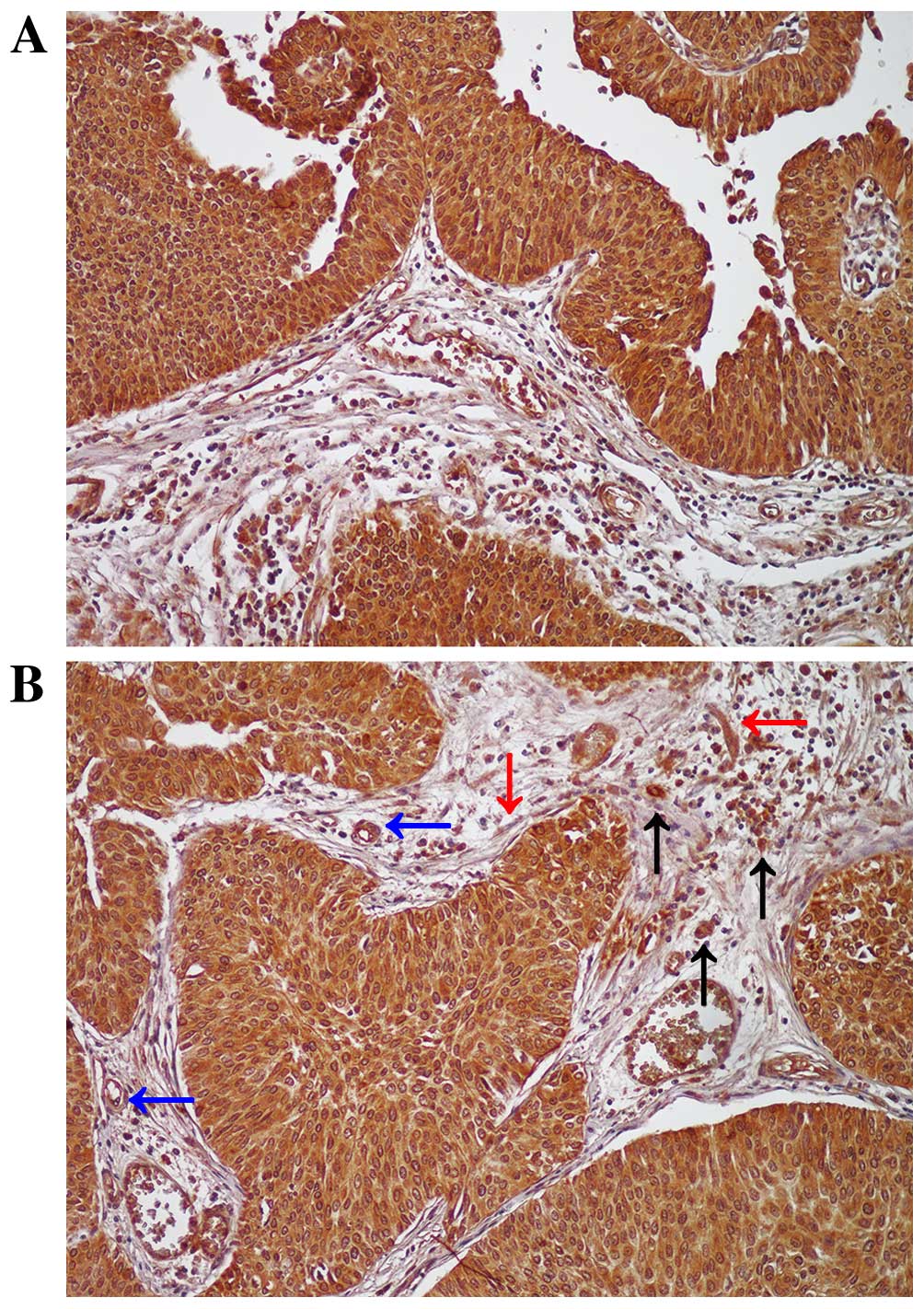
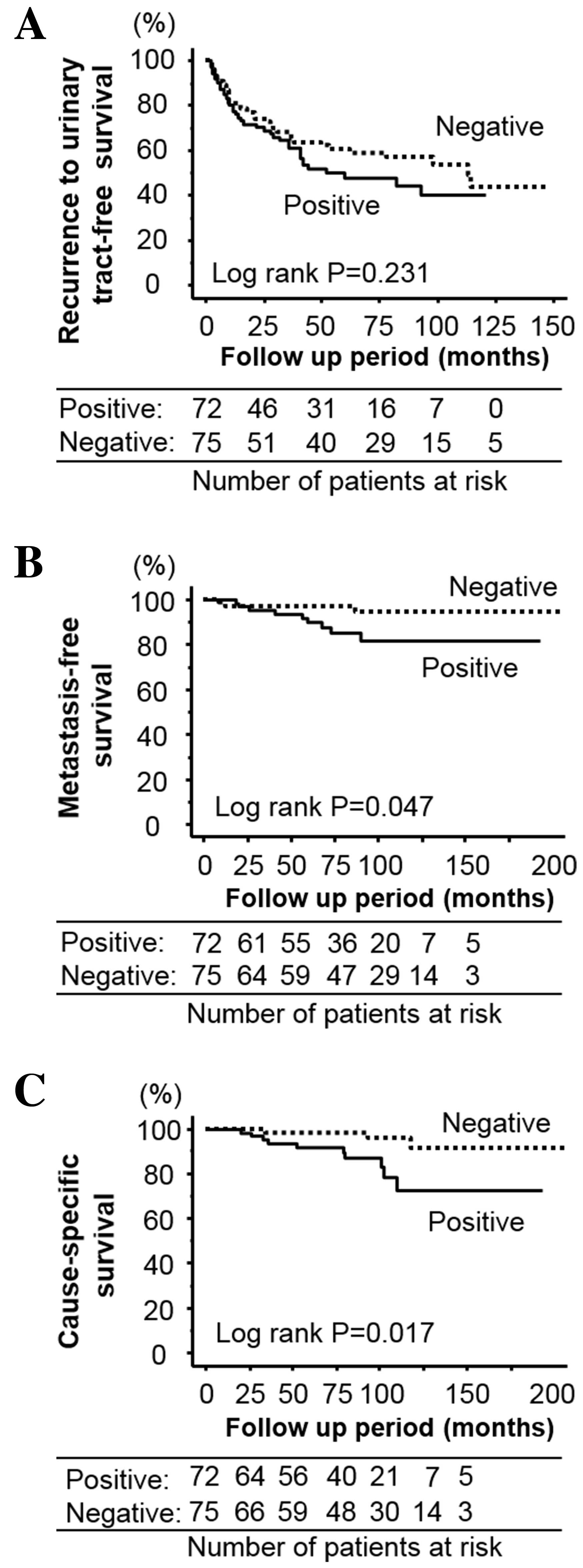
|
1
|
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP,
Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, Newling DW and
Kurth K: Predicting recurrence and progression in individual
patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A
combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur
Urol. 49:466–477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cookson MS, Herr HW, Zhang ZF, Soloway S,
Sogani PC and Fair WR: The treated natural history of high risk
superficial bladder cancer: 15-year outcome. J Urol. 158:62–67.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van Rhijn BW, Burger M, Lotan Y, Solsona
E, Stief CG, Sylvester RJ, Witjes JA and Zlotta AR: Recurrence and
progression of disease in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: From
epidemiology to treatment strategy. Eur Urol. 56:430–442. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
D'Costa JJ, Goldsmith JC, Wilson JS, Bryan
RT and Ward DG: A systematic review of the diagnostic and
prognostic value of urinary protein biomarkers in Urothelial
bladder cancer. Bladder Cancer. 2:301–317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pospisilova S, Pazourkova E, Horinek A,
Brisuda A, Svobodova I, Soukup V, Hrbacek J, Capoun O, Hanus T,
Mares J, et al: MicroRNAs in urine supernatant as potential
non-invasive markers for bladder cancer detection. Neoplasma.
63:799–808. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Miyata Y, Kanda S, Ohba K, Nomata K,
Hayashida Y, Eguchi J, Hayashi T and Kanetake H: Lymphangiogenesis
and angiogenesis in bladder cancer: Prognostic implications and
regulation by vascular endothelial growth factors-A, -C, and -D.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:800–806. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ding W, Gou Y, Sun C, Xia G, Wang H, Chen
Z, Tan J, Xu K and Qiang D: Ki-67 is an independent indicator in
non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC); combination of EORTC
risk scores and Ki-67 expression could improve the risk
stratification of NMIBC. Urol Oncol. 32:42.e13–e19. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Miyata Y, Watanabe S, Sagara Y, Mitsunari
K, Matsuo T, Ohba K and Sakai H: High expression of HuR in
cytoplasm, but not nuclei, is associated with malignant
aggressiveness and prognosis in bladder cancer. PLoS One.
8:e590952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang W, Jiang H, Zhu H, Zhang H, Gong J,
Zhang L and Ding Q: Overexpression of high mobility group box 1 and
2 is associated with the progression and angiogenesis of human
bladder carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 5:884–888. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tenhunen R, Marver HS and Schmid R: The
enzymatic conversion of heme to bilirubin by microsomal heme
oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 61:748–755. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Applegate LA, Luscher P and Tyrrell RM:
Induction of heme oxygenase: A general response to oxidant stress
in cultured mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 51:974–978.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fang J, Akaike T and Maeda H:
Antiapoptotic role of heme oxygenase (HO) and the potential of HO
as a target in anticancer treatment. Apoptosis. 9:27–35. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lane D, Gray EA, Mathur RS and Mathur SP:
Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor-C by nicotine
in cervical cancer cell lines. Am J Reprod Immnol. 53:153–158.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Degese MS, Mendizabal JE, Gandini NA,
Gutkind JS, Molinolo A, Hewitt SM, Curino AC, Coso OA and
Facchinetti MM: Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in non-small cell
lung cancer (NSCLC) and its correlation with clinical data. Lung
Cancer. 77:168–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Was H, Cichon T, Smolarczyk R, Rudnicka D,
Stopa M, Chevalier C, Leger JJ, Lackowska B, Grochot A, Bojkowska
K, et al: Overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 in murine melanoma:
Increased proliferation and viability of tumor cells, decreased
survival of mice. Am J Pathol. 169:2181–2198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ferrando M, Gueron G, Elguero B, Giudice
J, Salles A, Leskow FC, Jares-Erijman EA, Colombo L, Meiss R,
Navone N, et al: Heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) challenges the angiogenic
switch in prostate cancer. Angiogenesis. 14:467–479. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miyata Y, Kanda S, Mitsunari K, Asai A and
Sakai H: Heme oxygenase-1 expression is associated with tumor
aggressiveness and outcomes in patients with bladder cancer: A
correlation with smoking intensity. Transl Res. 164:468–476. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kopparapu PK, Boorjian SA, Robinson BD,
Downes M, Gudas LJ, Mongan NP and Persson JL: Expression of VEGF
and its receptors VEGFR1/VEGFR2 is associated with invasiveness of
bladder cancer. Anticancer Res. 33:2381–2390. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sobin DH and Wittekind CH: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumours. 6th. Wiley-Liss; New York: pp.
199–202. 2002
|
|
20
|
Sauter G, Algaba F, Amin MB, Busch C,
Cheville J, Gasser T, Grignon DJ, Hofstädter F, Lopez-Beltran A and
Epstein JI: Non-invasive urothelial tumoursWorld Health
Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of
Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organ. Eble JN,
Sauter G, Epstein JI and Sesterhenn IA: IARC Press; Lyon, France:
pp. 110–123. 2004
|
|
21
|
Miyata Y, Kanda S, Ohba K, Nomata K,
Eguchi J, Hayashida Y and Kanetake H: Tumor lymphangiogenesis in
transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract: Association
with clinicopathological features and prognosis. J Urol.
176:348–353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyata Y, Koga S, Kanda S, Nishikido M,
Hayashi T and Kanetake H: Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in renal
cell carcinoma: Correlation with tumor cell proliferation,
apoptosis, angiogenesis, expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2,
and survival. Clin Cancer Res. 9:1741–1749. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miyata Y, Kanda S, Nomata K, Hayashida Y
and Kanetake H: Expression of metalloproteinase-2,
metalloproteinase-9, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in
transitional cell carcinoma of upper urinary tract: Correlation
with tumor stage and survival. Urology. 63:602–608. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gandini NA, Fermento ME, Salomón DG,
Blasco J, Patel V, Gutkind JS, Molinolo AA, Facchinetti MM and
Curino AC: Nuclear localization of heme oxygenase-1 is associated
with tumor progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.
Exp Mol Pathol. 93:237–245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Banerjee P, Basu A, Wegiel B, Otterbein
LE, Mizumura K, Gasser M, Waaga-Gasser AM, Choi AM and Pal S: Heme
oxygenase-1 promotes survival of renal cancer cells through
modulation of apoptosis- and autophagy-regulating molecules. J Biol
Chem. 287:32113–32123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yin Y, Liu Q, Wang B, Chen G, Xu L and
Zhou H: Expression and function of heme oxygenase-1 in human
gastric cancer. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 237:362–371. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Andrés NC, Fermento ME, Gandini NA, Romero
AL, Ferro A, Donna LG, Curino AC and Facchinetti MM: Heme
oxygenase-1 has antitumoral effects in colorectal cancer:
Involvement of p53. Exp Mol Pathol. 97:321–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yanagawa T, Omura K, Harada H, Nakaso K,
Iwasa S, Koyama Y, Onizawa K, Yusa H and Yoshida H: Heme
oxygenase-1 expression predicts cervical lymph node metastasis of
tongue squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 40:21–27. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miyake M, Fujimoto K, Anai S, Ohnishi S,
Kuwada M, Nakai Y, Inoue T, Matsumura Y, Tomioka A, Ikeda T, et al:
Heme oxygenase-1 promotes angiogenesis in urothelial carcinoma of
the urinary bladder. Oncol Rep. 25:653–660. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yim MS, Ha YS, Kim IY, Yun SJ, Choi YH and
Kim WJ: HMOX1 is an important prognostic indicator of nonmuscle
invasive bladder cancer recurrence and progression. J Urol.
185:701–705. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Miyake M, Fujimoto K, Anai S, Ohnishi S,
Nakai Y, Inoue T, Matsumura Y, Tomioka A, Ikeda T, Tanaka N and
Hirao Y: Clinical significance of heme oxygenase-1 expression in
non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Urol Int. 85:355–363. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim JH and Park J: Prognostic significance
of heme oxygenase-1, S100 calcium-binding protein A4, and
syndecan-1 expression in primary non-muscle-invasive bladder
cancer. Hum Pathol. 45:1830–1838. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Miyake M, Ishii M, Kawashima K, Kodama T,
Sugano K, Fujimoto K and Hirao Y: siRNA-mediated knockdown of the
heme synthesis and degradation pathways: Modulation of treatment
effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy in
urothelial cancer cell lines. Photochem Photobiol. 85:1020–1027.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin H, Huang BR, Yeh WL, Lee CH, Huang SS,
Lai CH, Lin H and Lu DY: Antineuroinflammatory effects of lycopene
via activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein
kinase-α1/heme oxygenase-1 pathways. Neurobiol Aging. 35:191–202.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin HH, Chiang MT, Chang PC and Chau LY:
Myeloid heme oxygenase-1 promotes metastatic tumor colonization in
mice. Cancer Sci. 106:299–306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|