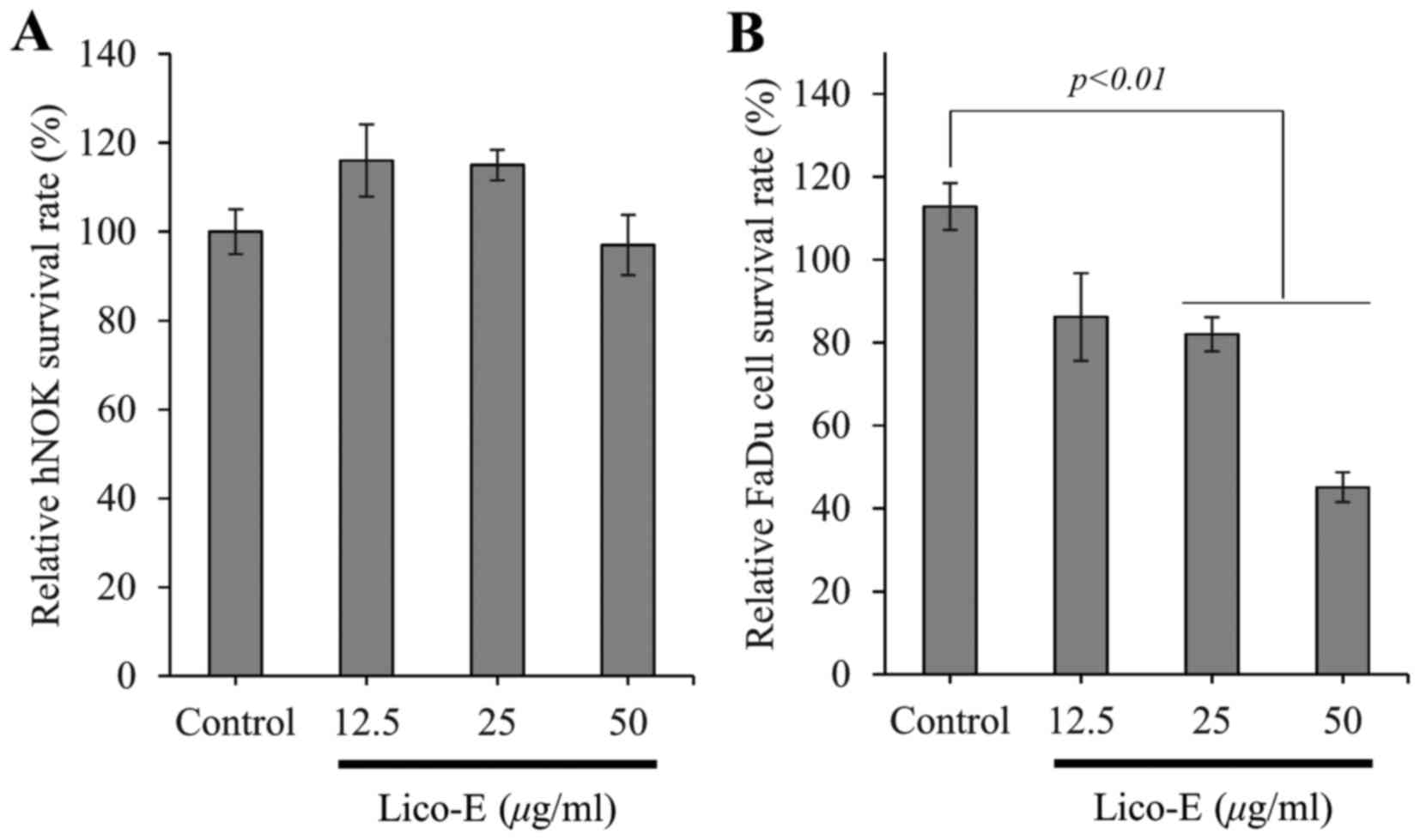
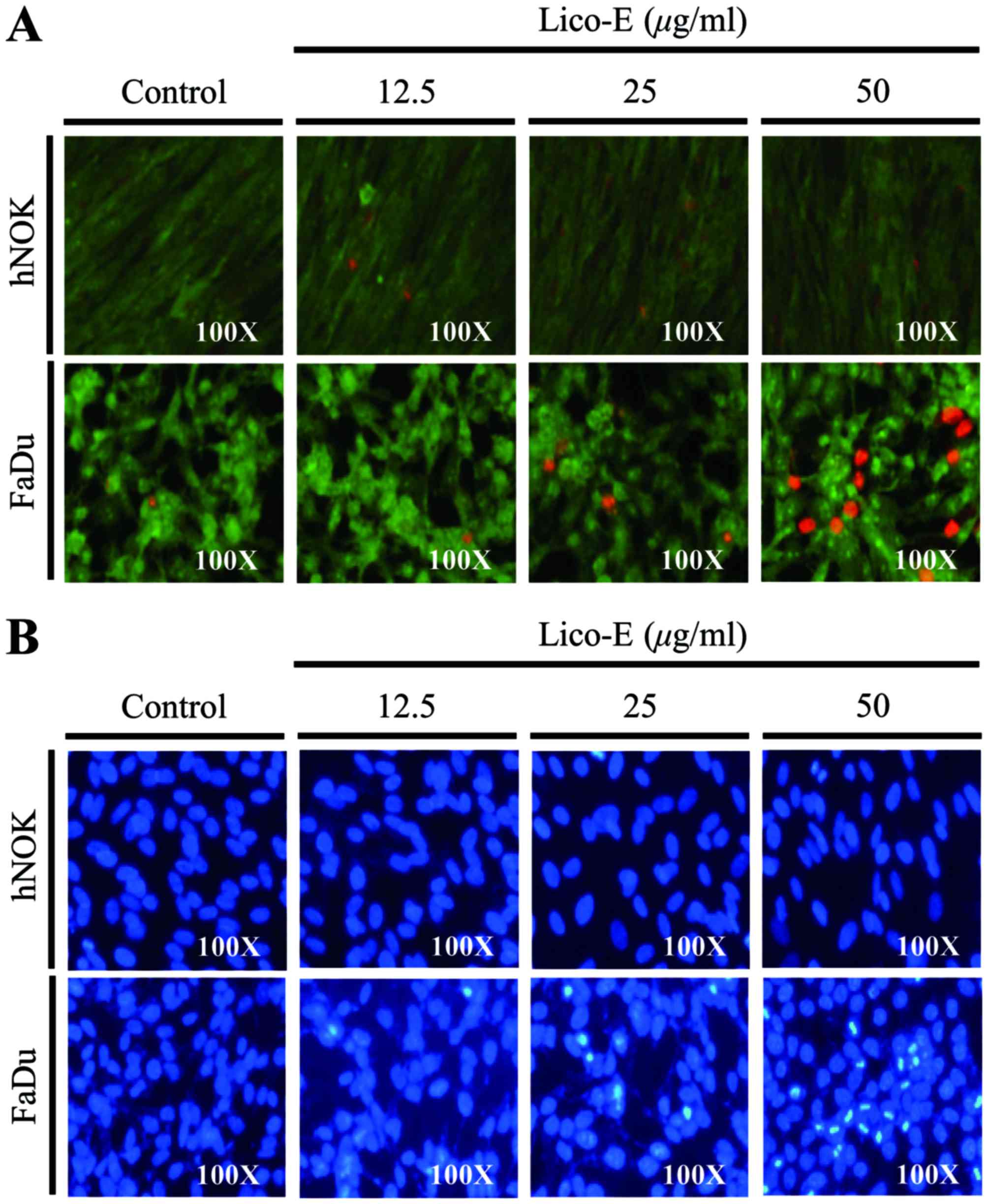
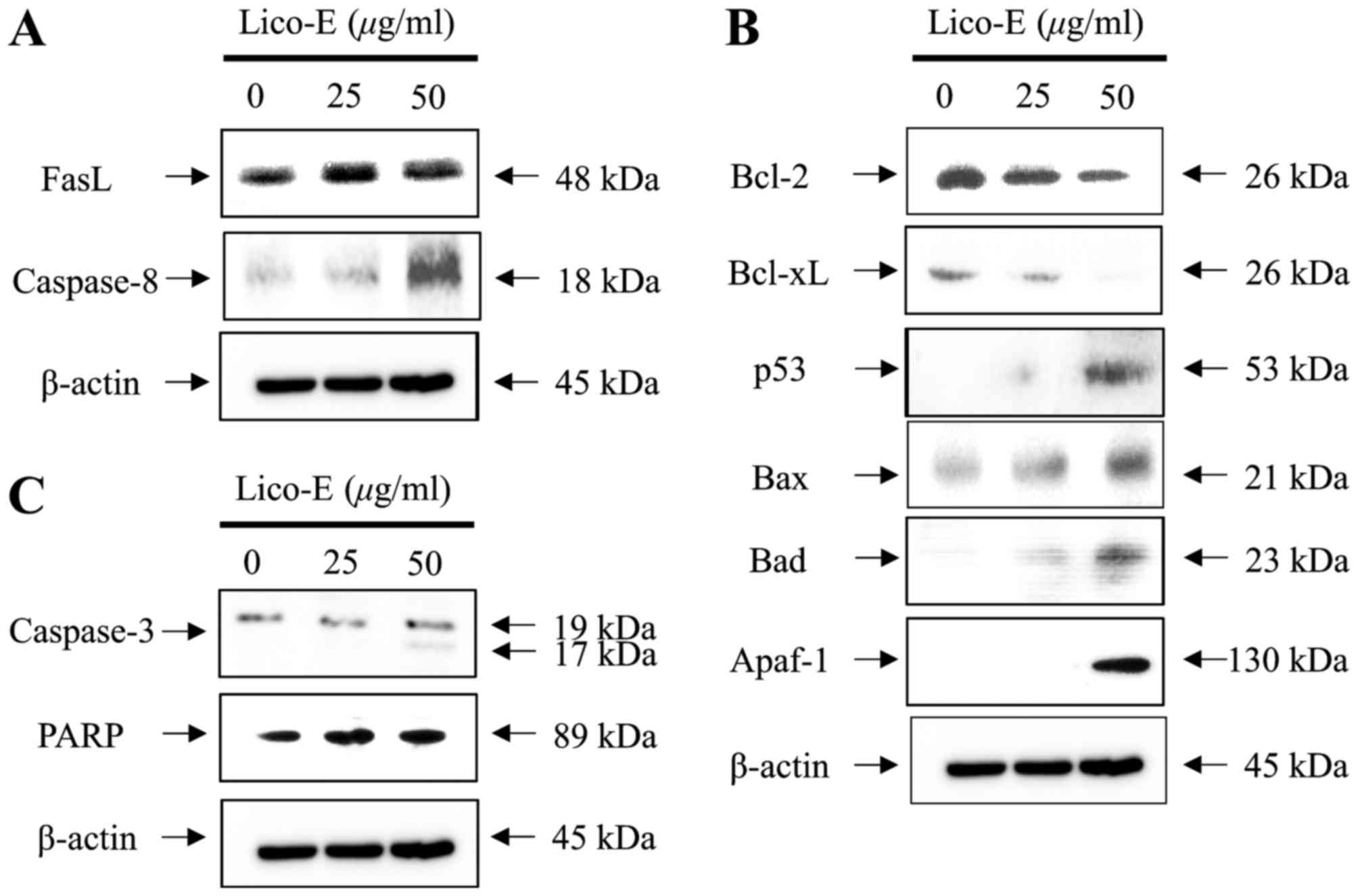
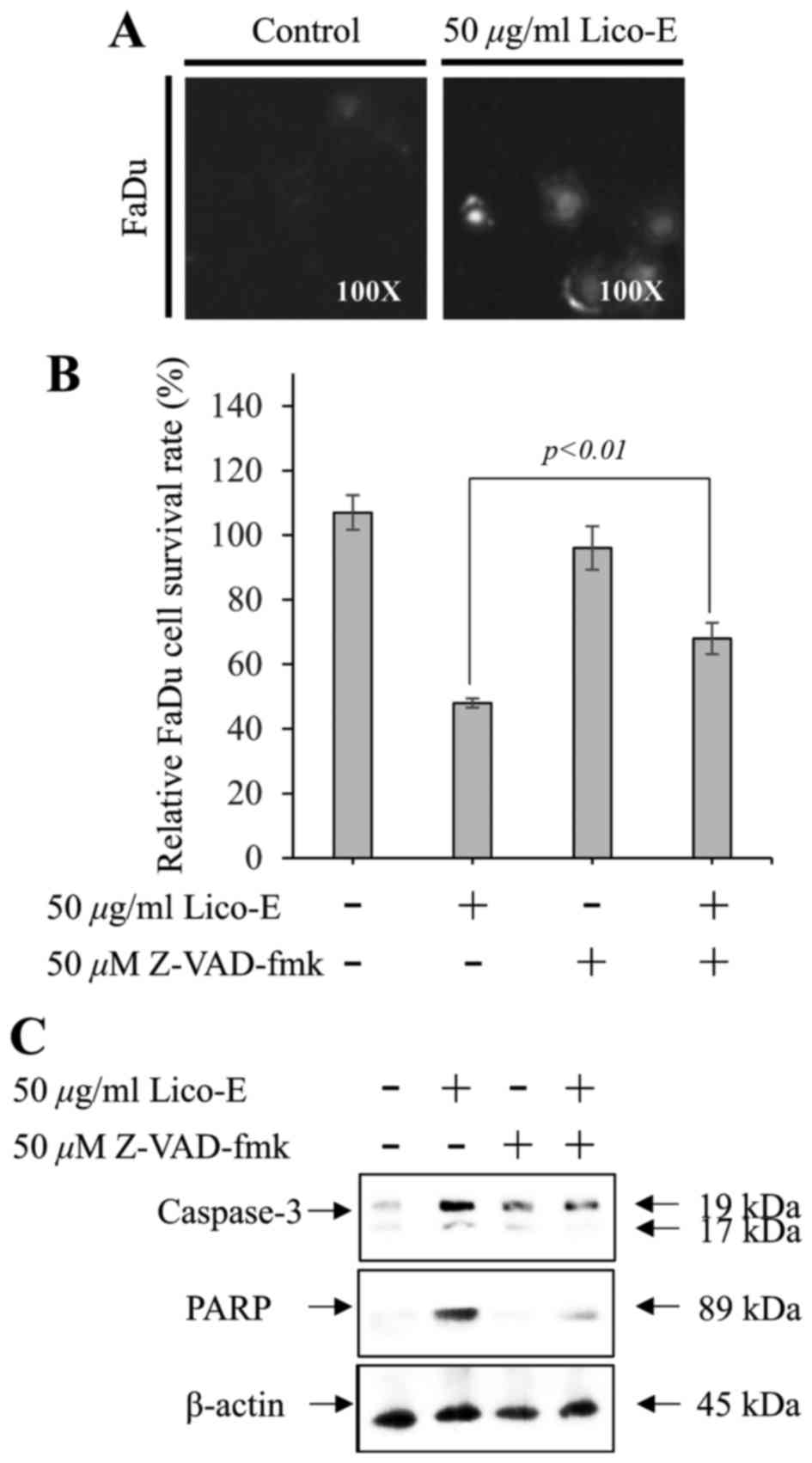
|
1
|
Sturgis EM and Miller RH: Second primary
malignancies in the head and neck cancer patient. Ann Otol Rhinol
Laryngol. 104:946–954. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rothman KJ: The effect of alcohol
consumption on risk of cancer of the head and neck. Laryngoscope.
88:(1 Pt 2 Suppl 8). S51–S55. 1978.
|
|
3
|
Marron M, Boffetta P, Zhang ZF, Zaridze D,
Wünsch-Filho V, Winn DM, Wei Q, Talamini R, Szeszenia-Dabrowska N,
Sturgis EM, et al: Cessation of alcohol drinking, tobacco smoking
and the reversal of head and neck cancer risk. Int J Epidemiol.
39:182–196. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hashibe M, Hunt J, Wei M, Buys S, Gren L
and Lee YC: Tobacco, alcohol, body mass index, physical activity,
and the risk of head and neck cancer in the prostate, lung,
colorectal, and ovarian (PLCO) cohort. Head Neck. 35:914–922. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin YS, Jen YM, Wang BB, Lee JC and Kang
BH: Epidemiology of oral cavity cancer in taiwan with emphasis on
the role of betel nut chewing. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec.
67:230–236. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Smith EM, Rubenstein LM, Haugen TH,
Pawlita M and Turek LP: Complex etiology underlies risk and
survival in head and neck cancer human papillomavirus, tobacco, and
alcohol: A case for multifactor disease. J Oncol. 2012:5718622012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park MR, Kim SG, Cho IA, Oh D, Kang KR,
Lee SY, Moon SM, Cho SS, Yoon G, Kim CS, et al: Licochalcone-A
induces intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis via ERK1/2 and p38
phosphorylation-mediated TRAIL expression in head and neck squamous
carcinoma FaDu cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 77:34–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chi AC, Day TA and Neville BW: Oral cavity
and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma-an update. CA Cancer J
Clin. 65:401–421. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Epstein JB, Thariat J, Bensadoun RJ,
Barasch A, Murphy BA, Kolnick L, Popplewell L and Maghami E: Oral
complications of cancer and cancer therapy: From cancer treatment
to survivorship. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:400–422. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fesik SW: Promoting apoptosis as a
strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:876–885.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen H, Zeng G, Sun B, Cai X, Bi L, Tang G
and Yang Y: A polysaccharide from Glycyrrhiza inflata
Licorice inhibits proliferation of human oral cancer cells by
inducing apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway. Tumour Biol.
36:4825–4831. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee CK, Park KK, Lim SS, Park JH and Chung
WY: Effects of the licorice extract against tumor growth and
cisplatin-induced toxicity in a mouse xenograft model of colon
cancer. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:2191–2195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fu Y, Hsieh TC, Guo J, Kunicki J, Lee MY,
Darzynkiewicz Z and Wu JM: Licochalcone-A, a novel flavonoid
isolated from licorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra), causes G2
and late-G1 arrests in androgen-independent PC-3 prostate cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 322:263–270. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jo EH, Kim SH, Ra JC, Kim SR, Cho SD, Jung
JW, Yang SR, Park JS, Hwang JW, Aruoma OI, et al: Chemopreventive
properties of the ethanol extract of Chinese licorice
(Glycyrrhiza uralensis) root: Induction of apoptosis and G1
cell cycle arrest in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
230:239–247. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cho JJ, Chae JI, Yoon G, Kim KH, Cho JH,
Cho SS, Cho YS and Shim JH: Licochalcone A, a natural chalconoid
isolated from Glycyrrhiza inflata root, induces apoptosis
via Sp1 and Sp1 regulatory proteins in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 45:667–674. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kinghorn AD, Pan L, Fletcher JN and Chai
H: The relevance of higher plants in lead compound discovery
programs. J Nat Prod. 74:1539–1555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wittschier N, Faller G and Hensel A:
Aqueous extracts and polysaccharides from liquorice roots
(Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) inhibit adhesion of Helicobacter
pylori to human gastric mucosa. J Ethnopharmacol. 125:218–223.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee SK, Park KK, Park JH, Lim SS and Chung
WY: The inhibitory effect of roasted licorice extract on human
metastatic breast cancer cell-induced bone destruction. Phytother
Res. 27:1776–1783. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tamir S, Eizenberg M, Somjen D, Stern N,
Shelach R, Kaye A and Vaya J: Estrogenic and antiproliferative
properties of glabridin from licorice in human breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 60:5704–5709. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoon G, Jung YD and Cheon SH: Cytotoxic
allyl retrochalcone from the roots of Glycyrrhiza inflata.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 53:694–695. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee HN, Cho HJ, Lim DY, Kang YH, Lee KW
and Park JH: Mechanisms by which licochalcone e exhibits potent
anti-inflammatory properties: Studies with phorbol ester-treated
mouse skin and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophages.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:10926–10943. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou T, Deng X and Qiu J: Antimicrobial
activity of licochalcone E against Staphylococcus aureus and its
impact on the production of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 22:800–805. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim SS, Lim J, Bang Y, Gal J, Lee SU, Cho
YC, Yoon G, Kang BY, Cheon SH and Choi HJ: Licochalcone E activates
Nrf2/antioxidant response element signaling pathway in both
neuronal and microglial cells: Therapeutic relevance to
neurodegenerative disease. J Nutr Biochem. 23:1314–1323. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park HG, Bak EJ, Woo GH, Kim JM, Quan Z,
Kim JM, Yoon HK, Cheon SH, Yoon G, Yoo YJ, et al: Licochalcone E
has an antidiabetic effect. J Nutr Biochem. 23:759–767. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kwon SJ, Park SY, Kwon GT, Lee KW, Kang
YH, Choi MS, Yun JW, Jeon JH, Jun JG and Park JH: Licochalcone E
present in licorice suppresses lung metastasis in the 4T1 mammary
orthotopic cancer model. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 6:603–613. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
International head and neck cancer
epidemiology consortium: Update no. 19. Head Neck. 37:1401–1402.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Howren MB, Christensen AJ, Karnell LH and
Funk GF: Psychological factors associated with head and neck cancer
treatment and survivorship: Evidence and opportunities for
behavioral medicine. J Consult Clin Psychol. 81:299–317. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ohnishi S and Takeda H: Herbal medicines
for the treatment of cancer chemotherapy-induced side effects.
Front Pharmacol. 6:142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee KH: Research and future trends in the
pharmaceutical development of medicinal herbs from Chinese
medicine. Public Health Nutr. 3:515–522. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng F, Du Q, Peng C, Wang N, Tang H, Xie
X, Shen J and Chen J: A review: The pharmacology of
isoliquiritigenin. Phytother Res. 29:969–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Song NR, Kim JE, Park JS, Kim JR, Kang H,
Lee E, Kang YG, Son JE, Seo SG, Heo YS and Lee KW: Licochalcone A,
a polyphenol present in licorice, suppresses UV-induced COX-2
expression by targeting PI3K, MEK1, and B-Raf. Int J Mol Sci.
16:4453–4470. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuwajima H, Taneda Y, Chen WZ, Kawanishi
T, Hori K, Taniyama T, Kobayashi M, Ren J and Kitagawa I: Variation
of chemical constituents in processed licorice roots: Quantitative
determination of saponin and flavonoid constituents in bark removed
and roasted licorice roots. Yakugaku Zasshi. 119:945–955. 1999.(In
Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stewart PM and Prescott SM: Can licorice
lick colon cancer? J Clin Invest. 119:760–763. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu C, Liu H, Du J, Mo B, Qi H, Wang X, Ye
S and Li Z: Estrogenic activities of extracts of Chinese licorice
(Glycyrrhiza uralensis) root in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 113:209–216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jo EH, Hong HD, Ahn NC, Jung JW, Yang SR,
Park JS, Kim SH, Lee YS and Kang KS: Modulations of the Bcl-2/Bax
family were involved in the chemopreventive effects of licorice
root (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch) in MCF-7 human breast
cancer cell. J Agric Food Chem. 52:1715–1719. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zeng G, Shen H, Yang Y, Cai X and Xun W:
Licochalcone A as a potent antitumor agent suppresses growth of
human oral cancer SCC-25 cells in vitro via caspase-3 dependent
pathways. Tumour Biol. 35:6549–6555. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yuan X, Li T, Xiao E, Zhao H, Li Y, Fu S,
Gan L and Wang Z, Zheng Q and Wang Z: Licochalcone B inhibits
growth of bladder cancer cells by arresting cell cycle progression
and inducing apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 65:242–251. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yuan X, Li D, Zhao H, Jiang J, Wang P, Ma
X, Sun X and Zheng Q: Licochalcone A-induced human bladder cancer
T24 cells apoptosis triggered by mitochondria dysfunction and
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biomed Res Int. 2013:4742722013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang HC, Tsai LL, Tsai JP, Hsieh SC, Yang
SF, Hsueh JT and Hsieh YH: Licochalcone A inhibits the migration
and invasion of human lung cancer cells via inactivation of the Akt
signaling pathway with downregulation of MMP-1/−3 expression.
Tumour Biol. 35:12139–12149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiao XY, Hao M, Yang XY, Ba Q, Li M, Ni
SJ, Wang LS and Du X: Licochalcone A inhibits growth of gastric
cancer cells by arresting cell cycle progression and inducing
apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 302:69–75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yo YT, Shieh GS, Hsu KF, Wu CL and Shiau
AL: Licorice and licochalcone-A induce autophagy in LNCaP prostate
cancer cells by suppression of Bcl-2 expression and the mTOR
pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 57:8266–8273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chang HJ, Yoon G, Park JS, Kim MH, Baek
MK, Kim NH, Shin BA, Ahn BW, Cheon SH and Jung YD: Induction of
apoptosis by the licochalcone E in endothelial cells via modulation
of NF-kappaB and Bcl-2 Family. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:2290–2293. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Oberhammer FA, Hochegger K, Fröschl G,
Tiefenbacher R and Pavelka M: Chromatin condensation during
apoptosis is accompanied by degradation of lamin A+B, without
enhanced activation of cdc2 kinase. J Cell Biol. 126:827–837. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weissmann C: Fas ligand and Fas: a death
factor and its receptor. Jpn J Cancer Res. 85:inside front cover.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li Y, Wang H, Wang Z, Makhija S, Buchsbaum
D, LoBuglio A, Kimberly R and Zhou T: Inducible resistance of tumor
cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
receptor 2-mediated apoptosis by generation of a blockade at the
death domain function. Cancer Res. 66:8520–8528. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ikner A and Ashkenazi A: TWEAK induces
apoptosis through a death-signaling complex comprising
receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1), Fas-associated death domain
(FADD) and caspase-8. J Biol Chem. 286:21546–21554. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J: Cleavage of
BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas
pathway of apoptosis. Cell. 94:491–501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fischer B, Coelho D, Dufour P, Bergerat
JP, Denis JM, Gueulette J and Bischoff P: Caspase 8-mediated
cleavage of the pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family member BID in
p53-dependent apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 306:516–522.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|