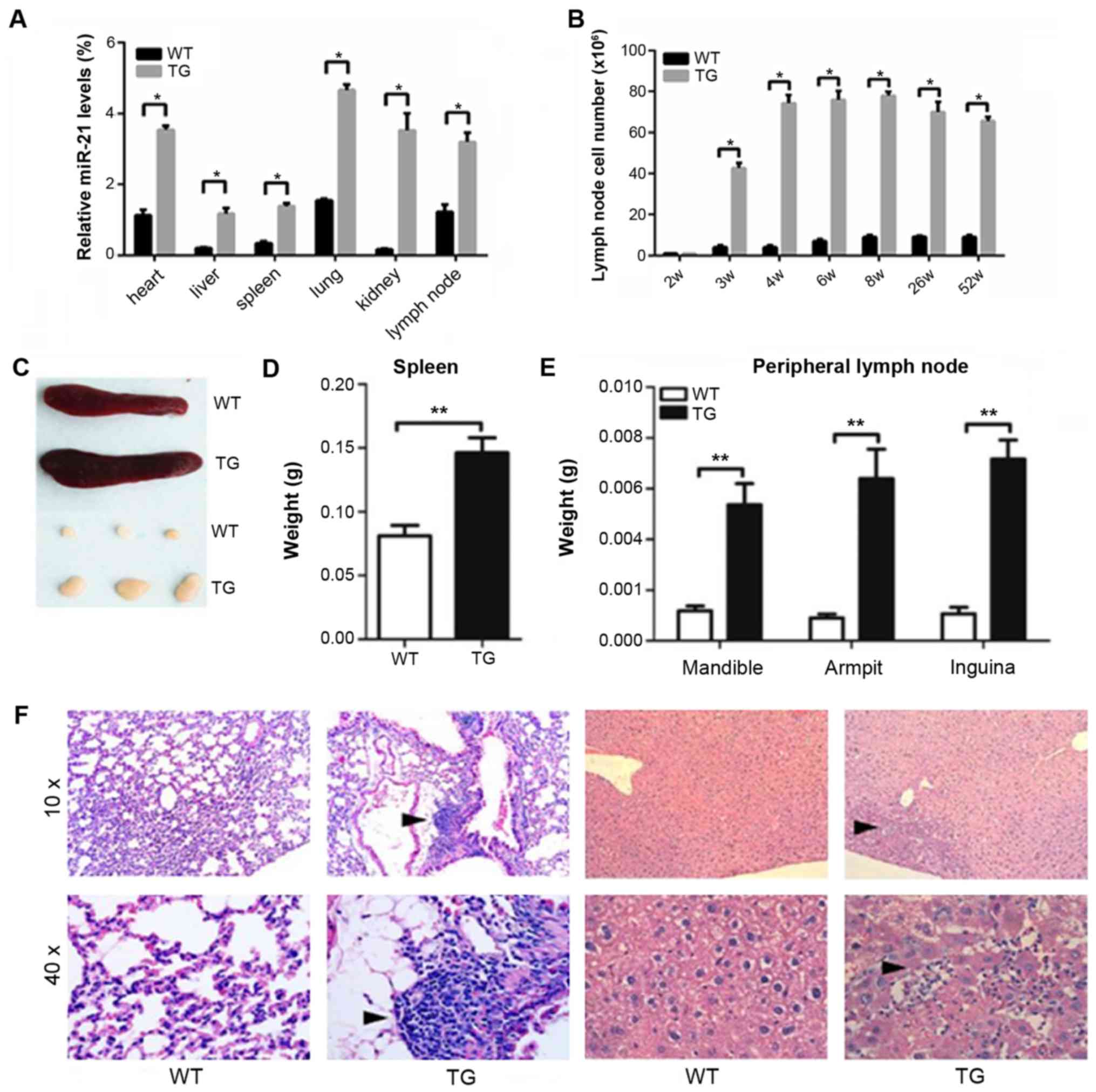
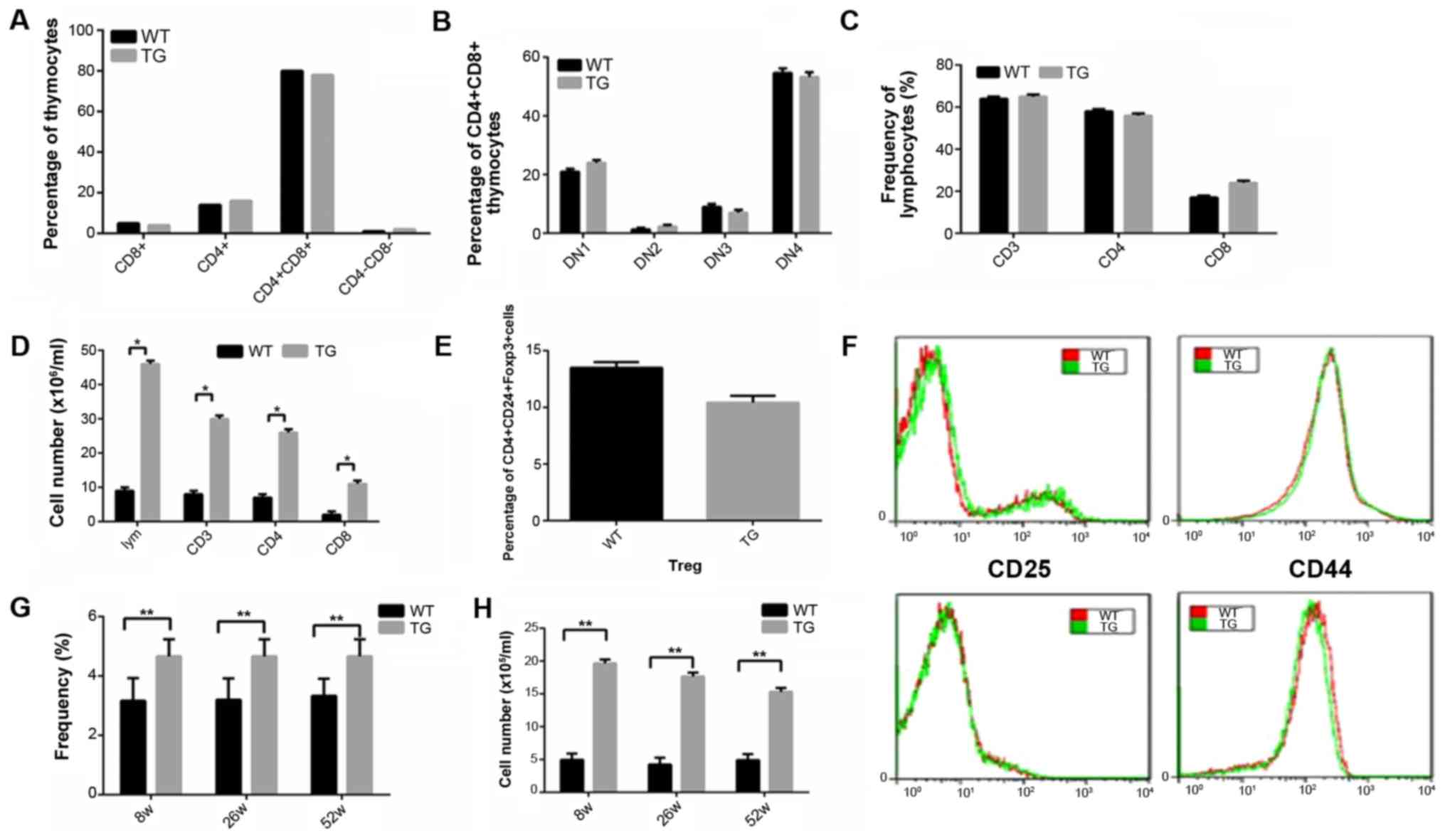
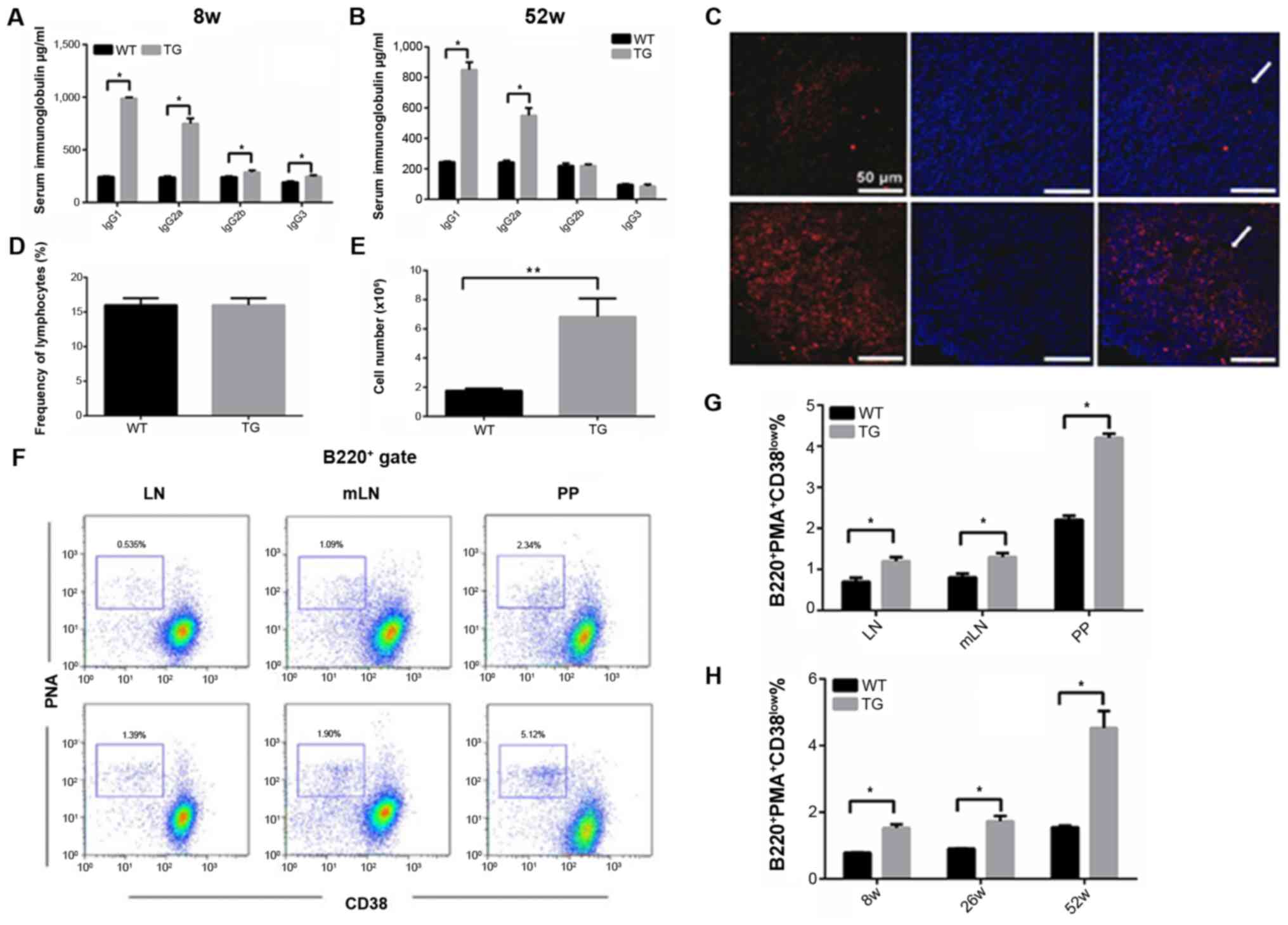
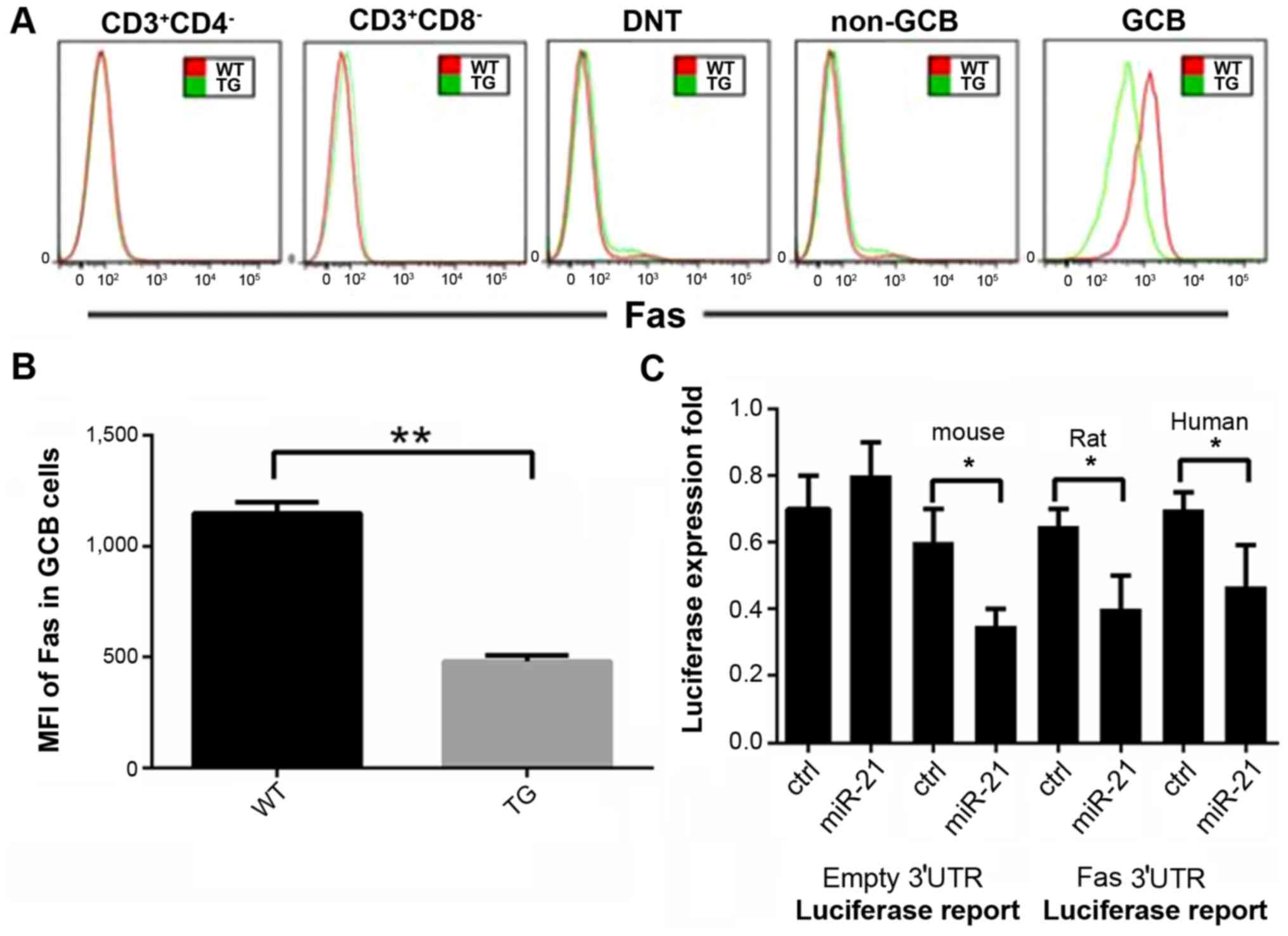
|
1
|
Halász T, Horváth G, Pár G, Werling K,
Kiss A, Schaff Z and Lendvai G: miR-122 negatively correlates with
liver fibrosis as detected by histology and FibroScan. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:7814–7823. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Croci S, Zerbini A, Boiardi L, Muratore F,
Bisagni A, Nicoli D, Farnetti E, Pazzola G, Cimino L, Moramarco A,
et al: MicroRNA markers of inflammation and remodelling in temporal
arteries from patients with giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis.
20:78462015.
|
|
3
|
Punga AR, Andersson M, Alimohammadi M and
Punga T: Disease specific signature of circulating miR-150-5p and
miR-21-5p in myasthenia gravis patients. J Neurol Sci. 356:90–96.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu XN, Ye YX, Niu JW, Li Y, Li X, You X,
Chen H, Zhao LD, Zeng XF, Zhang FC, et al: Defective PTEN
regulation contributes to B cell hyperresponsiveness in systemic
lupus erythematosus. Sci Transl Med. 6:246ra99. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Quinn SR and O'Neill LA: The role of
microRNAs in the control and mechanism of action of IL-10. Curr Top
Microbiol Immunol. 380:145–155. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma X, Zhou J, Zhong Y, Jiang L, Mu P, Li
Y, Singh N, Nagarkatti M and Nagarkatti P: Expression, regulation
and function of microRNAs in multiple sclerosis. Int J Med Sci.
11:810–818. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang ZM, Fang M, Wang JP, Cai PC, Wang P
and Hu LH: Clinical relevance of plasma miR-21 in new-onset
systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J Clin Lab Anal. 28:446–451.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Haider BA, Baras AS, McCall MN, Hertel JA,
Cornish TC and Halushka MK: A critical evaluation of microRNA
biomarkers in non-neoplastic disease. PLoS One. 9:e895652014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smigielska-Czepiel K, van den Berg A,
Jellema P, van der Lei RJ, Bijzet J, Kluiver J, Boots AM, Brouwer E
and Kroesen BJ: Comprehensive analysis of miRNA expression in
T-cell subsets of rheumatoid arthritis patients reveals defined
signatures of naive and memory Tregs. Genes Immun. 15:115–125.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chafin CB, Regna NL, Hammond SE and Reilly
CM: Cellular and urinary microRNA alterations in NZB/W mice with
hydroxychloroquine or prednisone treatment. Int Immunopharmacol.
17:894–906. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bao H, Hu S, Zhang C, Shi S, Qin W, Zeng
C, Zen K and Liu Z: Inhibition of miRNA-21 prevents fibrogenic
activation in podocytes and tubular cells in IgA nephropathy.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 444:455–460. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang H, Peng W, Ouyang X, Li W and Dai Y:
Circulating microRNAs as candidate biomarkers in patients with
systemic lupus erythematosus. Transl Res. 160:198–206. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mycko MP, Cichalewska M, Machlanska A,
Cwiklinska H, Mariasiewicz M and Selmaj KW: MicroRNA-301a
regulation of a T-helper 17 immune response controls autoimmune
demyelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:pp. E1248–E1257. 2012;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stagakis E, Bertsias G, Verginis P, Nakou
M, Hatziapostolou M, Kritikos H, Iliopoulos D and Boumpas DT:
Identification of novel microRNA signatures linked to human lupus
disease activity and pathogenesis: miR-21 regulates aberrant T cell
responses through regulation of PDCD4 expression. Ann Rheum Dis.
70:1496–1506. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pan W, Zhu S, Yuan M, Cui H, Wang L, Luo
X, Li J, Zhou H, Tang Y and Shen N: MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-148a
contribute to DNA hypomethylation in lupus CD4+ T cells
by directly and indirectly targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. J
Immunol. 184:6773–6781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ruan Q, Wang T, Kameswaran V, Wei Q,
Johnson DS, Matschinsky F, Shi W and Chen YH: The microRNA-21-PDCD4
axis prevents type 1 diabetes by blocking pancreatic beta cell
death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:pp. 12030–12035. 2011;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bostjancic E and Glavac D: Importance of
microRNAs in skin morphogenesis and diseases. Acta Dermatovenerol
Alp Pannonica Adriat. 17:95–102. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alisi A, Da Sacco L, Bruscalupi G,
Piemonte F, Panera N, de Vito R, Leoni S, Bottazzo GF, Masotti A
and Nobili V: Mirnome analysis reveals novel molecular determinants
in the pathogenesis of diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Lab Invest. 91:283–293. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dey N, Das F, Mariappan MM, Mandal CC,
Ghosh-Choudhury N, Kasinath BS and Choudhury GG: MicroRNA-21
orchestrates high glucose-induced signals to TOR complex 1,
resulting in renal cell pathology in diabetes. J Biol Chem.
286:25586–25603. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bergman P, James T, Kular L, Ruhrmann S,
Kramarova T, Kvist A, Supic G, Gillett A, Pivarcsi A and Jagodic M:
Next-generation sequencing identifies microRNAs that associate with
pathogenic autoimmune neuroinflammation in rats. J Immunol.
190:4066–4075. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fognani E, Giannini C, Piluso A, Gragnani
L, Monti M, Caini P, Ranieri J, Urraro T, Triboli E, Laffi G, et
al: Role of microRNA profile modifications in hepatitis C
virus-related mixed cryoglobulinemia. PLoS One. 8:e629652013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu WD, Pan HF, Li JH and Ye DQ:
MicroRNA-21 with therapeutic potential in autoimmune diseases.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 17:659–665. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koelsch KA, Webb R, Jeffries M, Dozmorov
MG, Frank MB, Guthridge JM, James JA, Wren JD and Sawalha AH:
Functional characterization of the MECP2/IRAK1 lupus risk haplotype
in human T cells and a human MECP2 transgenic mouse. J Autoimmun.
41:168–174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kimura J, Ichii O, Miyazono K, Nakamura T,
Horino T, Otsuka-Kanazawa S and Kon Y: Overexpression of Toll-like
receptor 8 correlates with the progression of podocyte injury in
murine autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Sci Rep. 4:72902014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong L, Wang X, Tan J, Li H, Qian W, Chen
J, Chen Q, Wang J, Xu W, Tao C, et al: Decreased expression of
microRNA-21 correlates with the imbalance of Th17 and Treg cells in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2213–2224.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
van der Geest KS, Smigielska-Czepiel K,
Park JA, Abdulahad WH, Kim HW, Kroesen BJ, van den Berg A, Boots
AM, Lee EB and Brouwer E: SF Treg cells transcribing high levels of
Bcl-2 and microRNA-21 demonstrate limited apoptosis in RA.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 54:950–958. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|