events in the metastatic process defined by analysis of the
sequential dissemination of subpopulations of a mouse mammary
tumor. Cancer Res. 52:1399–1405. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tao K, Fang M, Alroy J and Sahagian GG:
Imagable 4T1 model for the study of late stage breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 8:2282008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu Q, Sun T, Tian H, Wang C and Zhou H:
Ultrasound-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C)
gene microbubble transfection inhibits growth of MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. Oncol Res. 20:297–301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo B, Zhang Y, Luo G, Li L and Zhang J:
Lentivirus-mediated small interfering RNA targeting VEGF-C
inhibited tumor lymphangiogenesis and growth in breast carcinoma.
Anat Rec (Hoboken). 292:633–639. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|