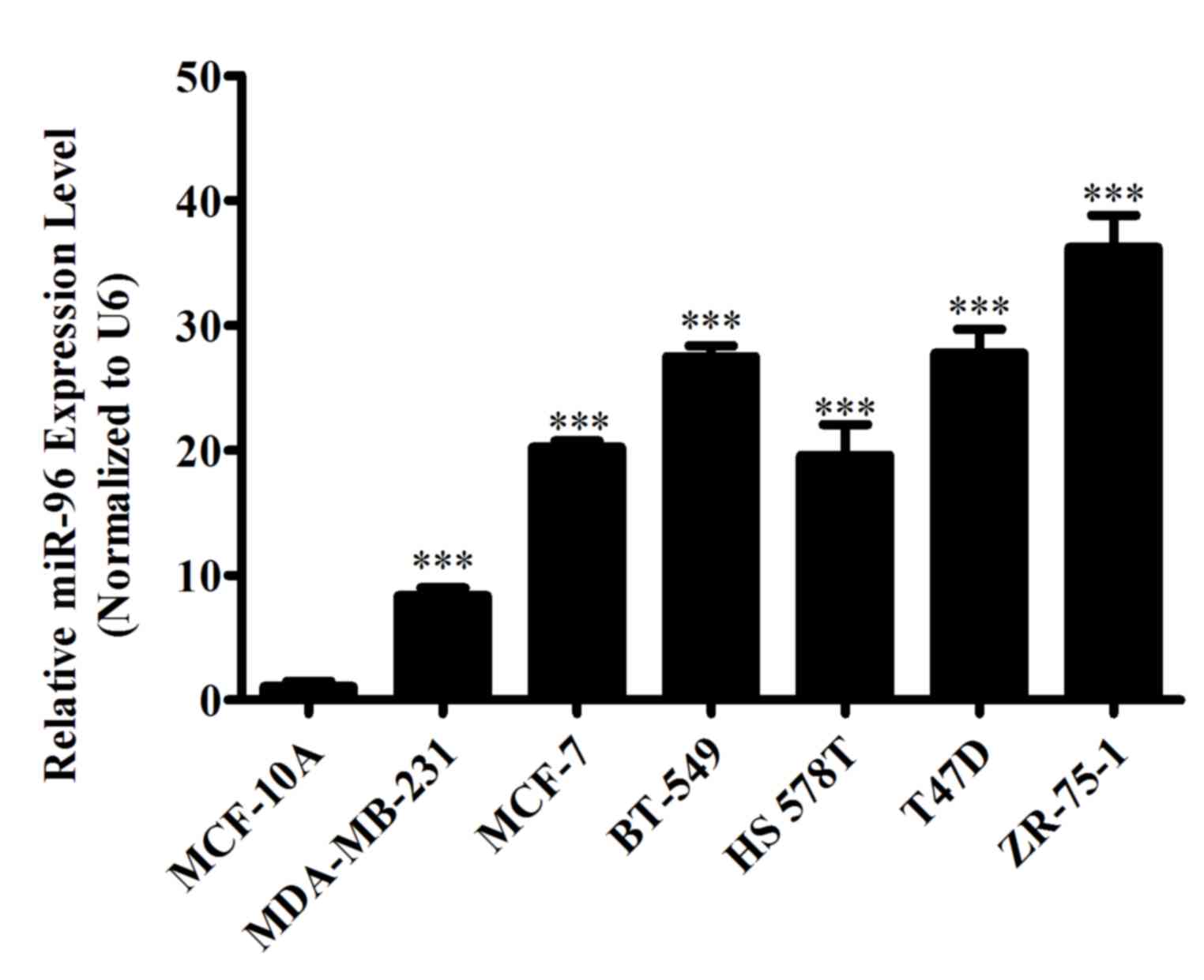
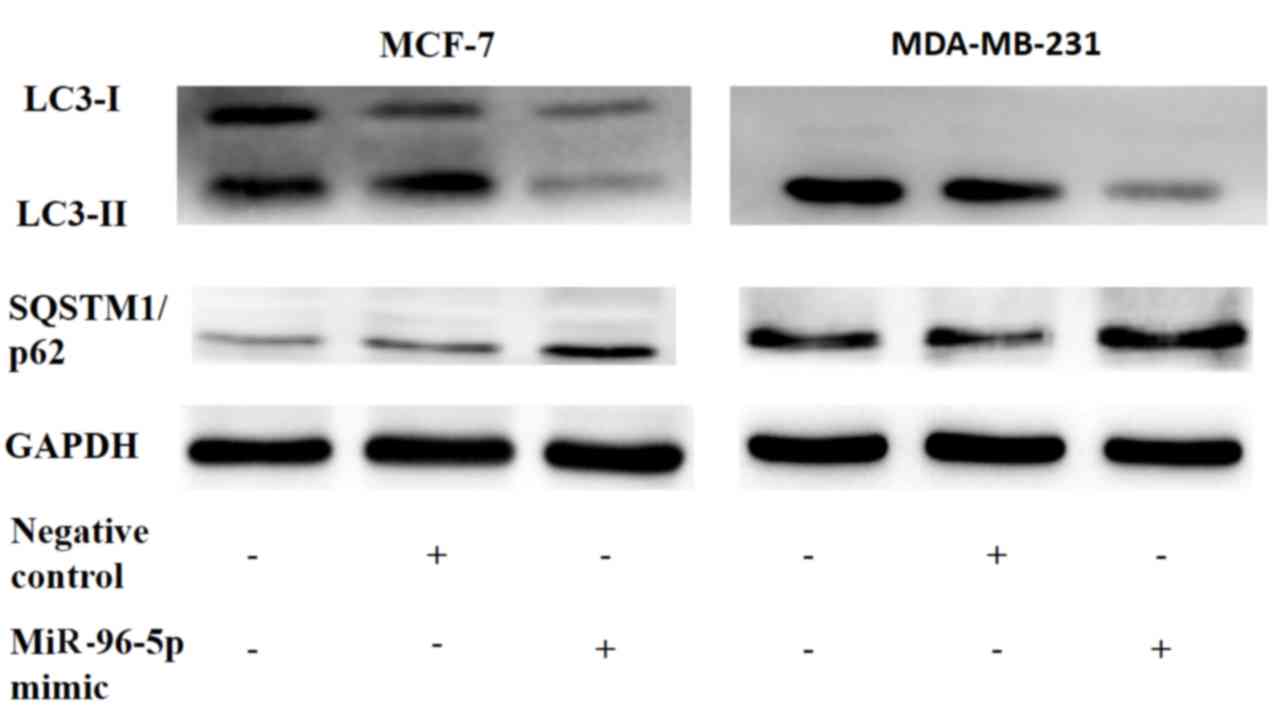
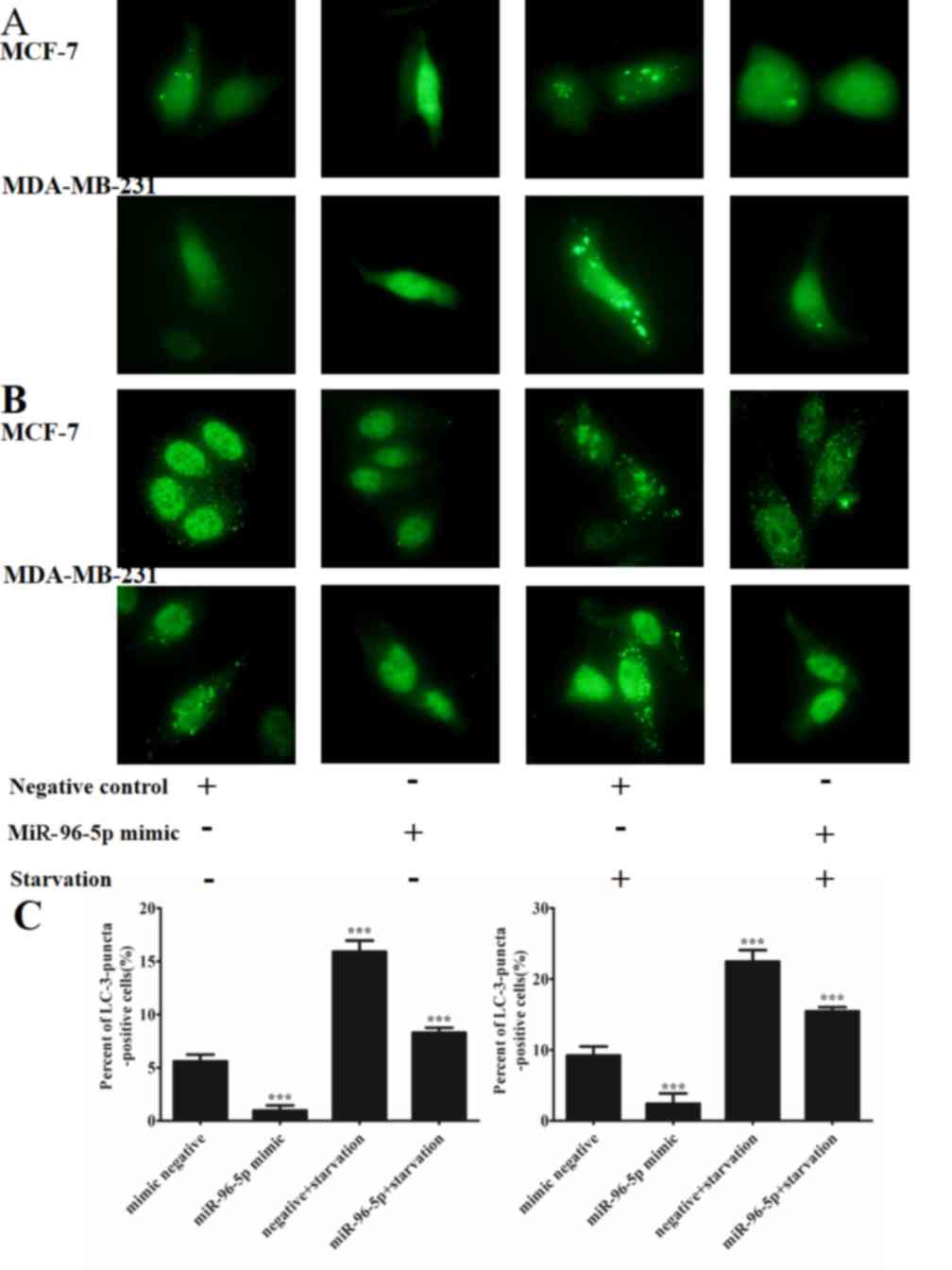
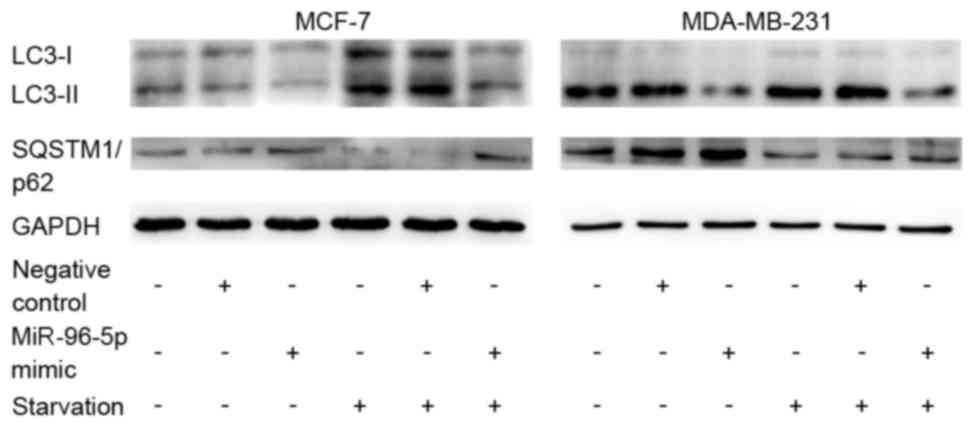
|
1
|
Libson S and Lippman M: A review of
clinical aspects of breast cancer. Int Rev Psychiatry. 26:4–15.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
White E and Dipaola RS: The double-edged
sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5308–5316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kamada Y, Sekito T and Ohsumi Y: Autophagy
in yeast: A TOR-mediated response to nutrient starvation. Curr Top
Microbiol Immunol. 279:73–84. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krustev LP: Cell autophagy of the liver in
starvation and undernutrition. Bibl Nutr Dieta. 145–154.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Karantza-Wadsworth V, Patel S, Kravchuk O,
Chen G, Mathew R, Jin S and White E: Autophagy mitigates metabolic
stress and genome damage in mammary tumorigenesis. Genes Dev.
21:1621–1635. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chera S, Buzgariu W, Ghila L and Galliot
B: Autophagy in hydra: A response to starvation and stress in early
animal evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:1432–1443. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T:
Autophagosome formation in mammalian cells. Cell Struct Funct.
27:421–429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
De Duve C and Wattiaux R: Functions of
lysosomes. Annu Rev Physiol. 28:435–492. 1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Noda T, Suzuki K and Ohsumi Y: Yeast
autophagosomes: De novo formation of a membrane structure. Trends
Cell Biol. 12:231–235. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kabeya Y, Kamada Y, Baba M, Takikawa H,
Sasaki M and Ohsumi Y: Atg17 functions in cooperation with Atg1 and
Atg13 in yeast autophagy. Mol Biol Cell. 16:2544–2553. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reggiori F, Tucker KA, Stromhaug PE and
Klionsky DJ: The Atg1-Atg13 complex regulates Atg9 and Atg23
retrieval transport from the pre-autophagosomal structure. Dev
Cell. 6:79–90. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kabeya Y, Kamada Y, Baba M, Takikawa H,
Sasaki M and Ohsumi Y: Atg17 functions in cooperation with Atg1 and
Atg13 in yeast autophagy. Mol Biol Cell. 16:2544–2553. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsushita M, Suzuki NN, Obara K, Fujioka
Y, Ohsumi Y and Inagaki F: Structure of Atg5. Atg16, a complex
essential for autophagy. J Biol Chem. 282:6763–6772. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsushita M, Suzuki NN, Fujioka Y, Ohsumi
Y and Inagaki F: Expression, purification and crystallization of
the Atg5-Atg16 complex essential for autophagy. Acta Crystallogr
Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 62:1021–1023. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K,
Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H and Levine B: Induction of autophagy and
inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature. 402:672–676. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Codogno P and Meijer AJ: Atg5: More than
an autophagy factor. Nat Cell Biol. 8:1045–1047. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fujioka Y, Noda NN, Fujii K, Yoshimoto K,
Ohsumi Y and Inagaki F: In vitro reconstitution of plant Atg8 and
Atg12 conjugation systems essential for autophagy. J Biol Chem.
283:1921–1928. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nishino I: Autophagic vacuolar myopathies.
Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 3:64–69. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rubinsztein DC, Difiglia M, Heintz N,
Nixon RA, Qin ZH, Ravikumar B, Stefanis L and Tolkovsky A:
Autophagy and its possible roles in nervous system diseases, damage
and repair. Autophagy. 1:11–22. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakai A, Yamaguchi O, Takeda T, Higuchi Y,
Hikoso S, Taniike M, Omiya S, Mizote I, Matsumura Y, Asahi M, et
al: The role of autophagy in cardiomyocytes in the basal state and
in response to hemodynamic stress. Nat Med. 13:619–624. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miller S and Krijnse-Locker J:
Modification of intracellular membrane structures for virus
replication. Nat Rev Microbiol. 6:363–374. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakagawa I, Amano A, Mizushima N, Yamamoto
A, Yamaguchi H, Kamimoto T, Nara A, Funao J, Nakata M, Tsuda K, et
al: Autophagy defends cells against invading group A streptococcus.
Science. 306:1037–1040. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kubisch J, Türei D, Földvári-Nagy L, Dunai
ZA, Zsákai L, Varga M, Vellai T, Csermely P and Korcsmáros T:
Complex regulation of autophagy in cancer - Integrated approaches
to discover the networks that hold a double-edged sword. Semin
Cancer Biol. 23:252–261. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lorin S, Hamaï A, Mehrpour M and Codogno
P: Autophagy regulation and its role in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
23:361–379. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu B, Wen X and Cheng Y: Survival or
death: Disequilibrating the oncogenic and tumor suppressive
autophagy in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X, Li B, Chen Y, Ren X,
Liu CG and Yang JM: Regulation of autophagy by a beclin 1-targeted
microRNA, miR-30a, in cancer cells. Autophagy. 5:816–823. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tekirdag KA, Korkmaz G, Ozturk DG, Agami R
and Gozuacik D: MIR181A regulates starvation- and rapamycin-induced
autophagy through targeting of ATG5. Autophagy. 9:374–385. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Korkmaz G, le Sage C, Tekirdag KA, Agami R
and Gozuacik D: MiR-376b controls starvation and mTOR
inhibition-related autophagy by targeting ATG4C and BECN1.
Autophagy. 8:165–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sacheli R, Nguyen L, Borgs L, Vandenbosch
R, Bodson M, Lefebvre P and Malgrange B: Expression patterns of
miR-96, miR-182 and miR-183 in the development inner ear. Gene Expr
Patterns. 9:364–370. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu W, Liu X, He J, Chen D, Hunag Y and
Zhang YK: Overexpression of members of the microRNA-183 family is a
risk factor for lung cancer: A case control study. BMC Cancer.
11:3932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mihelich BL, Khramtsova EA, Arva N,
Vaishnav A, Johnson DN, Giangreco AA, Martens-Uzunova E, Bagasra O,
Kajdacsy-Balla A and Nonn L: MiR-183-96-182 cluster is
overexpressed in prostate tissue and regulates zinc homeostasis in
prostate cells. J Biol Chem. 286:44503–44511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
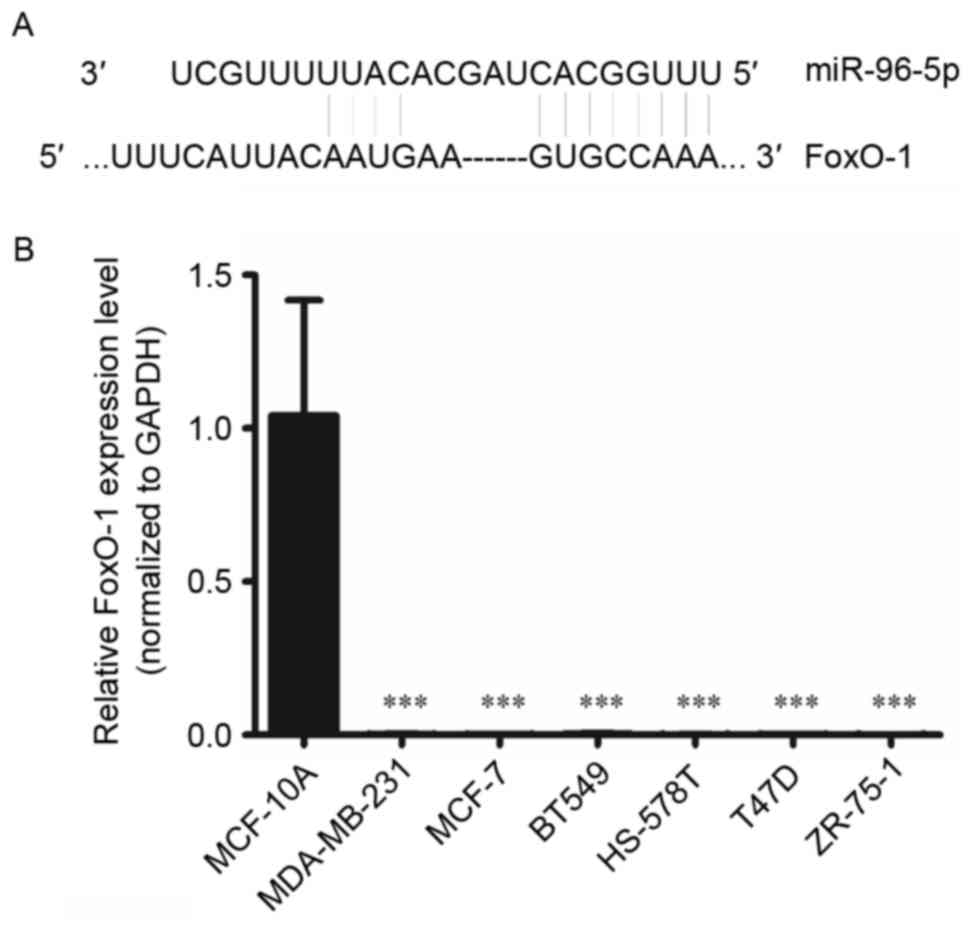
Fendler A, Jung M, Stephan C, Erbersdobler
A, Jung K and Yousef GM: The antiapoptotic function of miR-96 in
prostate cancer by inhibition of FOXO1. PLoS One. 8:e808072013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu S, Lu Z, Liu C, Meng Y, Ma Y, Zhao W,
Liu J, Yu J and Chen J: MiRNA-96 suppresses KRAS and functions as a
tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res.
70:6015–6025. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin H, Dai T, Xiong H, Zhao X, Chen X, Yu
C, Li J, Wang X and Song L: Unregulated miR-96 induces cell
proliferation in human breast cancer by downregulating
transcriptional factor FOXO3a. PLoS One. 5:e157972010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96 and miR-182 in breast cancer
cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li J, Li P, Chen T, Gao G, Chen X, Du Y,
Zhang R, Yang R, Zhao W, Dun S, et al: Expression of microRNA-96
and its potential functions by targeting FOXO3 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:685–692. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kundu ST, Byers LA, Peng DH, Roybal JD,
Diao L, Wang J, Tong P, Creighton CJ and Gibbons DL: The miR-200
family and the miR-183~96~182 cluster target Foxf2 to inhibit
invasion and metastasis in lung cancers. Oncogene. 35:173–186.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu JJ, Wu YX, Zhao FJ and Xia SJ: MiR-96
promotes cell proliferation and clonogenicity by down-regulating of
FOXO1 in prostate cancer cells. Med Oncol. 31:9102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
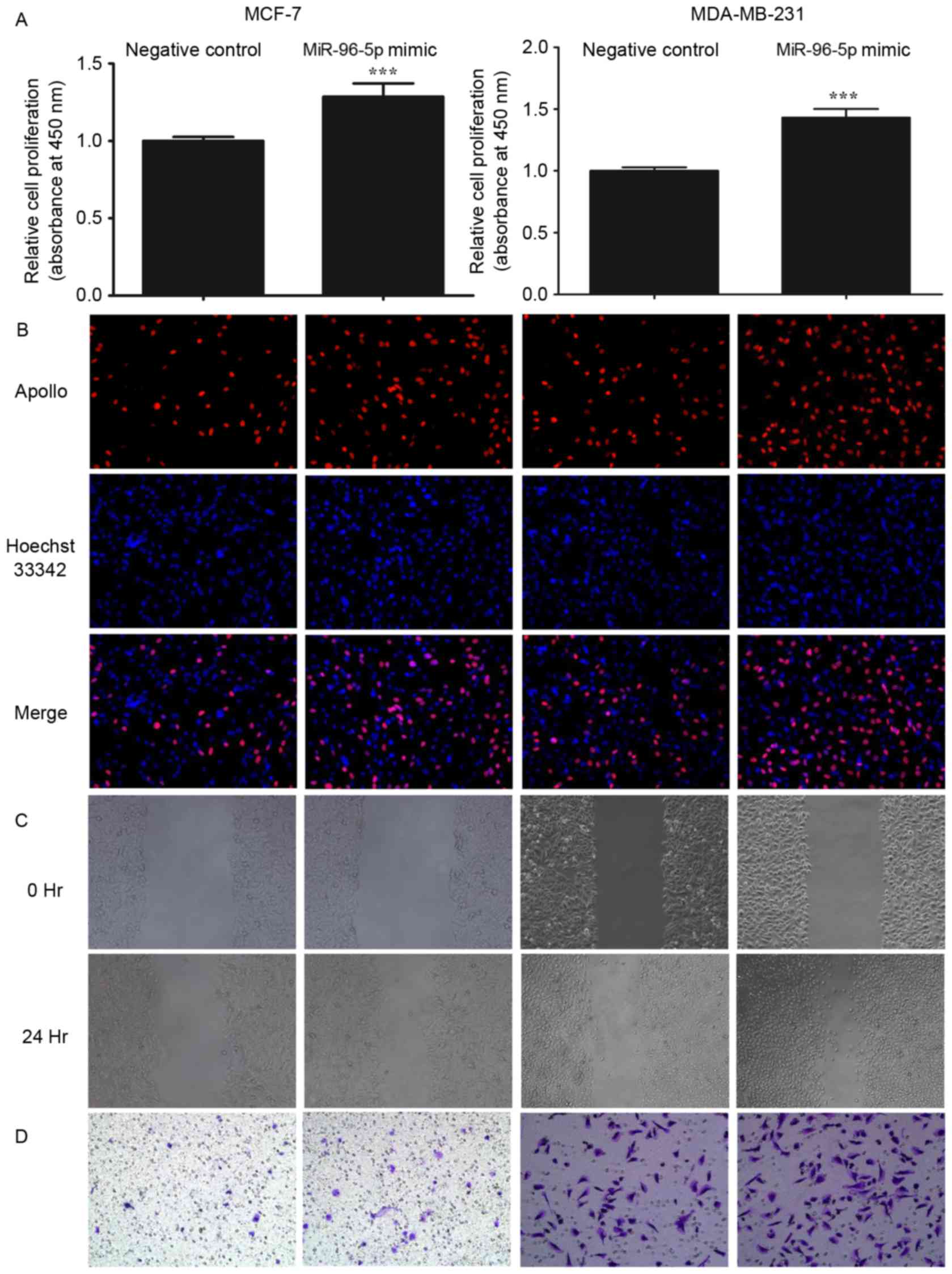
Haflidadóttir BS, Larne O, Martin M,
Persson M, Edsjö A, Bjartell A and Ceder Y: Upregulation of miR-96
enhances cellular proliferation of prostate cancer cells through
FOXO1. PLoS One. 8:e724002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou J, Liao W, Yang J, Ma K, Li X, Wang
Y, Wang D, Wang L, Zhang Y, Yin Y, et al: FOXO3 induces
FOXO1-dependent autophagy by activating the AKT1 signaling pathway.
Autophagy. 8:1712–1723. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vidal RL and Hetz C: Unspliced XBP1
controls autophagy through FoxO1. Cell Res. 23:463–464. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao Y, Li X, Cai MY, Ma K, Yang J, Zhou
J, Fu W, Wei FZ, Wang L, Xie D and Zhu WG: XBP-1u suppresses
autophagy by promoting the degradation of FoxO1 in cancer cells.
Cell Res. 23:491–507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xiao D, Bommareddy A, Kim SH, Sehrawat A,
Hahm ER and Singh SV: Benzyl isothiocyanate causes FoxO1-mediated
autophagic death in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
7:e325972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
van der Vos KE, Eliasson P,
Proikas-Cezanne T, Vervoort SJ, van Boxtel R, Putker M, van Zutphen
IJ, Mauthe M, Zellmer S, Pals C, et al: Modulation of glutamine
metabolism by the PI(3)K-PKB-FOXO network regulates autophagy. Nat
Cell Biol. 14:829–837. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
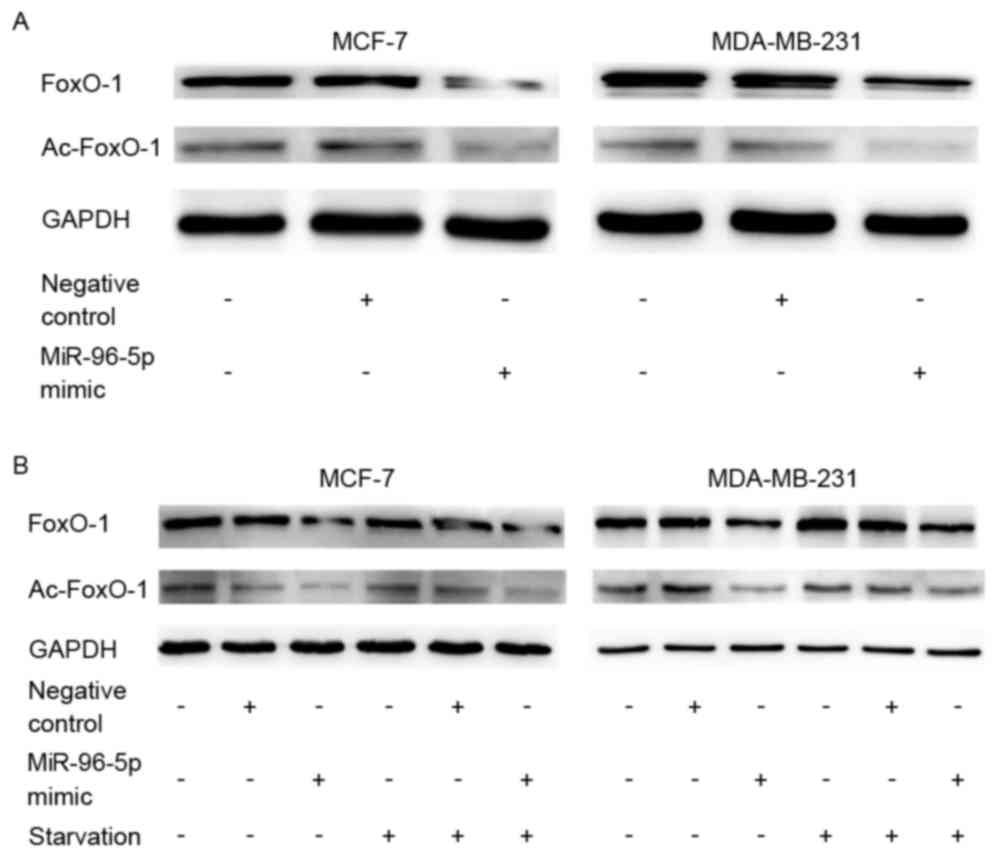
Hariharan N, Maejima Y, Nakae J, Paik J,
Depinho RA and Sadoshima J: Deacetylation of FoxO by Sirt1 plays an
essential role in mediating starvation-induced autophagy in cardiac
myocytes. Circ Res. 107:1470–1482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao Y, Yang J, Liao W, Liu X, Zhang H,
Wang S, Wang D, Feng J, Yu L and Zhu WG: Cytosolic FoxO1 is
essential for the induction of autophagy and tumour suppressor
activity. Nat Cell Biol. 12:665–675. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu HY, Han J, Cao SY, Hong T, Zhuo D, Shi
J, Liu Z and Cao W: Hepatic autophagy is suppressed in the presence
of insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia: inhibition of
FoxO1-dependent expression of key autophagy genes by insulin. J
Biol Chem. 284:31484–31492. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Krützfeldt J and Stoffel M: MicroRNAs: A
new class of regulatory genes affecting metabolism. Cell Metab.
4:9–12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xu XM, Qian JC, Deng ZL, Cai Z, Tang T,
Wang P, Zhang KH and Cai JP: Expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-96
and miR-135b is correlated with the clinical parameters of
colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 4:339–345. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sun WL, Chen J, Wang YP and Zheng H:
Autophagy protects breast cancer cells from epirubicin-induced
apoptosis and facilitates epirubicin-resistance development.
Autophagy. 7:1035–1044. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
White E and DiPaola RS: The double-edged
sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5308–5316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kang C and Avery L: To be or not to be,
the level of autophagy is the question: Dual roles of autophagy in
the survival response to starvation. Autophagy. 4:82–84. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Boya P, Reggiori F and Codogno P: Emerging
regulation and functions of autophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 15:713–720.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Münz C: Autophagy in cellular
transformation, survival and communication with the tumor
microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol. 23:299–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Macintosh RL and Ryan KM: Autophagy in
tumour cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 23:344–351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Milani M, Rzymski T, Mellor HR, Pike L,
Bottini A, Generali D and Harris AL: The role of ATF4 stabilization
and autophagy in resistance of breast cancer cells treated with
bortezomib. Cancer Res. 69:4415–4423. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Notte A, Ninane N, Arnould T and Michiels
C: Hypoxia counteracts taxol-induced apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast
cancer cells: Role of autophagy and JNK activation. Cell Death Dis.
4:e6382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jain K, Paranandi KS, Sridharan S and Basu
A: Autophagy in breast cancer and its implications for therapy. Am
J Cancer Res. 3:251–265. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xiao D, Bommareddy A, Kim SH, Sehrawat A,
Hahm ER and Singh SV: Benzyl isothiocyanate causes FoxO1-mediated
autophagic death in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
7:e325972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cufí S, Vazquez-Martin A,
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Corominas-Faja B, Cuyàs E, López-Bonet E,
Martin-Castillo B, Joven J and Menendez JA: The anti-malarial
chloroquine overcomes primary resistance and restores sensitivity
to trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer. Sci Rep. 3:24692013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cook KL, Shajahan AN and Clarke R:
Autophagy and endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 11:1283–1294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xue LY, Chiu SM and Oleinick NL: Atg7
deficiency increases resistance of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells
to photodynamic therapy. Autophagy. 6:248–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Maycotte P, Aryal S, Cummings CT, Thorburn
J, Morgan MJ and Thorburn A: Chloroquine sensitizes breast cancer
cells to chemotherapy independent of autophagy. Autophagy.
8:200–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Debnath J: The multifaceted roles of
autophagy in tumors-implications for breast cancer. J Mammary Gland
Biol Neoplasia. 16:173–187. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Di X, Shiu RP, Newsham IF and Gewirtz DA:
Apoptosis, autophagy, accelerated senescence and reactive oxygen in
the response of human breast tumor cells to adriamycin. Biochem
Pharmacol. 77:1139–1150. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gewirtz DA, Hilliker ML and Wilson EN:
Promotion of autophagy as a mechanism for radiation sensitization
of breast tumor cells. Radiother Oncol. 92:323–328. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H, Agostinis P,
Agrawal DK, Aliev G, Askew DS, Baba M, Baehrecke EH, Bahr BA,
Ballabio A, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of
assays for monitoring autophagy in higher eukaryotes. Autophagy.
4:151–175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang Y, Gan B, Liu D and Paik JH: FoxO
family members in cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 12:253–259. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kousteni S: FoxO1: A molecule for all
seasons. J Bone Miner Res. 26:912–917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
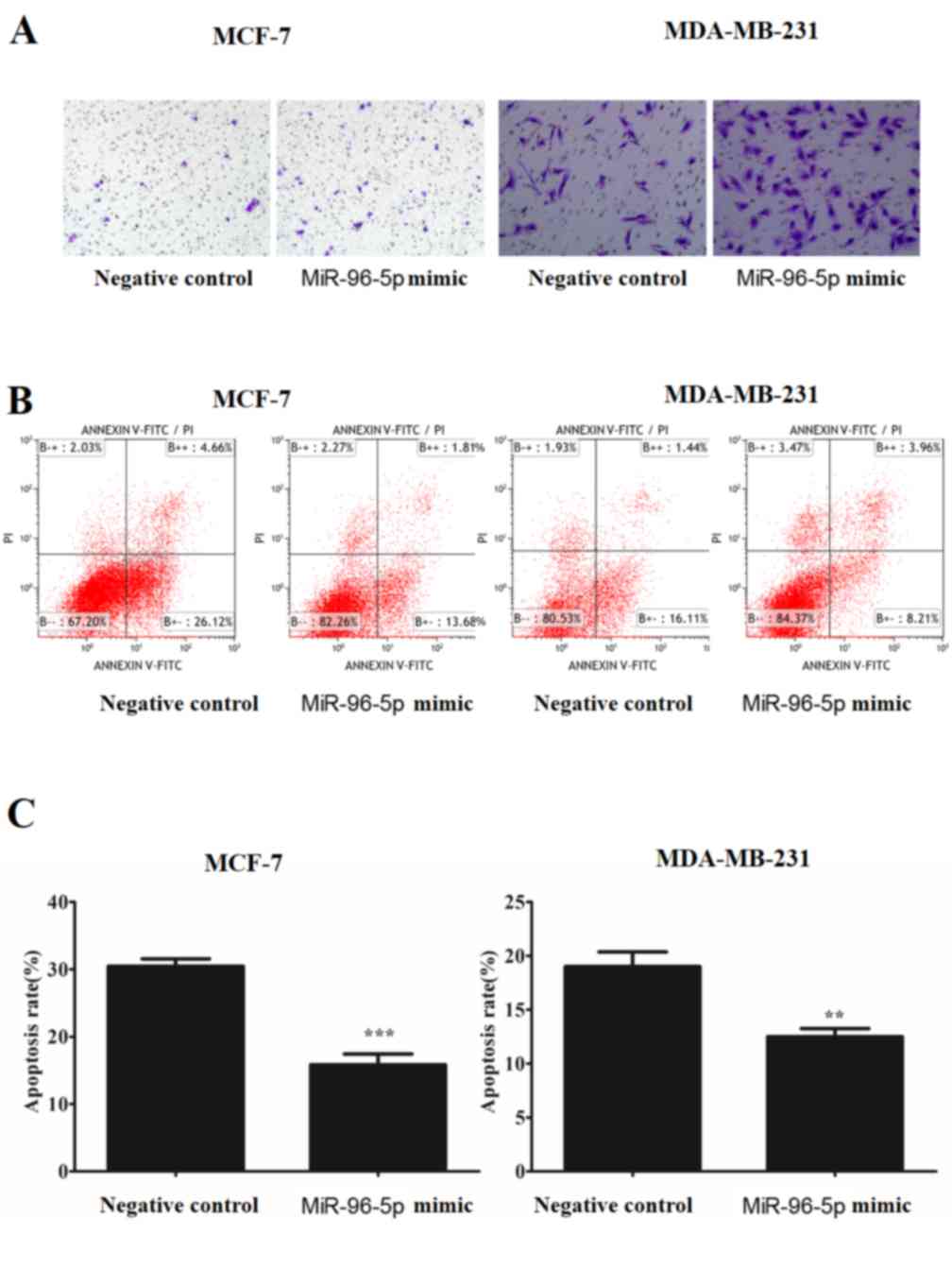
Guo Y, Liu H, Zhang H, Shang C and Song Y:
MiR-96 regulates FOXO1-mediated cell apoptosis in bladder cancer.
Oncol Lett. 4:561–565. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Haflidadóttir BS, Larne O, Martin M,
Persson M, Edsjö A, Bjartell A and Ceder Y: Upregulation of miR-96
enhances cellular proliferation of prostate cancer cells through
FOXO1. PLoS One. 8:e724002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Chen C, Xu T, Zhou J, Yan Y, Li W, Yu H,
Hu G, Ding X, Chen J and Lu Y: High cytoplasmic FOXO1 and pFOXO1
expression in astrocytomas are associated with worse surgical
outcome. PLoS One. 8:e692602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhao Y, Wang Y and Zhu WG: Applications of
post-translational modifications of FoxO family proteins in
biological functions. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:276–282. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ma Y, Yang HZ, Dong BJ, Zou HB, Zhou Y,
Kong XM and Huang YR: Biphasic regulation of autophagy by miR-96 in
prostate cancer cells under hypoxia. Oncotarget. 5:9169–9182. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|