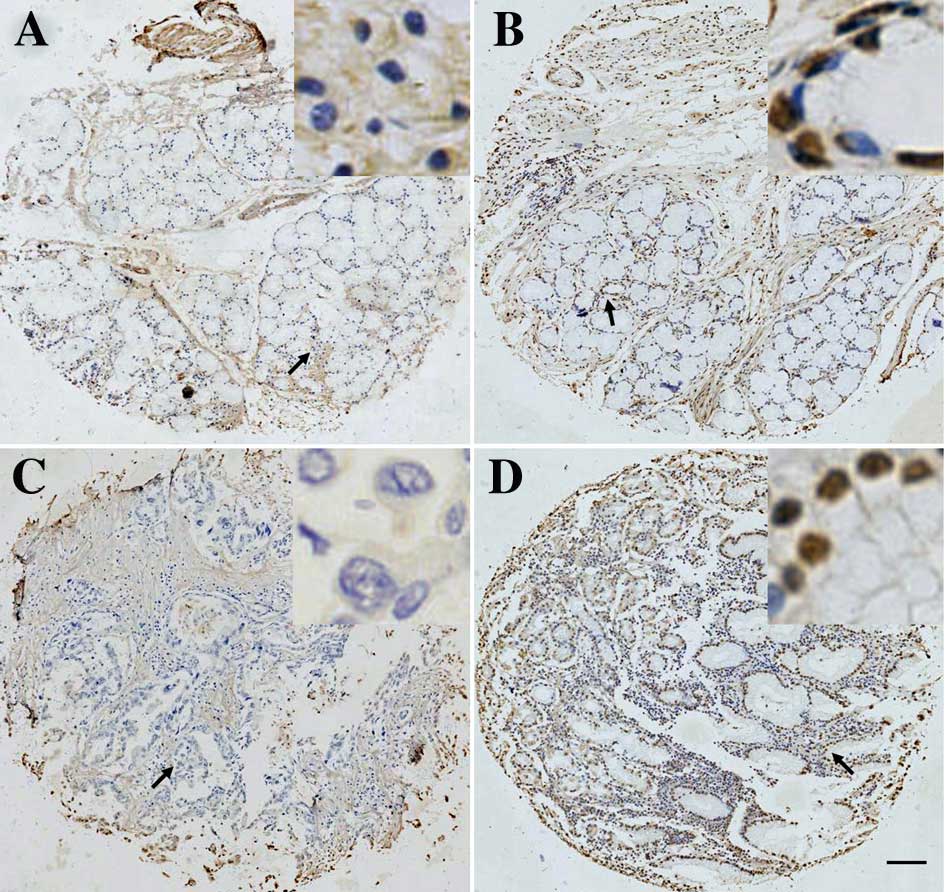
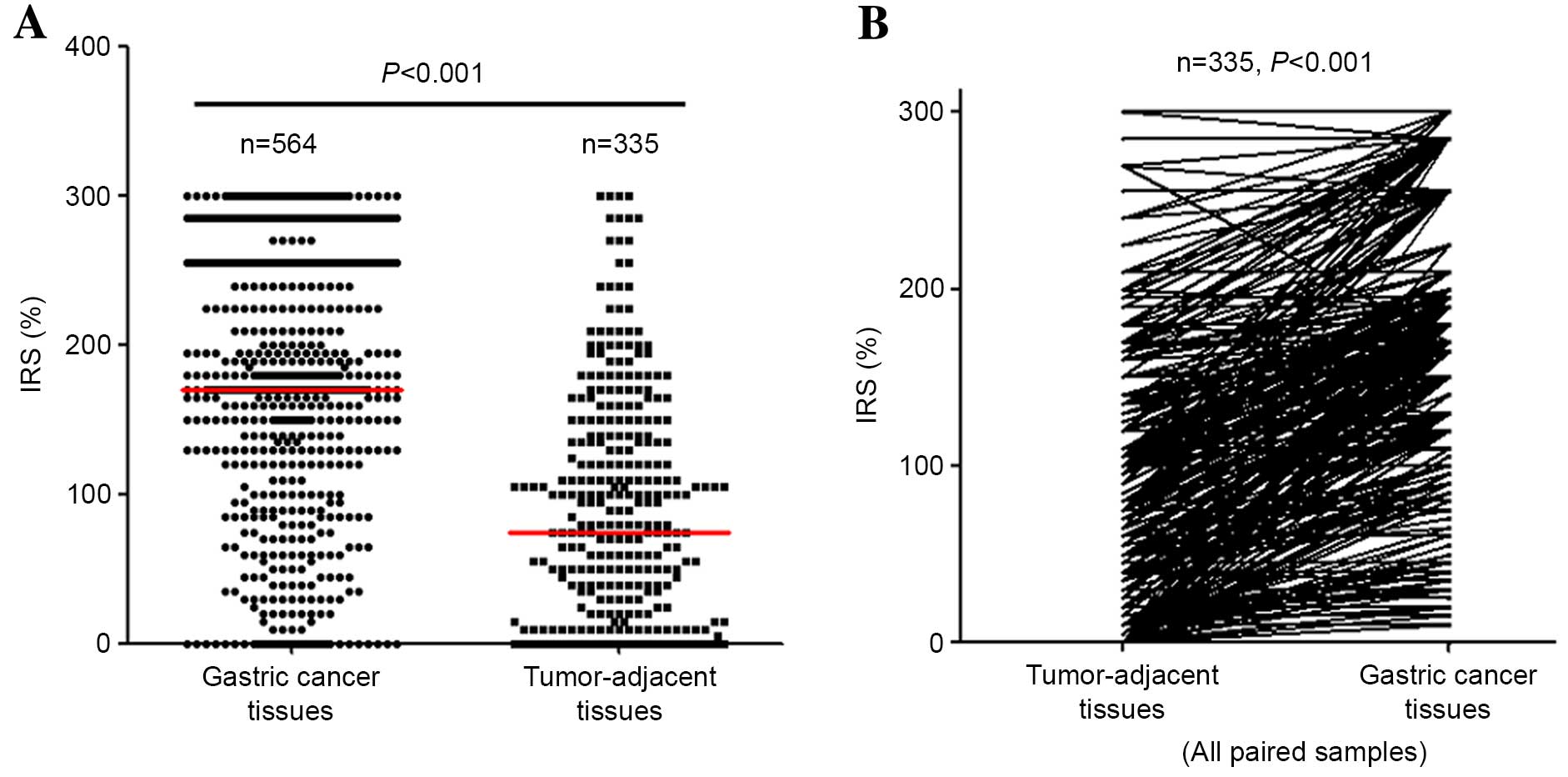
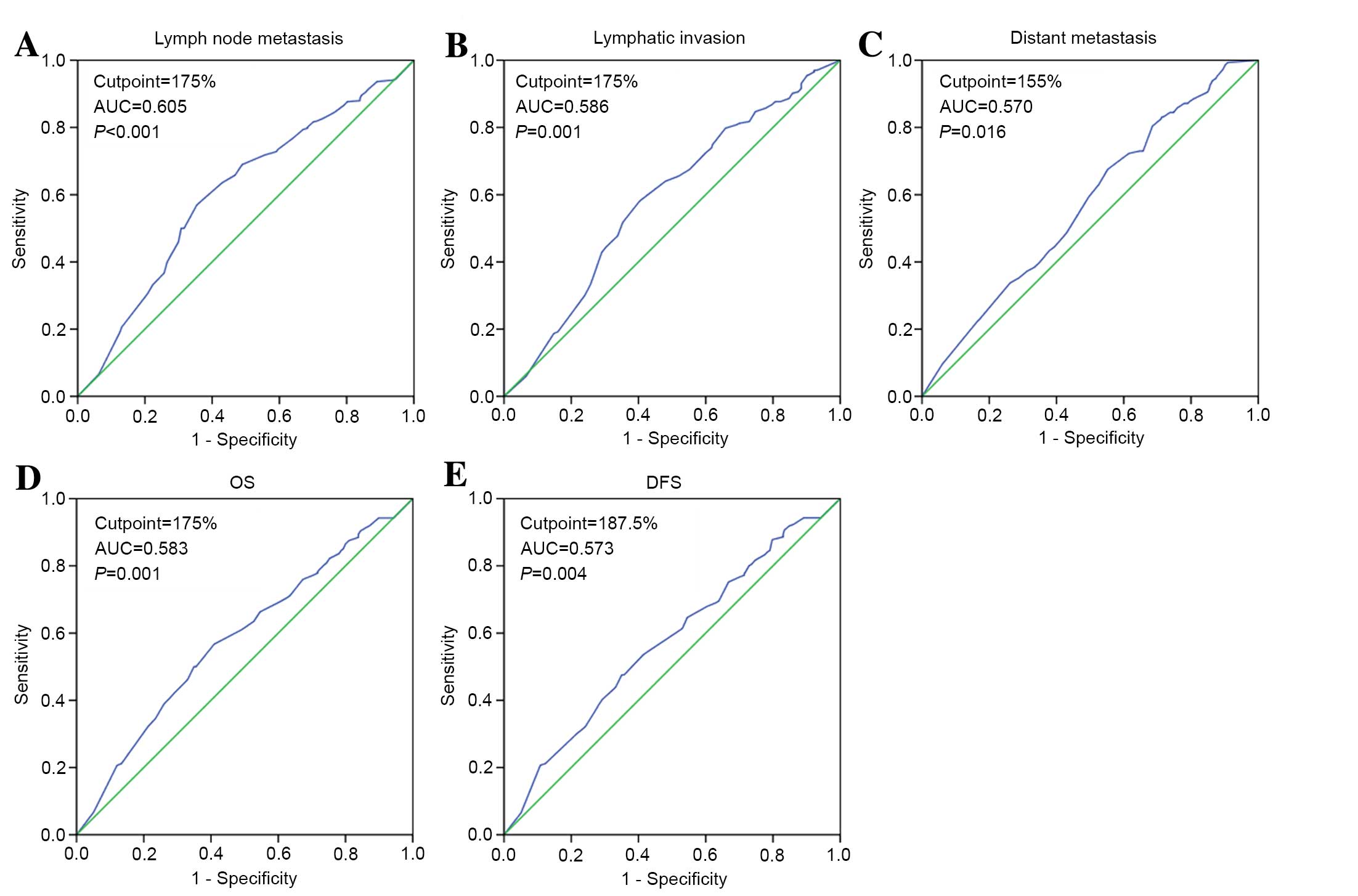
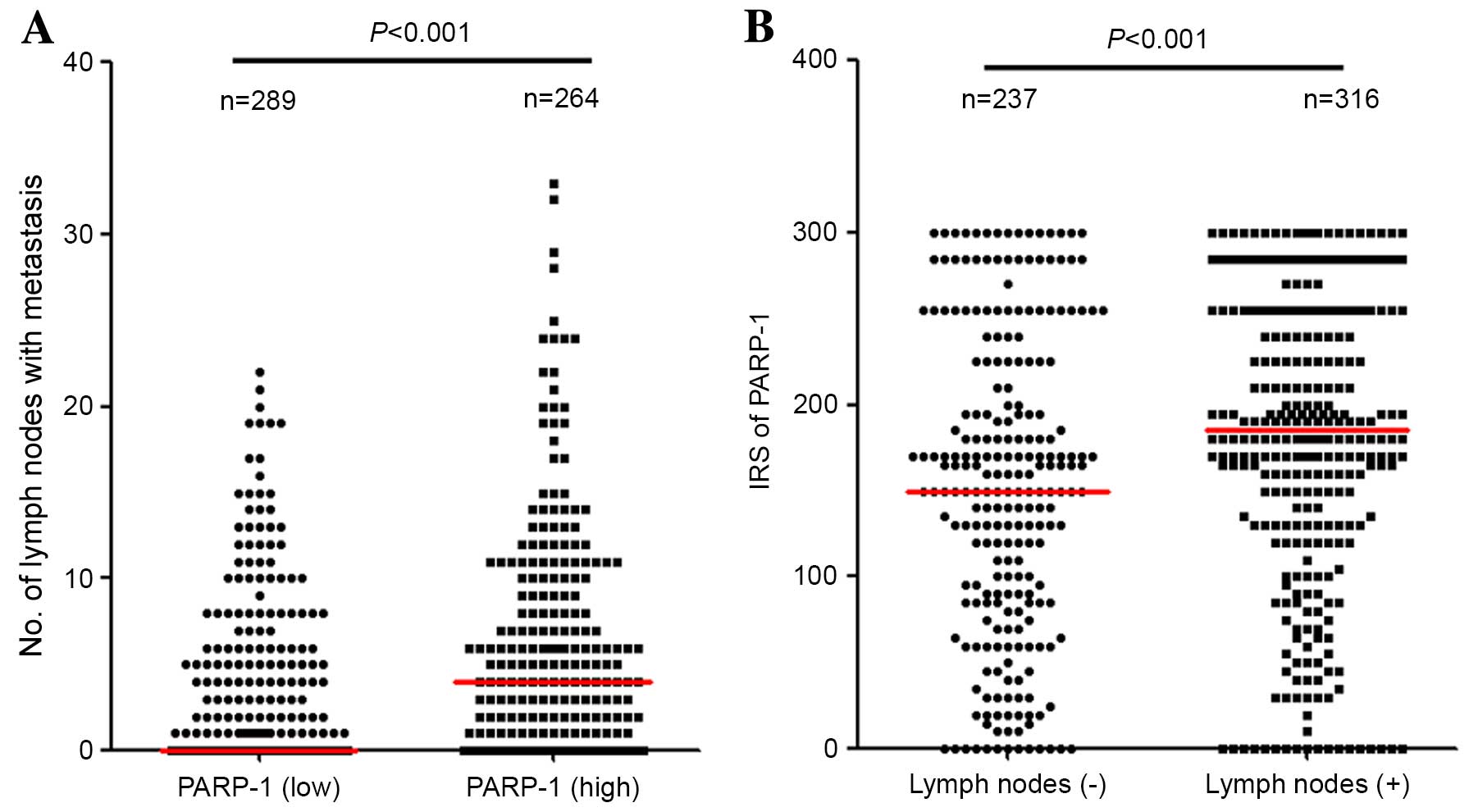
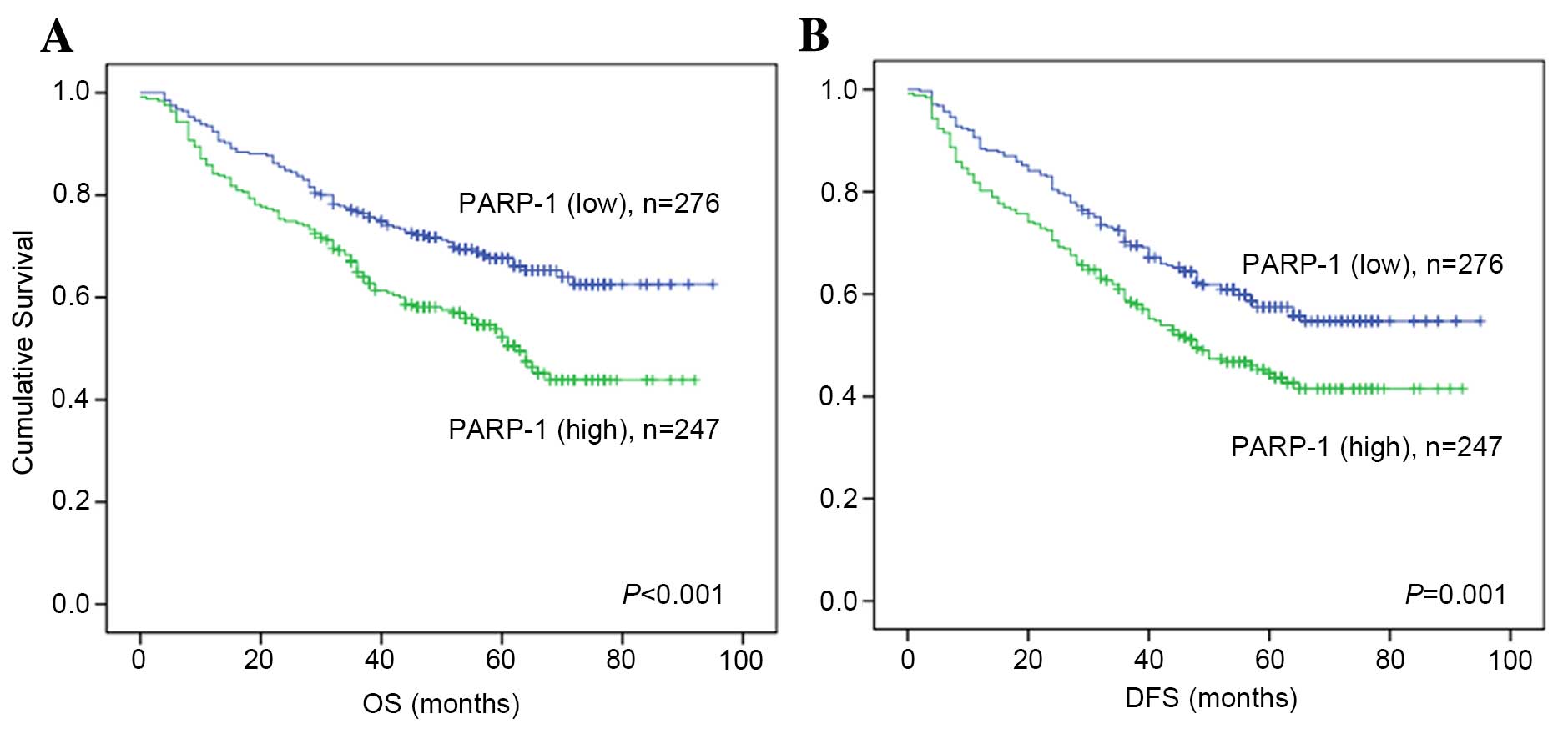
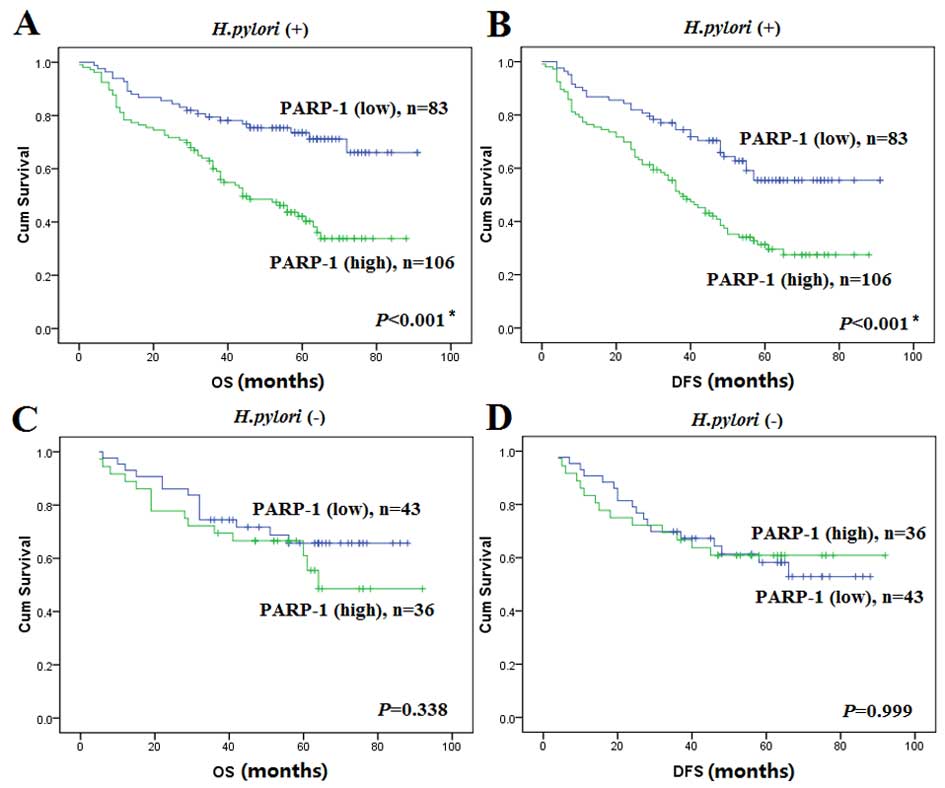
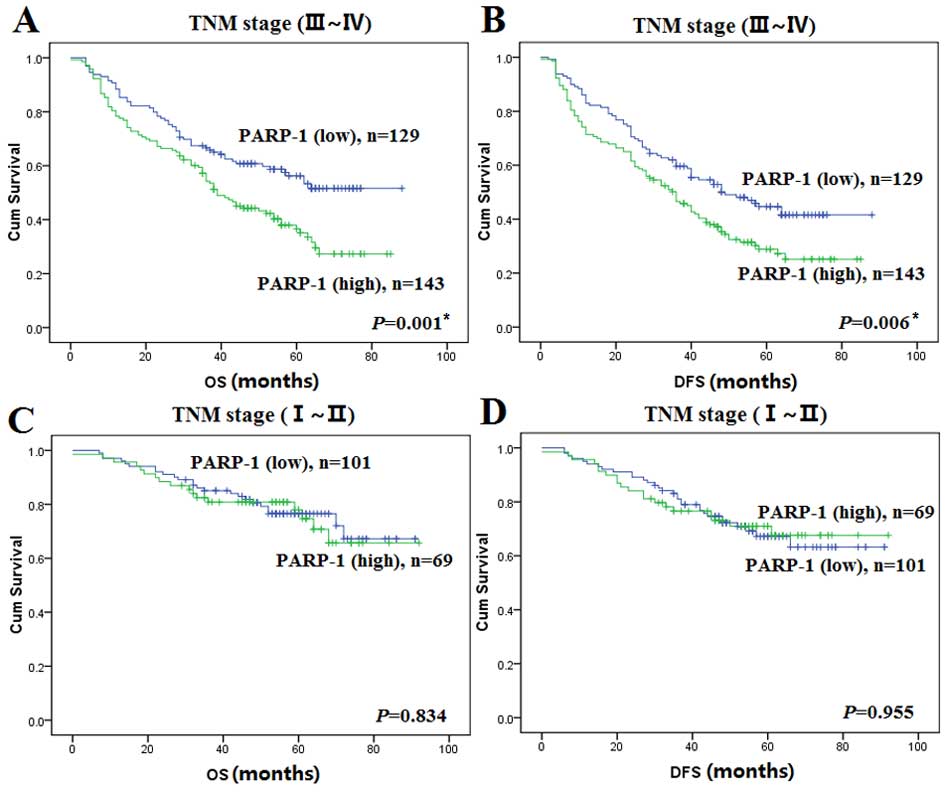
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lordick F, Allum W, Carneiro F, Mitry E,
Tabernero J, Tan P, Van Cutsem E, van de Velde C and Cervantes A:
Unmet needs and challenges in gastric cancer: The way forward.
Cancer Treat Rev. 40:692–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hakmé A, Wong HK, Dantzer F and Schreiber
V: The expanding field of poly (ADP-ribosyl)ation reactions.
‘Protein modifications: Beyond the usual suspects’ review series.
EMBO Rep. 9:1094–1100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hottiger MO, Hassa PO, Luscher B, Schuler
H and Koch-Nolte F: Toward a unified nomenclature for mammalian
ADP-ribosyltransferases. Trends Biochem Sci. 35:208–219. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Michels J, Vitale I, Saparbaev M, Castedo
M and Kroemer G: Predictive biomarkers for cancer therapy with PARP
inhibitors. Oncogene. 33:3894–3907. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chambon P, Weill JD and Mandel P:
Nicotinamide mononucleotide activation of new DNA-dependent
polyadenylic acid synthesizing nuclear enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 11:39–43. 1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sugimura T and Miwa M: Poly (ADP-ribose):
Historical perspective. Mol Cell Biochem. 138:5–12. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Davies JR, Jewell R, Affleck P, Anic GM,
Randerson-Moor J, Ozola A, Egan KM, Elliott F, García-Casado Z,
Hansson J, et al: Inherited variation in the PARP1 geneand survival
from melanoma. Int J Cancer. 135:1625–1633. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bacalini MG, Di Lonardo D, Catizone A,
Ciccarone F, Bruno T, Zampieri M, Guastafierro T, Calabrese R,
Fanciulli M, Passananti C, et al: Poly (ADP-ribosyl)ation affects
stabilization of Che-1 protein in response to DNA damage. DNA
Repair (Amst). 10:380–389. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schreiber V, Dantzer F, Ame JC and de
Murcia G: Poly (ADP-ribose): Novel functions for an old molecule.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:517–528. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Staibano S, Pepe S, Lo Muzio L, Somma P,
Mascolo M, Argenziano G, Scalvenzi M, Salvatore G, Fabbrocini G,
Molea G, et al: Poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase 1
expression in malignant melanomas from photoexposed areas of the
head and neck region. Hum Pathol. 36:724–731. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nosho K, Yamamoto H, Mikami M, Taniguchi
H, Takahashi T, Adachi Y, Imamura A, Imai K and Shinomura Y:
Overexpression of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) in the
early stage of colorectal carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer.
42:2374–2381. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rojo F, Garcia-Parra J, Zazo S, Tusquets
I, Ferrer-Lozano J, Menendez S, Eroles P, Chamizo C, Servitja S,
Ramírez-Merino N, et al: Nuclear PARP-1 protein overexpression is
associated with poor overall survival in early breast cancer. Ann
Oncol. 23:1156–1164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mego M, Cierna Z, Svetlovska D, Macak D,
Machalekova K, Miskovska V, Chovanec M, Usakova V, Obertova J,
Babal P and Mardiak J: PARP expression in germ cell tumours. J Clin
Pathol. 66:607–612. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun Y, Gallacchi D, Zhang EY, Reynolds SB,
Robinson L, Malinowska IA, Chiou TT, Pereira AM, Li C, Kwiatkowski
DJ, et al: Rapamycin-resistant poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1
overexpression is a potential therapeutic target in
lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 51:738–749.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weaver AN and Yang ES: Beyond DNA Repair:
Additional functions of PARP-1 in cancer. Front Oncol. 3:2902013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rouleau M, Patel A, Hendzel MJ, Kaufmann
SH and Poirier GG: PARP inhibition: PARP1 and beyond. Nat Rev
Cancer. 10:293–301. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Benafif S and Hall M: An update on PARP
inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
8:519–528. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O'Shaughnessy J, Osborne C, Pippen JE,
Yoffe M, Patt D, Rocha C, Koo IC, Sherman BM and Bradley C:
Iniparib plus chemotherapy in metastatic triple-negative breast
cancer. N Engl J Med. 364:205–214. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kummar S, Ji J, Morgan R, Lenz HJ, Puhalla
SL, Belani CP, Gandara DR, Allen D, Kiesel B, Beumer JH, et al: A
phase I study of veliparib in combination with metronomic
cyclophosphamide in adults with refractory solid tumors and
lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1726–1734. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Q, Li Y, Li X, Zhou W, Shi B, Chen H
and Yuan W: PARP-1 Val762Ala polymorphism, CagA+ H.
pylori infection and risk for gastric cancer in Han Chinese
population. Mol Biol Rep. 36:1461–1467. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim J, Pyun JA, Cho SW, Lee K and Kwack K:
Lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer is associated with the
interaction between poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 and matrix
metallopeptidase 2. DNA Cell Biol. 30:1011–1017. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He W, Liu T, Shan Y, Zhu K and Li Y: PARP1
polymorphisms increase the risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese
population. Mol Diagn Ther. 16:35–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Le TV, Suh JH, Kim N and Park HJ: In
silico identification of poly (ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 inhibitors
and their chemosensitizing effects against cisplatin-resistant
human gastric cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 23:2642–2646.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu HR, Meng LY, Lin ZY, Shen Y, Yu YQ and
Zhu YZ: Cochinchina momordica seed extract induces apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest in human gastric cancer cells via PARP and p53
signal pathways. Nutr Cancer. 64:1070–1077. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fielding JW, Roginski C, Ellis DJ, Jones
BG, Powell J, Waterhouse JA and Brookes VS: Clinicopathological
staging of gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 71:677–680. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Krishnakumar R and Kraus WL: The PARP side
of the nucleus: Molecular actions, physiological outcomes, and
clinical targets. Mol Cell. 39:8–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cepeda V, Fuertes MA, Castilla J, Alonso
C, Quevedo C, Soto M and Pérez JM: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1
(PARP-1) inhibitors in cancer chemotherapy. Recent Pat Anticancer
Drug Discov. 1:39–53. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mégnin-Chanet F, Bollet MA and Hall J:
Targeting poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity for cancer therapy.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:3649–3662. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shimizu S, Nomura F, Tomonaga T, Sunaga M,
Noda M, Ebara M and Saisho H: Expression of poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase in human hepatocellular carcinoma and analysis of biopsy
specimens obtained under sonographic guidance. Oncol Rep.
12:821–825. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Miwa M and Masutani M:
PolyADP-ribosylation and cancer. Cancer Sci. 98:1528–1535. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brustmann H: Poly(adenosine
diphosphate-ribose) polymerase expression in serous ovarian
carcinoma: Correlation with p53, MIB-1, and outcome. Int J Gynecol
Pathol. 26:147–153. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rodriguez MI, Peralta-Leal A, O'Valle F,
Rodriguez-Vargas JM, Gonzalez-Flores A, Majuelos-Melguizo J, López
L, Serrano S, de Herreros AG, Rodríguez-Manzaneque JC, et al:
PARP-1 regulates metastatic melanoma through modulation of
vimentin-induced malignant transformation. PLoS Genet.
9:e10035312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li M, Threadgill MD, Wang Y, Cai L and Lin
X: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition down-regulates expression
of metastasis-related genes in CT26 colon carcinoma cells.
Pathobiology. 76:108–116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pu H, Horbinski C, Hensley PJ, Matuszak
EA, Atkinson T and Kyprianou N: PARP-1 regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in prostate tumorigenesis.
Carcinogenesis. 35:2592–2601. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lönn P, van der Heide LP, Dahl M, Hellman
U, Heldin CH and Moustakas A: PARP-1 attenuates Smad-mediated
transcription. Mol Cell. 40:521–532. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Virág L and Szabó C: The therapeutic
potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev.
54:375–429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Barboro P, Repaci E, D'Arrigo C and Balbi
C: The role of nuclear matrix proteins binding to matrix attachment
regions (Mars) in prostate cancer cell differentiation. PLoS One.
7:e406172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chiou SH, Jiang BH, Yu YL, Chou SJ, Tsai
PH, Chang WC, Chen LK, Chen LH, Chien Y and Chiou GY: Poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 regulates nuclear reprogramming and
promotes iPSC generation without c-Myc. J Exp Med. 210:85–98. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xie KJ, He HE, Sun AJ, Liu XB, Sun LP and
Dong XJ: Expression of ERCC1, MSH2 and PARP1 in non-small cell lung
cancer and prognostic value in patients treated with platinum-based
chemotherapy. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2591–2596. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Donizy P, Pietrzyk G, Halon A, Kozyra C,
Gansukh T, Lage H, Surowiak P and Matkowski R: Nuclear-cytoplasmic
PARP-1 expression as an unfavorable prognostic marker in lymph
node-negative early breast cancer: 15-year follow-up. Oncol Rep.
31:1777–1787. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Goncalves A, Finetti P, Sabatier R,
Gilabert M, Adelaide J, Borg JP, Chaffanet M, Viens P, Birnbaum D
and Bertucci F: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 mRNA expression in
human breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
127:273–281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Aiad HA, Kandil MA, El-Tahmody MA,
Abulkheir IL, Abulkasem FM, Elmansori AA and Aleskandarany MA: The
prognostic and predictive significance of PARP-1 in locally
advanced breast cancer of Egyptian patients receiving neoadjuvant
chemotherapy. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 23:571–579. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Klauschen F, von Winterfeld M, Stenzinger
A, Sinn BV, Budczies J, Kamphues C, Bahra M, Wittschieber D,
Weichert W, Striefler J, et al: High nuclear
poly-(ADP-ribose)-polymerase expression is prognostic of improved
survival in pancreatic cancer. Histopathology. 61:409–416. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Moss SF, Calam J, Agarwal B, Wang S and
Holt PR: Induction of gastric epithelial apoptosis by Helicobacter
pylori. Gut. 38:498–501. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wagner S, Beil W, Westermann J, Logan RP,
Bock CT, Trautwein C, Bleck JS and Manns MP: Regulation of gastric
epithelial cell growth by Helicobacter pylori: Offdence for a major
role of apoptosis. Gastroenterology. 113:1836–1847. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Atherton JC: The pathogenesis of
Helicobacter pylori-induced gastro-duodenal diseases. Annu Rev
Pathol. 1:63–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Polk DB and Peek RM Jr: Helicobacter
pylori: Gastric cancer and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:403–414.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen Y, Wang Y, Xu W and Zhang Z: Analysis
on the mechanism of Helicobacter pylori-induced apoptosis in
gastric cancer cell line BGC-823. Int J Mol Med. 16:741–745.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nossa CW, Jain P, Tamilselvam B, Gupta VR,
Chen LF, Schreiber V, Desnoyers S and Blanke SR: Activation of the
abundant nuclear factor poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 by
Helicobacter pylori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:19998–20003. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hassumi-Fukasawa MK, Miranda-Camargo FA,
Zanetti BR, Galano DF, Ribeiro-Silva A and Soares EG: Expression of
BAG-1 and PARP-1 in precursor lesions and invasive cervical cancer
associated with human papillomavirus (HPV). Pathol Oncol Res.
18:929–937. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nossa CW and Blanke SR: Helicobacter
pylori activation of PARP-1: Usurping a versatile regulator of host
cellular health. Gut Microbes. 1:373–378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|