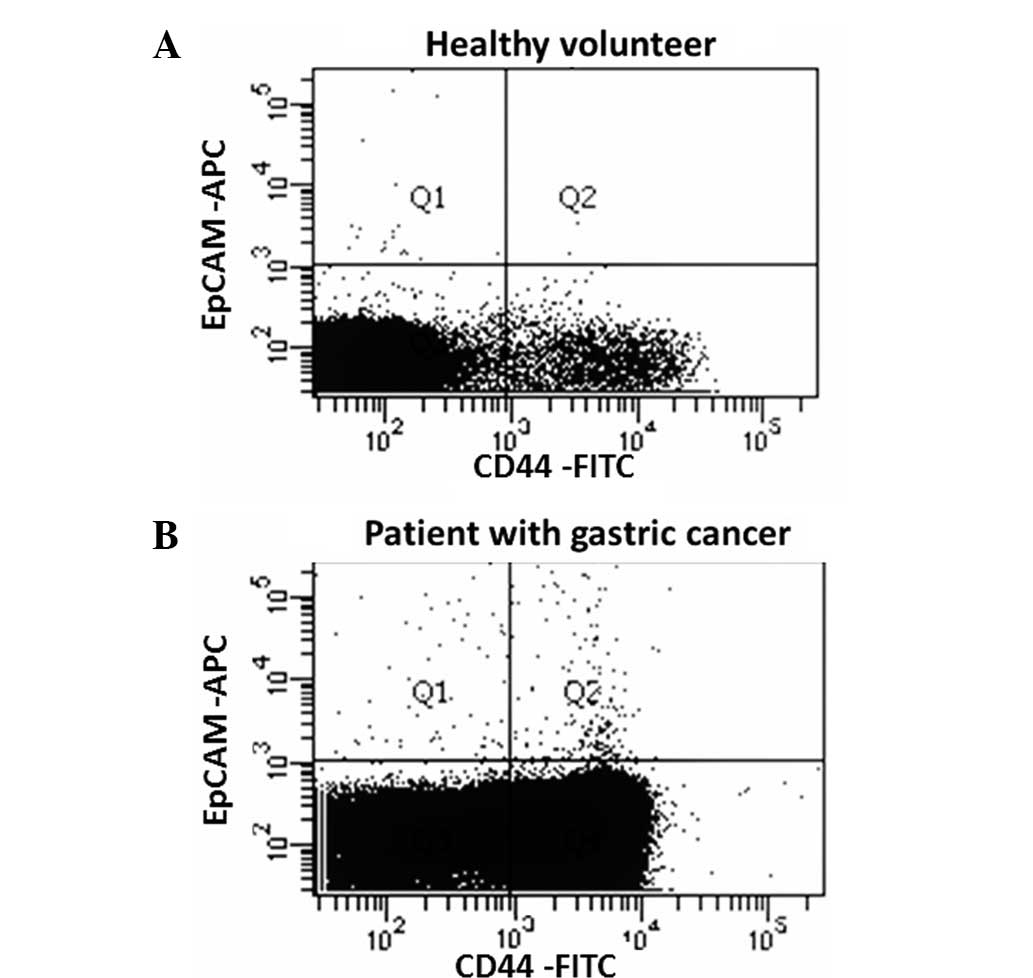
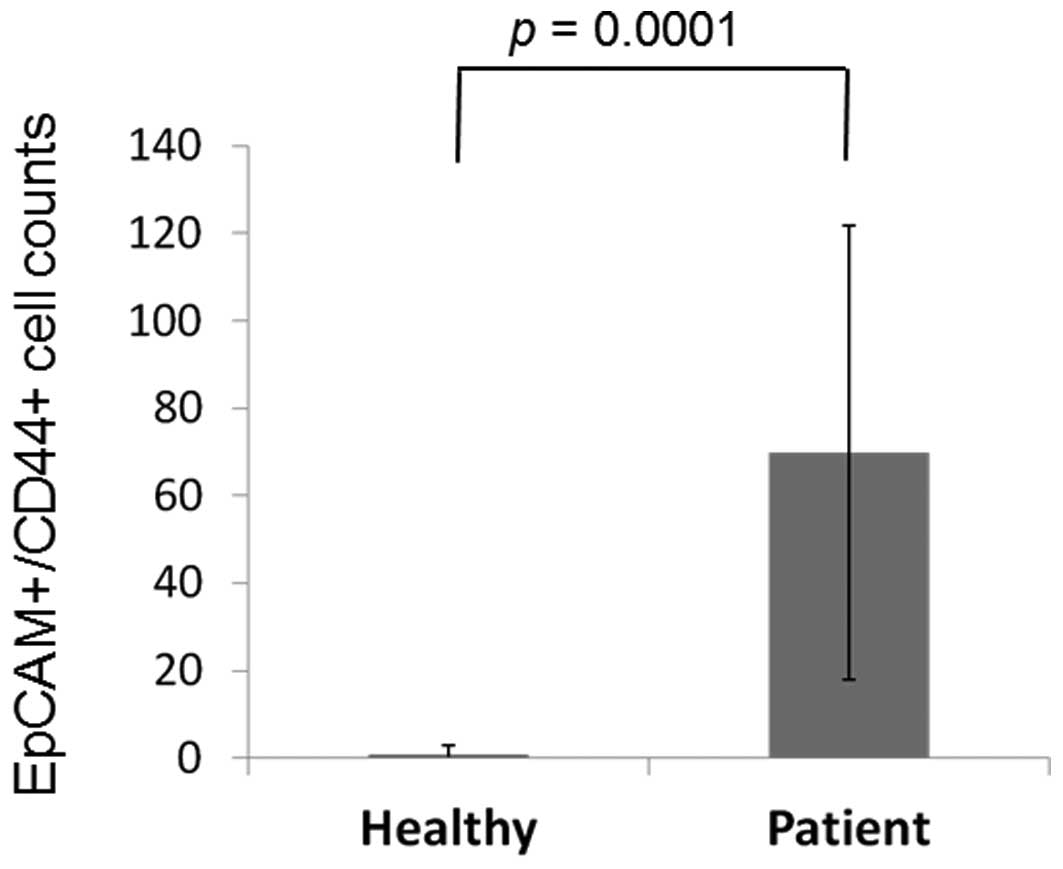
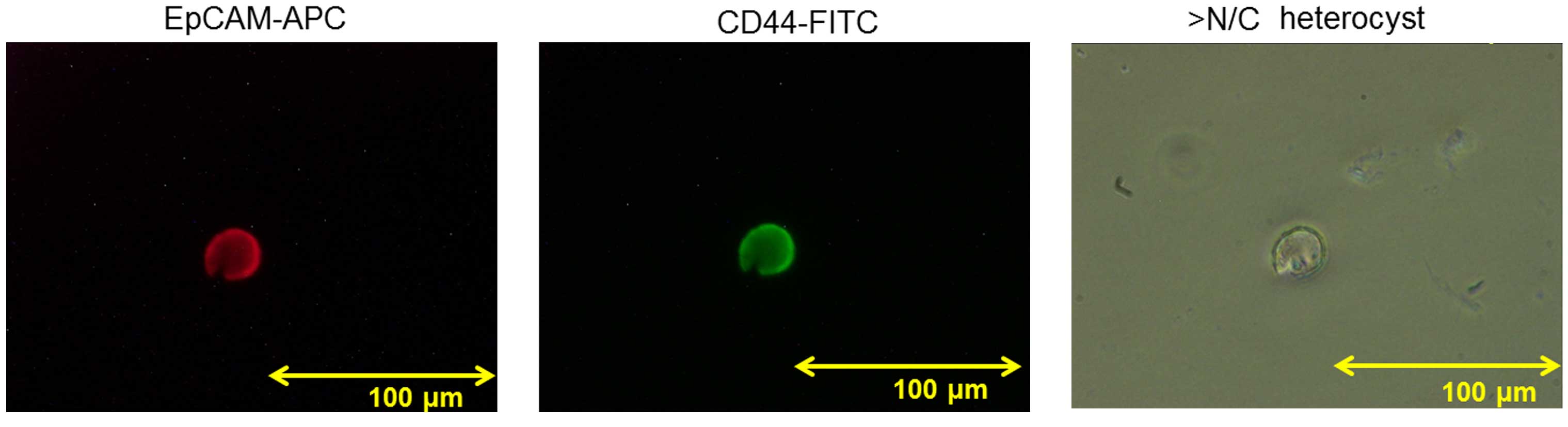
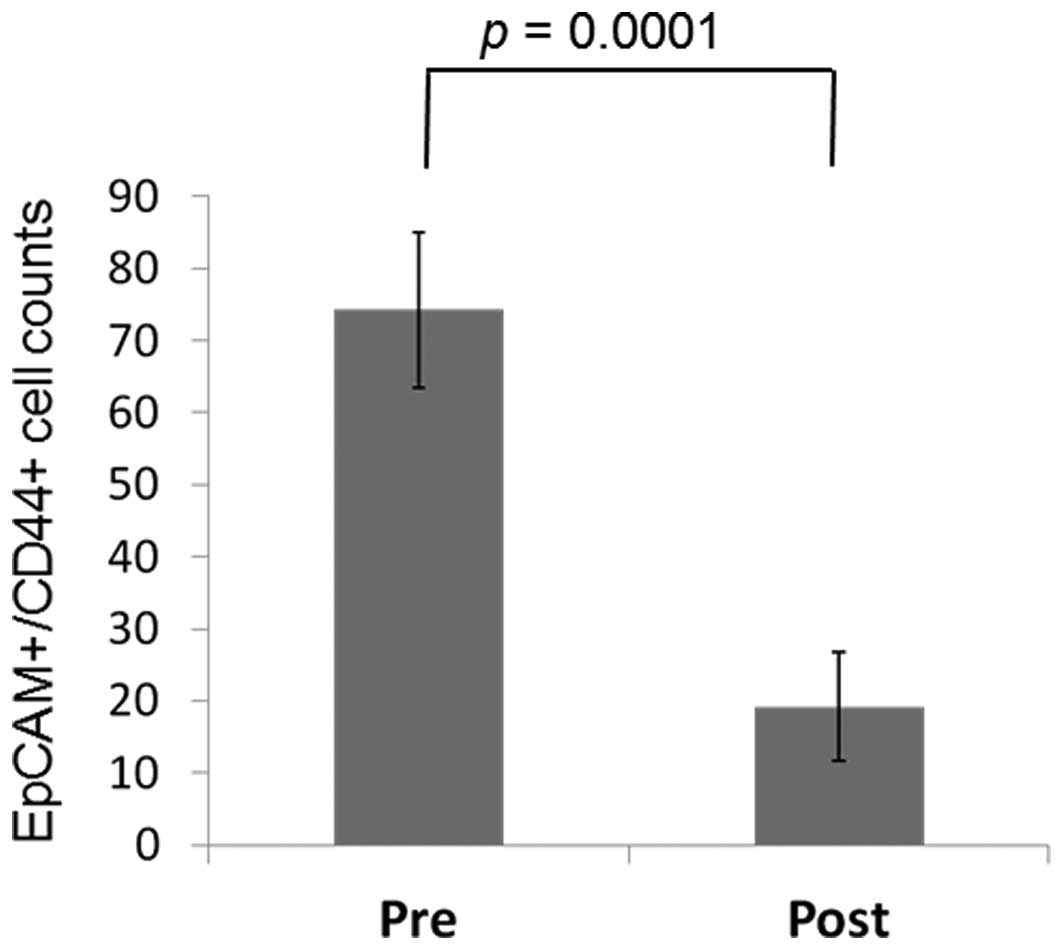
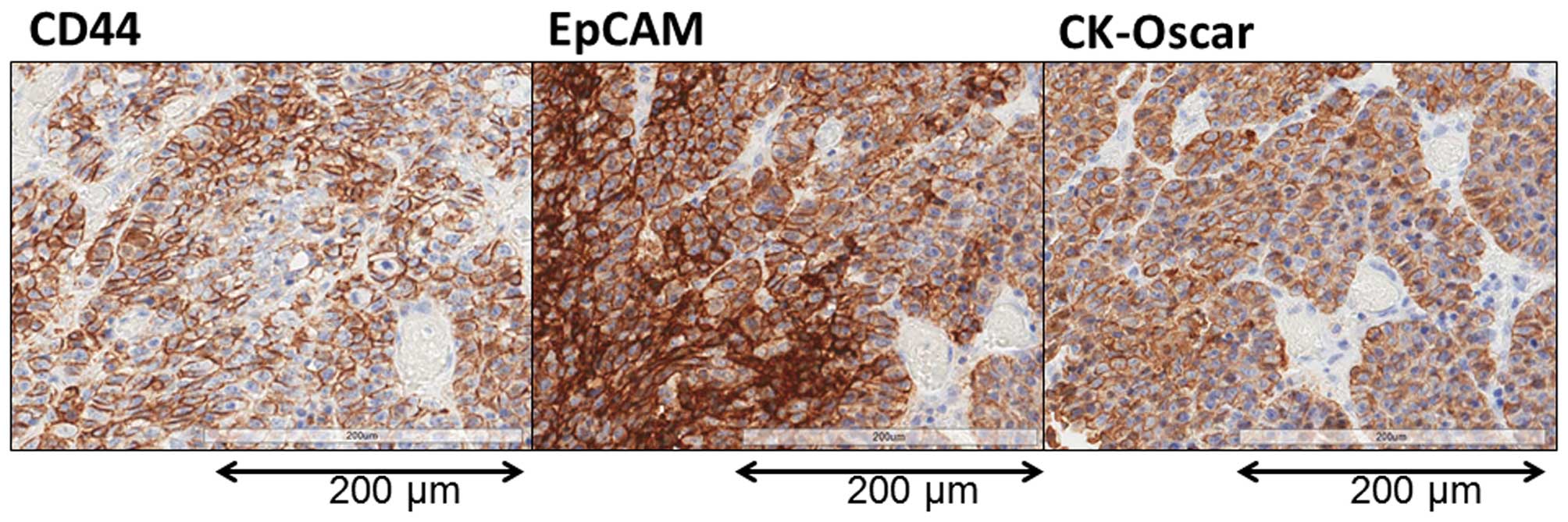
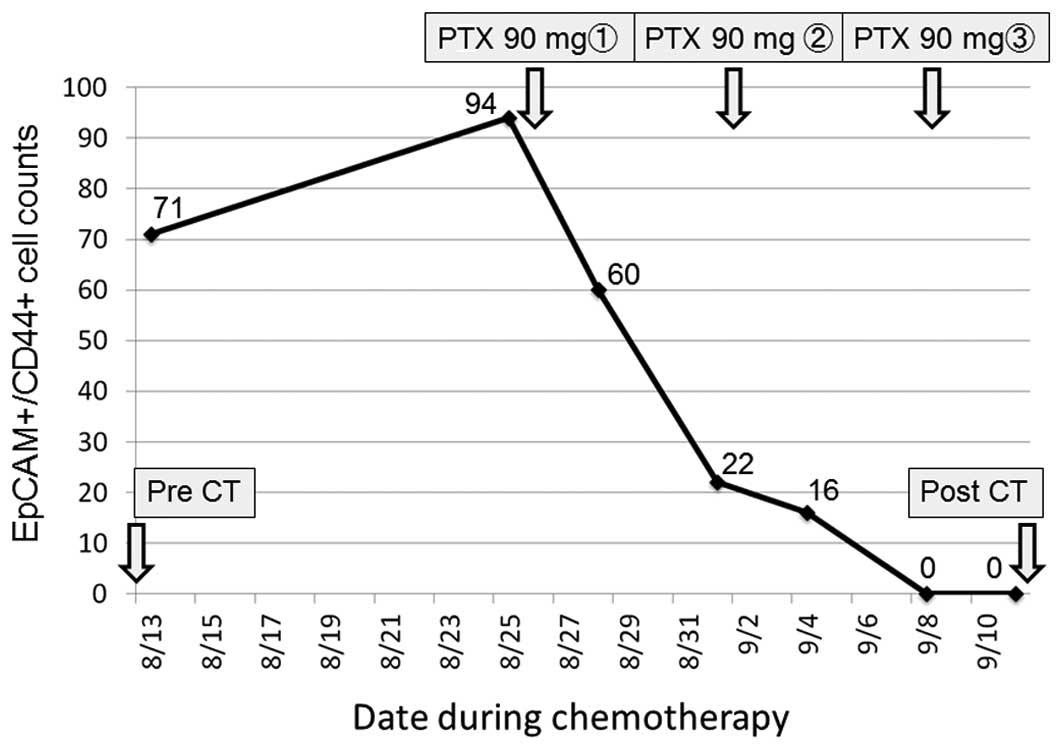
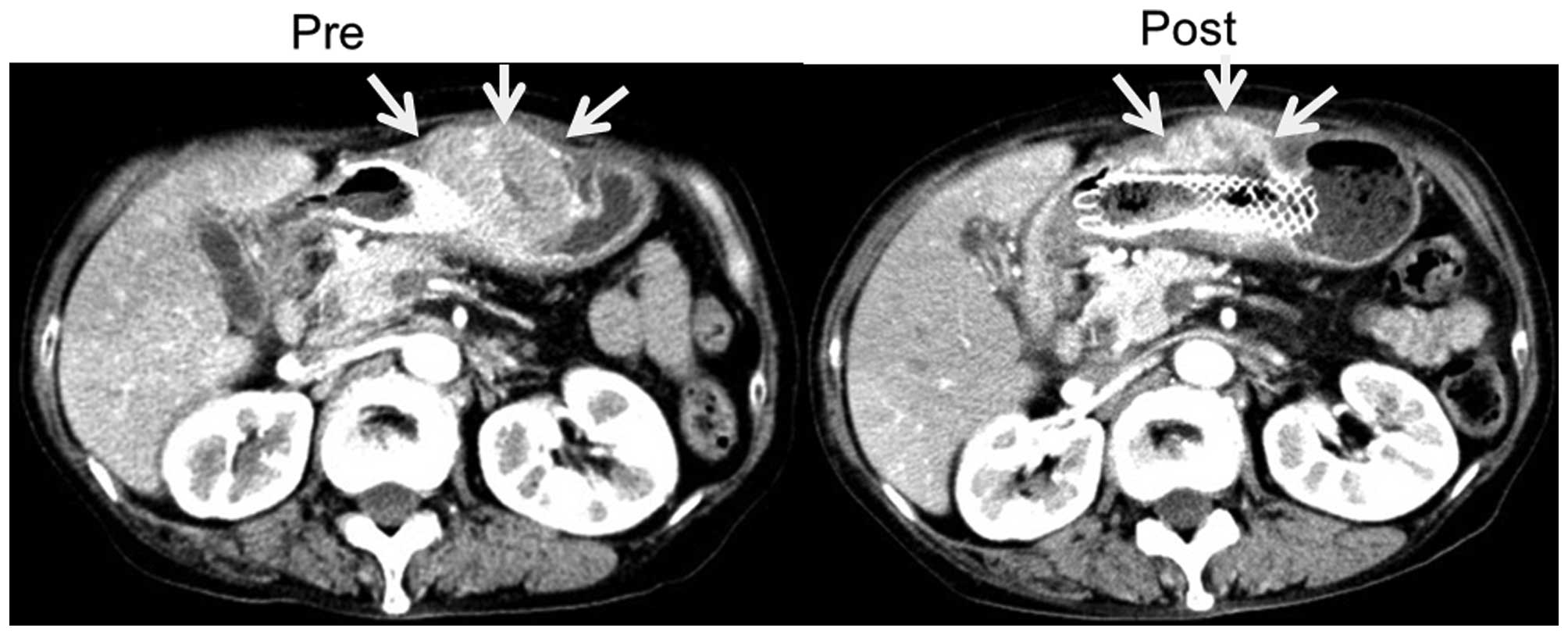
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008:GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siewert JR, Böttcher K, Roder JD, Busch R,
Hermanek P and Meyer HJ: Prognostic relevance of systemic lymph
node dissection in gastric carcinoma. German gastric carcinoma
study group. Br J Surg. 80:1015–1018. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ikeda Y, Mori M, Adachi Y, Matsushima T,
Sugimachi K and Saku M: Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) in stage IV
gastric cancer as a risk factor for liver metastasis: A univariate
and multivariate analysis. J Surg Oncol. 53:235–238. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Furukawa H, Hiratsuka M, Iwanaga T, Imaoka
S, Ishikawa O, Kabuto T, Sasaki Y, Kameyama M, Ohigashi H, Nakamori
S, et al: Adjuvant chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer. Nippon
Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 97:312–316. 1996.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Palli D: Epidermiology of gastric cancer:
An evaluation of available evidence. J Gastroenterol. 35:(Suppl
12). S84–S89. 2000.
|
|
6
|
Hughes AD and King MR: Manobiotechnology
for the capture and manipulation of circulating tumor cells. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 4:291–309. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ross AH, Herlyn D, Iliopoulos D and
Koprowski H: Isolation and characterization of a
carcinoma-associated antigen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
135:297–303. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mostert B, Sleijfer S, Forkens JA and
Gratama JW: Circulating tumor cells (CTCs): Detection methods and
their clinical relevance in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev.
35:463–474. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL, Geiger B
and Krepler R: The catalog of human cytokeratins: Patterns of
expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell.
31:11–24. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Osborn M, van Lessen G, Weber K, Klöppel G
and Altmannsberger M: Differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal
carcinomas by using monoclonal antibodies specific for individual
keratin polypeptides. Lab Invest. 55:497–504. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cohen SJ, Punt CJ, Iannotti N, Saidman BH,
Sabbath KD, Gabrail NY, Picus J, Morse M, Mitchell E, Miller MC, et
al: Relationship of circulating tumor cells to tumor response,
progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:3213–3221. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ,
Stopeck A, Matera J, Miller MC, Reuben JM, Doyle GV, Allard WJ,
Terstappen LW and Hayes DF: Circulating tumor cells, disease
progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J
Med. 351:781–791. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
de Bono JS, Scher HI, Montgomery RB,
Parker C, Miller MC, Tissing H, Doyle GV, Terstappen LW, Pienta KJ
and Raghavan D: Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit
from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:6302–6309. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grover PK, Cummins AG, Price TJ,
Roberts-Thomson IC and Hardingham JE: Circulating tumor cells: The
evolving concept and the inadequacy of their enrichment by
EpCAM-based methodology for basic and clinical cancer research. Ann
Oncol. 25:1506–1516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wicha MS and Hayes DF: Circulating tumor
cells: Not all detected cells are bad and not all bad cells are
detected. J Clin Oncol. 29:1508–1511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, Wang SS,
Shibata W, Vigneshwaran R, Gordon SA, Shimada Y and Wang TC:
Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface
marker CD44. Stem Cells. 27:1006–1020. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang W, Dong LP, Zhang N and Zhao CH: Role
of cancer stem cell marker CD44 in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis.
Int J Exp Med. 7:5059–5066. 2014.
|
|
19
|
Yamaguchi A, Goi T, Yu J, Hirono Y, Ishida
M, Iida A, Kimura T, Takeuchi K, Katayama K and Hirose K:
Expression of CD44v6 in advanced gastric cancer and its
relationship to hematogenous metastasis and long-term prognosis. J
Surg Oncol. 79:230–235. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamaguchi A, Saito M, Goi T, Iida A,
Takeuchi K, Hirose K, Nakagawara G, Urano T, Furukawa K and Shiku
H: Exrpession of CD44 variant exons 8–10 in gastric cancer. Jpn J
Cancer Res. 86:1166–1171. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 7th. Wiley-Blackwell;
2009
|
|
22
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–47.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Battifora H: Clinical applications of the
immunohistochemistry of filamentous proteins. Am J Surg Pathol 12
Suppl. 1:24–42. 1988.
|
|
24
|
Gown AM and Vogel AM: Monoclonal
antibodies to human intermediate filament proteins. III. Analysis
of tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 84:413–424. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Knapp AC and Franke WW: Spontaneous losses
of control of cytokeratin gene expression in transformed,
non-epithelial human cells occurring at different levels of
regulation. Cell. 59:67–79. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lewis JE, Olsen KD and Sebo TJ: Spindle
cell carcinoma of the larynx: review of 26 cases including DNA
content and immunohistochemistry. Hum Pathol. 28:664–673. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mueller JD, Stein HJ, Oyang T, Natsugoe S,
Feith M, Werner M and Rüdiger Siewert J: Frequency and clinical
impact of lymph node micrometastasis and tumor cell
microinvolvement in patients with adenocarcinoma of the
esophagogastric junction. Cancer. 89:1874–1882. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sato F, Shimada Y, Li Z, Watanabe G, Maeda
M and Imamura M: Lymph node micrometastasis and prognosis in
patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Surg.
88:426–432. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miller JM, Astles R, Baszler T, Chapin K,
Carey R, Garcia L, Gray L, Larone D, Pentella M, Pollock A, et al:
Guidelines for safe work practices in human and animal medical
diagnostic laboratories. Recommendations of a CDC-convened,
Biosafety Blue Ribbon Panel. MMWR Suppl. 61:1–102. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Paterlini-Brechot P and Benali NL:
Circulating tumor cells (CTC) detection: Clinical impact and future
directions. Cancer Lett. 253:180–204. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Okumura T, Wang SSW, Takashi S, Tu SP, Ng
V, Ericksen RE, Rustgi AK and Wang TC: Identification of a bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cell subset that can
contribute to the gastric epithelium. Lab Invest. 89:1410–1422.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matsusaka S, Suenaga M, Mishima Y,
Kuniyoshi R, Takagi K, Terui Y, Mizunuma N and Hatake K:
Circulating tumor cell as a surrogate marker for determining
response to chemotherapy in Japanese patients with metastatic
colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 102:1188–1192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moreno JG, Miller MC, Gross S, Allard WJ,
Gomella LG and Terstappen LW: Circulating tumor cells predict
survival in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Urology.
65:713–718. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hiraiwa K, Takeuchi H, Hasegawa H, Saikawa
Y, Suda K, Ando T, Kumagai K, Irino T, Yoshikawa T, Matsuda S, et
al: Clinical significance of circulating tumor cells in blood from
patients with gastrointestinal cancers. Ann Surg Oncol.
15:3092–3100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lianidou ES and Markou A: Circulating
tumor cells in breast cancer: Detection system, molecular
characterization, and future challenges. Clin Chem. 57:1242–1255.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakamura S, Yagata H, Ohno S, Yamaguchi H,
Iwata H, Tsunoda N, Ito Y, Tokudome N, Toi M, Kuroi K and Suzuki E:
Multi-center study evaluating circutating tumor cells as a
surrogate for response to treatment and overall survival in
metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 17:199–204. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Diehn M, Cho RW and Clarke MF: Therapeutic
implications of the cancer stem cell hypothesis. Semin Radiat
Oncol. 19:78–86. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Meng S, Tripathy D, Frenkel EP, Shete S,
Naftalis EZ, Huth JF, Beitsch PD, Leitch M, Hoover S, Euhus D, et
al: Circulating tumor cells in patients with breast cancer
dormancy. Clin Cancer Res. 10:8152–8162. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hayes DF and Smerage J: Is there a role
for circulating tumor cells in the management of breast cancer?
Clin Cancer Res. 14:3646–3650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sergeant G, van Eijsden R, Roskams T, Van
Duppen V and Topal B: Pancreatic cancer circulating tumor cells
express a cell motility gene signature that predicts survival after
surgery. BMC Cancer. 12:5272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Swennenhuis JF, Reumers J, Thys K,
Aerssens J and Terstappen LW: Efficiency of whole genome
amplification of single circulating tumor cells enriched by
CellSearch and sorted by FACS. Genome Med. 5:1062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Iinuma H, Watanabe T, Mimori K, Adachi M,
Hayashi N, Tamura J, Matsuda K, Fukushima R, Okinaga K, Sasako M
and Mori M: Clinical significance of circulating tumor cells,
including cancer stem-like cells, in peripheral blood for
recurrence and prognosis in patients with Dukes' stage B and C
colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:1547–1555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang NF, Shi L, Li H, Hu Y, Du W, Liu W,
Zheng J, Huang S and Qu X: Detection of circulating tumor cells and
tumor stem cells in patients with breast cancer by flow cytometry:
A valuable tool for diagnosis and prognosis evaluation. Tumor Biol.
33:561–569. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Theodoropoulos PA, Polioudaki H, Agelaki
S, Kallergi G, Saridaki Z, Mavroudis D and Georgoulias V:
Circulating tumor cells with a putative stem cell phenotype in
peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer. Cancer Lett.
288:99–106. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li M, Zhang B, Zhang Z, Liu X, Qi X, Zhao
J, Jiang Y, Zhai H, Ji Y and Luo D: Stem cell-like circulating
tumor cells indicate poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Biomed Res
Int. 2014:9812612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lu J, Huang CM, Zheng CH, Li P, Xie JW,
Wang JB and Lin JX: Consideration of tumor size improves the
accuracy of TNM predictions in patients with gastric cancer after
curative gastrectomy. Surg Oncol. 22:167–171. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|