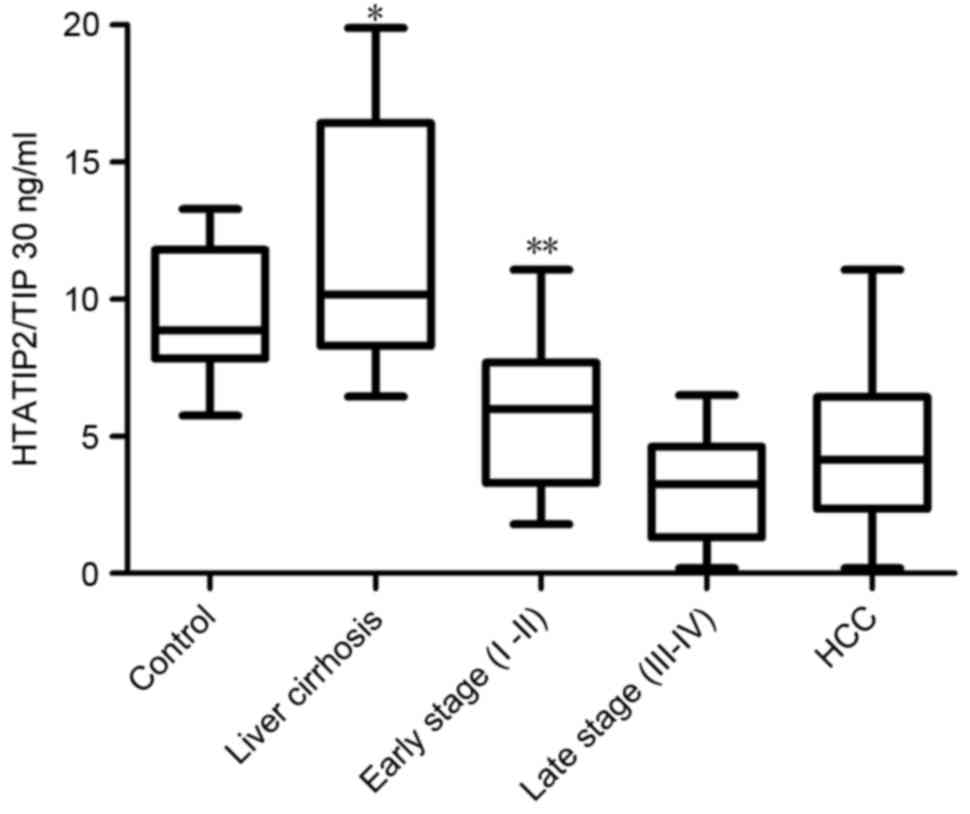
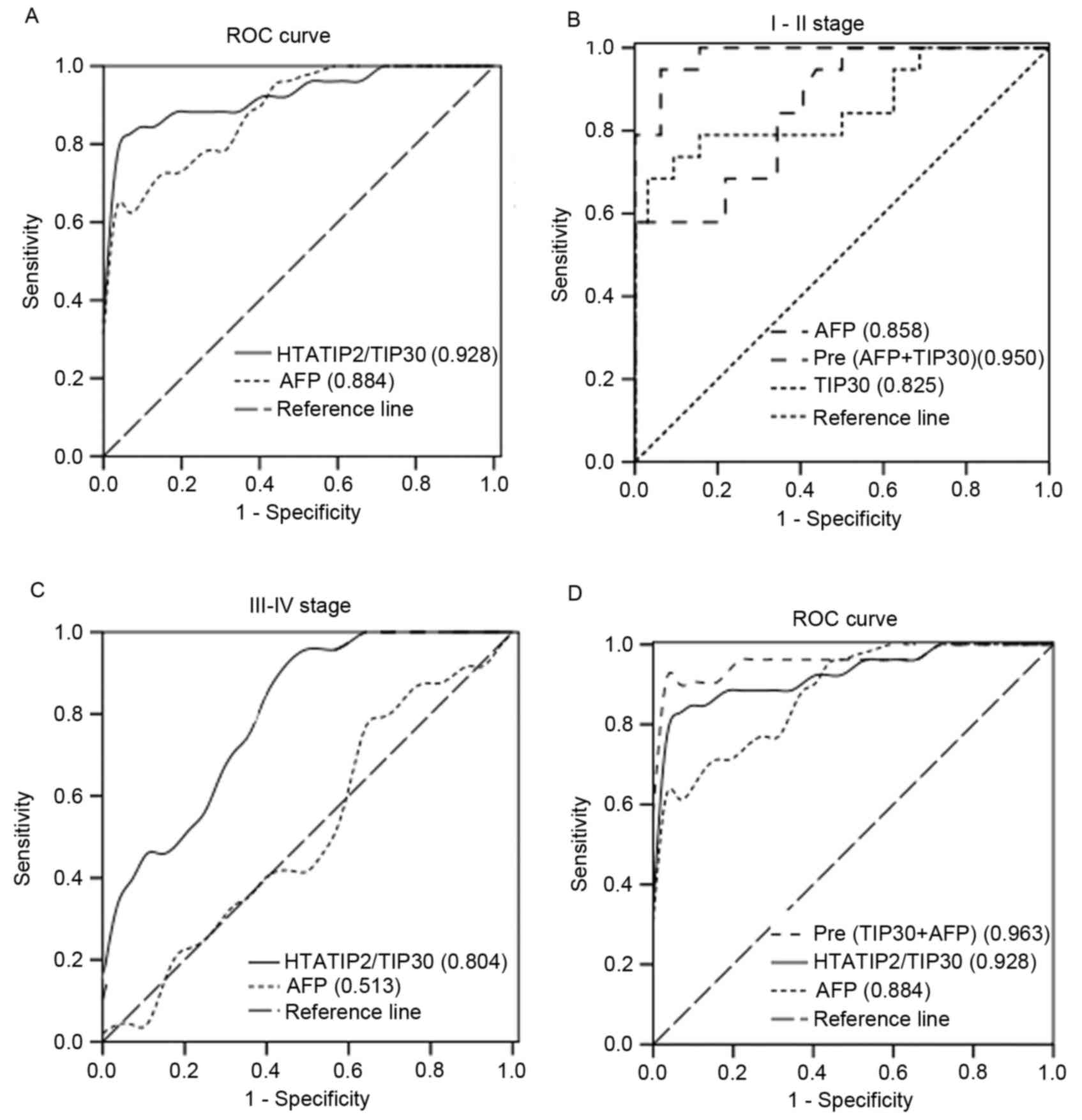
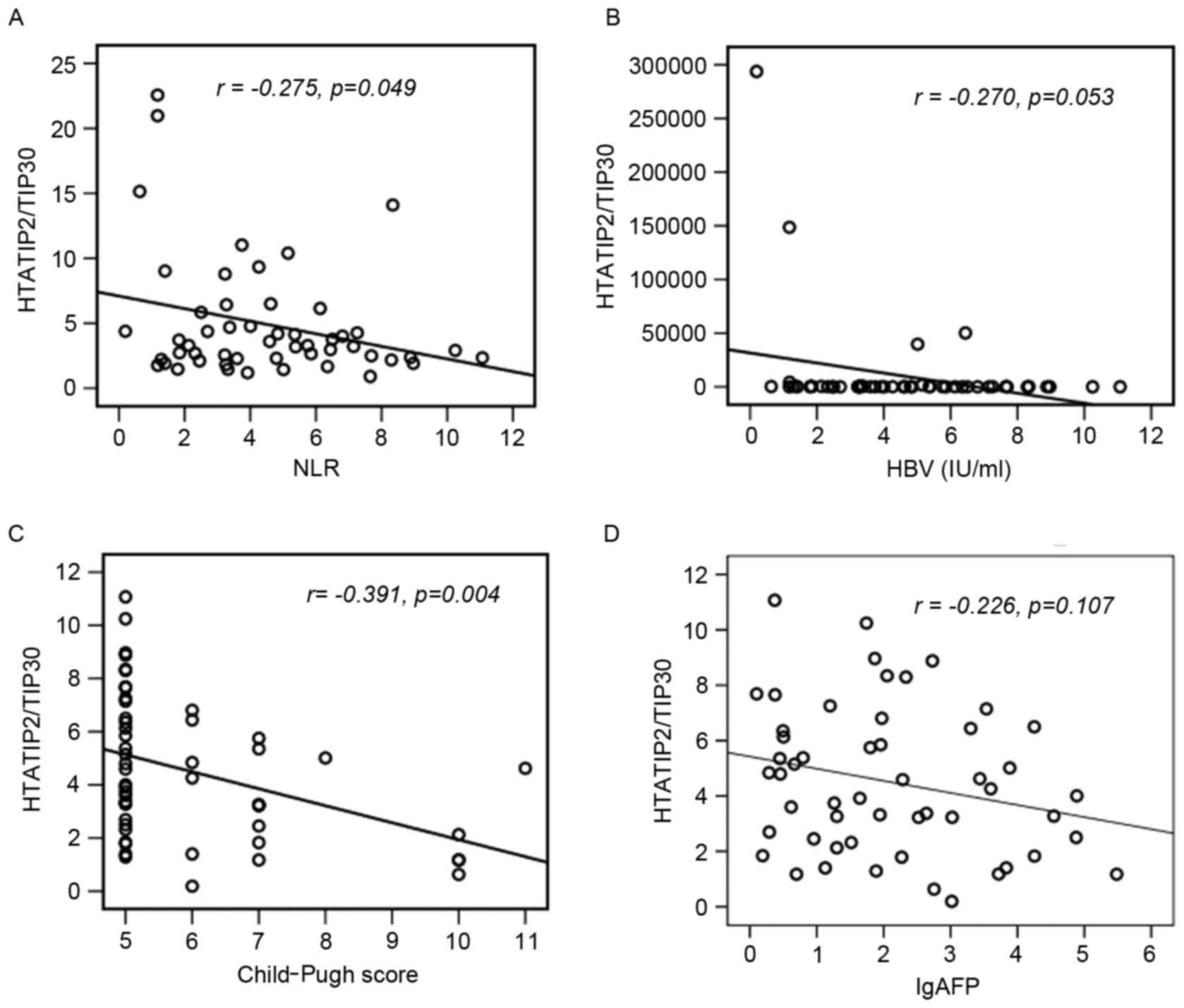
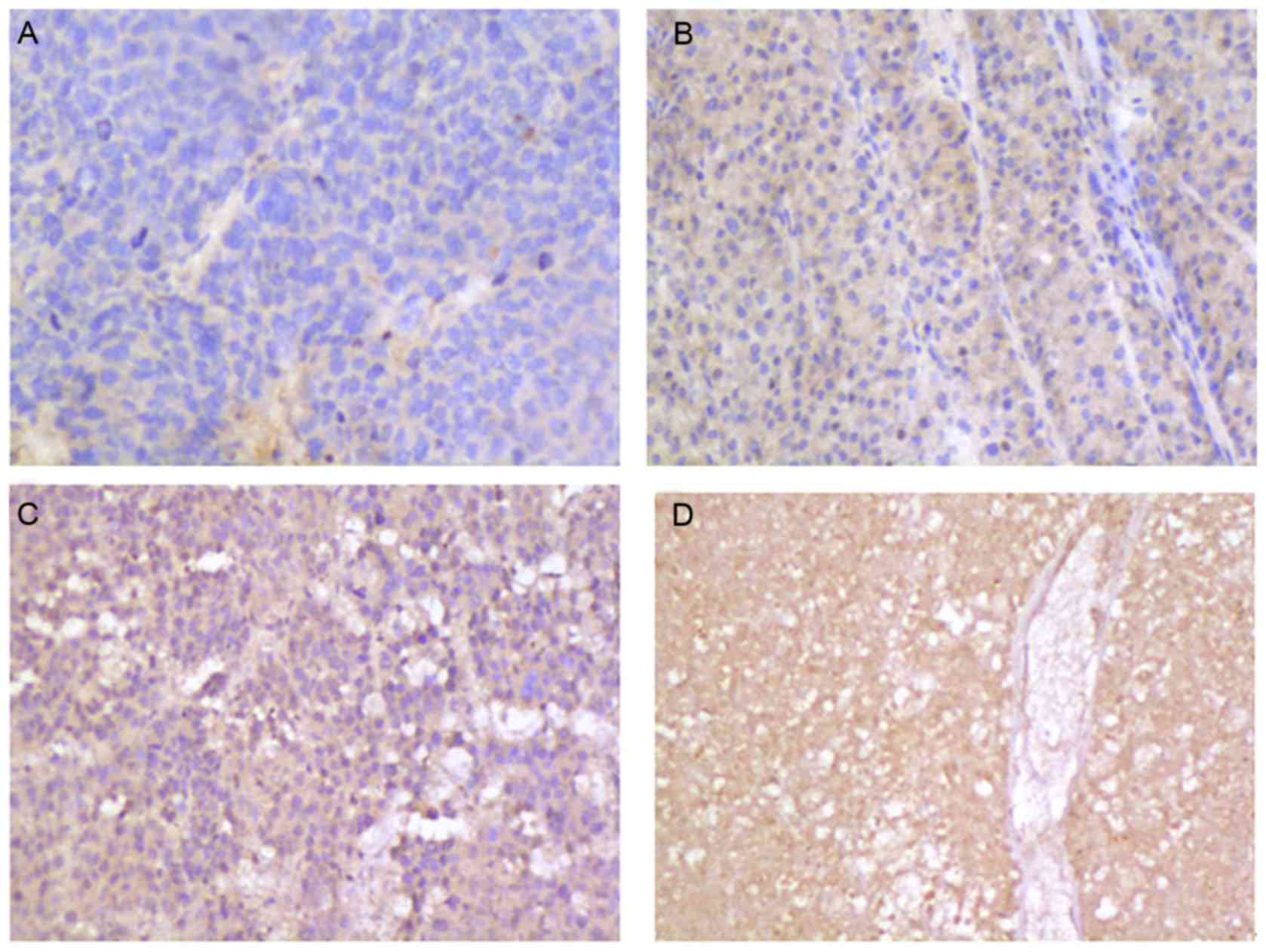
|
1
|
Kudo M, Han KH, Kokudo N, Cheng AL, Choi
BI, Furuse J, Izumi N, Park JW, Poon RT and Sakamoto M: Liver
cancer working group report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 40 Suppl 1:i19–i27.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yau T, Chan P, Epstein R and Poon RT:
Management of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of
targeted therapy. Liver Int. 29:10–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Song P, Tobe RG, Inagaki Y, Kokudo N,
Hasegawa K, Sugawara Y and Tang W: The management of hepatocellular
carcinoma around the world: A comparison of guidelines from 2001 to
2011. Liver Int. 32:1053–1063. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Farinati F, Marino D, de Giorgio M, Baldan
A, Cantarini M, Cursaro C, Rapaccini G, Del Poggio P, Di Nolfo MA,
Benvegnù L, et al: Diagnostic and prognostic role of
alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma: Both or neither? Am
J Gastroenterol. 101:524–532. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Villanueva A, Minguez B, Forner A, Reig M
and Llovet JM: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Novel molecular approaches
for diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. Annu Rev Med. 61:317–328.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xiao H, Tao Y, Greenblatt J and Roeder RG:
A cofactor, TIP30, specifically enhances HIV-1 Tat-activated
transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:pp. 2146–2151. 1998;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morán S, Rodríguez-Leal G, Marín-López E,
Arista J, Poo JL, Vargas-Vorackova F, Kershenobich D and Uribe M:
Primary biliary cirrhosis: Clinical features and survival of a
mexican population. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 61:212–219. 1996.(In
Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang C, Mori M, Gao S, Li A, Hoshino I,
Aupperlee MD, Haslam SZ and Xiao H: Tip30 deletion in MMTV-Neu mice
leads to enhanced EGFR signaling and development of estrogen
receptor-positive and progesterone receptor-negative mammary
tumors. Cancer Res. 70:10224–10233. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ito M, Jiang C, Krumm K, Zhang X, Pecha J,
Zhao J, Guo Y, Roeder RG and Xiao H: TIP30 deficiency increases
susceptibility to tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 63:8763–8767.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao J, Zhang X, Shi M, Xu H, Jin J, Ni H,
Yang S, Dai J, Wu M and Guo Y: TIP30 inhibits growth of HCC cell
lines and inhibits HCC xenografts in mice in combination with 5-FU.
Hepatology. 44:205–215. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumtepe Y, Halici Z, Sengul O, Kunak CS,
Bayir Y, Kilic N, Cadirci E, Pulur A and Bayraktutan Z: High serum
HTATIP2/TIP30 level in serous ovarian cancer as prognostic or
diagnostic marker. Eur J Med Res. 18:182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tong X, Li K, Luo Z, Lu B, Liu X, Wang T,
Pang M, Liang B, Tan M, Wu M, et al: Decreased TIP30 expression
promotes tumor metastasis in lung cancer. Am J Pathol.
174:1931–1939. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo S, Jing W, Hu X, Zhou X, Liu L, Zhu M,
Yin F, Chen R, Zhao J and Guo Y: Decreased TIP30 expression
predicts poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer patients. Int J
Cancer. 134:1369–1378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi M, Yan SG, Xie ST and Wang HN:
Tip30-induced apoptosis requires translocation of Bax and involves
mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1783:263–274.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao J, Chen J, Lu B, Dong L, Wang H, Bi
C, Wu G, Guo H, Wu M and Guo Y: TIP30 induces apoptosis under
oxidative stress through stabilization of p53 messenger RNA in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:4133–4141. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao J, Lu B, Xu H, Tong X, Wu G, Zhang X,
Liang A, Cong W, Dai J, Wang H, et al: Thirty-kilodalton
Tat-interacting protein suppresses tumor metastasis by inhibition
of osteopontin transcription in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 48:265–275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang C, Pecha J, Hoshino I, Ankrapp D and
Xiao H: TIP30 mutant derived from hepatocellular carcinoma
specimens promotes growth of HepG2 cells through up-regulation of
N-cadherin. Cancer Res. 67:3574–3582. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu B, Ma Y, Wu G, Tong X, Guo H, Liang A,
Cong W, Liu C, Wang H, Wu M, et al: Methylation of Tip30 promoter
is associated with poor prognosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7405–7412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song C, Wang F, Cheng K, Wei X, Bian Y,
Wang K, Tan Y, Wang H, Ye M and Zou H: Large-scale quantification
of single amino-acid variations by a variation-associated database
search strategy. J Proteome Res. 13:241–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shtivelman E: A link between metastasis
and resistance to apoptosis of variant small cell lung carcinoma.
Oncogene. 14:2167–2173. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li J, Zhang C, Xing Y, Janicki JS,
Yamamoto M, Wang XL, Tang DQ and Cui T: Up-regulation of p27 (kip1)
contributes to Nrf2-mediated protection against angiotensin
II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 90:315–324. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiao H, Palhan V, Yang Y and Roeder RG:
TIP30 has an intrinsic kinase activity required for up-regulation
of a subset of apoptotic genes. EMBO J. 19:956–963. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Berasain C and Avila MA: The EGFR
signalling system in the liver: From hepatoprotection to
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol. 49:9–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang P, Xu X, Wang L, Zhu B, Wang X and
Xia J: The role of EGF-EGFR signalling pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma inflammatory microenvironment. J Cell Mol Med.
18:218–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang C, Li A, Gao S, Zhang X and Xiao H:
The TIP30 protein complex, arachidonic acid and coenzyme A are
required for vesicle membrane fusion. PLoS One. 6:e212332011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li A, Zhang C, Gao S, Chen F, Yang C, Luo
R and Xiao H: TIP30 loss enhances cytoplasmic and nuclear EGFR
signaling and promotes lung adenocarcinogenesis in mice. Oncogene.
32:2273–2281, 2281e. 1–12. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shan SG, Gao YT, Xu YJ, Huang Y, Zhang Q,
Zhai DK, Li JB, Wang FM, Jing X, Du Z and Wang YJ: Gradually
increased Golgi protein 73 expression in the progression of benign
liver diseases to precancerous lesions and hepatocellular carcinoma
correlates with prognosis of patients. Hepatol Res. 43:1199–1210.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen TM, Lin CC, Huang PT and Wen CF:
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio associated with mortality in early
hepatocellular carcinoma patients after radiofrequency ablation. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:553–561. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang ZL, Luo J, Chen MS, Li JQ and Shi M:
Blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts survival in patients
with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial
chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 22:702–709. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bai F, Yano Y, Fukumoto T, Takebe A,
Tanaka M, Kuramitsu K, Anggorowati N, Rinonce HT, Widasari DI,
Saito M, et al: Quantification of pregenomic RNA and covalently
closed circular DNA in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Hepatol. 2013:8492902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang HI, Sherman M, Su J, Chen PJ, Liaw
YF, Iloeje UH and Chen CJ: Nomograms for risk of hepatocellular
carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J
Clin Oncol. 28:2437–2444. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mittal S and El-Serag HB: Epidemiology of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Consider the population. J Clin
Gastroenterol. 47 Suppl:S2–S6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zipprich A, Garcia-Tsao G, Rogowski S,
Fleig WE, Seufferlein T and Dollinger MM: Prognostic indicators of
survival in patients with compensated and decompensated cirrhosis.
Liver Int. 32:1407–1414. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Colli A, Fraquelli M, Casazza G, Massironi
S, Colucci A, Conte D and Duca P: Accuracy of ultrasonography,
spiral CT, magnetic resonance and alpha-fetoprotein in diagnosing
hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol.
101:513–523. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|