Introduction
Human osteosarcoma, mainly arising from osteoid
tissue and producing immature bones, is the most common primary
malignancy of the bone in adolescents (1–3), with an
incidence rate of 4–5 cases/million worldwide (4). Despite current therapeutic strategies
combining adjuvant chemotherapy, surgery and occasionally
radiotherapy, the 5-year survival rate and prognosis of
osteosarcoma patients remain poor, since there is a significant
proportion of osteosarcoma patients with a high risk of local
relapse or distant metastasis following curative resection of the
primary tumor and intensive chemotherapy (5,6). The
5-year survival rate of these patients is only 50–60%, and nearly
40% of osteosarcoma patients succumb to lung metastases (7,8).
Therefore, it is urgently required to develop novel and efficient
alternative strategies for the diagnosis of osteosarcoma patients
at an early stage and for improved prognosis by selecting more
efficient therapeutic approaches.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) are non-coding RNAs of
18–25 nucleotides in length with highly conserved sequences across
different species in plants, animals and DNA viruses (9,10), which
have been demonstrated to play a major role in the regulation of
virtually all cellular processes and gene expression at the
post-transcriptional level by binding to the 3′-untranslated region
of their target messenger RNAs (11,12).
Recently, several studies have shown that aberrant miRNA expression
is associated with the genesis and homeostasis of multiple types of
cancer (13–19). Particularly in osteosarcoma, miR-21
was significantly overexpressed in osteosarcoma, and promoted
invasion and migration in osteosarcoma cells (13). Subsequent studies also demonstrated
that miR-100 (14), miR-204 (15), miR-144 (16), miR-195 (17), miR-26b (18) and miR-195 (19) were linked to the carcinogenesis,
progression and prognosis of osteosarcoma. Furthermore, miRNAs have
also been detected in human serum in remarkably stable forms
(20), which makes serum miRNA
patterns possible to be non-invasive cancer biomarkers with high
sensitivity and specificity (21–23). As
expected, numerous publications have reported that serum miRNAs
exhibited different levels between cancer patients and healthy
controls (24–26) and could served as stable blood-based
biomarkers in various cancers (27,28), which
further highlighted the potential of circulating miRNAs as
non-invasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for cancerous
diseases. Regarding osteosarcoma, recent studies revealed that the
decreased expression of miR-195 in serum may be a novel biomarker
for screening osteosarcoma and may predict poor prognosis (29). The muscle-specific miRNAs miR-133b and
miR-206 were also demonstrated to be downregulated in the serum of
osteosarcoma patients (30). Notably,
serum miR-133b and miR-206 were all independent prognostic
biomarkers for overall and progression-free survival of
osteosarcoma patients (30). Serum
miR-21 also was demonstrated to be a good candidate for a
therapeutic target and a potential biomarker for the prediction of
chemotherapeutic sensitivity and prognosis in patients with
osteosarcoma (31).
A previous study revealed that miR-300 was increased
in osteosarcoma tissues and cell lines compared with paired
adjacent non-cancerous bone and osteoblastic cells (32). In addition, miR-300 was observed to
promote proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells (32). However, there are still no studies on
the expression profile, diagnostic or prognostic significance of
serum miR-300 in osteosarcoma patients.
In the current study, the role of miR-300 in
osteosarcoma was systematically investigated by a two-phase study.
In the first phase, quantitative analyses of miR-300 in a subset of
serum samples from osteosarcoma patients and healthy control
subjects were performed to determine the feasibility of its
detection in the circulation. In the second phase, the clinical
significance of miR-300 as a potential biomarker for diagnosis and
prognosis of osteosarcoma patients was evaluated.
Materials and methods
Patients and specimens
Tissue and serum-based specimen collection and
studies were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the 401
Hospital of PLA (Qingdao, China). All patients provided written
consent and indicated willingness to donate their blood and tissue
samples for research. A total of 114 patients were enrolled in the
present study, of whom, 97 patients received curative resection and
17 patients received palliative resection at the 401 Hospital of
PLA from January 2004 to December 2009. None of the patients
enrolled received radiotherapy or chemotherapy prior to the
operation. All tumors were clinically and histologically diagnosed
as osteosarcoma. Inclusion criteria for all cases included: i)
Unambiguous histology and absence of mixed tumor types; and ii)
absence of any treatment prior to surgery. The clinicopathological
characteristics of the patients are presented in Table I. Patients were followed up subsequent
to surgical treatment until March 2015, with a median follow-up
time of 83 months (range, 12–131 months). During the follow-up
period, 54 patients (47.4%) succumbed to the disease.
 | Table I.Association of miR-300 expression with
clinicopathological features of osteosarcoma. |
Table I.
Association of miR-300 expression with
clinicopathological features of osteosarcoma.
|
|
| miR-300
expression |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Clinicopathological
features | No. of cases | High (n) | Low (n) | P-value |
|---|
| Age (years) | 114 | 68 | 46 | 0.252 |
|
<55 | 64 | 35 | 29 |
|
|
≥55 | 50 | 33 | 17 |
|
| Gender |
|
|
| 0.446 |
|
Male | 58 | 37 | 21 |
|
|
Female | 56 | 31 | 25 |
|
| Tumor size
(cm) |
|
|
| 0.258 |
|
>8 | 62 | 40 | 22 |
|
| ≤8 | 52 | 28 | 24 |
|
| Clinical stage |
|
|
| 0.012a |
|
IIA | 48 | 22 | 26 |
|
|
IIB/III | 66 | 46 | 20 |
|
| Metastasis |
|
|
| 0.035a |
|
Present | 18 | 15 | 3 |
|
|
Absent | 96 | 53 | 43 |
|
RNA extraction and reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
For miRNA quantification, total miRNA was extracted
from the sera of osteosarcoma patients and healthy controls using
miRNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Inc., Valencia, CA, USA), according to
the manufacturer's protocol. Synthetic cel-miR-39 (catalogue no.
219610; Qiagen, Inc.) was added as a spike-in control miRNA into
each sample to normalize the sample-to-sample variation in the RNA
isolation step and to detect the purification efficiency. TaqMan
MicroRNA Reverse Transcription kit (Applied Biosystems; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) was used to detect and
quantify the miRNA expression. Primer sequences used for PCR were
as follows: Forward, 5′-TATACAAGGGCAGACTCTCTCT-3′ and reverse,
5′-GTGCAGGTTCCGAGGT-3′ for miR-300; forward,
5′-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACATATACT-3′ and reverse,
5′-ACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTC-3′ for U6. PCR was performed under the
following conditions: 30 cycles of 95°C for 30 sec, 57°C for 30 sec
and 72°C for 1 min. Data were analyzed with ABI 7500 software
v.2.0.1 (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), with
automatic quantification cycle (Cq) settings for adapting baseline
and threshold for Cq determination (32). Each sample was examined in triplicate,
and the quantity of the PCR products was normalized to U6 (Applied
Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
Statistical analyses
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS
statistical software version 21.0 (IBM SPSS, Armonk, NY, USA).
Mann-Whitney U analyses of variance were used to evaluate
statistical differences in serum miRNA expression between unpaired
groups. The correlation of miR-300 expression between osteosarcoma
tissues and serum was determined by Spearman's correlation
analysis. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare miR-300
expression in paired serum samples obtained prior to surgical tumor
resection and 7 days after surgical tumor resection. Receiver
operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to determine
the diagnostic performance of miR-300 expression levels in
distinguishing patients with osteosarcoma from healthy control
subjects. Sensitivity against 100% minus specificity was plotted
for each cutoff threshold, and the area under the curve (AUC)
values that reflected the probability of correctly identifying
osteosarcoma patients from control subjects were computed. The
optimal cutoff thresholds for diagnosis were obtained by the
Youden's index. By using the optimal cutoff value, the sensitivity,
specificity, and positive and negative predictive values were
calculated. Survival curves were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier
method, and distributions were evaluated by the long-rank test. Cox
proportional hazard models of factors associated with survival were
used to calculate the hazard ratios (HRs) and to identify factors
that affect survival. The differences in characteristics between
two groups were examined by the χ2 test and the Fisher's
exact test. All P-values were determined from two-sided tests, and
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
Relative expression of serum miR-300
in osteosarcoma patients
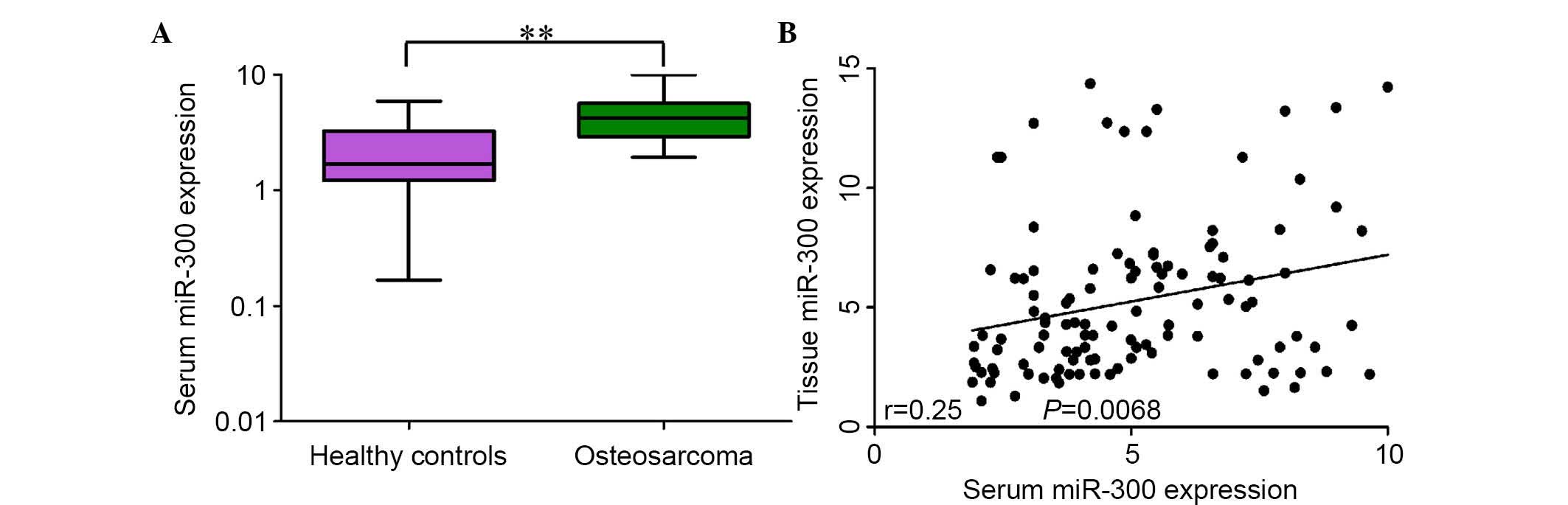
The level of serum miR-300 in osteosarcoma patients
was investigated. It was observed that the relative expression of
serum miR-300 in 114 osteosarcoma patients was significantly higher
than that in healthy controls (P=0.007; Fig. 1A). Furthermore, the expression of
serum miR-300 was significantly associated with the expression of
tissue miR-300 in osteosarcoma patients (Spearman's correlation:
r=0.25, P=0.0068; Fig. 1B).
Diagnostic value of serum miR-300
expression in osteosarcoma patients
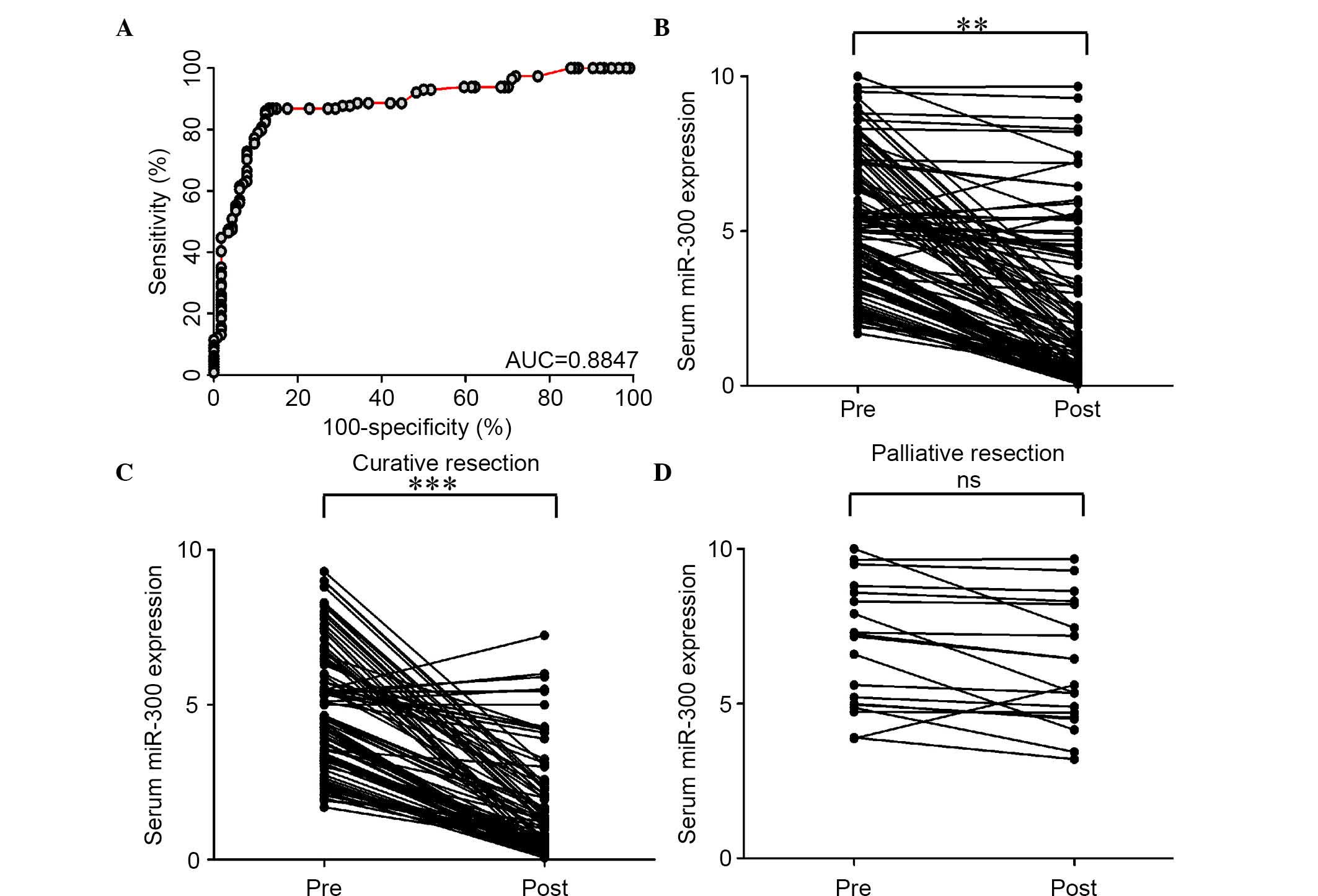
ROC curve analysis illustrated that serum miR-300
expression was a potential biomarker for discriminating
osteosarcoma patients from healthy controls, with an AUC of 0.8847
(Fig. 2A). Using a cutoff value of
2.63, the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative
predictive values were 84.2, 88.6, 89.7 and 84.9%, respectively, to
identify a patient with osteosarcoma.
Alterations of serum miR-300 levels in
patients with osteosarcoma
The serum levels of miR-300 significantly decreased
following surgery in the same subset of osteosarcoma patients
(P=0.009; Fig. 2B). However, when
data were analyzed based on potentially curative or palliative
surgeries, serum miR-300 levels significantly decreased in patients
with potentially curative surgeries (P=0.0006; Fig. 2C). Contrarily, no significant
differences were observed in miR-300 levels prior or subsequent to
surgery in patients with palliative resections (Fig. 2D).
Upregulation of serum miR-300 levels
is associated with advanced clinicopathological characteristics of
osteosarcoma patients
Next, it was investigated whether serum miR-300
expression correlated with clinicopathological characteristics of
patients with osteosarcoma. As shown in Table I, serum miR-300 was significantly
upregulated in osteosarcoma patients with advanced clinical stage
(P=0.0120) and metastasis status (P=0.0350). However, there was no
correlation of serum miR-300 expression with other clinical
features such as age, gender or tumor size (all P>0.05).
Upregulation of serum miR-300 levels
is associated with poor overall survival and progression-free
survival rates in osteosarcoma
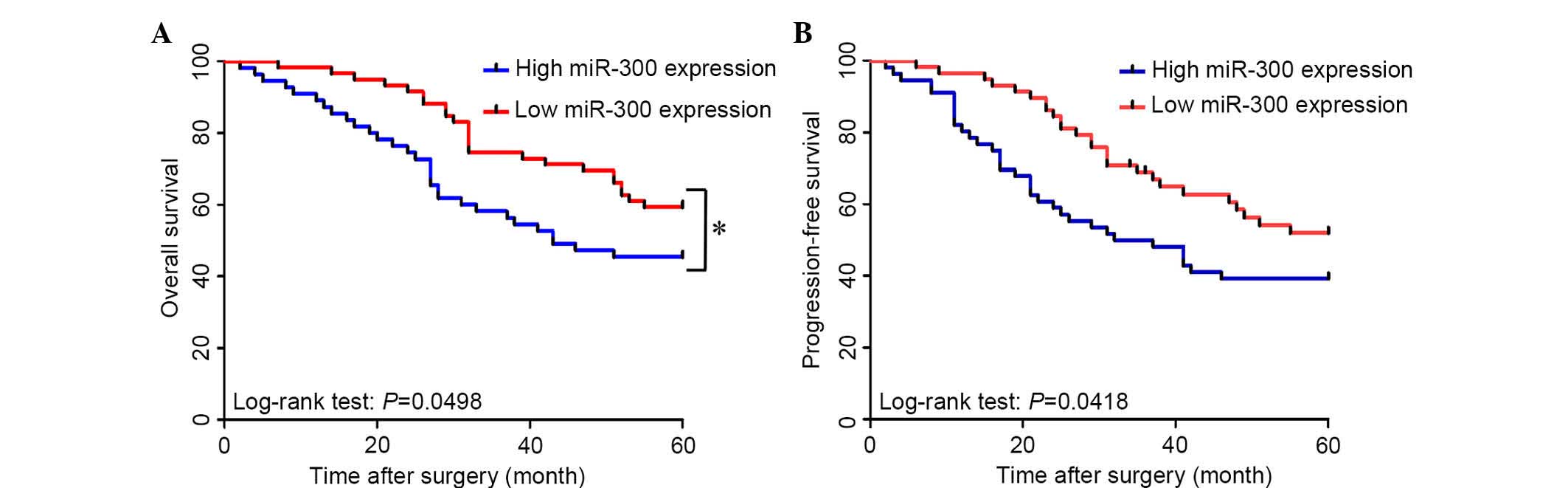
The association between miR-300 expression and
overall survival or progression-free survival was investigated
using Kaplan-Meier analysis and log-rank test. Significant
differences in overall survival and progression-free survival were
detected between the high serum miR-300 expression group and the
low serum miR-300 group (log-rank test: P=0.0498 and P=0.0418,
respectively; Fig. 3A and B).
Patients with high serum miR-300 expression tended to have shorter
overall and progression-free survival times than patients with low
serum miR-300 expression.
Upregulation of serum miR-300 levels
is associated with poor prognosis in osteosarcoma patients
Univariate analysis identified clinical stage,
metastasis status and high expression of serum miR-300 as poor
prognostic factors for overall survival and progression-free
survival (all P<0.05; Table II),
whereas neither age, gender or tumor size were significantly
associated with overall survival or progression-free survival. To
test whether the prognostic value of high serum miR-300 expression
was independent of other risk factors for poor overall and
progression-free survival, a multivariate analysis was performed
using a Cox proportional hazard model. Multivariate analyses
including age, gender, tumor size, clinical stage, metastasis
status and serum miR-300 expression demonstrated that high serum
miR-300 expression was an independent predictor for poor overall
and progression-free survival in osteosarcoma patients [HR=4.698,
95% confidence interval (CI)=1.562–8.369, P=0.0140 and HR=4.406,
95% CI=1.268–6.986, P=0.0130, respectively; Table III). Significant results were also
obtained for advanced clinical stage and metastasis status, whereas
all other parameters were not significant independent prognostic
markers for overall survival or progression-free survival.
 | Table II.Univariate survival analysis of
overall survival and disease-free survival in 114 patients with
osteosarcoma. |
Table II.
Univariate survival analysis of
overall survival and disease-free survival in 114 patients with
osteosarcoma.
|
| Overall
survival | Disease-free
survival |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|
| miR-300
expression | 5.964 | 2.349–10.697 | 0.009a | 5.112 | 2.136–9.482 | 0.019a |
| Clinical stage | 4.936 | 1.989–8.587 | 0.011a | 3.216 | 2.102–6.964 | 0.031a |
| Metastasis
status | 6.102 | 3.652–11.036 | 0.006a | 5.563 | 2.645–8.254 | 0.012a |
 | Table III.Multivariate survival analysis of
overall survival and disease-free survival in 114 patients with
osteosarcoma. |
Table III.
Multivariate survival analysis of
overall survival and disease-free survival in 114 patients with
osteosarcoma.
|
| Overall
survival | Disease-free
survival |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|
| miR-300
expression | 4.698 | 1.562–8.369 | 0.014a | 4.406 | 1.268–6.986 | 0.013a |
| Clinical stage | 3.869 | 1.269–6.858 | 0.021a | 3.597 | 1.369–7.639 | 0.029a |
| Metastasis
status | 3.165 | 1.197–5.459 | 0.036a | 3.664 | 1.569–4.987 | 0.027a |
Discussion
In the current study, the serum expression levels of
miR-300 were detected in osteosarcoma patients and healthy
controls, and their upregulation in the peripheral blood of
osteosarcoma patients was confirmed. Furthermore, the diagnostic
value of serum miR-300 in osteosarcoma was also evaluated by two
steps. Initially, it was observed that the relative expression of
serum miR-300 in osteosarcoma patients was significantly higher
than that in healthy controls, and that the expression of serum
miR-300 correlated significantly with the expression of tissue
miR-300. The diagnostic value of serum miR-300 in the early
detection of osetosarcoma was evaluated by yield AUC curves. It was
observed that serum miR-300 could efficiently differentiate
osteosarcoma patients from healthy controls (AUC=0.8847). Taken
together, these results confirmed that the extraction of RNA and
identification of miR-300 in the serum of individuals diagnosed
with osteosarcoma is feasible, and offered the first description
that miR-300 could be an effective diagnostic biomarker with high
sensitivity and specificity for osteosarcoma.
Another important finding of our study is that serum
miR-300 expression also serves as a prognostic biomarker for
osteosarcoma. Our results are consistent with those from previous
studies that demonstrated that miR-300 could promote cell
proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma cells (32). The present study identified the
prognostic role of serum miR-300 in osteosarcoma by three steps.
Initially, it was observed that the expression of serum miR-300 was
significantly correlated with the expression of tissue miR-300.
Then, it was noticed that serum miR-300 was also significantly
correlated with progression-free and overall survival of
osteosarcoma patients by Kaplan-Meier and univariate analyses.
Finally, it was identified that serum miR-300 was an independent
prognostic biomarker for patients with osteosarcoma by multivariate
analysis. Our findings that high levels of serum miR-300 indicate a
poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma are also an important
step forward in the further identification of a non-invasive
biomarker for osteosarcoma. To the best of our knowledge, the
present study represents the first demonstration that serum miR-300
may not only be a diagnostic biomarker for osteosarcoma but may
also aid to predict metastases or tumor recurrence with high
accuracy.
The aberrant expression of miR-300 is a frequent
event in multiple types of solid cancer, suggesting its important
roles in carcinogenesis and cancer progression (32–34).
Similar to other miRNAs, the expression pattern and functions of
miR-300 may be different in various types of cancer, in a
tissue-specific manner, dependent on the cellular context (32,33). For
example, Yu et al reported that miR-300 was downregulated in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells and in breast cancer
cells. Downregulation of miR-300 was required for the initiation
and maintenance of the transforming growth factor-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (33). Thus, miR-300 could inhibit cell
invasion and metastasis by negatively regulating EMT in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma. By contrast, the expression of
miR-300 was upregulated in glioma tissues and glioma stem-like
cells, and overexpression of miR-300 could promote the self-renewal
and cell proliferation of glioma stem-like cells (34). Similarly, the expression of miR-300
was also reported to be elevated in osteosarcoma tissues and cell
lines compared with that in adjacent non-tumor bone tissues and
osteoblastic cells (32). Notably,
the overexpression of miR-300 could promote cell proliferation and
invasion in osteosarcoma cells (32).
In the present study, elevated serum miR-300 expression was
identified in osteosarcoma patients, and its significant
association with adverse clinicopathological features was
confirmed, further suggesting the oncogenic role of miRNAs in
osteosarcoma. These findings were consistent with those from a
previous study, which reported that miR-300 could promote cell
proliferation and cell invasion in vitro for the first time
(32).
Although our current study indicates that serum
miR-300 may be a promising screening tool for osteosarcoma, we
acknowledge two potential limitations of using miR-300 as a single
biomarker for the early detection of osteosarcoma. First,
circulating expression of miR-300 has been described in numerous
solid cancers besides osteosarcoma, including glioma and head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma (33,34). As a
consequence, it may be challenging to differentiate whether
circulating miR-300 expression is specifically associated with
osteosarcoma itself or is a common phenomenon that manifests during
the progression of any cancer as a result of perturbations in the
host immune response (35,36). Second, although it is highly unlikely
to have a substantial impact, the use of serum miR-300 expression
levels as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker must be validated
in diverse ethnic populations, since the clinical specimens
analyzed in our study were solely from patients of Chinese
origin.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that
serum miR-300 was an effective diagnostic biomarker in osteosarcoma
patients. Besides, it was also demonstrated that serum miR-300
levels were more frequently elevated in osteosarcoma patients with
adverse clinical stage and presence of distant metastasis than
osteosarcoma patients without adverse clinical stage and presence
of distant metastasis. Multivariate survival analyses demonstrated
that serum miR-300 was an independent prognostic factor for both
progression-free and overall survival in osteosarcoma patients. Our
results provide compelling evidence for the potential usefulness of
serum miR-300 as a non-invasive screening tool and effective
prognostic tool in patients with osteosarcoma.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
miRNAs
|
microRNAs
|
|
RT-qPCR
|
reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction
|
|
ROC
|
receiver operating characteristic
|
|
AUC
|
area under the curve
|
References
|
1
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Teicher BA: Searching for molecular
targets in sarcoma. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:1–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kager L, Zoubek A, Pötschger U, Kastner U,
Flege S, Kempf-Bielack B, Branscheid D, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Primary metastatic osteosarcoma: Presentation
and outcome of patients treated on neoadjuvant cooperative
osteosarcoma study group protocols. J Clin Oncol. 21:2011–2018.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bacci G, Briccoli A, Rocca M, Ferrari S,
Donati D, Longhi A, Bertoni F, Bacchini P, Giacomini S, Forni C, et
al: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for osteosarcoma of the extremities
with metastases at presentation: Recent experience at the Rizzoli
institute in 57 patients treated with cisplatin, doxorubicin, and a
high dose of methotrexate and ifosfamide. Ann Oncol. 14:1126–1134.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Marina N, Gebhardt M, Teot L and Gorlick
R: Biology and therapeutic advances for pediatric osteosarcoma.
Oncologist. 9:422–441. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gorlick R: Current concepts on the
molecular biology of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:467–478.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bruland ØS, Bauer H, Alvegaard T and
Smeland S: Treatment of osteosarcoma. The Scandinavian sarcoma
group experience. Cancer Treat Res. 152:309–318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R,
Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, et al:
Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human
microRNAs. Nat Genet. 37:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ying HC, Xu HY, Lv J, Ying TS and Yang Q:
MicroRNA signatures of platinum-resistance in ovarian cancer. Eur J
Gynaecol Oncol. 36:16–20. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ziyan W, Shuhua Y, Xiufang W and Xiaoyun
L: MicroRNA-21 is involved in osteosarcoma cell invasion and
migration. Med Oncol. 28:1469–1474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bi Y, Jing Y and Cao Y: Overexpression of
miR-100 inhibits growth of osteosarcoma through FGFR3. Tumour Biol.
36:8405–8411. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi Y, Huang J, Zhou J, Liu Y, Fu X, Li Y,
Yin G and Wen J: MicroRNA-204 inhibits proliferation, migration,
invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma
cells via targeting Sirtuin 1. Oncol Rep. 34:399–406.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang W, Zhou X and Wei M: MicroRNA-144
suppresses osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by targeting ROCK1
and ROCK2. Oncotarget. 6:10297–10308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han K, Chen X, Bian N, Ma B, Yang T, Cai
C, Fan Q, Zhou Y and Zhao TB: MicroRNA profiling identifies MiR-195
suppresses osteosarcoma cell metastasis by targeting CCND1.
Oncotarget. 6:8875–8889. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Du JY, Wang LF, Wang Q and Yu LD: miR-26b
inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis induction
via the downregulation of
6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3 driven
glycolysis in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 33:1890–1898.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mao JH, Zhou RP, Peng AF, Liu ZL, Huang
SH, Long XH and Shu Y: microRNA-195 suppresses osteosarcoma cell
invasion and migration in vitro by targeting FASN. Oncol Lett.
4:1125–1129. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kosaka N, Iguchi H and Ochiya T:
Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for
cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 101:2087–2092. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K,
Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, et al: Characterization of microRNAs
in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and
other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B,
Liggins AP, Pulford K, Banham AH, Pezzella F, Boultwood J,
Wainscoat JS, et al: Detection of elevated levels of
tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 141:672–675. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, Lam EK, Shin VY,
Yu J, Poon TC, Ng SS and Sung JJ: Differential expression of
microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: A potential
marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut. 58:1375–1381. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kong X, Du Y, Wang G, Gao J, Gong Y, Li L,
Zhang Z, Zhu J, Jing Q, Qin Y and Li Z: Detection of differentially
expressed microRNAs in serum of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
patients: miR-196a could be a potential marker for poor prognosis.
Dig Dis Sci. 56:602–609. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsujiura M, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S,
Shiozaki A, Takeshita H, Kosuga T, Konishi H, Morimura R, Deguchi
K, Fujiwara H, et al: Circulating microRNAs in plasma of patients
with gastric cancers. Br J Cancer. 102:1174–1179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DS and Pantel K:
Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat Rev
Cancer. 11:426–437. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney
KJ, Newell J and Kerin MJ: Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally
invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 251:499–505. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cai H, Zhao H, Tang J and Wu H: Serum
miR-195 is a diagnostic and prognostic marker for osteosarcoma. J
Surg Res. 194:505–510. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang C, Yao C, Li H, Wang G and He X:
Serum levels of microRNA-133b and microRNA-206 expression predict
prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4194–4203. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yuan J, Chen L, Chen X, Sun W and Zhou X:
Identification of serum microRNA-21 as a biomarker for
chemosensitivity and prognosis in human osteosarcoma. J Int Med
Res. 40:2090–2097. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xue Z, Zhao J, Niu L, An G, Guo Y and Ni
L: Up-regulation of miR-300 promotes proliferation and invasion of
osteosarcoma by targeting BRD7. PloS One. 10:e01276822015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu J, Xie F, Bao X, Chen W and Xu Q:
miR-300 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition and
metastasis by targeting twist in human epithelial cancer. Mol
Cancer. 13:1212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang D, Yang G, Chen X, Li C, Wang L, Liu
Y, Han D, Liu H, Hou X, Zhang W, et al: mir-300 promotes
self-renewal and inhibits the differentiation of glioma stem-like
cells. J Mol Neurosci. 53:637–644. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xiao J, Luo X, Lin H, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Wang
N, Zhang Y, Yang B and Wang Z: MicroRNA miR-133 represses HERG K+
channel expression contributing to QT prolongation in diabetic
hearts. J Biol Chem. 282:12363–12367. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Hur K, Nagasaka T,
Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Kusunoki M, Boland CR and Goel A: Serum miR-21
as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 105:849–859. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|