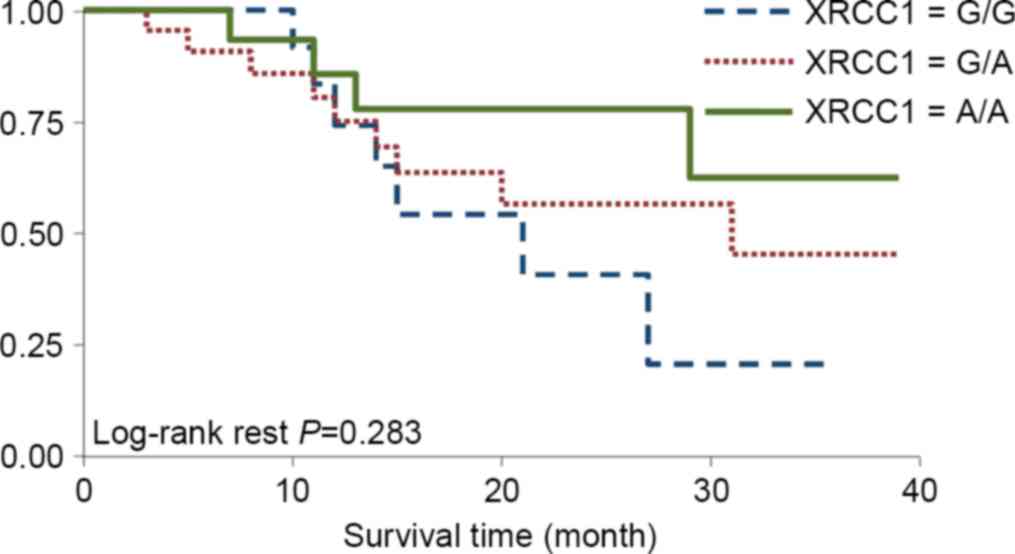
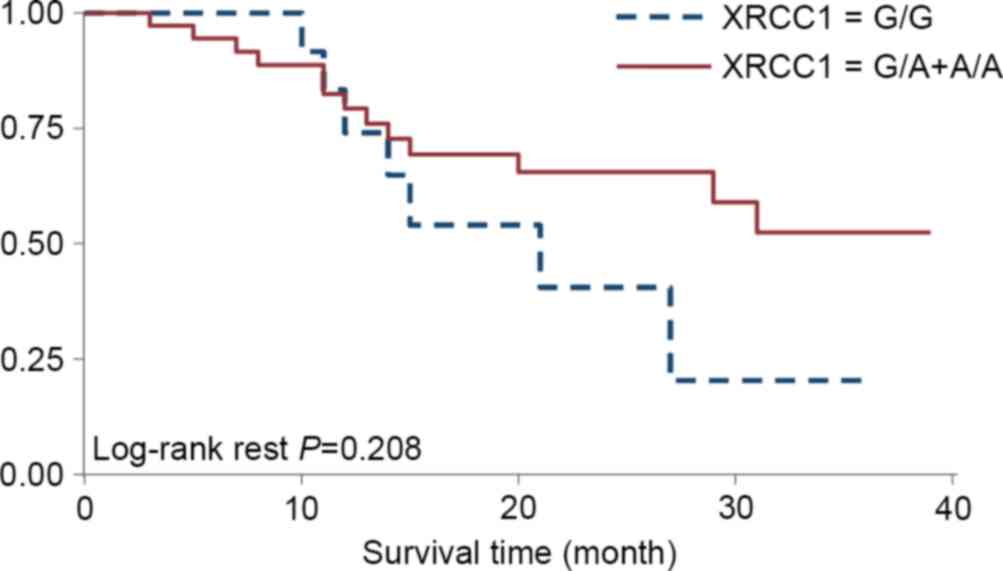
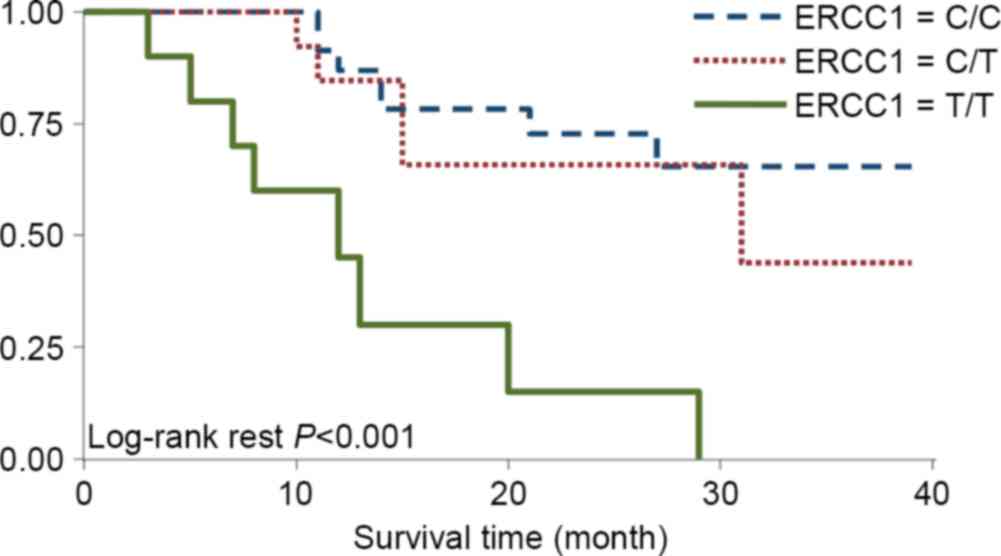
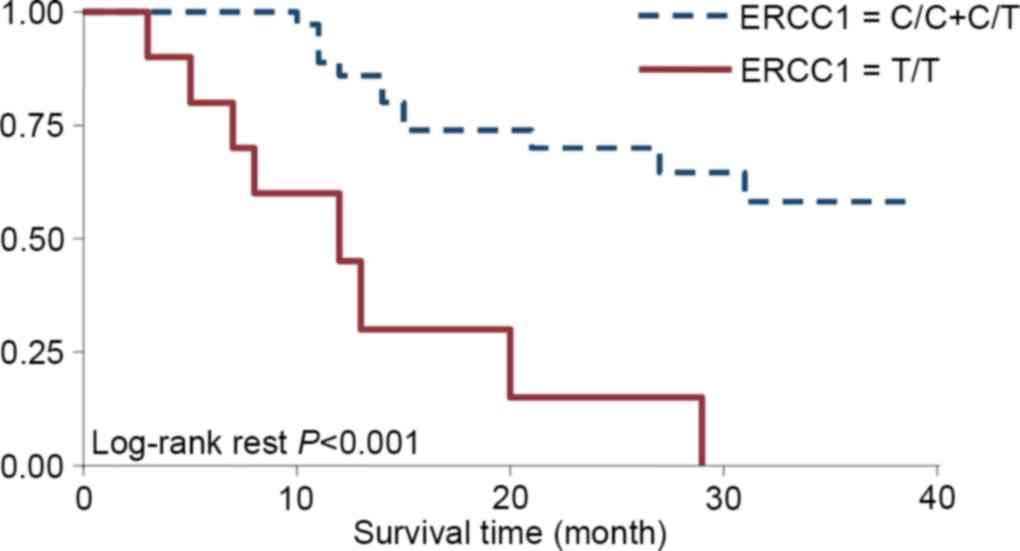
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
LortetTieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hongo M, Nagasaki Y and Shoji T:
Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Orient to Occident. Effects of
chronology, geography and ethnicity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:729–735. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kanai M, Matsumoto S, Nishimura T, Shimada
Y, Watanabe G, Kitano T, Misawa A, Ishiguro H, Yoshikawa K,
Yanagihara K, et al: Retrospective analysis of 27 consecutive
patients treated with docetaxel/nedaplatin combination therapy as a
second-line regimen for advanced esophageal cancer. Int J Clin
Oncol. 12:224–227. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A, Macdonald
JS, Martenson JA Jr, Al-Sarraf M, Byhardt R, Russell AH, Beitler
JJ, Spencer S, et al: Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced
escophageal cancer: Long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized
trial (RTOG85-01). Radiation therapy oncology group. JAMA.
281:1623–1627. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ,
Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, Richel DJ,
Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Hospers GA, Bonenkamp JJ, et al: Preoperative
chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J
Med. 366:2074–2084. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee MS, Mamon HJ, Hong TS, Choi NC, Fidias
PM, Kwak EL, Meyerhardt JA, Ryan DP, Bueno R, Donahue DM, et al:
Preoperative cetuximab, irinotecan, cisplatin, and radiation
therapy for patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer.
Oncologist. 18:281–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nutting CM, Bedford JL, Cosgrove VP, Tait
DM, Dearnaley DP and Webb S: A comparison of conformal and
intensity-modulated techniques for oesophageal radiotherapy.
Radiother Oncol. 61:157–163. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin SH, Wang L, Myles B, Thall PF,
Hofstetter WL, Swisher SG, Ajani JA, Cox JD, Komaki R and Liao Z:
Propensity score-based comparison of long-term outcomes with
3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy vs intensity-modulated
radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
84:1078–1085. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu CX and Tang G: Intensity-modulated arc
therapy: Principles, technologies and clinical implementation. Phys
Med Biol. 56:R31–R54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hayashi K, Ando N, Watanabe H, Ide H,
Nagai K, Aoyama N, Takiyama W, Ishida K, Isono K, Makuuchi H, et
al: Phase II evaluation of protracted infusion of cisplatin and
5-fluorouracil in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the
esophagus: A Japan esophageal oncology group (JEOG) Trial
(JCOG9407). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 31:419–423. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bleiberg H, Conroy T, Paillot B, Lacave
AJ, Blijham G, Jacob JH, Bedenne L, Namer M, De Besi P, Gay F, et
al: Randomised phase II study of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil
(5-FU) versus cisplatin alone in advanced squamous cell oesophageal
cancer. Eur J Cancer. 33:1216–1220. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang J, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Qu T, Mao Y, Zhu
H, Quan L, Xing P, Wang J, He J, et al: A phase II study of
biweekly paclitaxel and cisplatin chemotherapy for recurrent or
metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: ERCC1 expression
predicts response to chemotherapy. Med Oncol. 30:3432013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rosell R, Lord RV, Taron M and Reguart N:
DNA repair and cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Lung Cancer. 38:217–227. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Powell S and McMillan TJ: DNA damage and
repair following treatment with ionizing radiation. Radiother
Oncol. 19:95–108. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Malyapa RS, Bi C, Ahem EW and Roti JL
Roti: Detection of DNA damage by the alkaline comet assay after
exposure to low-dose gamma radiation. Radiat Res. 149:396–400.
1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim MK, Cho KJ, Kwon GY, Park SI, Kim YH,
Kim JH, Song HY, Shin JH, Jung HY, Lee GH, et al: Patients with
ERCC1-negative locally advanced esophageal cancers may benefit from
preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 14:4225–4231.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lindahl T and Wood RD: Quality control by
DNA repair. Science. 286:1897–1905. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wood RD, Mitchell M, Sgouros J and Lindahl
T: Human DNA repair genes. Science. 291:1284–1289. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thompson LH, Brookman KW, Jones NJ, Allen
SA and Carrano AV: Molecular cloning of the human XRCC1 gene, which
contacts defective DNA strand-break repair and sister chromatid
exchange. Mol Cell Biul. 10:6160–6171. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Thompson LH and West MG: XRCC1 keeps DNA
from getting stranded. Mutat Res. 459:1–18. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van Duin M, de Wit J, Odijk H, Westerveld
A, Yasui A, Koken MH, Hoeijmakers JH and Bootsma D: Molecular
characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA
cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene
RADIO. Cell. 44:913–923. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Su Y, Orelli B, Madireddy A, Niedernhofer
LJ and Schärer OD: Multiple DNA binding domains mediate the
function of the ERCC1-XPF protein in nucleotide excision repair. J
Biol Chem. 287:21846–21855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gregg SQ, Robinson AR and Niedernhofer LJ:
Physiological consequences of defects in ERCC1-XPF DNA repair
enndonuclease. DNA Repair (Amst). 10:781–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vaezi A, Feldman CH and Niedernhofer LJ:
ERCC1 and XRCC1 as biomarkers for lung and head and neck cancer.
Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 4:47–63. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Przybylowska-Sygut K, Stanczyk M, Kusinska
R, Kordek R and Majsterek I: Association of the Arg194Trp and the
Arg399Gln polymorphisms of the XRCC1 gene with risk occurrence and
the response to adjuvant therapy among Polish women with breast
cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 13:61–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu W, Wang S, Chen Q, Zhang Y, Ni P, Wu X,
Zhang J, Qiang F, Li A, Røe OD, et al: TXNL1-XRCC1 pathway
regulates cisplatin-induced cell death and contributes to
resistance in human gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10552014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen J, Zhao QW, Shi GM and Wang LR: XRCC1
Arg399Gln and clinical outcome of platinum-based treatment for
advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis in 17 studies.
J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 13:875–883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang Y and Xian L: The association between
the ERCC1/2 polymorphisms and the clinical outcomes of the
platinum-based chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 35:2905–2921.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zaanan A, Dalban C, Emile JF, Blons H,
Fléjou JF, Goumard C, Istanbullu M, Calmel C, Alhazmi K, Validire
P, et al: ERCC1, XRCC1 and GSTP1 single nucleotide polymorphisms
and survival of patients with colon cancer receiving
Oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. J Cancer. 5:425–432. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rice TW, Blackstone EH and Rusch VW: 7th
edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Esophagus and
esophagogastric Junction. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1721–1724. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Berger AC, Farma J, Scott WJ, Freedman G,
Weiner L, Cheng JD, Wang H and Goldberg M: Complete response to
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal carcinoma is associated
with significantly improved survival. J Clin Oncol. 23:4330–4337.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Urba SG, Orringer MB, Turrisi A,
Iannettoni M, Forastiere A and Strawderman M: Randomized trial of
preoperative chemoradiation versus surgery alone in patients with
locoregional esophageal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 19:305–313.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumors:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu X, Xiao H, Zhao B, Zhang X and Wang G:
DNA repair gene ERCC1 C118T polymorphism predicts sensitivity of
recurrent esophageal cancer to radiochemotherapy in a Chinese
population. Thorac Cancer. 6:741–748. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yoon HH and Forastiere AA: Locally
advanced esophageal adenocarcinoma: Current standards and molecular
predictors of outcome. Future Oncol. 4:413–425. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cornetta T, Festa F, Testa A and Cozzi R:
DNA damage repair and genetic polymorphisms: Assessment of
individual sensitivity and repair capacity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 66:537–545. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu X, Gu J, Wu TT, Swisher SG, Liao Z,
Correa AM, Liu J, Etzel CJ, Amos CI, Huang M, et al: Genetic
variatitions in radiation and chemotherapy drug action pathways
predict clinical outcomes in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
24:3789–3798. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoon HH, Catalano PJ, Murphy KM, Skaar TC,
Philips S, Powell M, Montgomery EA, Hafez MJ, Offer SM, Liu G, et
al: Genetic variation in DNA-repair pathways and response to
radiochemotherapy in esophageal adenocarcinoma: A retrospective
cohort study of the eastern cooperative oncology group. BMC Cancer.
11:1762011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Croteau DL, Peng Y and Van Houten B: DNA
repair gets physica: Mapping all XPA-binding site on ERCC1. DNA
Repair (Amst). 7:819–826. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Orelli B, McClendon TB, Tsodikov OV,
Ellenberger T, Niedernhofer LJ and Schärer OD: The XPA-binding
domain of ERCC1 is required for nucleotide excision repair but not
other DNA repair pathways. J Biol Chem. 285:3705–3712. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Risom L, Møller P, Vogel U, Kristjansen PE
and Loft S: X-ray induced oxidstive stress: DNA damage and gene
expression of ERCC1 and HOGG1 in mouse lung. Free Redic Res.
37:957–966. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ryu JS, Hong YC, Han HS, Lee JE, Kim S,
Park YM, Kim YC and Hwang TS: Association between polymorphisms of
ERCC1 and XPD and survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients
treated with cisplatin combination chemotherapy. Lung Cancer.
44:311–316. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Su D, Ma S, Liu P, Jiang Z, Lv W, Zhang Y,
Deng Q, Smith S and Yu H: Genetic polymorphisms and treatment
response in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
56:281–288. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhou C, Ren S, Zhou S, Zhang L, Su C,
Zhang Z, Deng Q and Zhang J: Predictive effects of ERCCl and XRCC3
SNP on efficacy of platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced NSCLC
patients. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 40:954–960. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Warnecke-Eberz U, Vallböhmer D, Alakus H,
Kütting F, Lurje G, Bollschweiler E, Wienand-Dorweiler A, Drebber
U, Hölscher AH and Metzger R: ERCC1 and XRCC1 gene polymorphisms
predict response to neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy in esophageal
cancer. J Gastrointest Surg. 13:1411–1421. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Almhanna K, Bentrem
DJ, Besh S, Chao J, Das P, Denlinger C, Fanta P, Fuchs CS, et al:
Esophageal and esophagogastric junction cancers, version 1.2015. J
Natl Compr Canc Netw. 13:194–227. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Alexander BM, Wang XZ, Niemierko A, Weaver
DT, Mak RH, Roof KS, Fidias P, Wain J and Choi NC: DNA repair
biomarkers predict response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in
esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 83:164–171. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen PC, Chen YC, Lai LC, Tsai MH, Chen
SK, Yang PW, Lee YC, Hsiao CK, Lee JM and Chuang EY: Use of
germline polymorphisms in predicting concurrent chemoradiotherapy
response in esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
82:1996–2003. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pan JY, Ajani JA, Gu J, Gong Y, Qin A,
Hung M, Wu X and Izzo JG: Association of Aurora-A (STK15) kinase
polymorphisms with clinical outcome of esophageal cancer treated
with preoperative chemoradiation. Cancer. 118:4346–4353. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|